Integumentary System
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
integumentary system
Consists of the skin, subcutaneous tissue and accessory structures
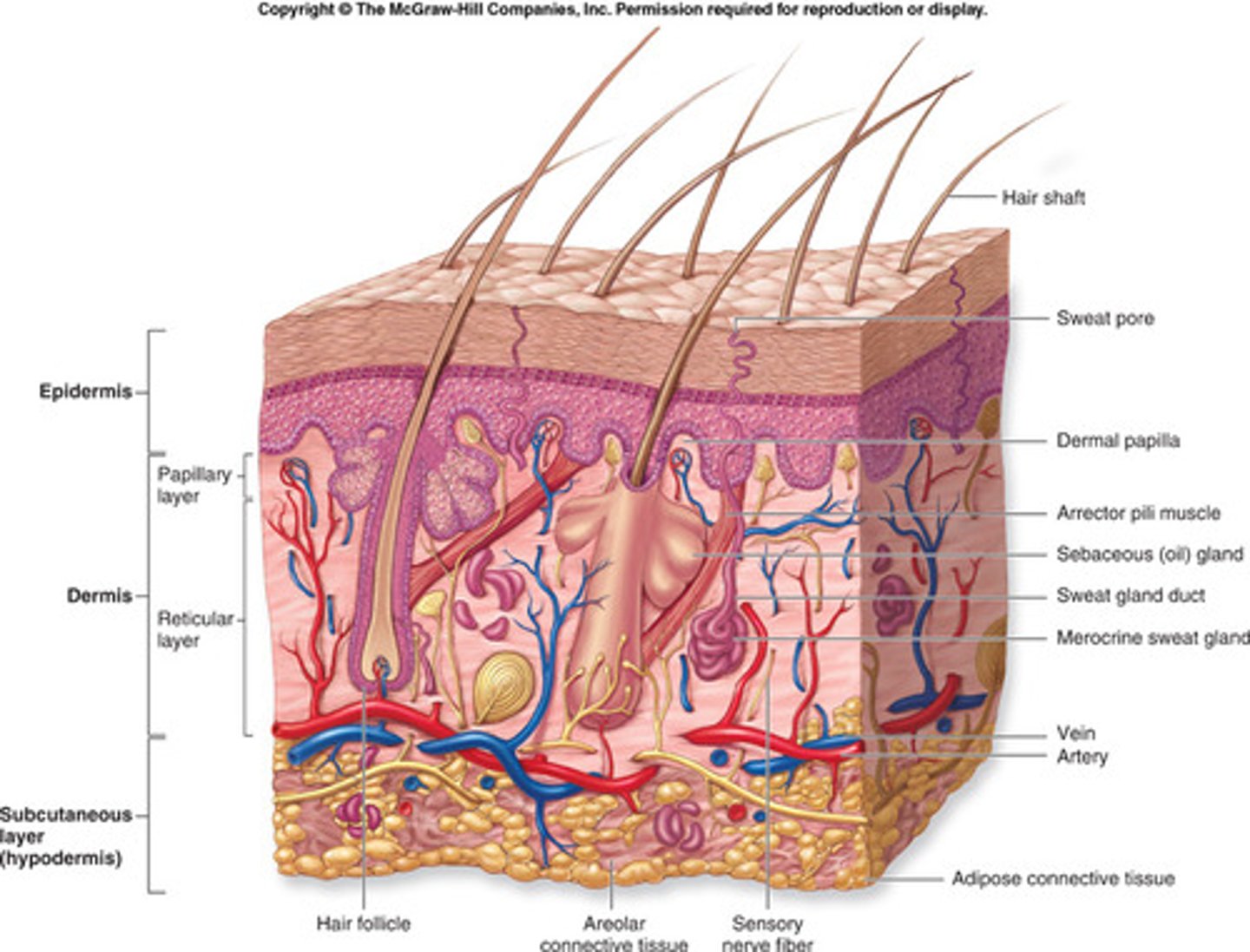
accessory structures of integumentary system
sweat glands, sebaceous glands, hair and nails
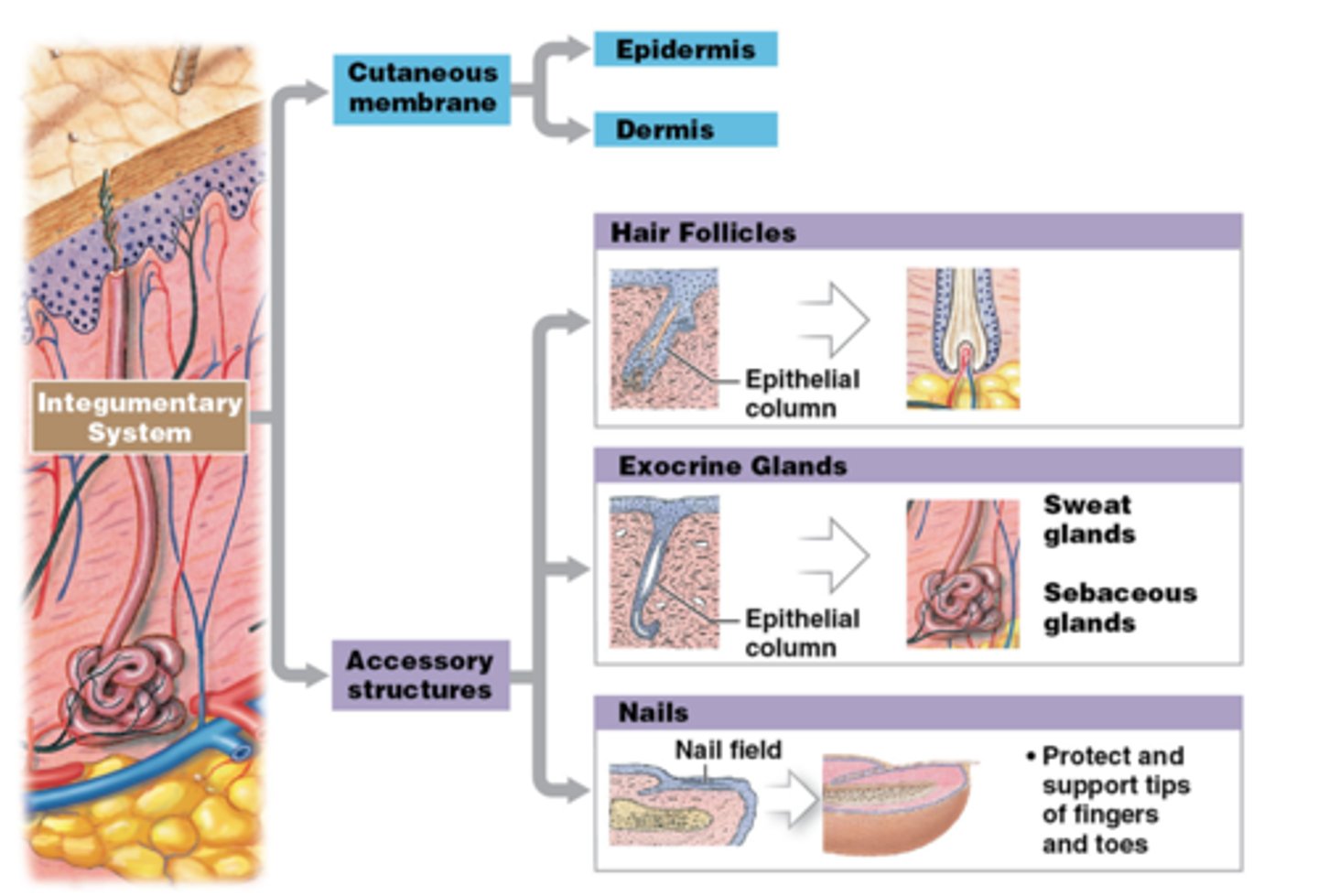
cutaneous membrane
another name for skin
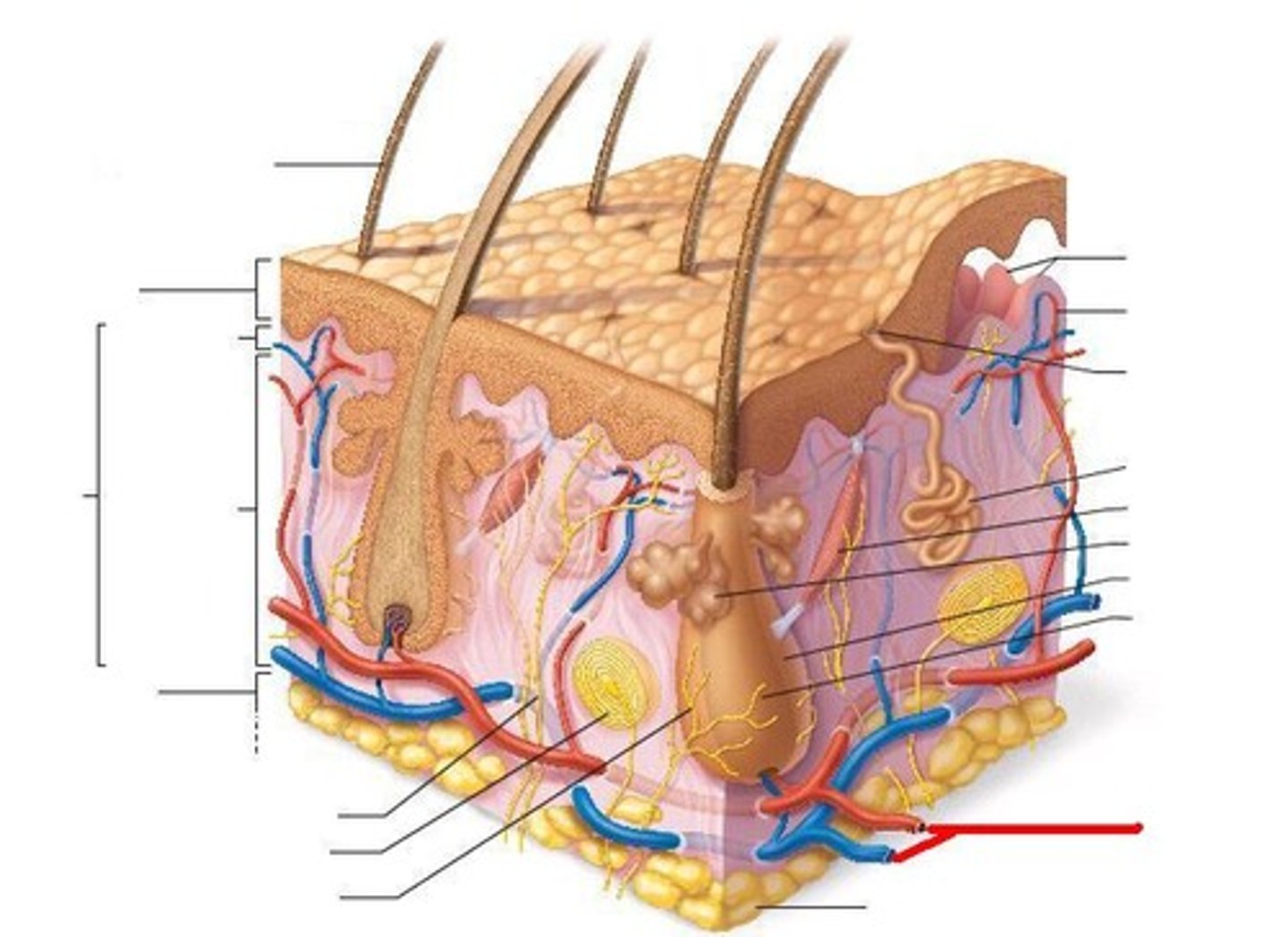
three layers of skin
epidermis, dermis, hypodermis
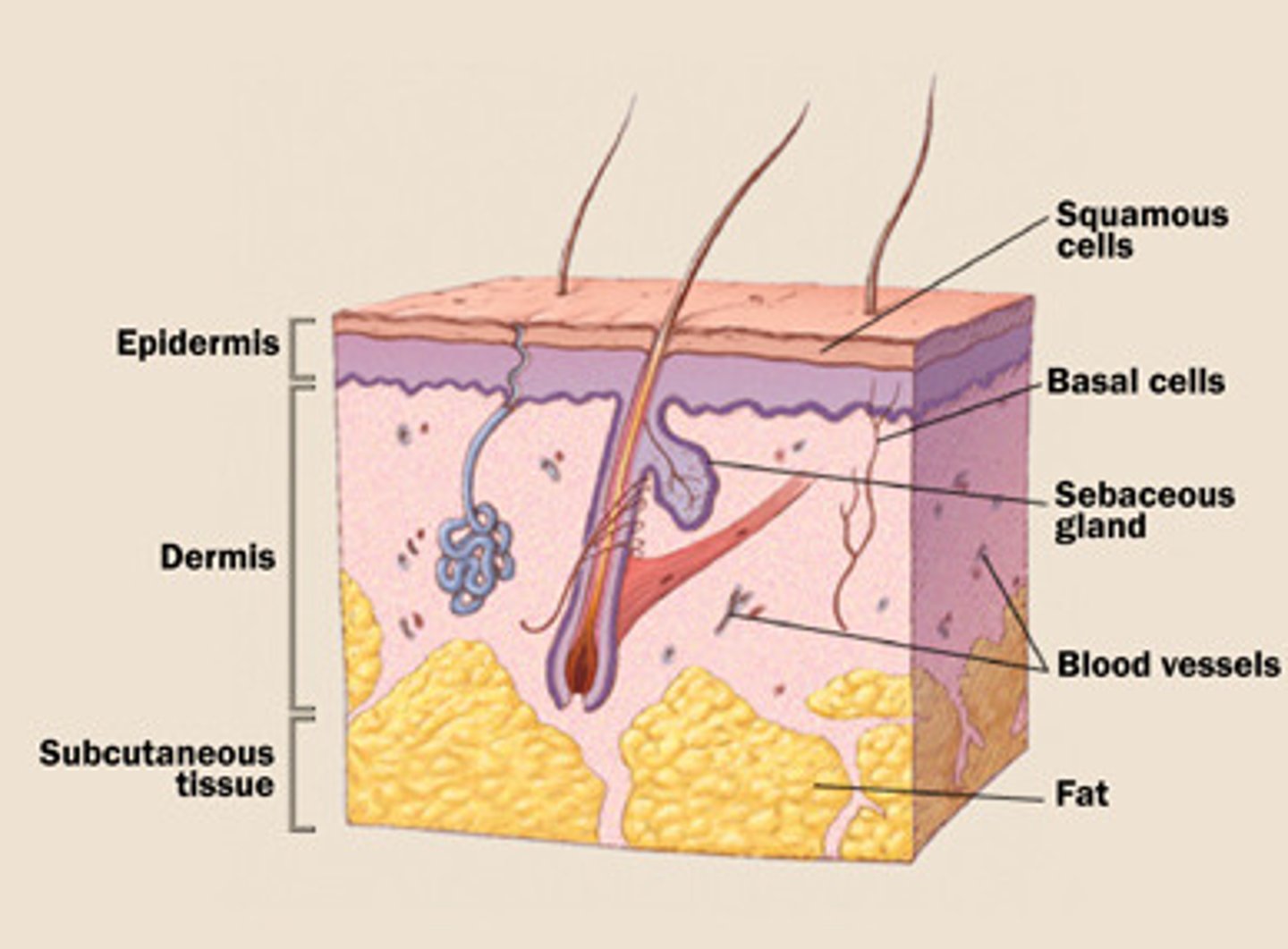
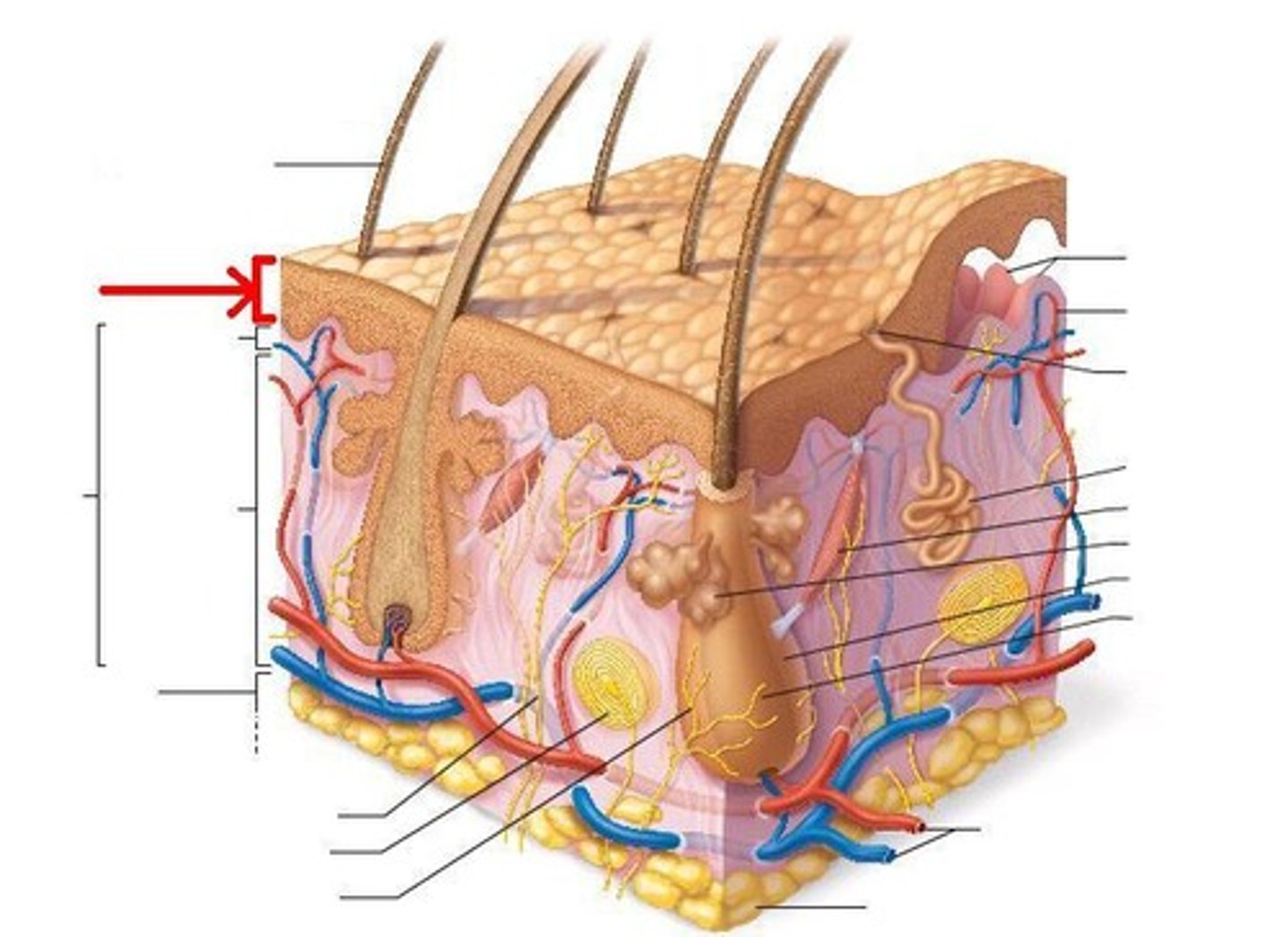
epidermis
outermost layer of skin
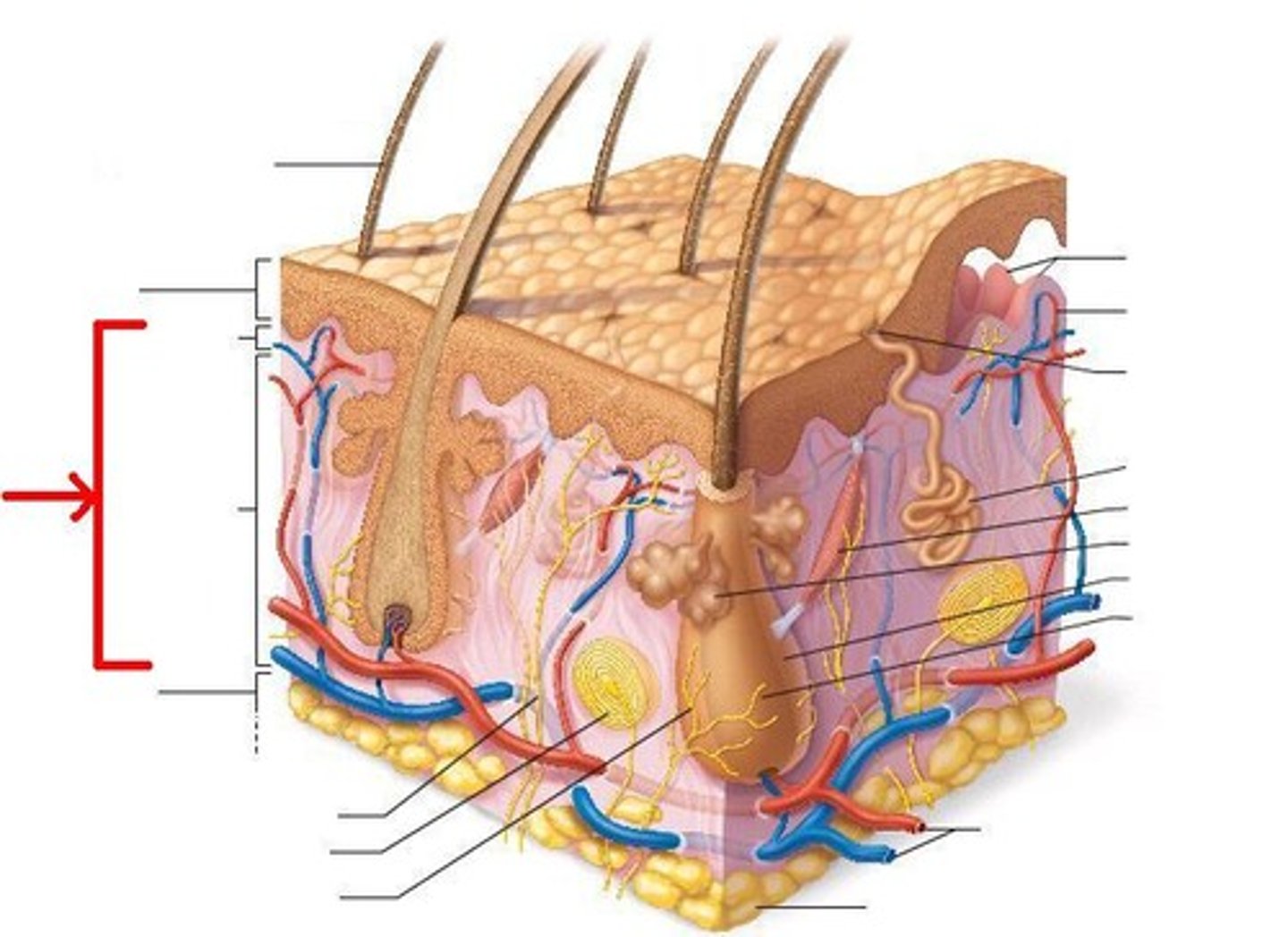
dermis
middle layer of skin
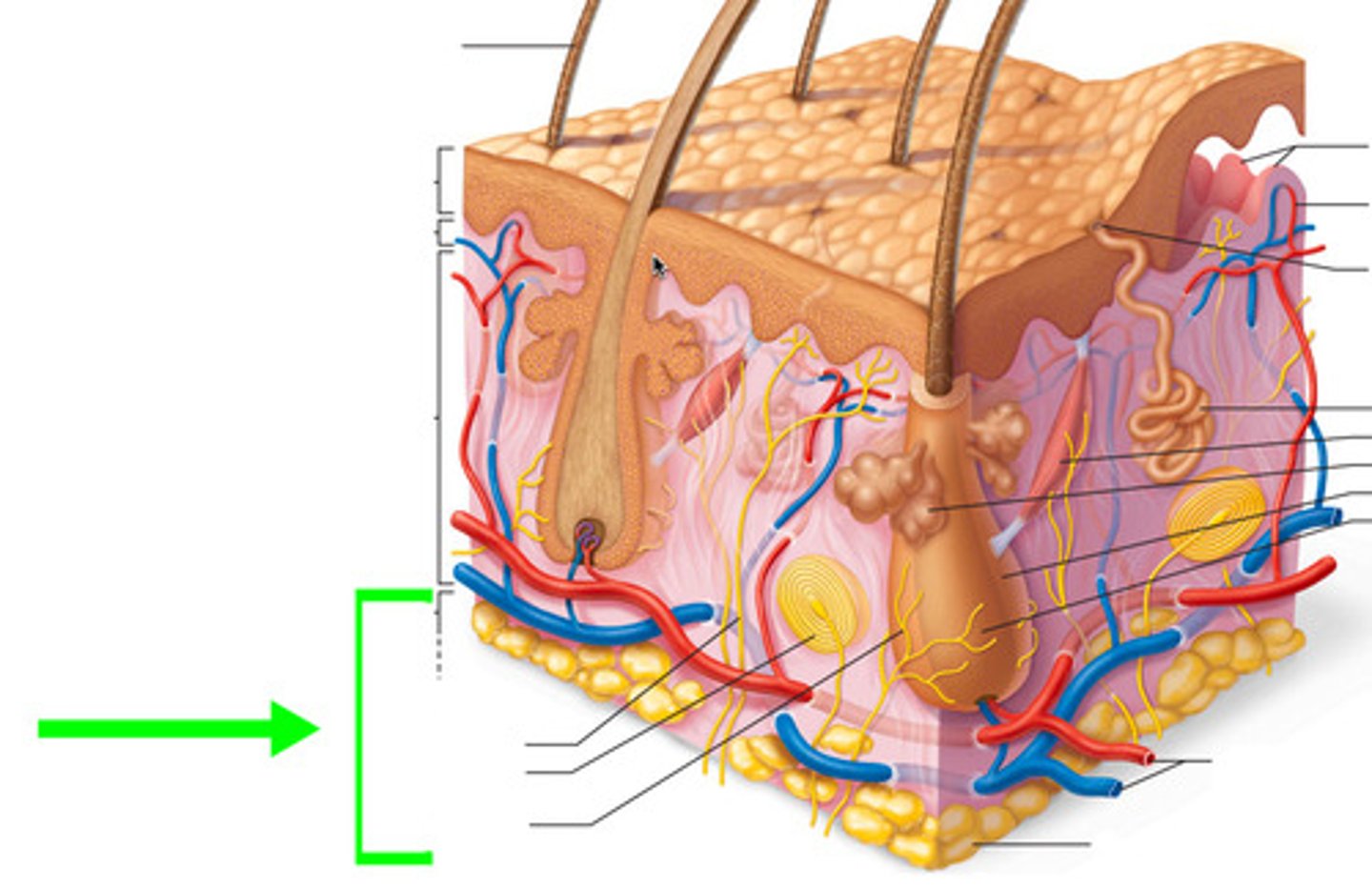
