Parasitology Exam 2
1/240
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
241 Terms
helminths
nematodes: roundworms
cestodes: tapeworms
trematodes: flukes
What are nematodes commonly known as?
Roundworms
What is the largest group of worms that infect humans?
Nematodes
How is the severity of disease caused by nematodes related to worm burden?
Disease is proportional to worm burden
Are nematodes directly fatal?
Rarely
What types of nematodes can cause infection?
Gut, filarial (microfilariae), and zoonotic
gut nematodes
•Enterobius vermicularis (pinworm)
•Trichuris trichiura (whipworm)
•Ascaris lumbricoides
•Hookworms
•Strongyloides stercoralis
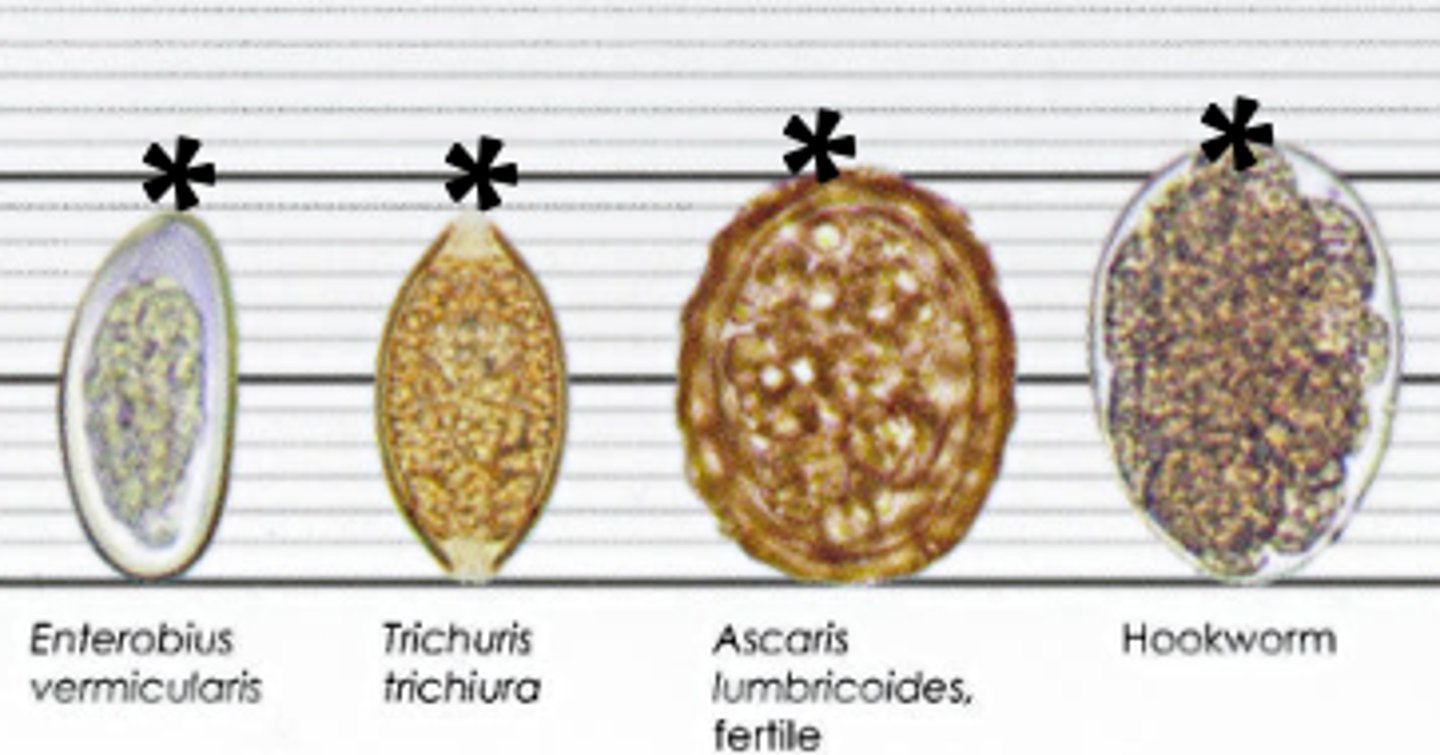
Are the eggs of gut nematodes usually seen?
