Anatomy of a Long Bone, Bone cells
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
Protects the ends of bones from wearing down
Articular Cartilage
Enters and exits bone through the nutrient foramen
Blood vessel
Full of red marrow
Spongy bone
How newly made blood cells leave the bone (not the hole)
Blood Vessel
The knobby end of your femur at the hip end
Proximal epiphysis
The long shaft in the middle of the bone
Diaphysis
Makes up the diaphysis and outside of long bones
Compact bone
Site of hemopoiesis
Red marrow
When this gets destroyed/used up, you get arthritis
Articular cartilage
The knobby end of your femur at the knee end
Distal epiphysis
Hollow space inside the diaphysis
Medullary cavity
Medullary cavity is inside this part of the bone (not type of bone; not layer)
Diaphysis
Full of stem cells
Red marrow
Name literally means “joint cartilage”
articular cartilage
Layer that lines the medullary cavity
Endosteum
Layer that lines the outside of the bone
Periosteum
Growth plates
Epiphyseal plate
Delivers nutrients and oxygen to the bone cells
Blood vessels
The knobby end of your humerus at the shoulder end
Proximal epiphysis
the knobby end of your humerus at the elbow end
Distal epiphysis
Name literally means “around bone”
Periosteum
Name literally means “inside bone”
Endosteum
Type of bone found inside the epiphyses
Spongy bone
Little hole in the bone that the blood vessel goes through
Nutrient foramen
made of cartilage, but ossify to bone each time you grow
Epiphyseal plate
Space full of yellow marrow
Medullary cavity
At age 25, fully ossifies
Epiphyseal plate
Means “Bone produce”