hypodermis
loose connective tissue layer of skin below the dermis
functions of the skin
protection, thermoregulation, cutaneous sensation, storage of chemical compounds, excretion of waste, synthesis of compounds
hair functions/structure
functions: protection, thermoregulation, sensation
structures: shaft, root, cuticle
nails functions/sturctures
functions: protection, increasing sensitivity
structures: nail body, free edge, matrix, cuticle, lunula
receptors
make it possible for body surface to act as a sense organ, relay messages to the brain
Lamellar (Pacini) corpuscle
detects pressure deep in the dermis
Tactile (Meissner) corpuscle
detects light touch
sebaceous gland
oil-secreting gland in the dermis that is associated with hair follicles
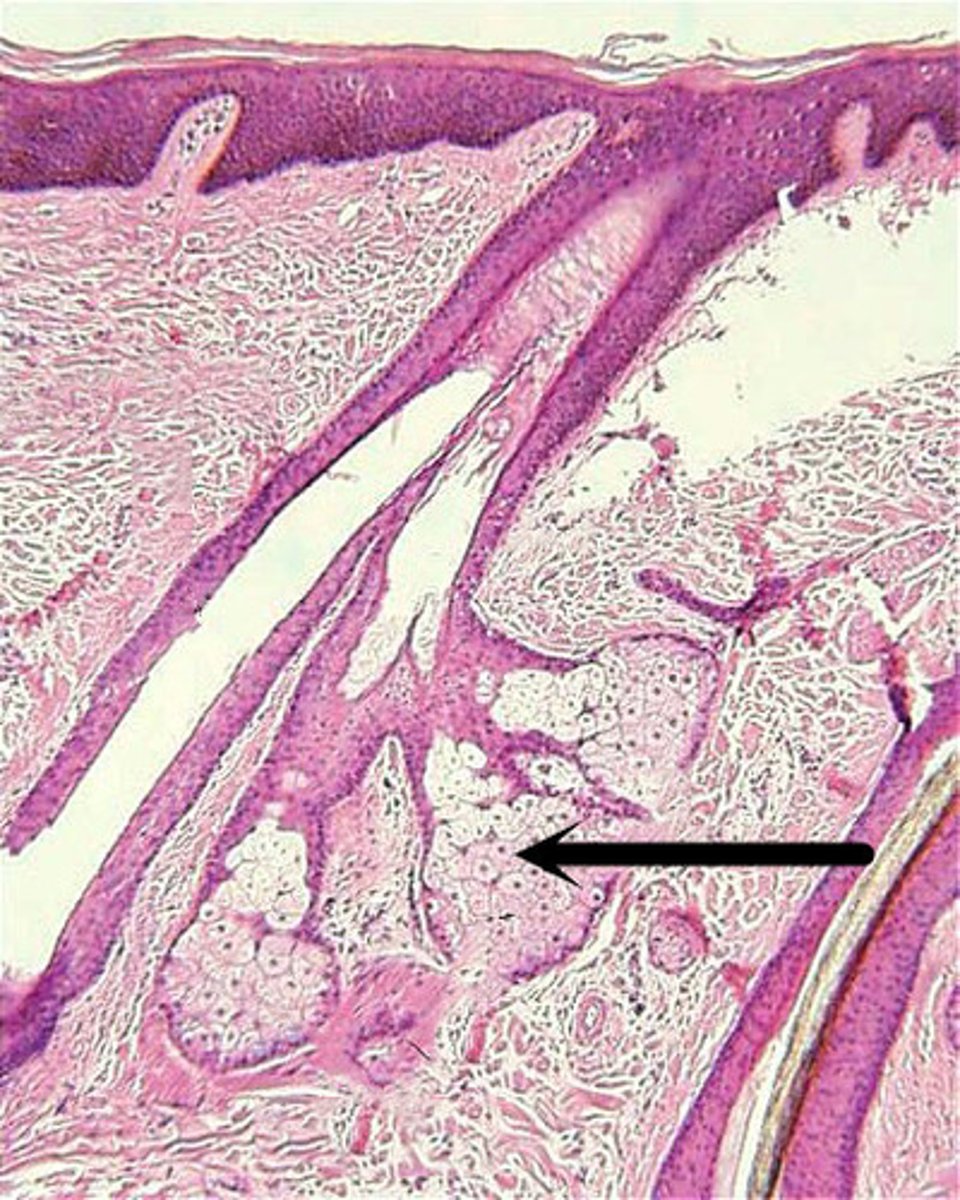
sweat gland
The glands that secrete sweat, located in the dermal layer of the skin.
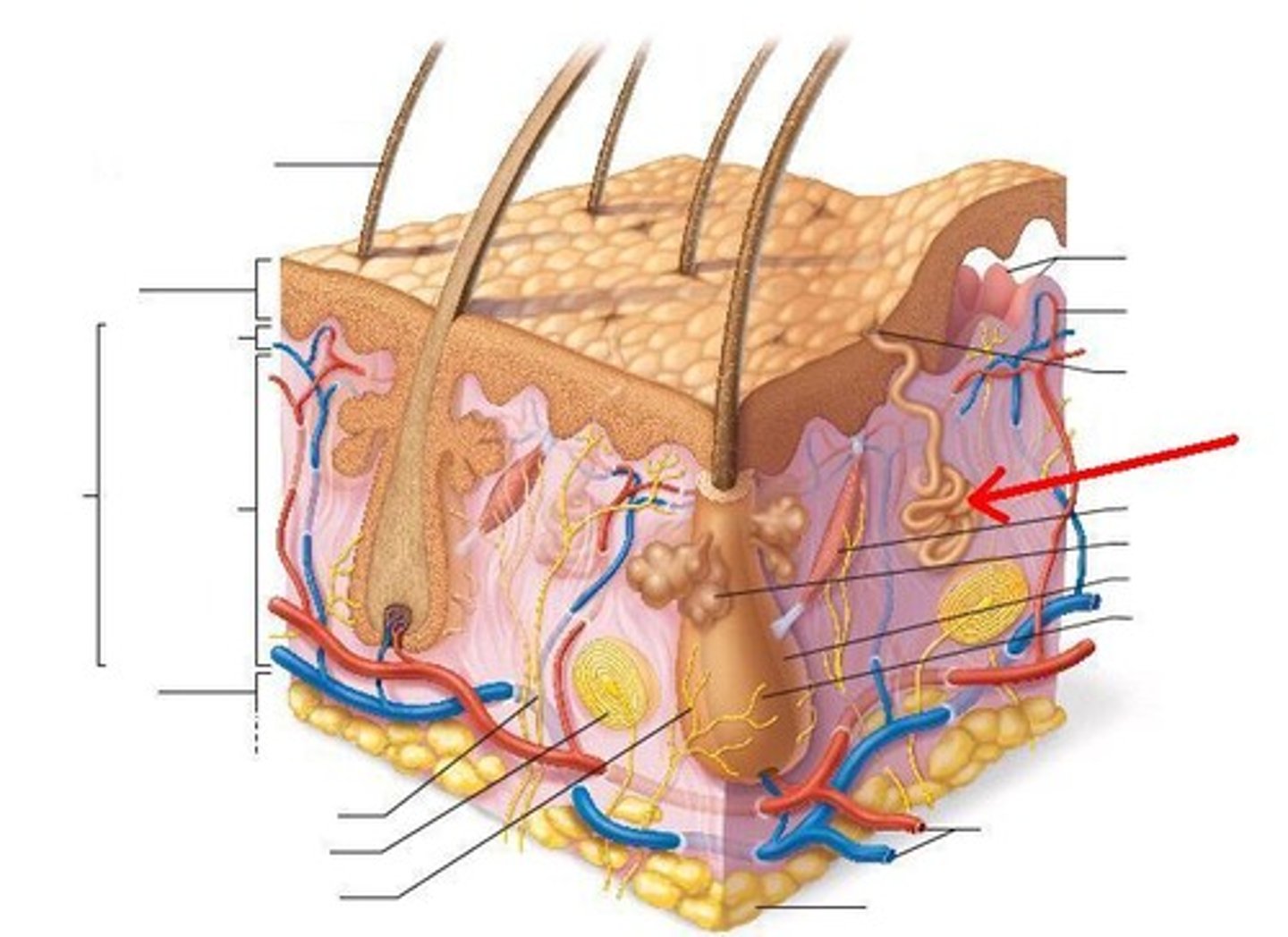
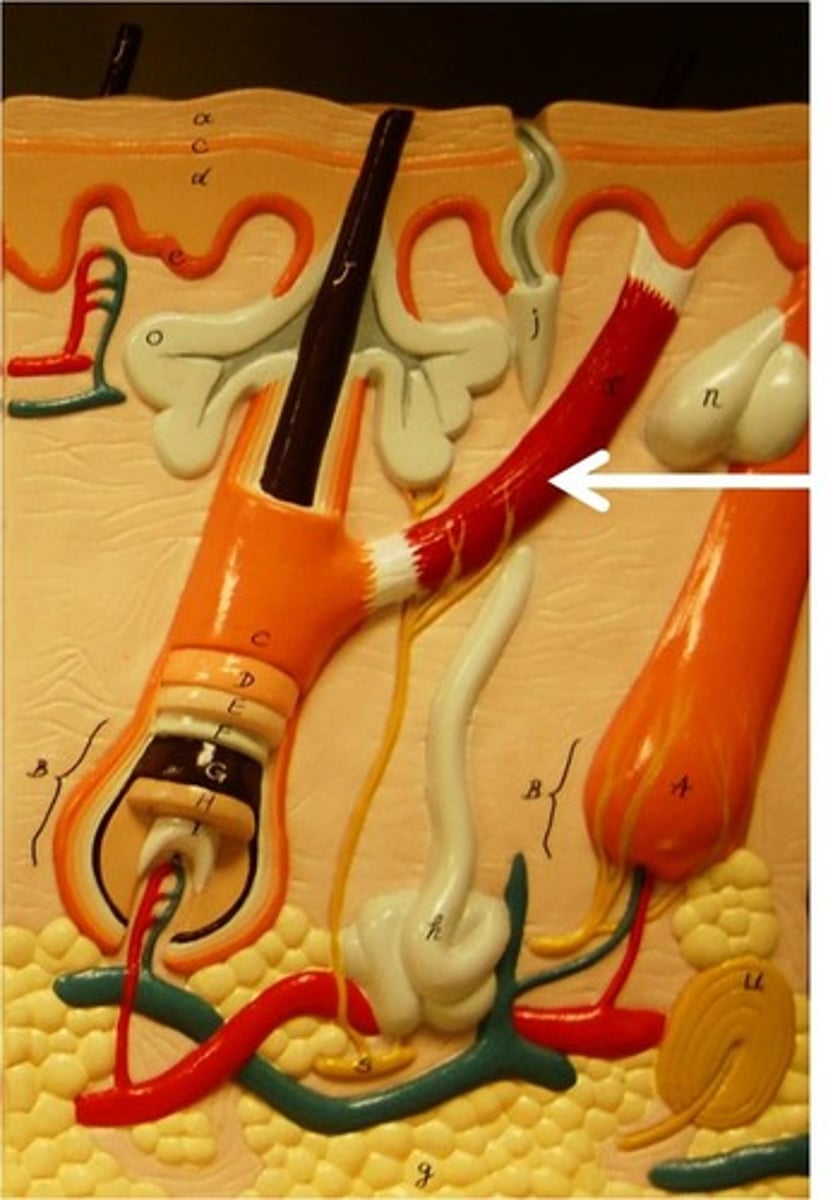
arrector pili muscle
An involuntary muscle fiber attached to the underside & base of the hair follicle
skin cancer
abnormal growth of skin cells
signs of skin cancer
Asymmetry
Border
Color
Diameter
Evolution
Abrasian
Scrape of the skin due to something abrasive
laceration
a cut, tear
puncture
a deep hole made by a sharp object such as a nail
Avulsion
An injury in which soft tissue is torn completely loose or is hanging as a flap.
