6- Diodes and Rectifiers
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
What is the function of an ideal diode?
It allows current to flow in one direction only — conducts in forward bias and blocks in reverse bias.
What happens to current after the threshold voltage in a real diode?
Current rises rapidly and exponentially.
What is reverse breakdown?
A large current flows in reverse bias if the voltage exceeds the breakdown limit, which may destroy the diode
What does the load-line method find?
The intersection point (Q-point) where the diode’s VI curve and circuit equation coincide, giving actual voltage and current.
What equation gives the load line for a diode circuit?
I=(VS−VD)/R.
What is the purpose of the load-line method?
To graphically determine the operating point of a nonlinear device like a diode.
Why is a series resistor used with an LED?
To limit current and prevent the LED from burning out
What is rectification?
The conversion of AC to DC using diodes.
What are the three stages of rectification?
-AC voltage reduced using transformer
-Low voltage AC rectified using diodes
-Pulses smoothed using capacitors, producing nearly constant DC voltage
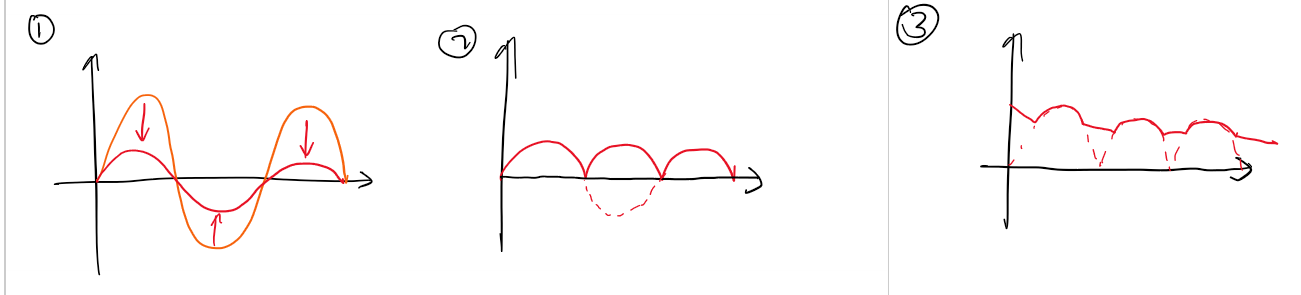
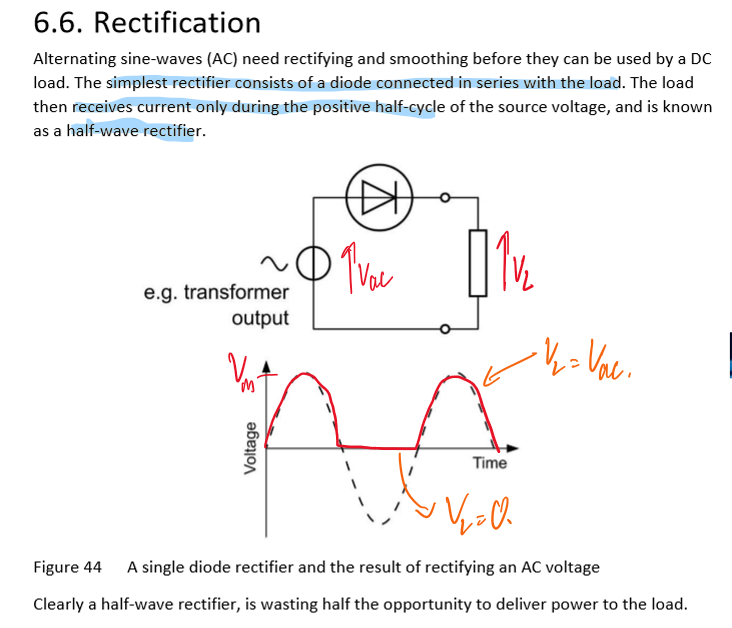
Describe a half-wave rectifier
One diode conducts on positive half-cycles; negative halves are blocked, producing pulsed DC.
What is the average voltage of a waveform?
2Vmax / pi
What is the average voltage of the waveform produced by the halfwave rectifier?
Vmax / pi
Main disadvantage of a half-wave rectifier?
Wastes half the AC waveform and gives poor efficiency
What is a full-wave rectifier?
A circuit that uses both halves of the AC waveform to produce smoother DC
Give an example of a full wave rectifier.
Bridge rectifier with 4 diodes
Why is a full-wave rectifier better than a half-wave?
Doubles the output power, so is more efficient
How does a bridge rectifier work?
Delivers both halfwaves to the load, inverting one so that they both become positive, flowing through the load in the same direction.