Diarrhea & Constipation
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
What is one of the most common causes of mortality in developing countries – especially in infants, and is responsible for ~1.8 million deaths/year?
acute infectious diarrhea
Alterations in fluid, nutrient and electrolyte handling are physiological causes of ___?
diarrhea
Alterations in motor and sensory functions are physiological causes of ___, ___ ____, and ____ ___?
IBS, chronic diarrhea, and chronic constipation
What is the term for difficult or infrequent defecation- defined individually, includes a normal BM range of 2-3/day to 1x/week, and is insignificant until it causes distension, impaction, or reduced quality of life?
constipation
What type of primary constipation is defined as:
normal rate but difficult evacuation- low fiber, low fluid, low exercise, suppression of reflexes
functional
What type of primary constipation is defined as:
impaired motor activity, infrequent BM, straining, distension, palpable stool LLQ
slow transit
What type of primary constipation is defined as:
failure of pelvic floor muscles, difficult defecation
pelvic floor dysfunction
What type of constipation occurs extrinsic to the intestine?
secondary
What will you see on a PE/DRE for a pt with constipation?
strictures, rectocele, prolapse, perineal descent
What are some ALARMING FEATURES?
Age 50+
Severe constipation
Bleeding (frank or FOBT)
FIT testing (fecal immunochemical test)
Family history of colon cancer or IBD
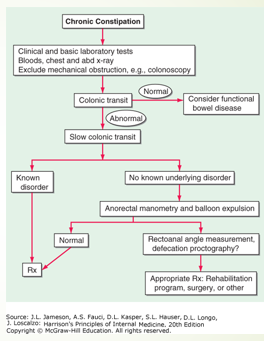
What are some diagnostic tools for constipation?
- CBC, CMP, Ca, TSH
- Colonoscopy/sigmoidoscopy
- Refractory constipation: manometry, balloon expulsion test
- Defecography in select patients
- Colon transit studies (ex Sitz markers) if defecatory studies normal
What are some treatments for constipation?
DETERMINE CAUSE
- Bulk forming: Metamucil, benefiber (with water! – or can worsen constipation
- Softener: Docusate
- Osmotic: miralax, lactulose, saline laxatives (MoM, mag citrate)
- Stimulant: bisacodyl, senna
A pt presents with abd cramping, bloating, stool leakage, with N/V and distention. Upon PE you see a hardened stool in the rectal vault. -- what is the likely dx?
fecal impaction
What is the tx for fecal impaction?
enema, digital disimpaction, laxatives, biofeedback therapy
What is the term for the passage of abnormally liquid or unformed stools at an increased frequency (>3/day)?
diarrhea
*(acute <2 wks, persistent 2-4 wks, chronic >4wks)
what is the term for the frequent passage of small volumes of stool- associated with rectal urgency, tenesmus, or feeling of incomplete evacuation-- typically seen with IBS or proctitis?
pseudo diarrhea
What is the term for involuntary discharge of rectal components?
fecal incontinence
MCC of non-infectious cause of diarrhea is what?
(10%of diarrhea cases)
SE of medication
90% of diarrheal cases are ______.
infectious
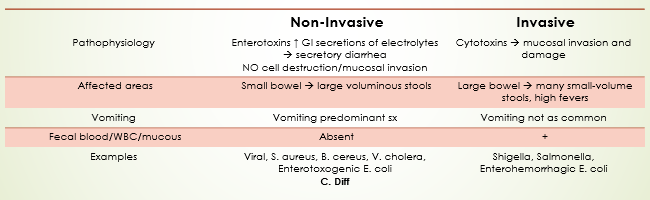
Distinguish between non-invasive vs invasive diarrhea
Non-Invasive | Invasive | |
Pathophysiology | Enterotoxins ↑ GI secretions of electrolytes à secretory diarrhea NO cell destruction/mucosal invasion | Cytotoxins à mucosal invasion and damage |
Affected areas | Small bowel à large voluminous stools | Large bowel à many small-volume stools, high fevers |
Vomiting | Vomiting predominant sx | Vomiting not as common |
Fecal blood/WBC/mucous | Absent | + |
Examples | Viral, S. aureus, B. cereus, V. cholera, Enterotoxogenic E. coli C. Diff | Shigella, Salmonella, Enterohemorrhagic E. coli |
What is the treatment for mild/moderate acute diarrhea (90% cases)?