first degree burn
A mild burn characterized by heat, pain, and reddening of the burned surface but not exhibiting blistering or charring of tissues - only epidermis is effected
second degree burn
A burn marked by pain, blistering - affects both epidermis and dermis
third degree burn
involves destruction of epidermis, dermis and subcutaneous (hypodermis) layer
fourth degree burn
burn in which full thickness of the skin and underlying muscle and bone is damaged
stratum corneum
outermost layer of epidermis
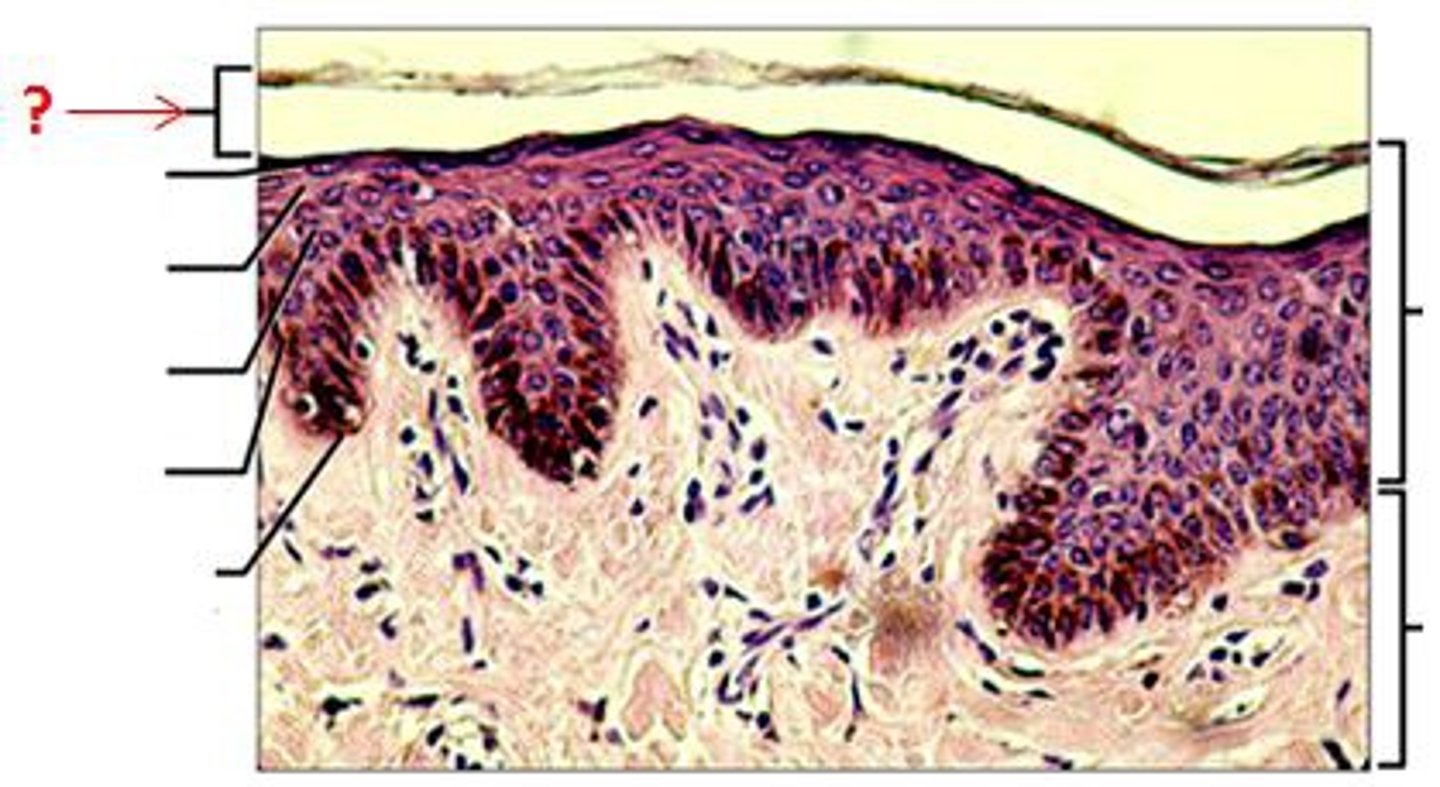
stratum lucidum