Yes, but not always!
What is the common name for Enterobius vermicularis?
Pinworms
What is the most common symptom of Enterobius vermicularis infection?
Nocturnal pruritus ani (nighttime anal itching)
What is the life cycle of Enterobius vermicularis?
Eggs are ingested, mature in the small intestine, and females travel to the perianal folds to lay eggs.
How long does it take for Enterobius vermicularis eggs to mature?
4-6 hours
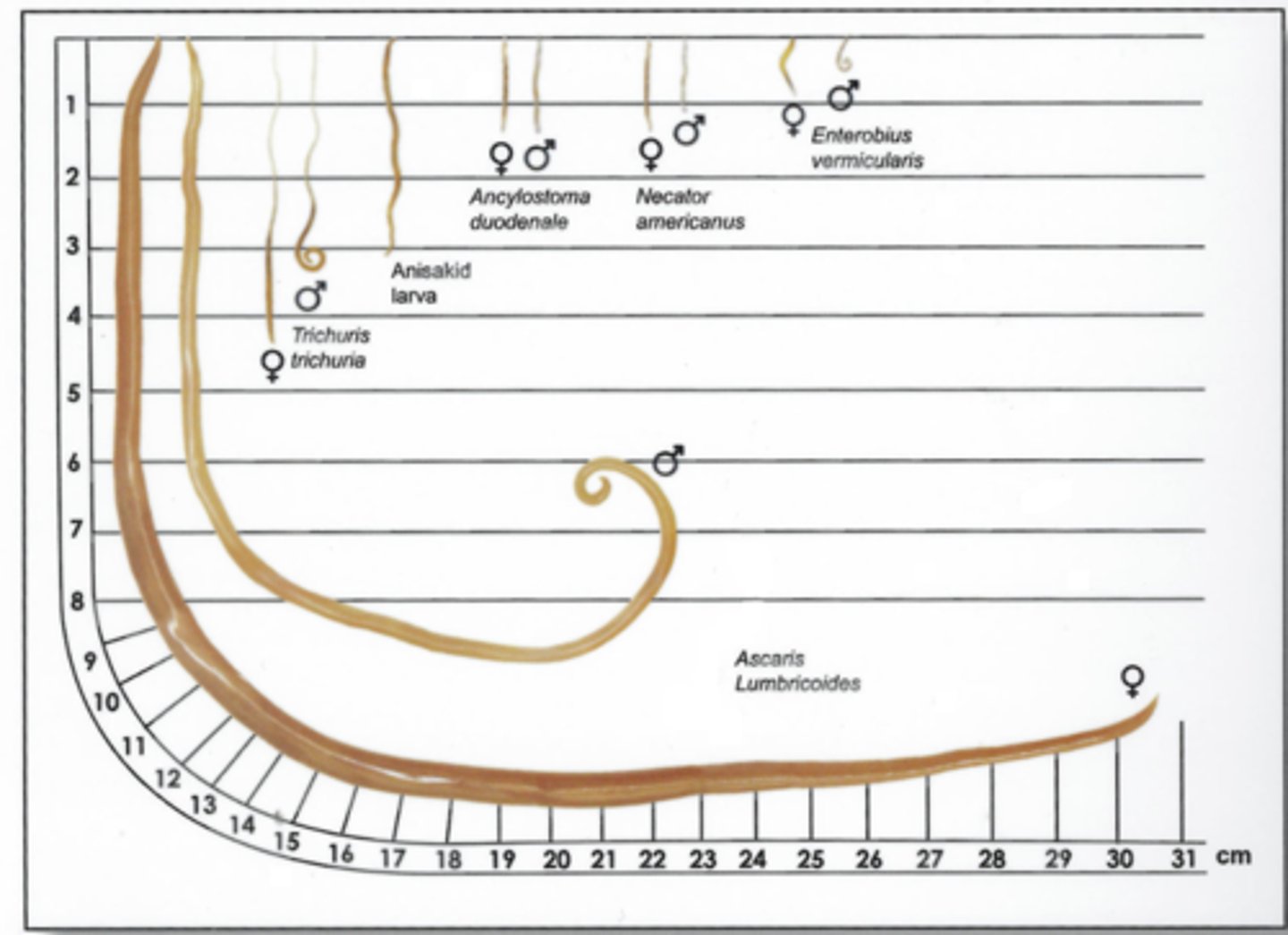
What is the morphology of adult female Enterobius vermicularis?