Low fiber diet, ORAL rehydration, fluids, BRAT diet, etc.
- antidiarrheals if NON- bloody (Loperamide, Bismuth)
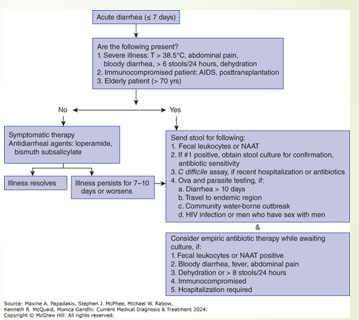
What is the tx for severe diarrhea?
Consider admission: severe dehydration, PO intolerant, worsening bloody diarrhea (pending Cx), severe abdominal pain, sepsis, > 70yo, immunocompromised, signs of HUS (AKI, thrombocytopenia, hemolytic anemia
ABX are generally not warranted for majority of acute diarrhea cases-- but if needed what are the abx of choice?
Cipro 500mg daily x 3 days
Azithromycin 1000mg Once or 500mg daily for 3 days
C. Diff: Vancomycin 125mg PO Q6hr x 10 days. (Flagyl 500mg IV Q8 if inpatient)
What should antibiotics be given in the treatment of diarrhea?
Documented fever, abdominal pain, bloody diarrhea
Bacillary dysentery (frequent scant bloody stools, fever, abdominal cramps, tenesmus) → presumptively due to Shigella
Returning travelers with a temperature of at least 38.5°C or signs of sepsis
What are the MCC of chronic (>4wks) diarrhea infections?
Giardia, E. histolytica, Cyclospora, nematodes
What type of diarrhea is due to Ingestion or Malabsorption of nonabsorbable substance in intestinal lumen secondary to fluid accumulation and there is a ⬇ in diarrhea with fasting and can be tested with a Hydrogen Breath Test?
osmotic diarrhea
What type of diarrhea is due to derangements in fluid and electrolyte transport across the enterocolonic mucosa and IS NOT CHANGED with fasting --- diarrhea still persists?
secretory diarrhea
What type of diarrhea is accompanied by pain, fever, and BLEEDING?
inflammatory diarrhea
*inflammation causes secretion and increased motility
what type of diarrhea is associated with WL, nutritional deficiencies, osmotic and steatorrhea (stool fat >7g/day)?
malabsorption diarrhea
What type of diarrhea can have both osmotic and secretory features and has IBS as the MCC in young adults?
dysmotility diarrhea
*IBS = lower abdominal pain, altered bowel habits, no weight loss/malabsorption
What type of diarrhea is unexplained?
factious diarrhea
What are the MCC of chronic diarrhea?
medications
IBS
lactose intolerance
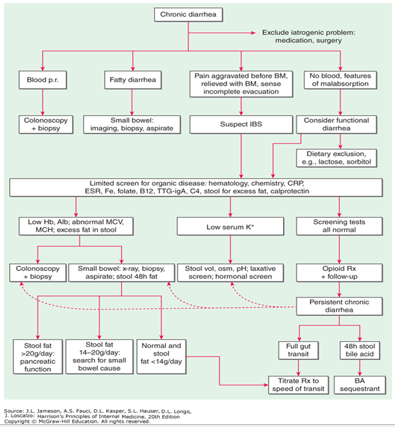
What are the red flags of chronic diarrhea?
nocturnal diarrhea
WL
anemia
(+) FOBT
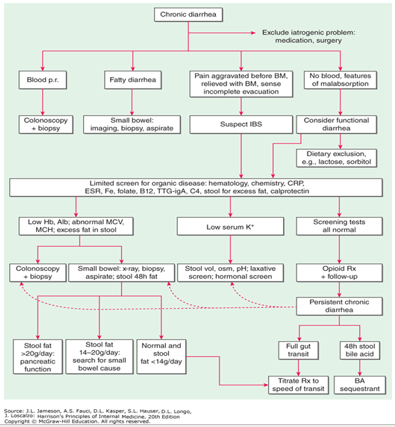
What does greasy/malodorous stool/diarrhea tell you?
malabsorption
What does bloody/pus stool/diarrhea tell you?
inflammatory
What does watery
stool/diarrhea tell you?
secretory or osmotic