a layer of the epidermis found only in the thick skin of the fingers, palms, and soles
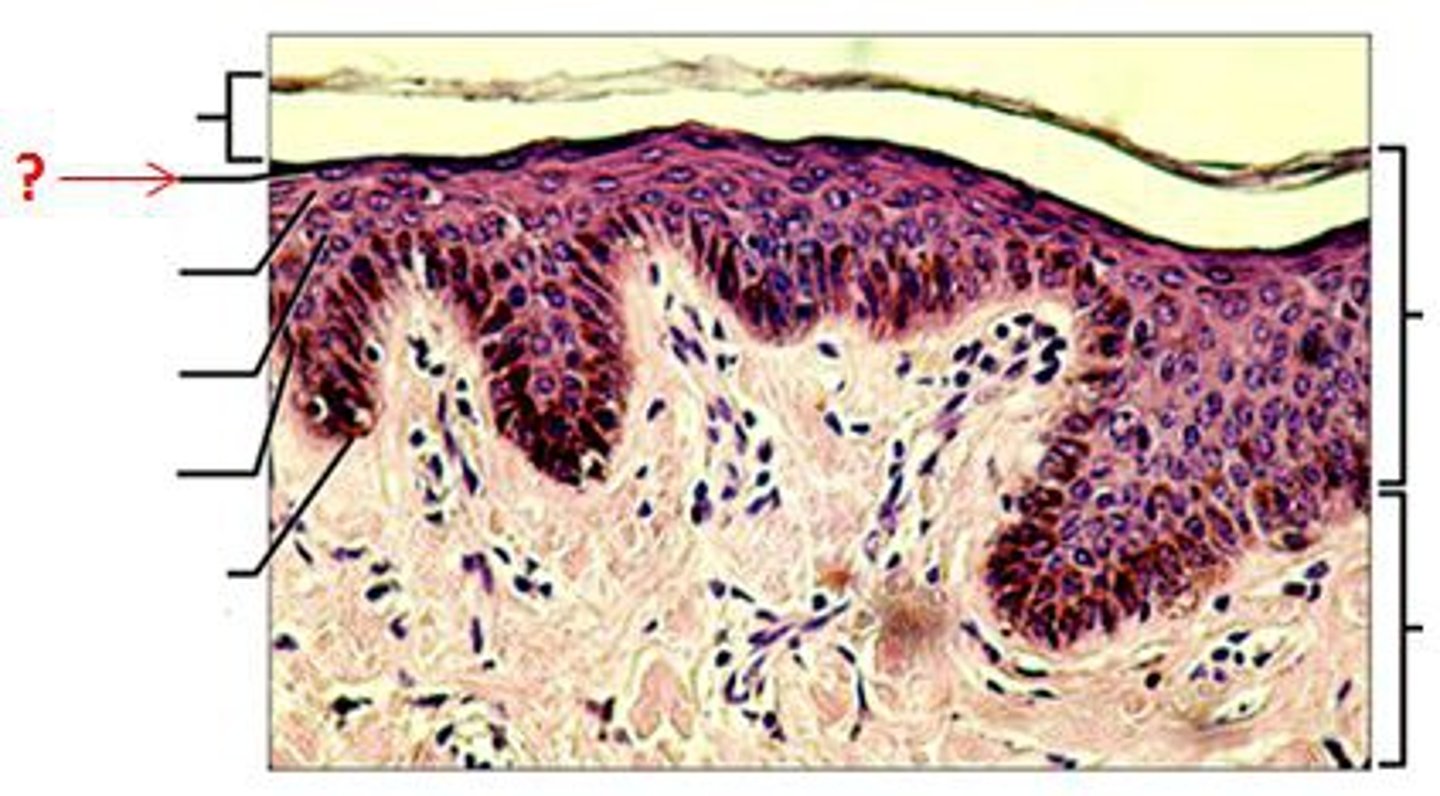
stratum granulosum
a layer of the epidermis that marks the transition between the deeper, metabolically active strata and the dead cells of the more superficial strata
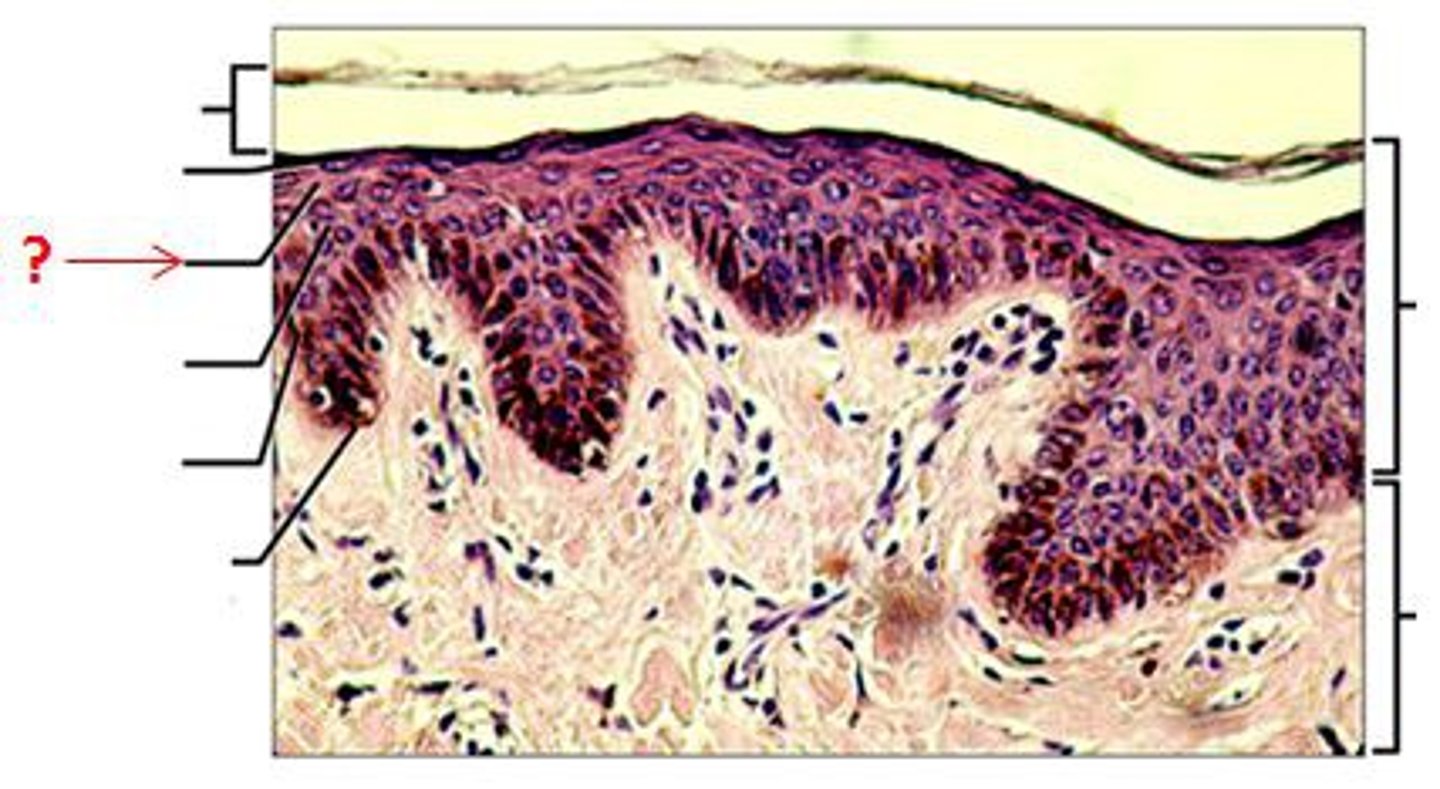
stratum spinosum
a layer of the epidermis that provides strength and flexibility to the skin
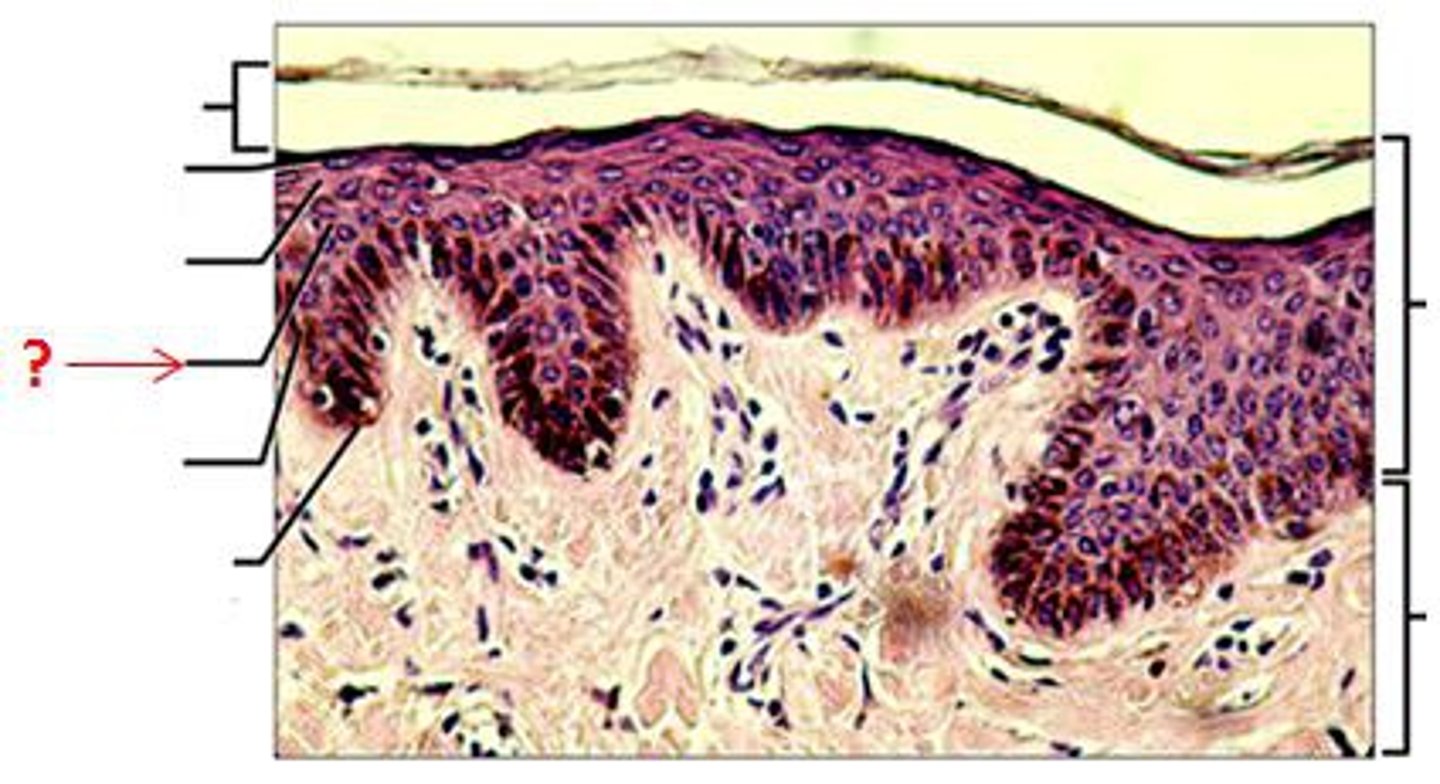
stratum basale
deepest layer of epidermis
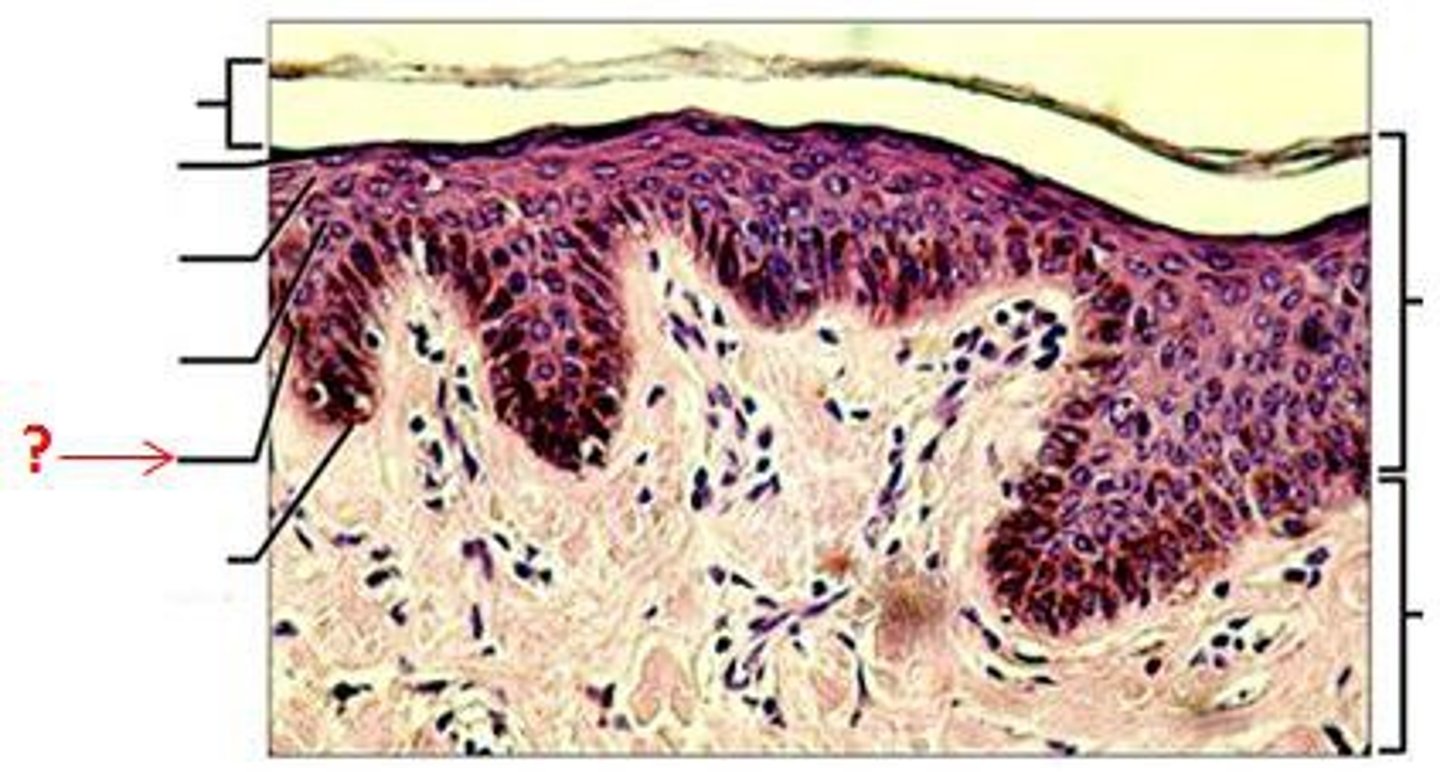
Keratinocytes