Pointed tail about 1 cm long
What is the morphology of Enterobius vermicularis eggs?
Medium size, oval but flattened on one end, resembling a 'D'
Do Enterobius vermicularis eggs require soil to develop into the infective stage?
No, they can develop without needing soil.
What method can be used to look for Enterobius vermicularis eggs?
Scotch tape method
Swube Tube
Why are adult Enterobius vermicularis worms rarely seen in stool?
They do not attach and may travel to other areas.
Who is most commonly affected by Enterobius vermicularis infections?
Children
What causes the itching associated with Enterobius vermicularis infection?
Glue-covered eggs
What is the common name for Trichuris?
Human whipworm
What is a key feature of the life cycle of Trichuris trichiura?
It requires soil incubation for eggs to mature.
How do Trichuris trichiura eggs develop into an infective stage?
They need soil for maturation, often from 'night soil' used as fertilizer.
Where do Trichuris trichiura eggs hatch in the human body?
In the small intestine.
What is the primary location of adult Trichuris trichiura in the human body?
Cecum of the intestine.
What is a significant symptom of severe Trichuris trichiura infection?
Trichuris dysentery syndrome, which can cause blood diarrhea.
What is a common complication associated with Trichuris trichiura infection?
Rectal prolapse
Describe the egg morphology of Trichuris trichiura.
They have mucoid bipolar plugs and are very oval in shape, like lemons
What is the adult morphology of Trichuris trichiura?
The head is thin, allowing it to insert into the intestine. The tail forms a spiral "whip", and is thicker.
What disease is caused by Ascaris lumbricoides?
Ascariasis
What are the clinical features of Ascaris lumbricoides infection in the lungs?
Loeffler's syndrome (dry cough, asthma, fever)
What are the clinical features of Ascaris lumbricoides infection in the intestine?
Vague abdominal discomfort, acute colicky pain, restless sleep, diarrhea, malabsorption
What is a major complication of Ascaris lumbricoides infection?
Intestinal obstruction
What is the life cycle of Ascaris lumbricoides?
Eggs develop in soil, larvae migrate to lungs, are coughed up and swallowed, then mature in the intestine.
What is the morphology of fertile Ascaris lumbricoides eggs?
Rounder
45-75 microns
Mammallations
Smoother
What is the morphology of infertile Ascaris eggs?
Oblong
90 microns long
Mammallations
What can happen to Ascaris lumbricoides eggs that lose their mammillations?
They can become decorticated
What is the adult worm morphology of Ascaris lumbricoides?
Largest gut nematode
How do Ascaris lumbricoides worms prevent being passed in the intestine?
They swim upstream instead of attaching.
How long can adult trematodes live for?
decades
What does an operculated egg indicate?
The egg goes into water
What are ectopic infections caused by Ascaris lumbricoides?
Infections in the appendix, pancreas, or bile ducts.
What is the common name Ancylostoma/Necator?
Hookworm
What are the clinical features of hookworm infection?
Ground itch (foot), Loeffler's syndrome, anemia due to blood loss
What is the life cycle of hookworm?
Eggs in feces mature into larvae, penetrate skin (usually in lower limb), migrate to lungs, are coughed up and swallowed, and then grow in the small intestine.
What is the egg morphology of hookworm?
Bumpy inside and smooth outside/cell wall
Inside is noticed first - cell wall is less easily visible
What is the adult worm morphology of Necator americanus?
Two cutting blades
What is the adult worm morphology of Ancylostoma duodenale?
Vampire teef
Ground itch
a skin condition caused by skin penetration of hookworm larvae, usually in lower limbs
Loeffler's syndrome
Symptoms associated with the lung migration stage of intestinal nematodes
How do hookworms cause anemia?
They bite into the intestinal mucosa and feed on blood (lil vampies)
What is the common name for Strongy?
Threadworm
What is the process by which Strongyloides stercoralis larvae enter the body?
Skin penetration
What kind of infection can Strongy cause?