osteogenic cell
means “bone bud/sprout”
osteoblast
means “bone cell”
osteocyte
means “bone break”
osteoclast
helps to break down old bone
osteoclast
this type of bone cell is mitotic
osteogenic cell
considered a “mature bone cell”
osteocyte
shaves away old bone when your bones are growing wider
osteoclast
NOT located in the periosteum
osteocyte
this type of bone cell becomes an osteocyte
osteoblast
Creates the matrix of bones
osteoblast
Cleans away dead bone after a fracture
osteoclast
Creates osteoblasts
osteogenic cell
located in the periosteum and endosteum
osteoblast, osteoclast, osteogenic cell
type of bone cell allows your bones to perform their daily functions
osteocyte
is a stem cell
osteogenic cell
gets buried and become another type of bone cell
osteoblast
located on epiphyseal plates and on the periosteum
osteoblast
located inside spongy and compact bone
osteocyte
creates the osteoid of bones
osteoblast
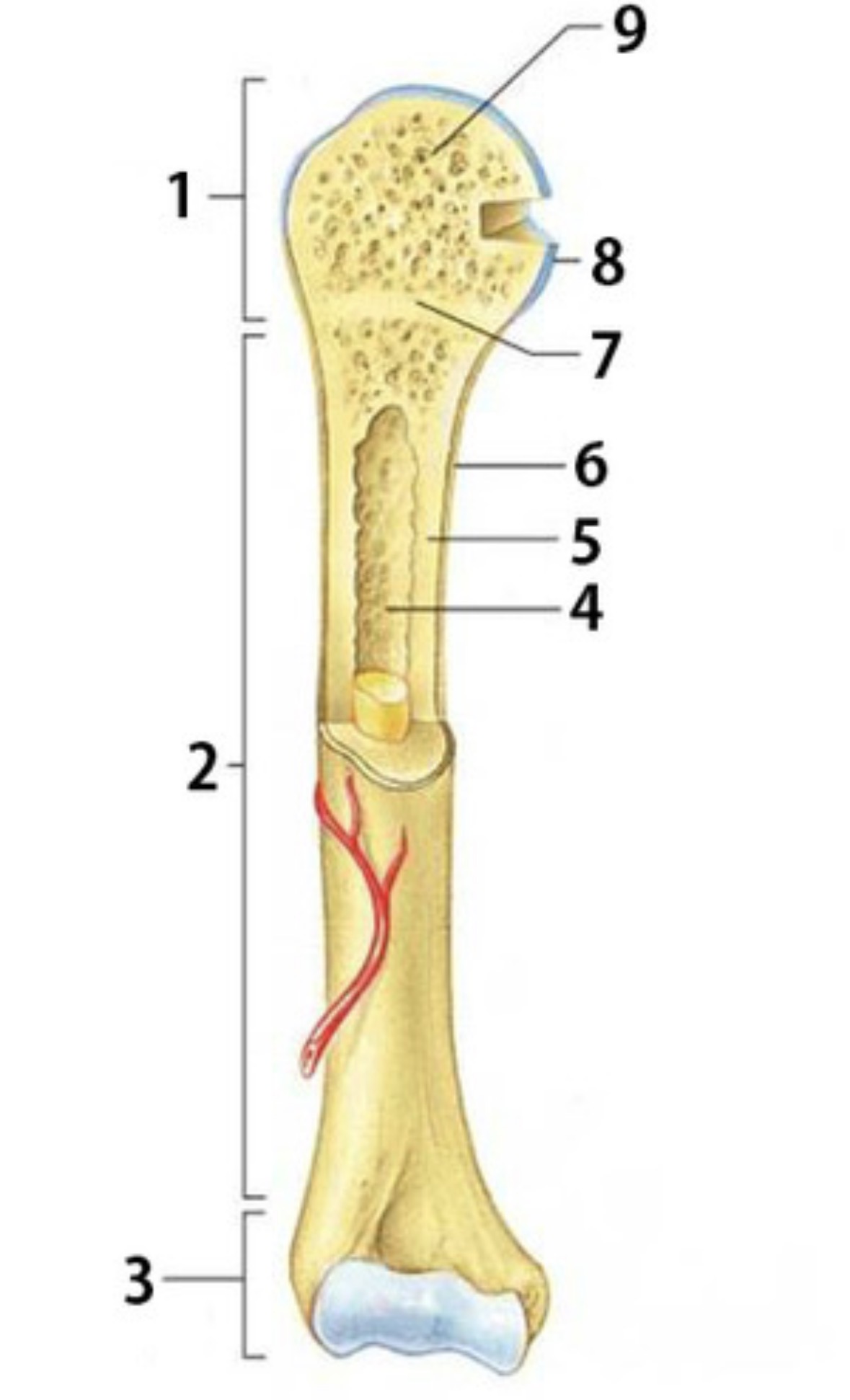
What is 1
Proximal epiphysis
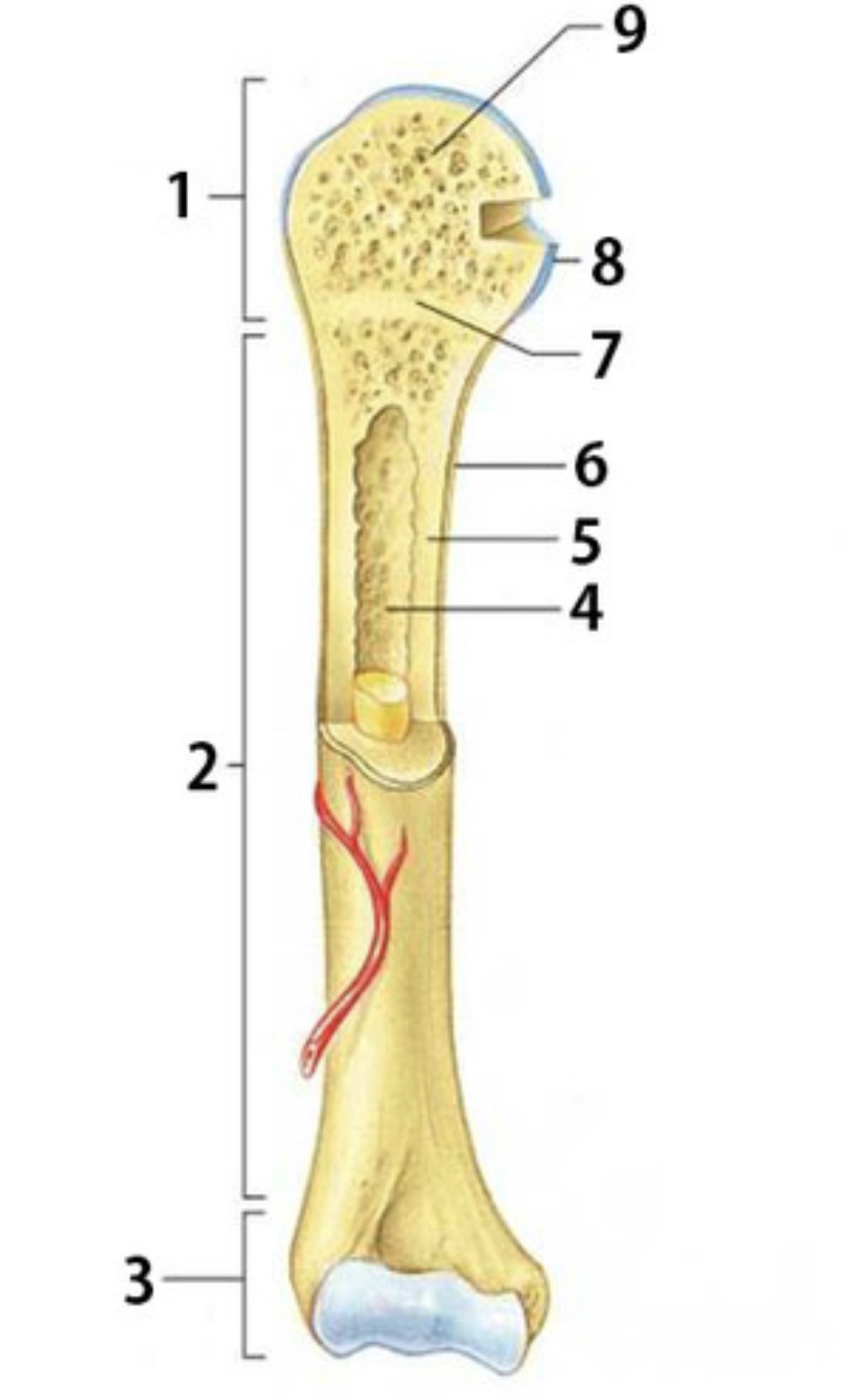
What is 2
Diaphysis
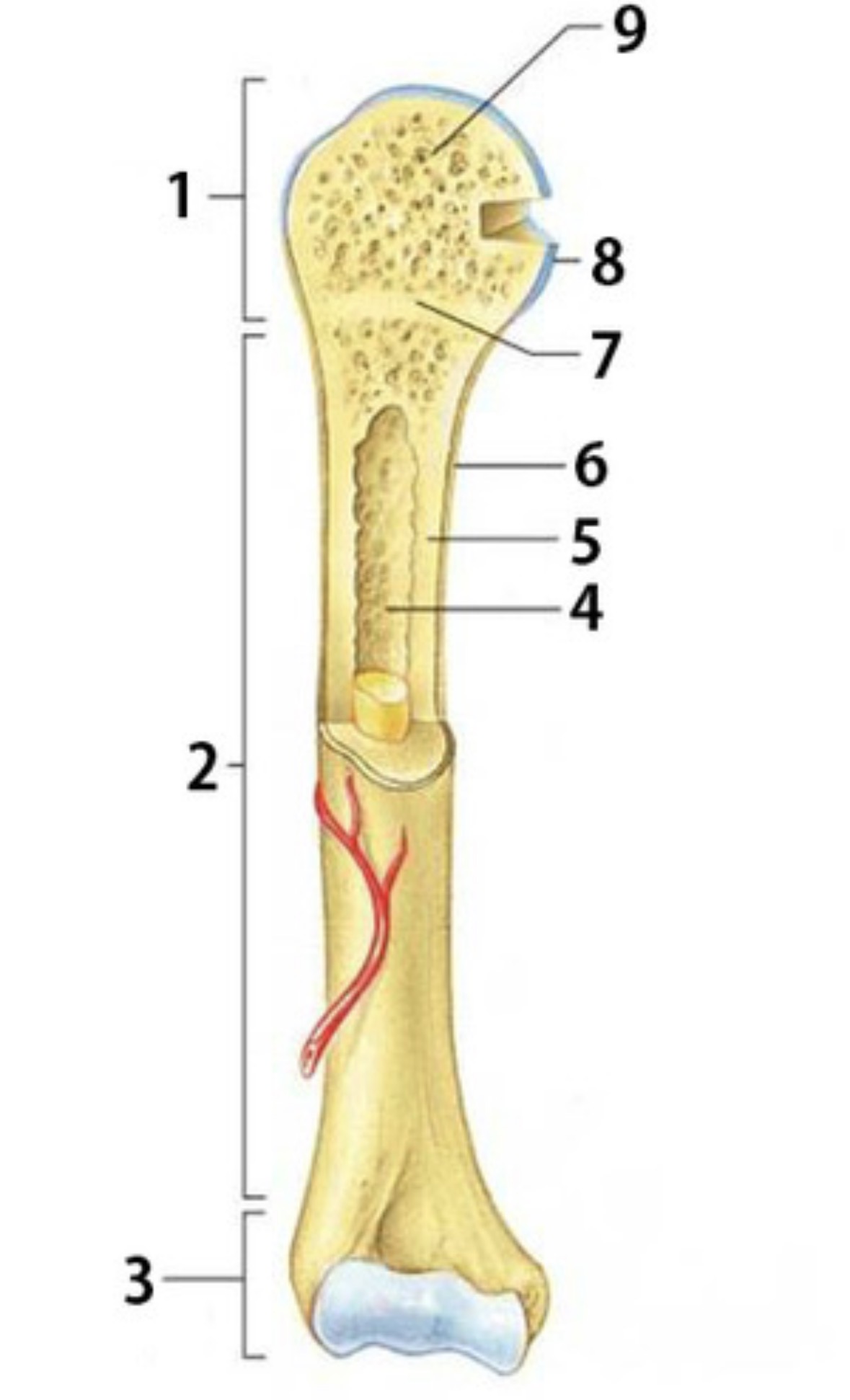
Identify 3
Distal epiphysis
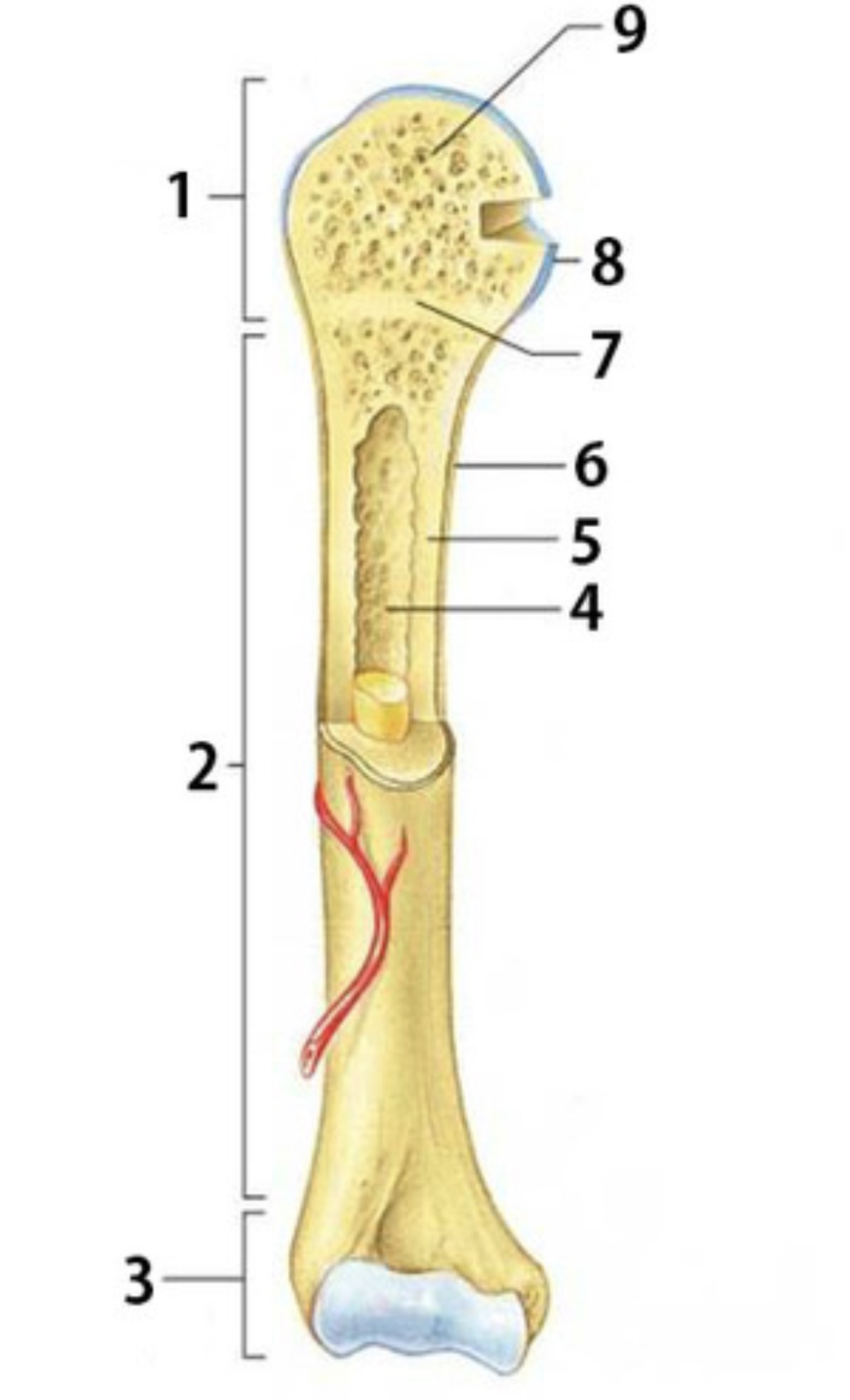
Identify the substance inside 4
Yellow marrow