The most abundant epidermal cells, they function mainly to produce keratin.
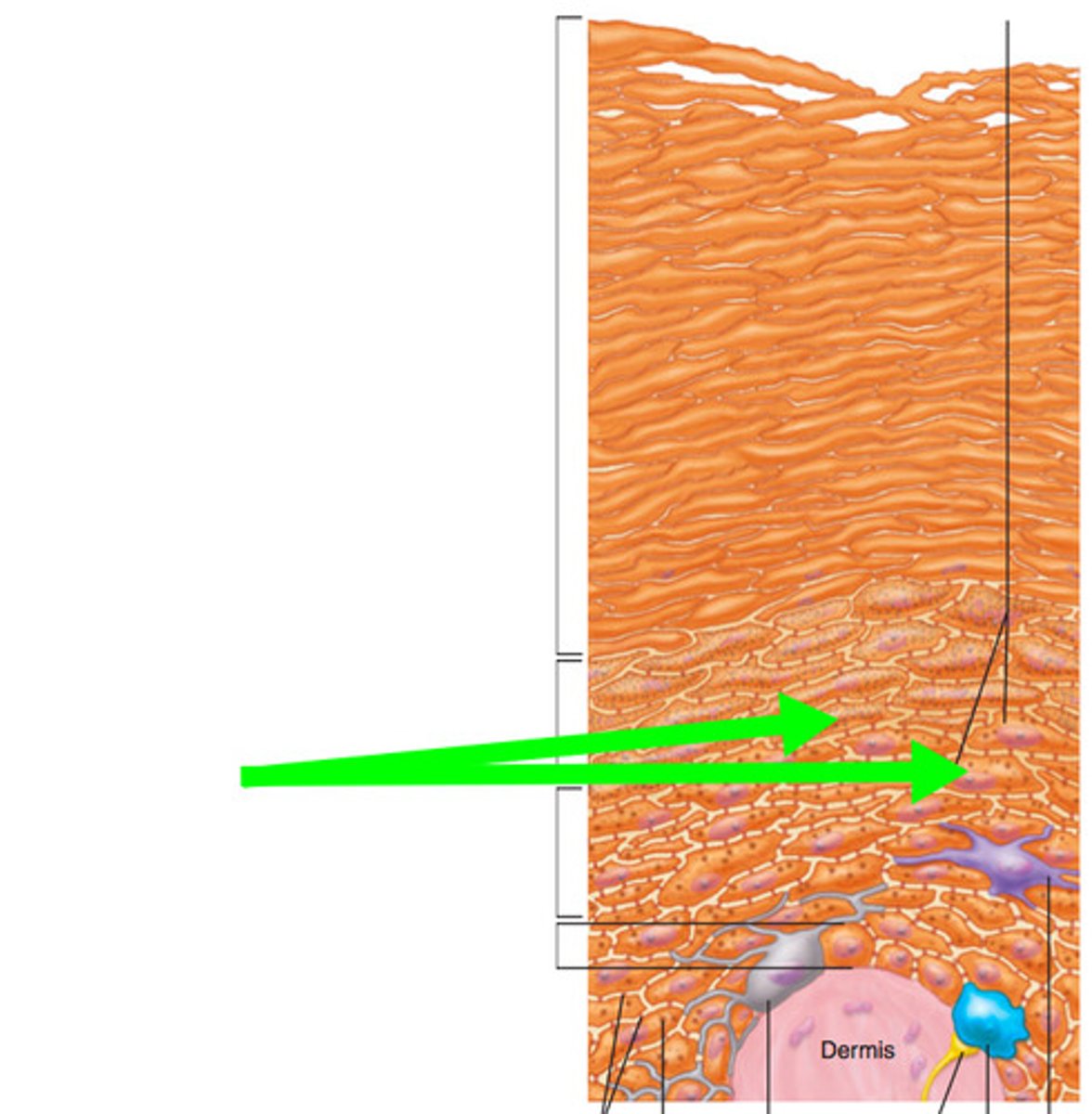
Melanocytes
cells that produce melanin
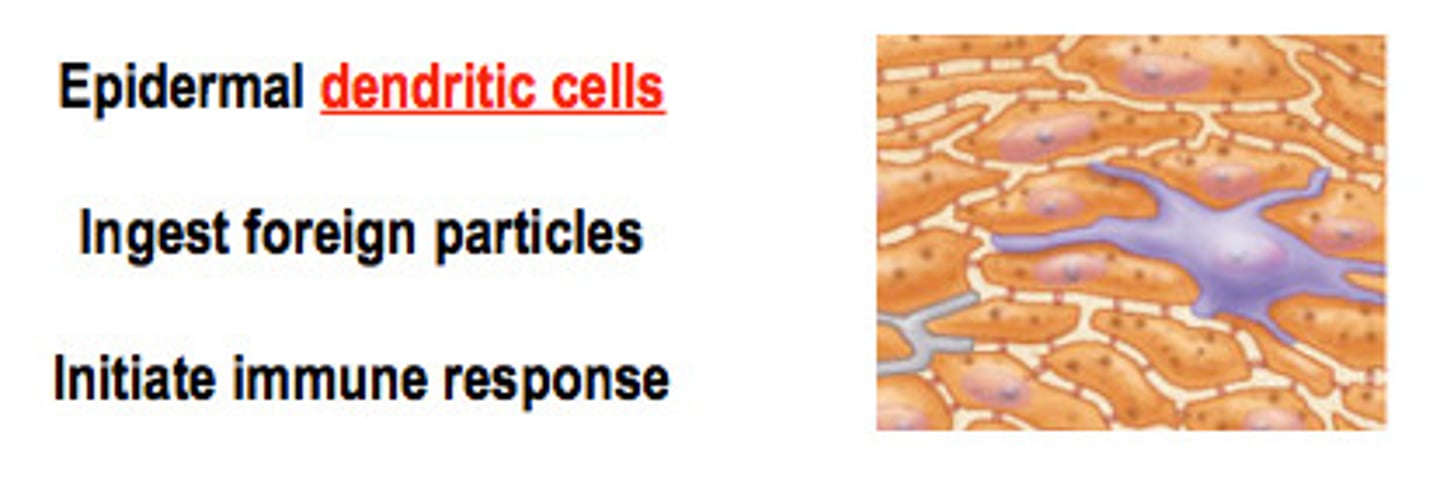
Langerhans cells
epidermal macrophages that help activate the immune system
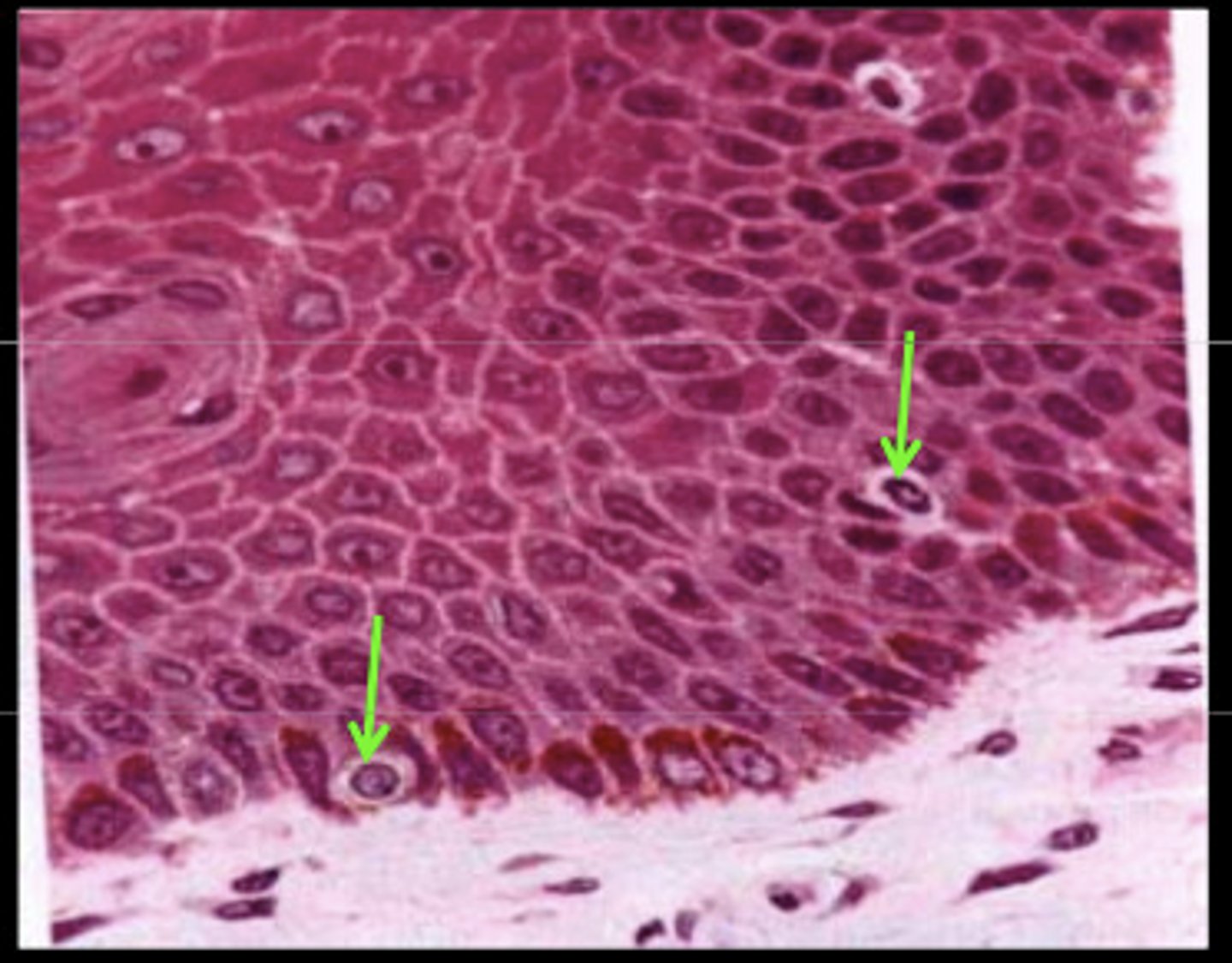
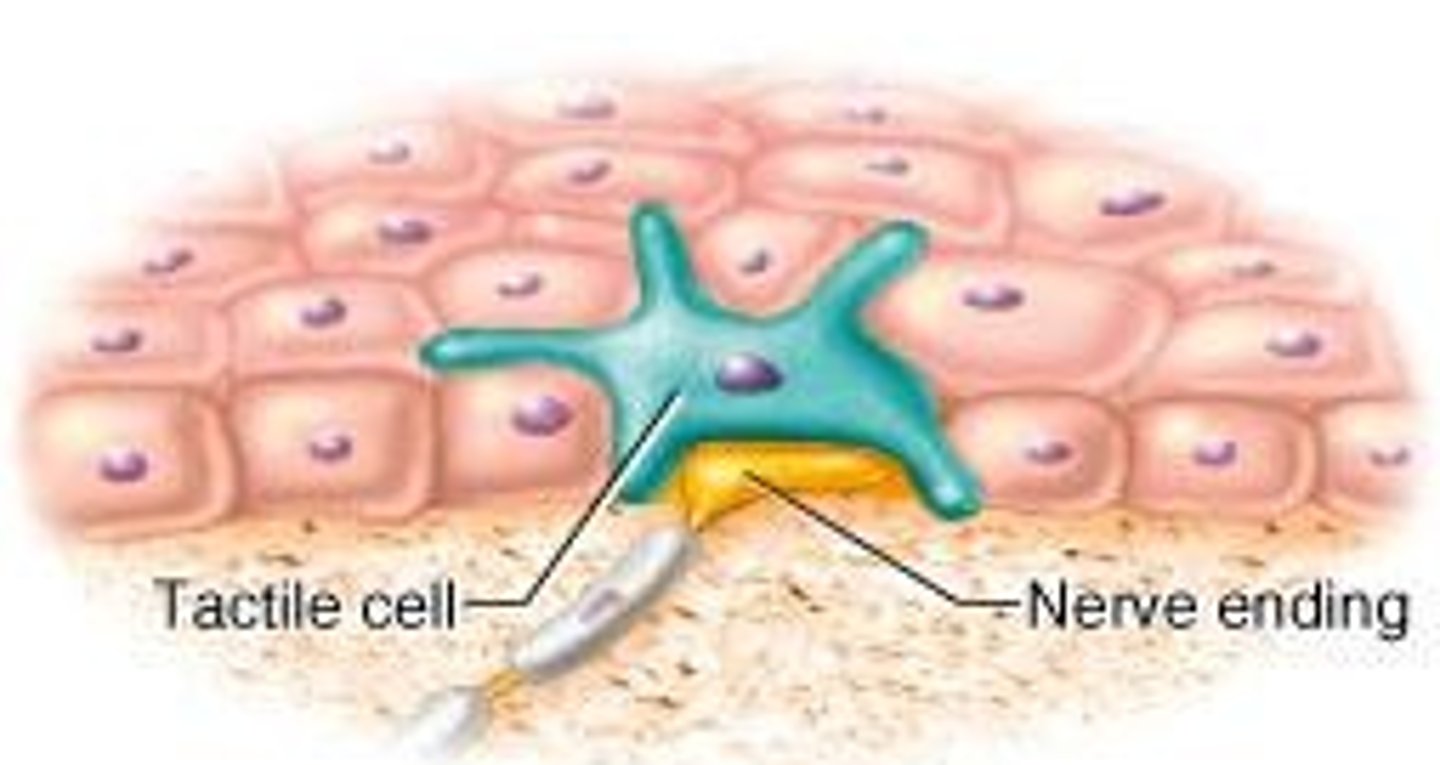
Merkel's cells
detect light touch and superficial pressure
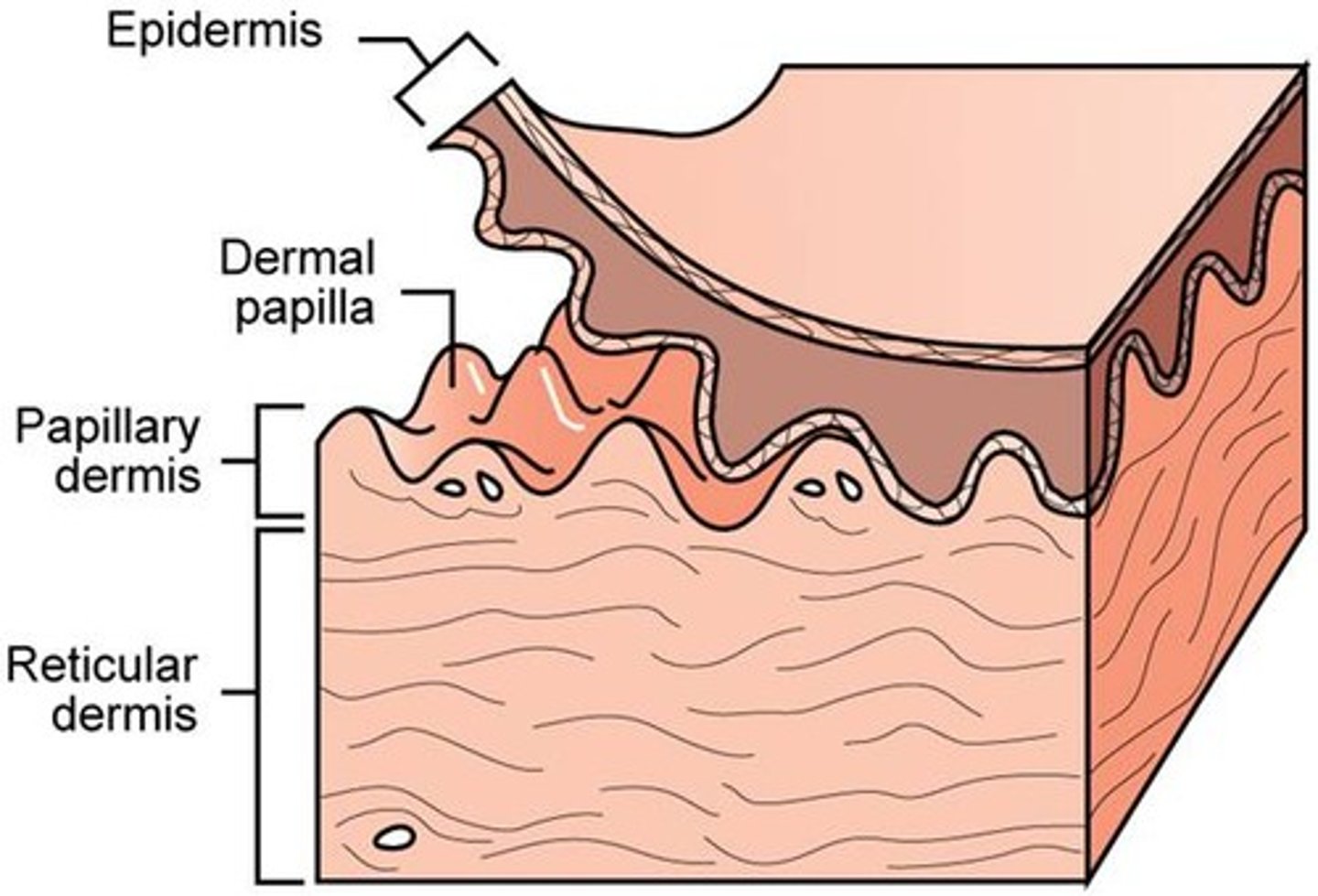
papillary layer
Outermost layer of the dermis, directly underneath the epidermis; made of loose connective tissue
