L6 Screening and Fragment Based Drug Discovery
1/4
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
5 Terms
What do cell based assays typically test for
Relevant functional outputs like apoptosis, cell proliferation and signalling.
Important features for an assay
-Can it identify if the desired effect is being accomplished by the compound. Positive controls can be used to verify.
-Does it have a good signal window, ensuring a positive result is properly distinguishable from a negative one
-Should be small-scale and automatable as thousands of tests may need to be run.
-If the compound is stored in an organic solvent, the assay need to not be sensitive to the solvent.
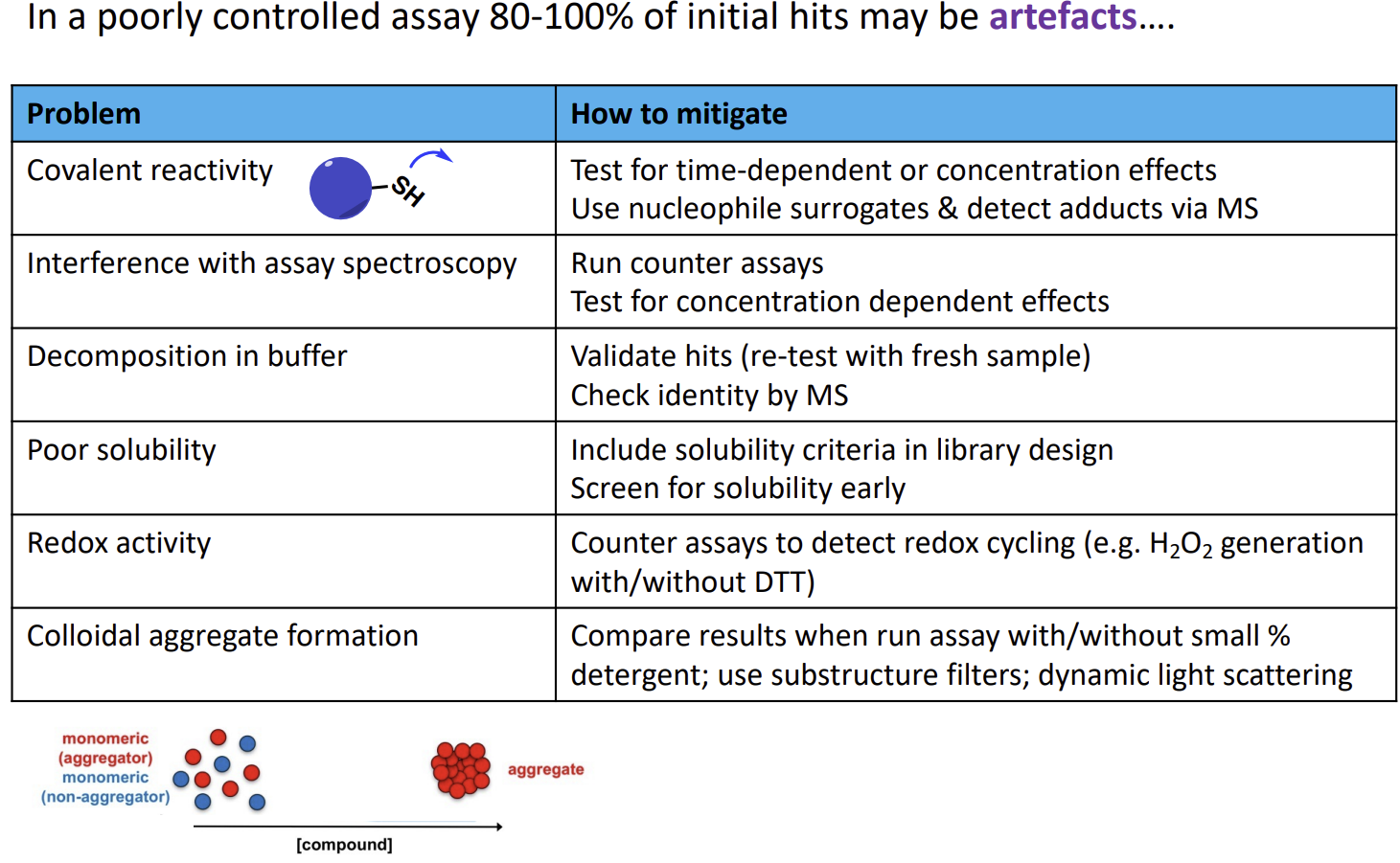
Potential issues with assays and their solutions