Ongoing autoinfection
What skin condition can result from Strongyloides stercoralis infection?
Ground itch
What syndrome can occur in the lungs due to Strongyloides stercoralis infection?
Loeffler's syndrome
What intestinal symptoms can Strongyloides stercoralis cause?
Bloody diarrhea and chronic colitis
How long can a Strongyloides stercoralis infection persist?
10-20 years
Why is Strongyloides infection particularly dangerous for immunocompromised individuals?
Hyperinfection can occur and be deadly
When might serology be used to diagnose Strongyloides?
To determine a previous exposure - often before an individual is immunosuppressed
What is the adult worm morphology of Strongyloides?
Are Strongy eggs seen?
No, and even larvae are difficult to see
What organism can be identified the agar culture method?
Strongy
Agar culture method
Stool is plated on agar and the migration of the larvae will drag bacteria with it in characteristic directional patterns
What type of food is commonly associated with anisakiasis?
Undercooked fish, particularly cod.
What happens to anisakis larvae in humans?
They cannot mature and instead burrow into the small intestine tissue, causing pain.
What are the symptoms of anisakiasis?
Violent abdominal pain.
What can happen to anisakis larvae after they burrow into human tissue?
They may die or curl up and wait to be eaten by another host.
What kind of nematode is Trichinella:
zoonotic
What type of meat is commonly associated with Trichinella spiralis infection?
Undercooked pork and bear.
What happens to the larvae of Trichinella spiralis after ingestion?
They are released into the intestine, mature, and go into circulation.
Is Trichinella symptomatic?
may be asymptomatic if the infection is light
Where do the larvae of Trichinella spiralis migrate after entering the bloodstream?
muscle tissue
What are some potential complications of Trichinella spiralis infection?
CNS involvement and myocarditis.
What symptoms can muscle encystment from Trichinella spiralis cause?
Myalgia and weakness.
What type of tissue do we examine to diagnose Trichinella spiralis infection?
Muscle tissue
Another name for the muscle cells containing encysted Trichinella
nurse cells
Practice associated with fecal-oral transmission of the nematodes
Use of night soil
scotch tape/swube method for E. vermicularis
Sticky side of clear tape is pressed to perianal folds in the morning to collect eggs
Which nematodes have a soil maturation phase?
Trichuris
Ascaris
Necator/Ancylostoma
Strongy
Which nematodes have a larval migration phase through the lungs?
Ascaris
Necator/Ancylostoma
Strongy
Which nematode is diagnosed by finding rhabditiform larvae in the stool?
Strongyloides
Which nematode is acquired through ingestion of contaminated meat?
Anisakis (fish)
Trichinella (pork, bear)
Which nematode has an auto-infective stage?
Strongyloides
Which nematodes infect humans via skin penetration?
Necator/Ancylostoma
Strongyloides
Cestodes
Tapeworms, flatworms
Types of cestodes
· Taenia solium
· Taenia saginata
· Diphyllobothrium latum
· Dipylidium caninum
· Hymenolepsis nana
· Echinococcus spp.
Where do most adult Cestodes/Tapeworms reside?
In the intestine
What can stool samples show in relation to Cestodes/Tapeworms?
Eggs and/or proglottids
What diseases are caused by larval tapeworms when humans are the intermediate host?
Cysticercosis and Echinococcosis
What methods are used to diagnose Cysticercosis and Echinococcosis?
Serology and examining larvae in tissue
What does the presence of hooklets in an egg indicate?
It is some kind of tapeworm
What is the general morphology of cestodes?
Long, flattened ribbonlike worms
Do cestodes have a gut or body cavity?
No, they absorb nutrients through their skin.
What are the main parts of an adult cestode?
Scolex (head), neck, and body (made of proglottids).
What are proglottids?
Self-contained hermaphroditic reproductive units.
How are proglottids connected to the rest of the cestode body?
By a common cuticle, nerve trunks, and excretory canals.
What is unique about the reproductive capability of each proglottid?
Each proglottid produces its own eggs.
What is the definitive host for Taenia species?
Humans
What type of reproduction occurs in the definitive host of Taenia?
Sexual reproduction
Where do adult Taenia worms reside in humans?
In the gut