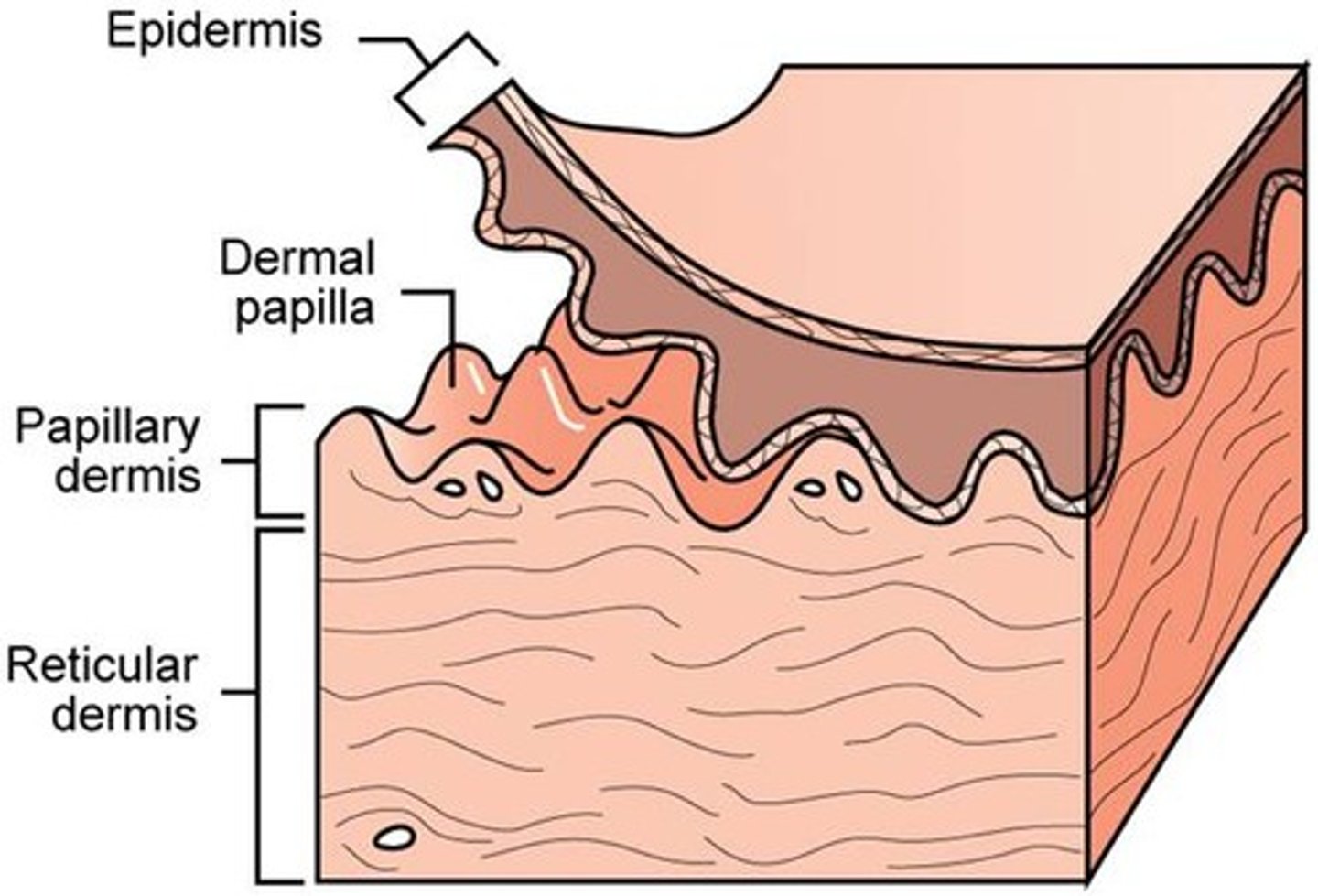
reticular layer
Deeper layer of the dermis; made of dense connective tissue
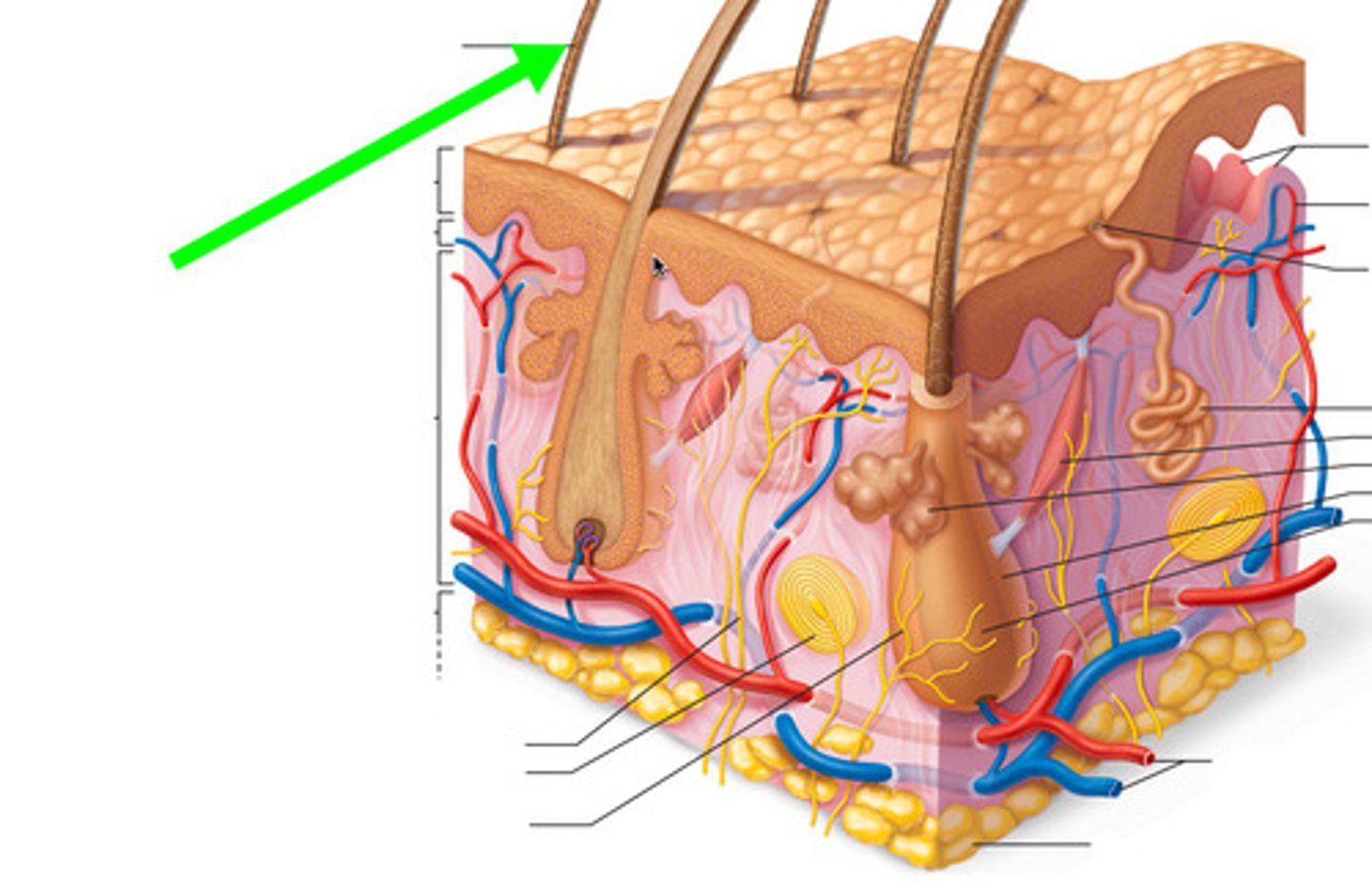
hair shaft
visible part of the hair
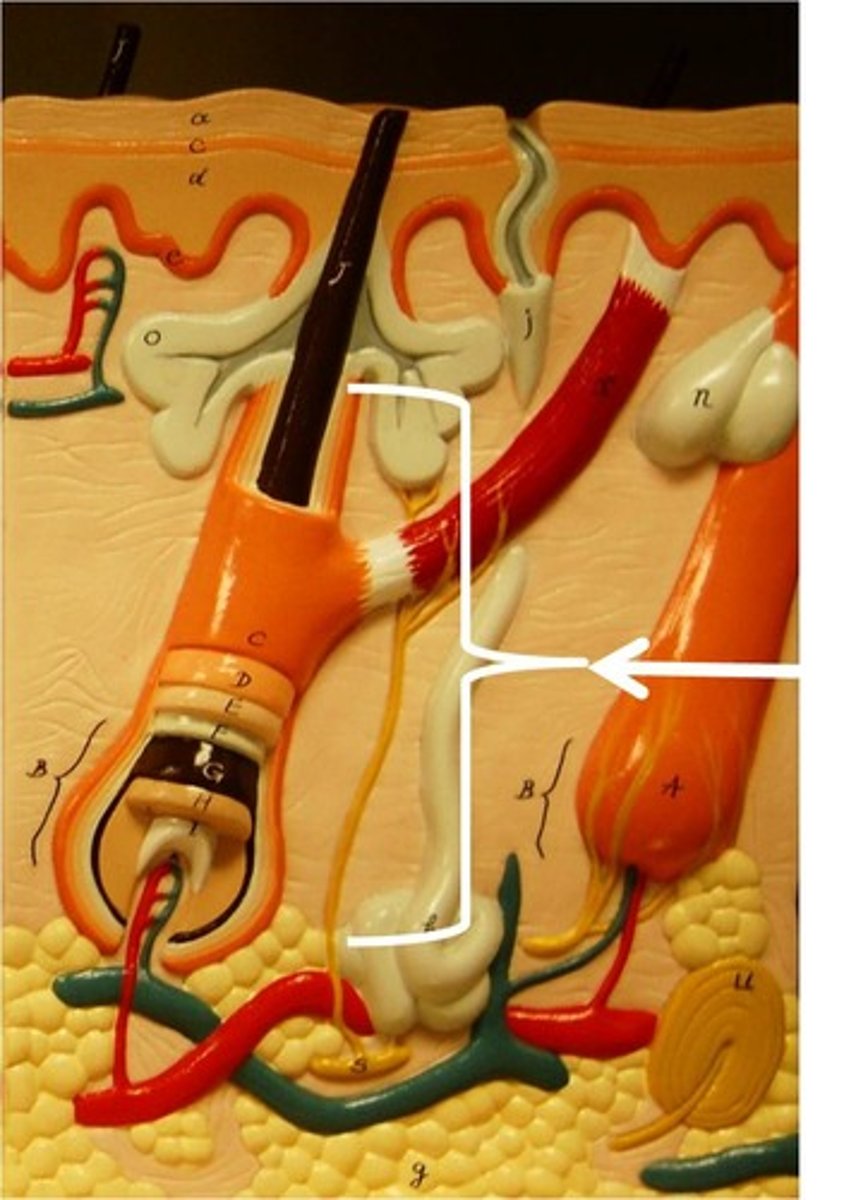
hair follicle
a small tubular cavity containing the root of a hair
serous membrane
Membrane that lines a cavity without an opening to the outside of the body
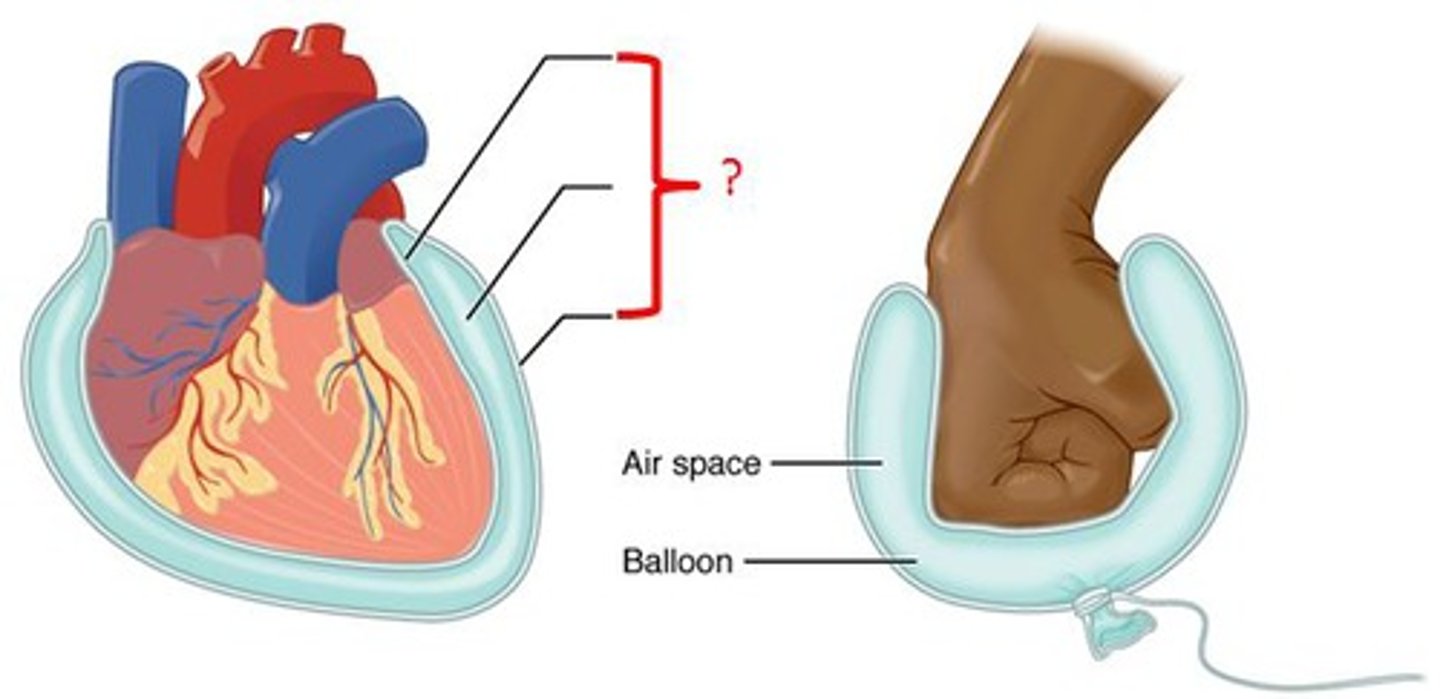
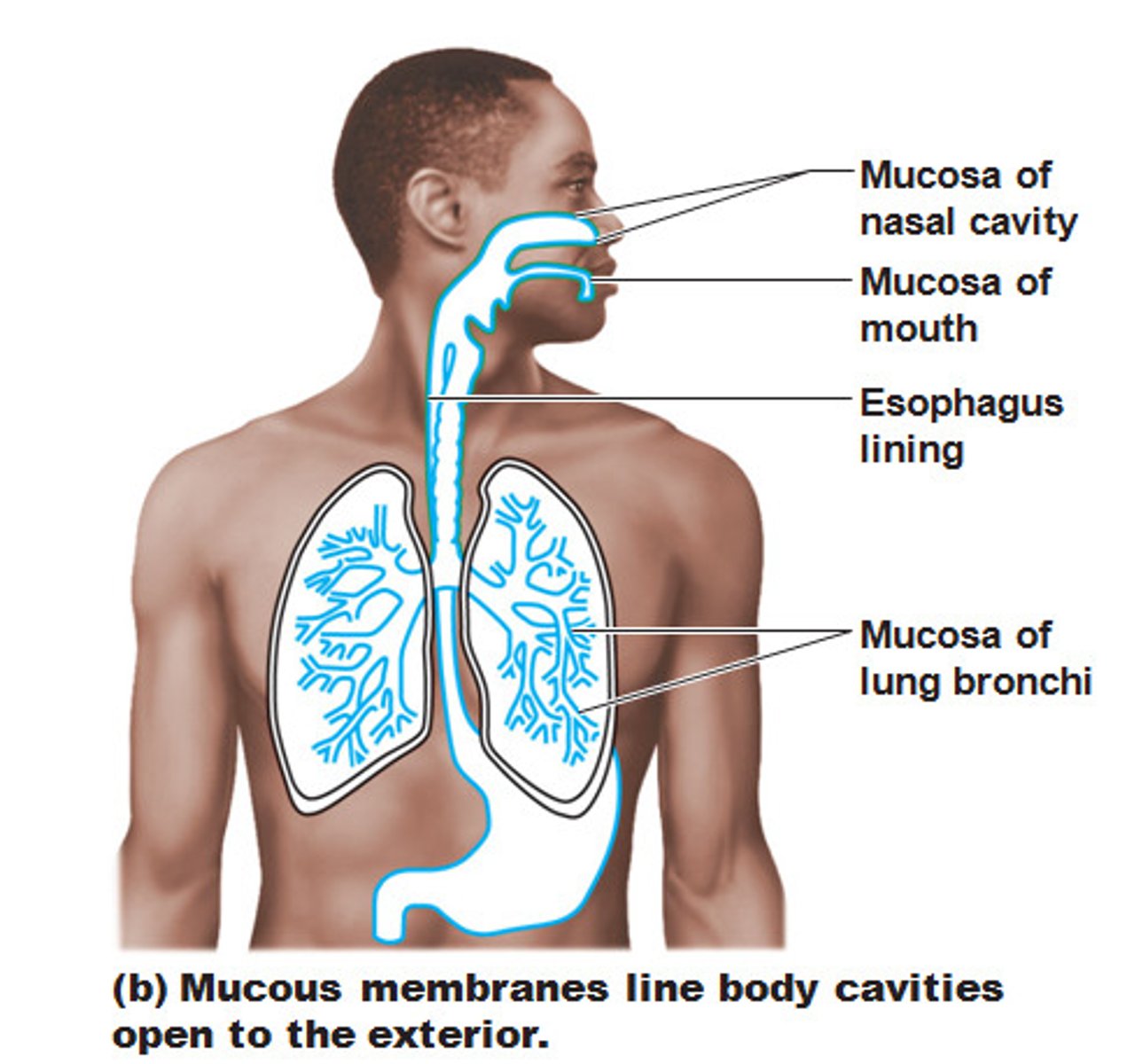
mucous membrane
Membrane that secretes mucus that lubricates the surface of organs and keeps them moist.