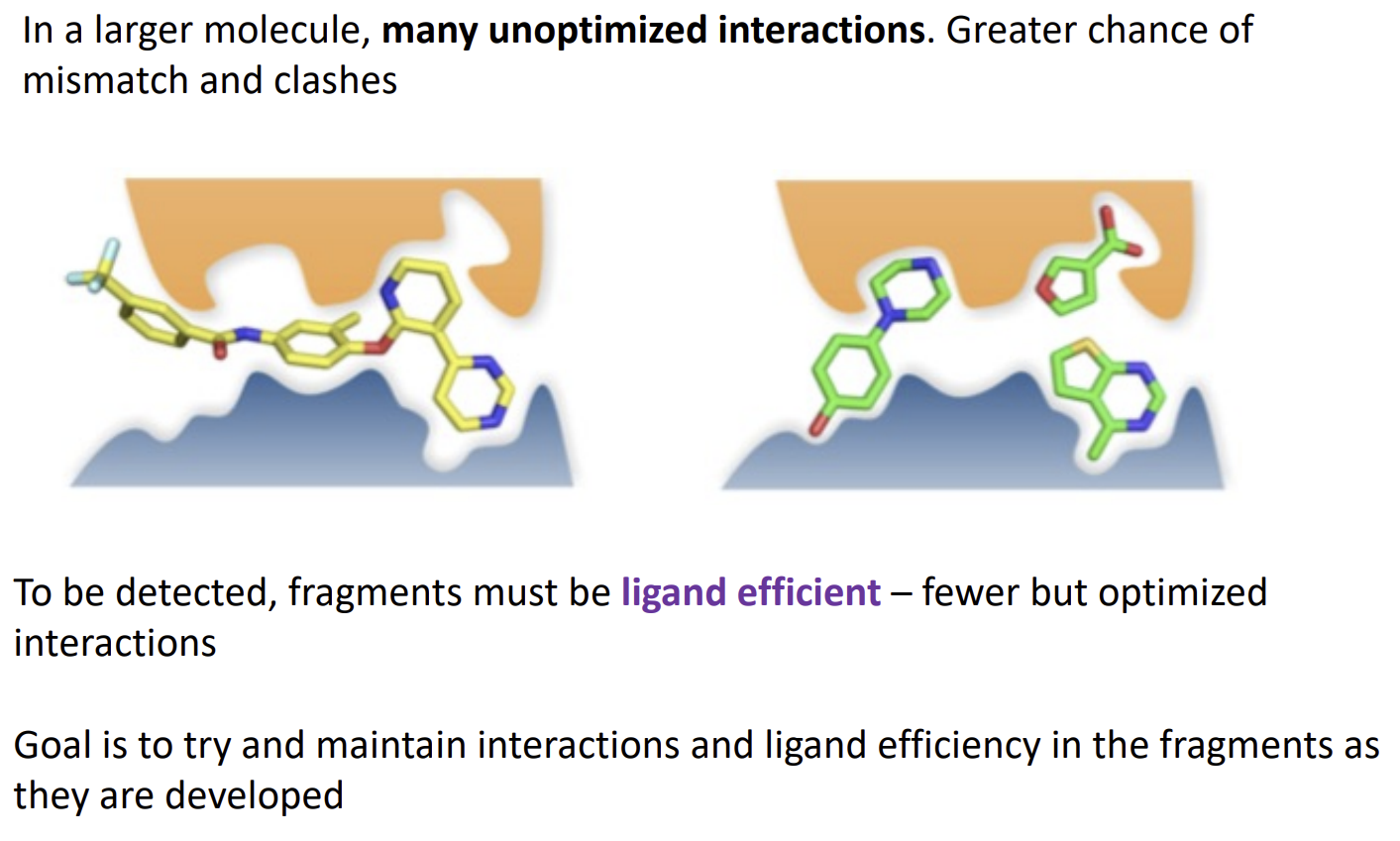
Fragment-based drug discovery principles
The molecule has weak potency (mM rather than uM) for a lead but has a low molecular weight so is very developable. It importantly has high quality interactions (as it has few interactions they have to be good)
Strategies to further develop fragments
Fragment growing - Enlarge the fragment to form favourable interactions with other regions in the binding site.
Fragment merging - in some cases two fragments could be combined if they interact with separate regions of the binding site and do not overlap except at a point where they could be joined.
Fragment linking - if two fragments bind in different regions you could join them using a linker.