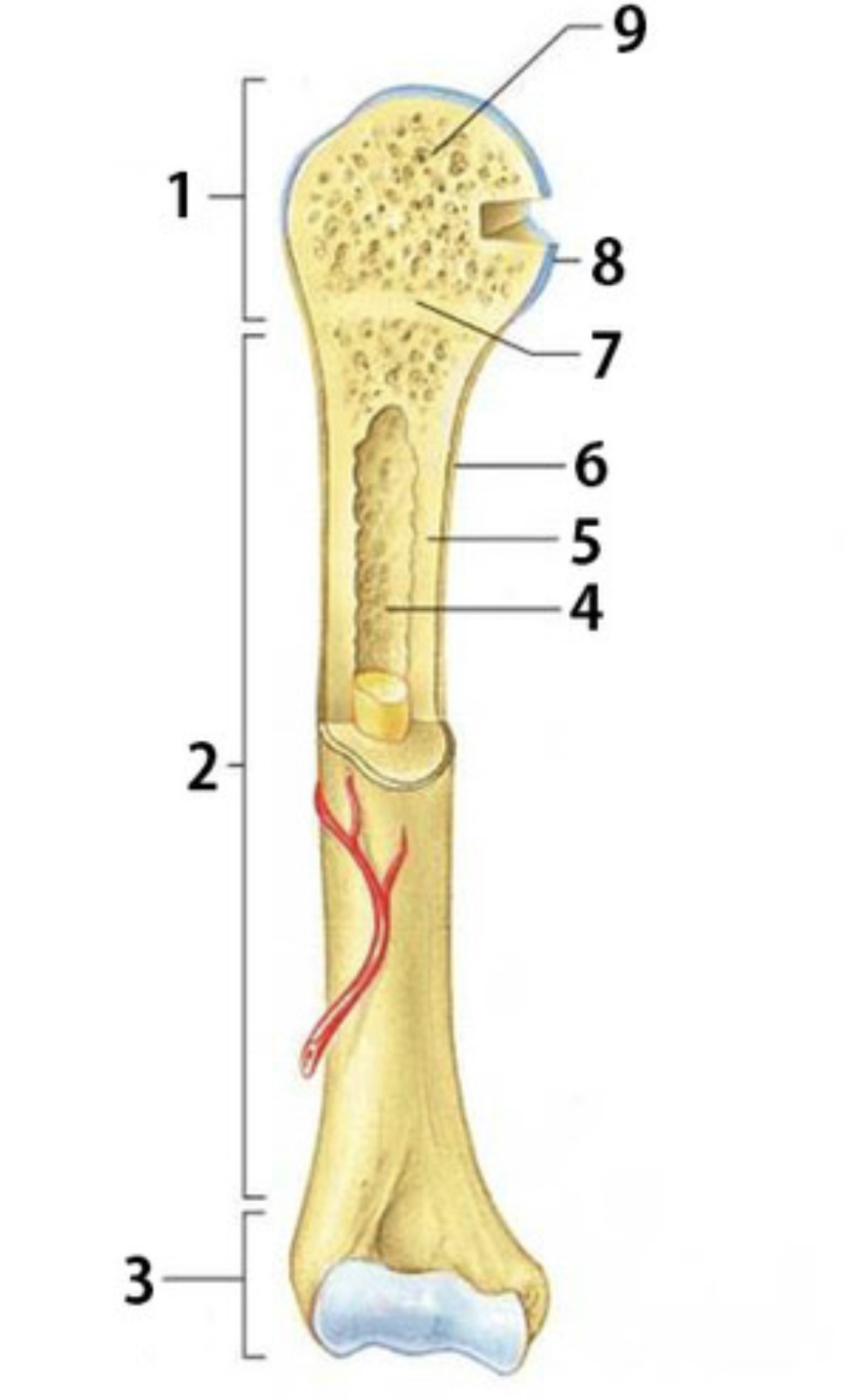
Identify 4
Medullary Cavity
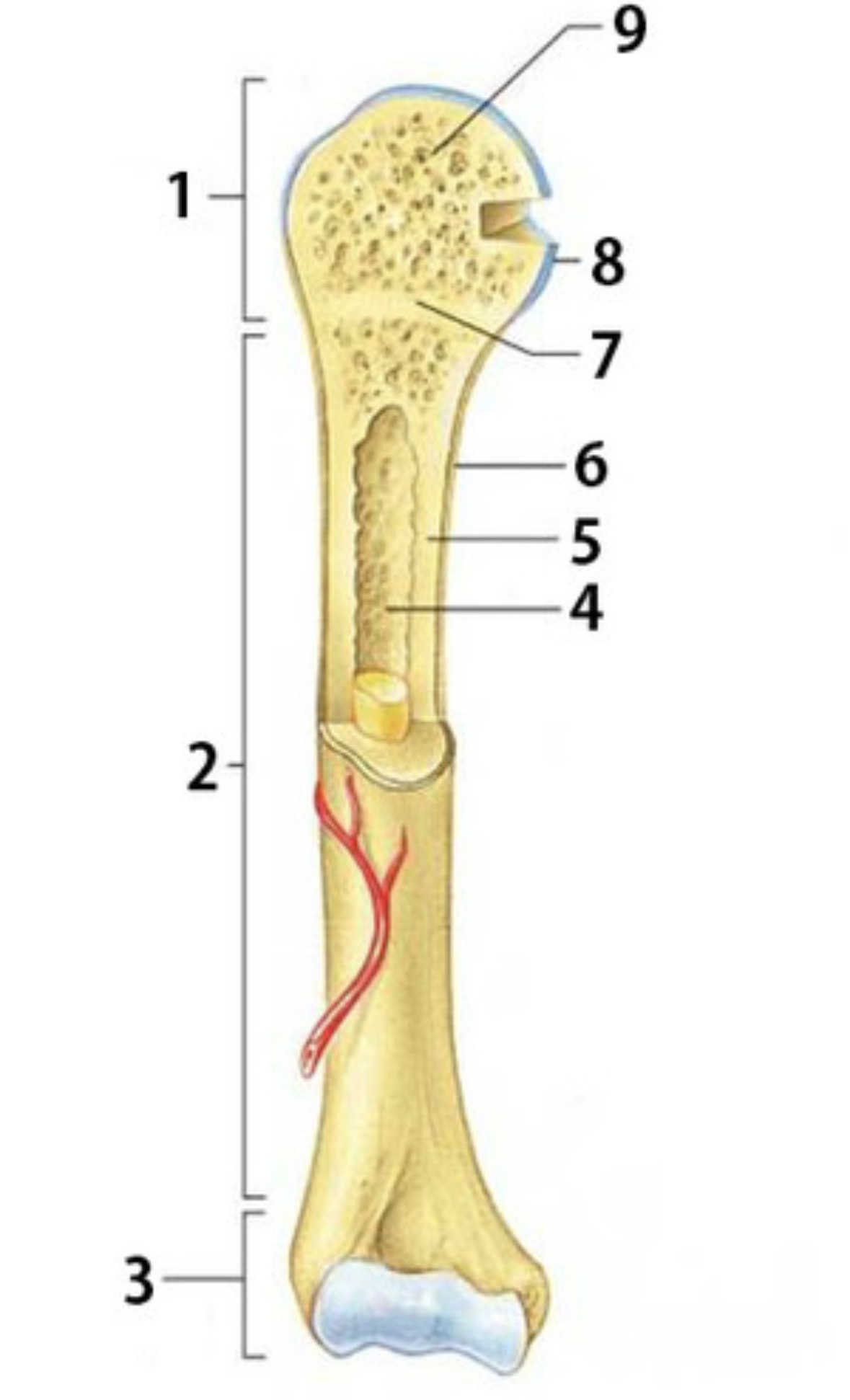
What is 5
compact bone
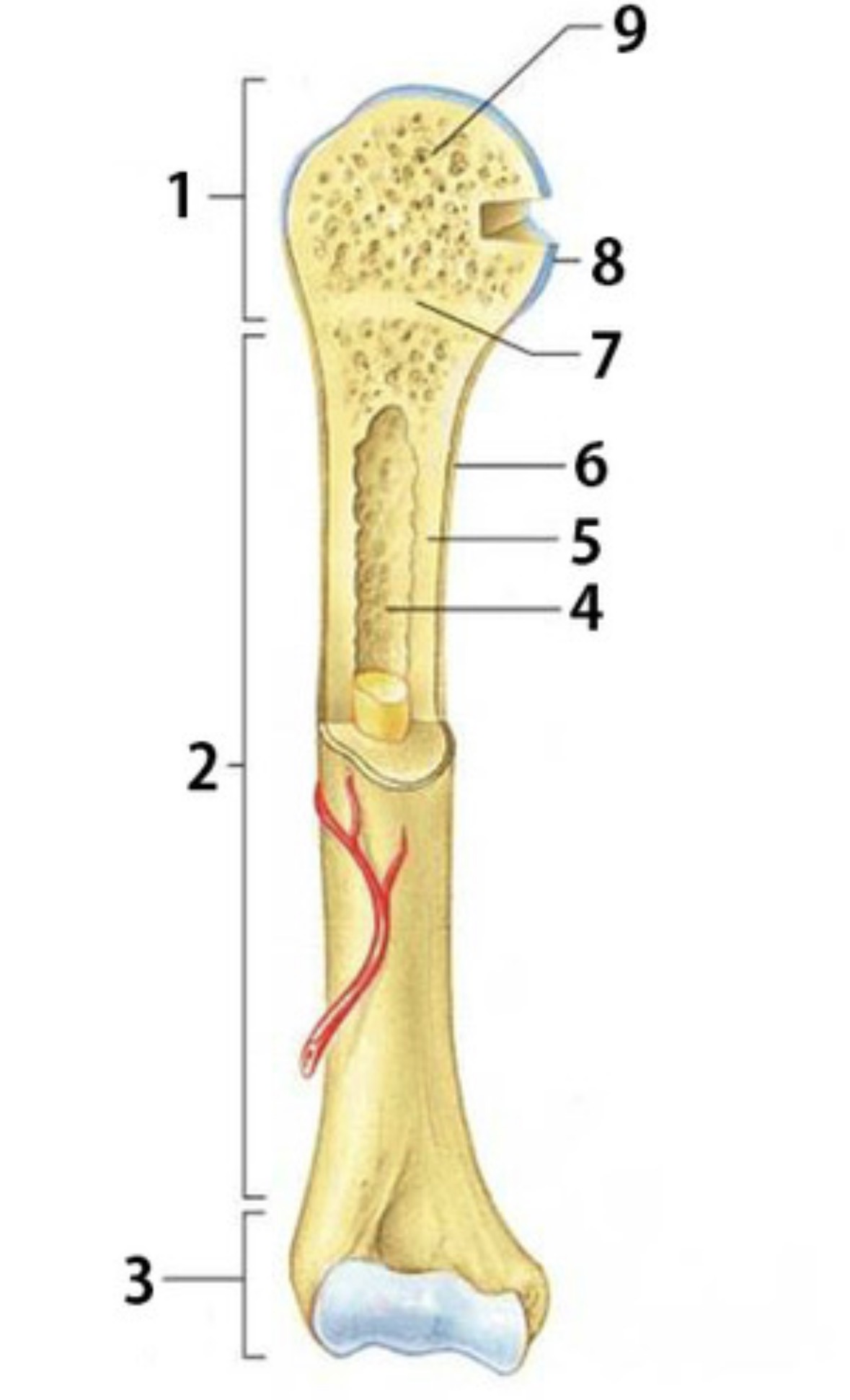
Identify 6
Periosteum
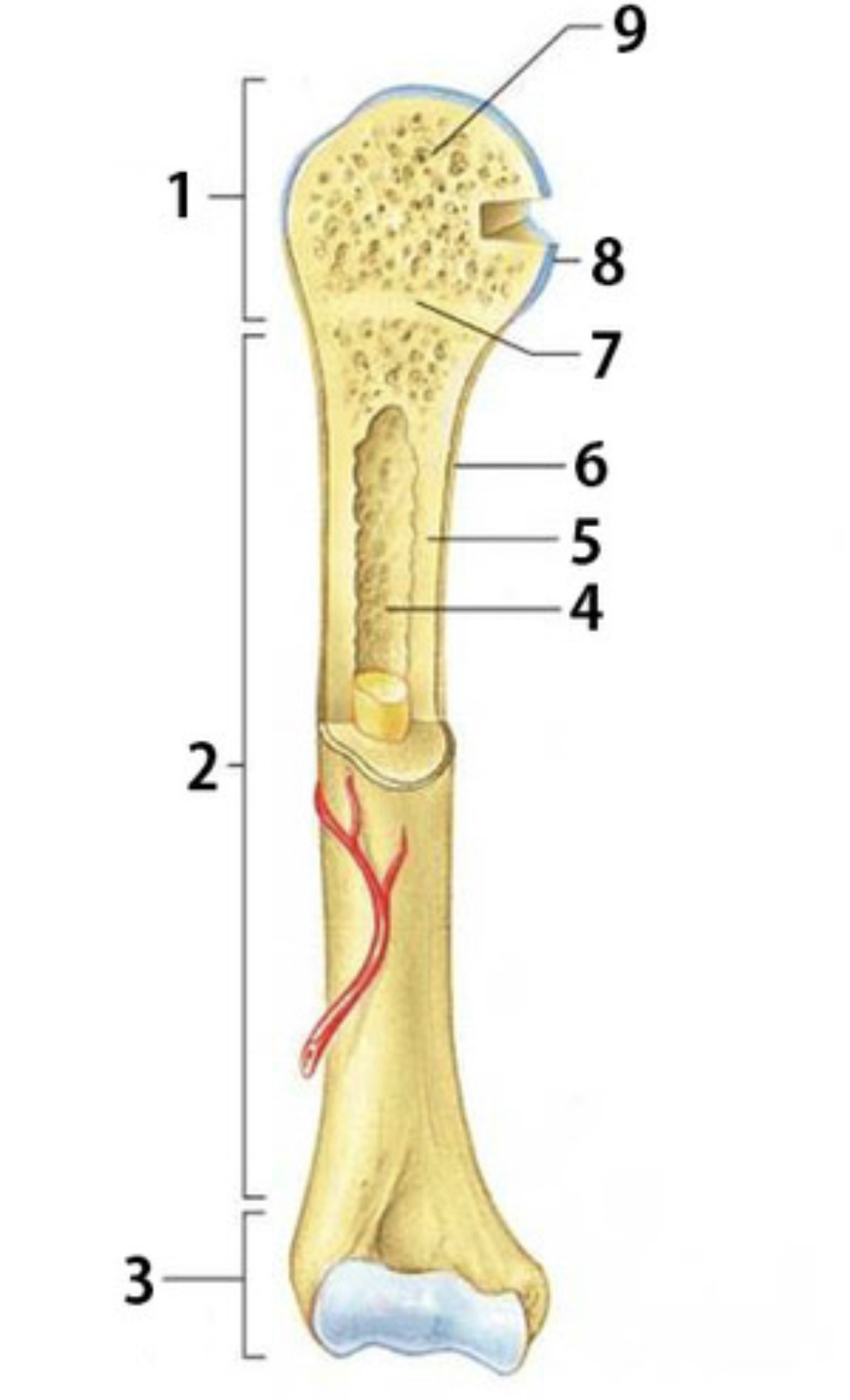
Identify 7
Epiphyseal plate
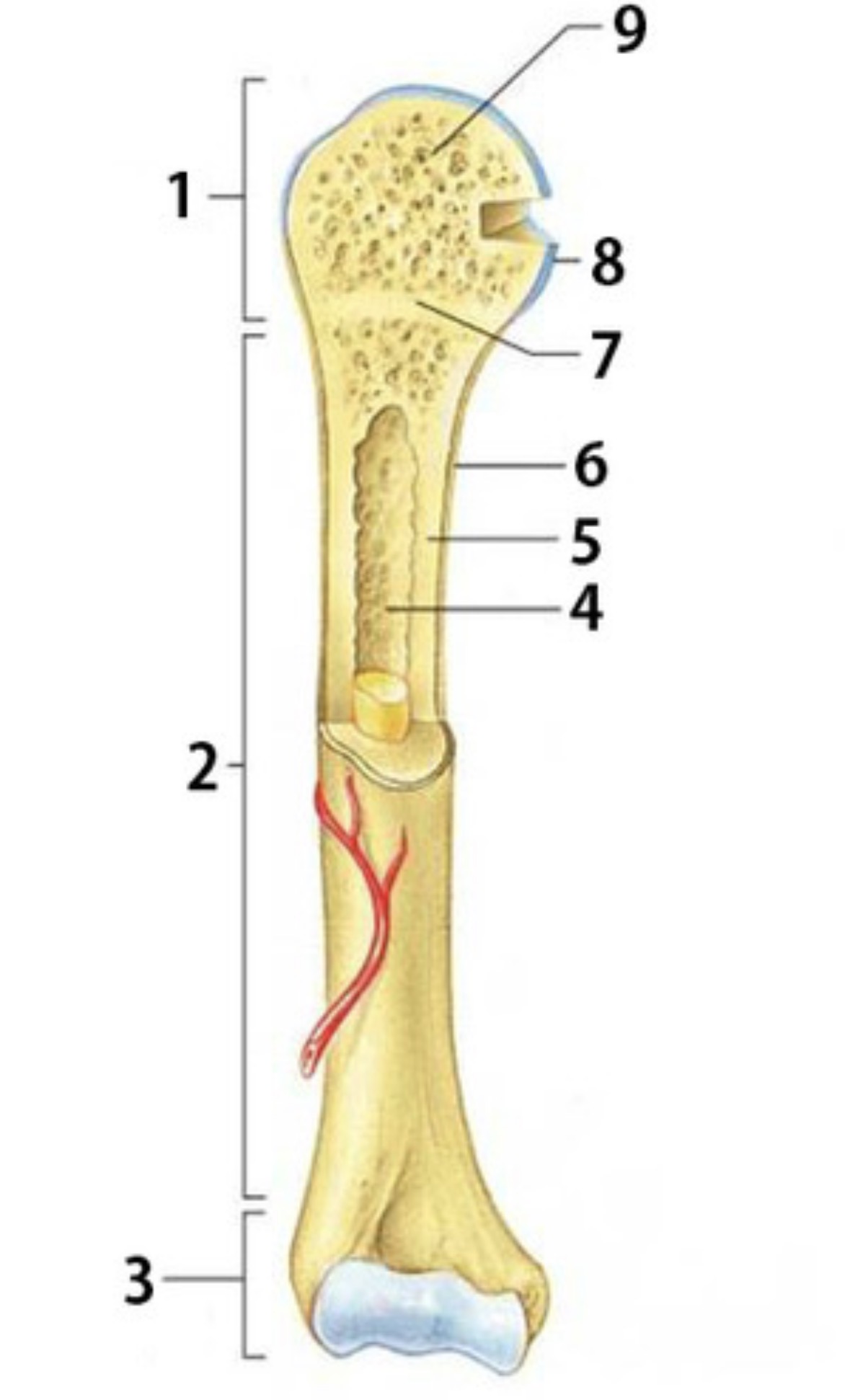
Identify 8
Articular cartilage
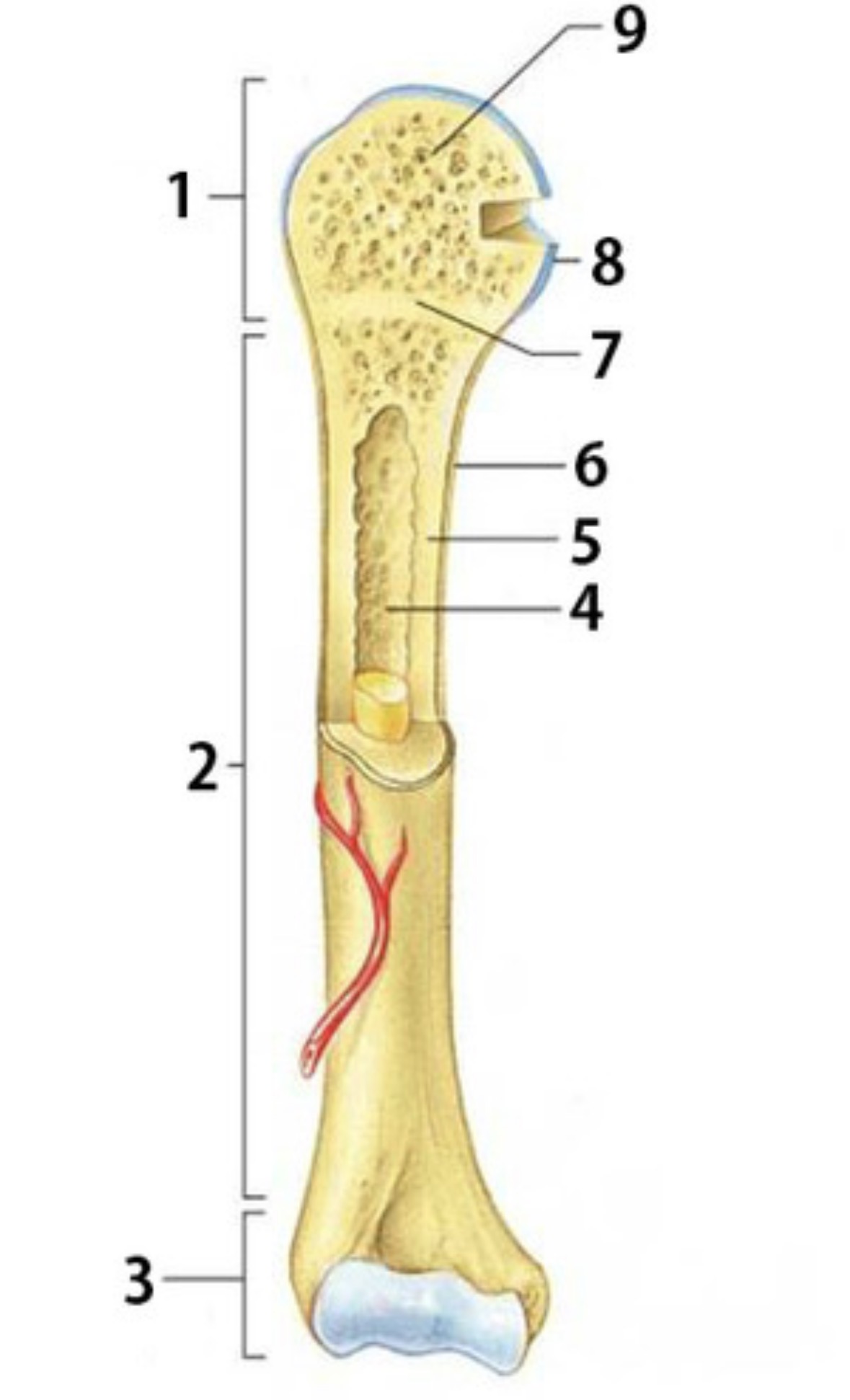
Identify the type of bone in 9
spongy bone