parietal portion
serous membrane that lines the walls of a body cavity
visceral portion
serous membrane that covers the surface of organs found in the body cavity
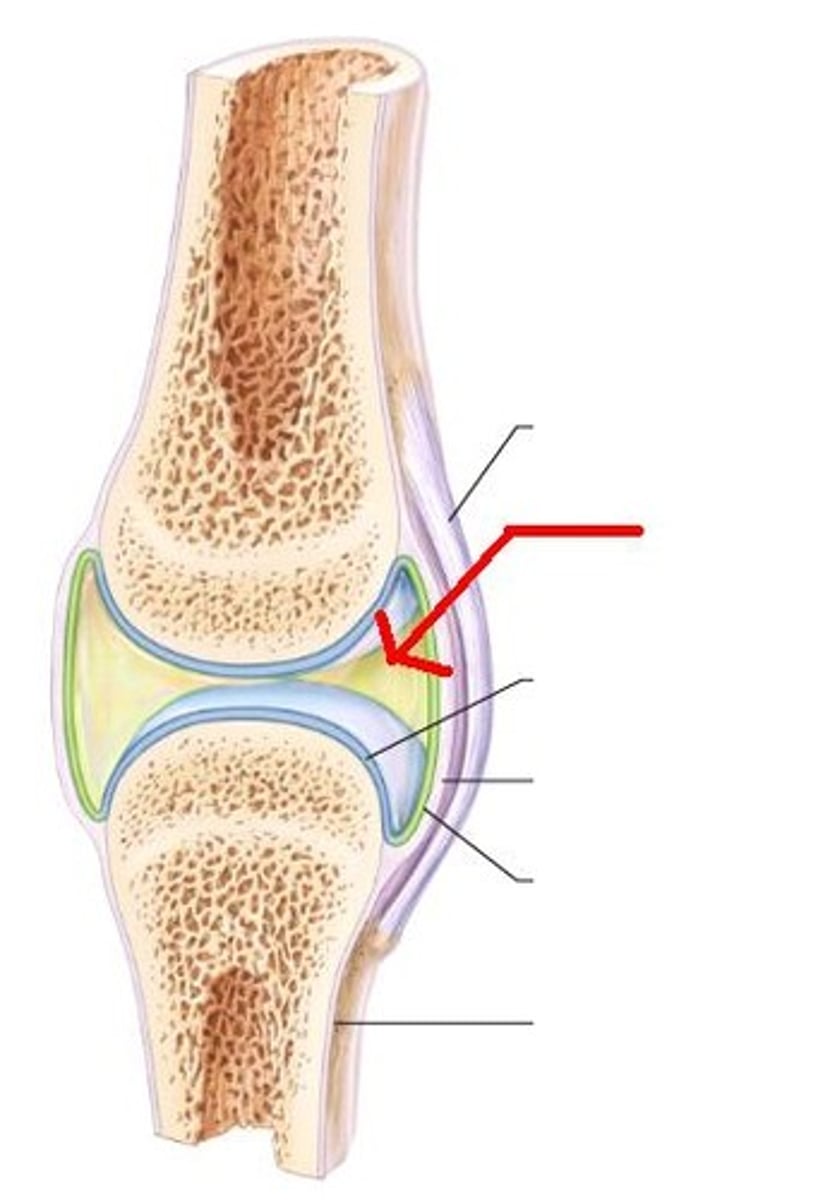
synovial membrane
The lining of a joint that secretes synovial fluid into the joint space.
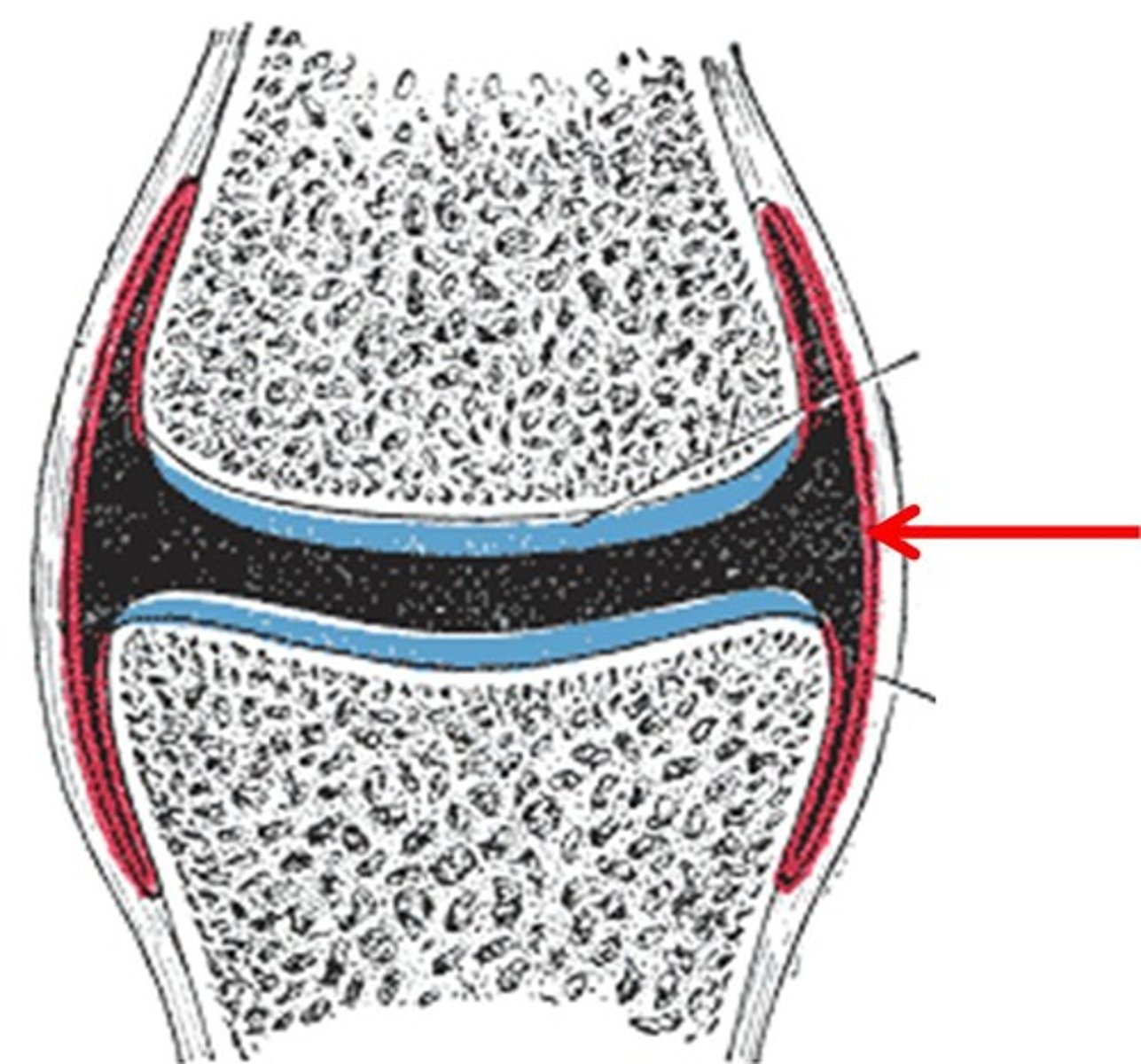
synovial fluid
joint-lubricating fluid secreted by the synovial membrane
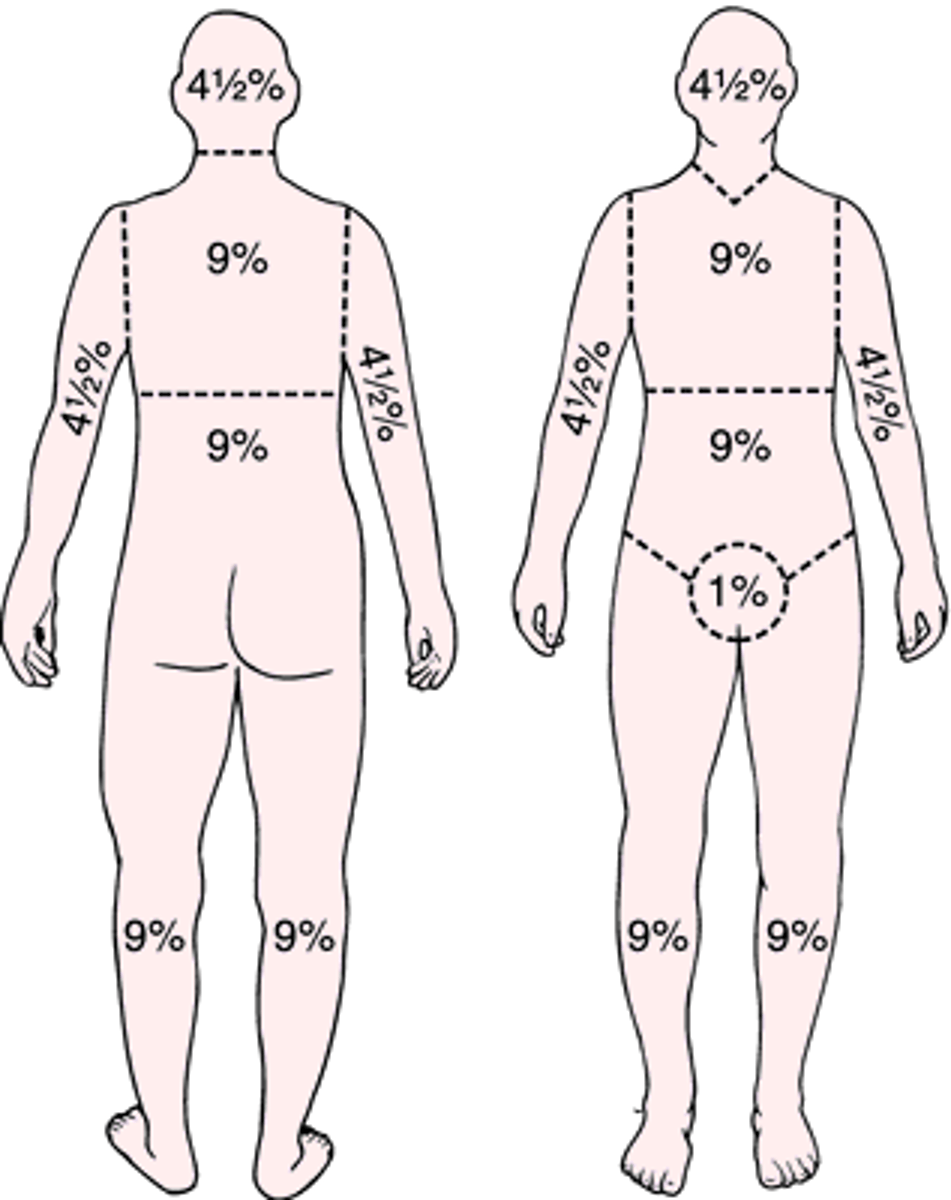
rule of nines
A system that assigns percentages to sections of the body, allowing calculation of the amount of skin surface involved in the burn area.