Bio animals quiz
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/47
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
1
New cards
absorption
The process of taking nutrients from the digestive system into the blood so they can be used in the body
2
New cards
amino acid
- amino + acid + variable “R” group
- link up diff. combinations to form diff. proteins
-sequence determined by genes
- chain of a/a- polypeptide
- 8/20 are “essential” in diet
-12/20 made by human body
- link up diff. combinations to form diff. proteins
-sequence determined by genes
- chain of a/a- polypeptide
- 8/20 are “essential” in diet
-12/20 made by human body
3
New cards
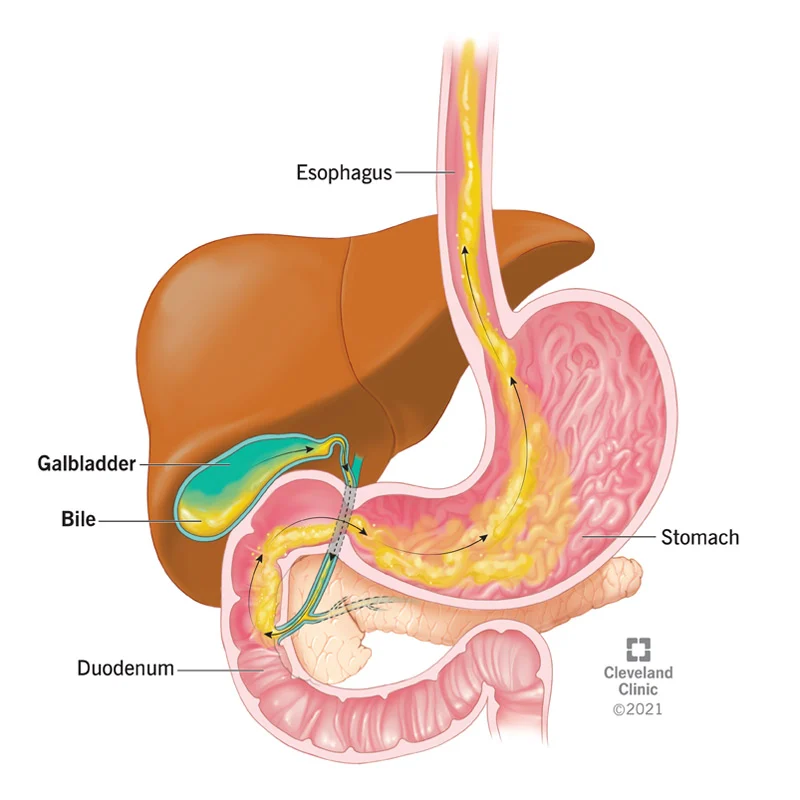
bile
- Formed by the liver
- fluid that is made and released by the liver and stored in the gallbladder
- fluid that is made and released by the liver and stored in the gallbladder
4
New cards
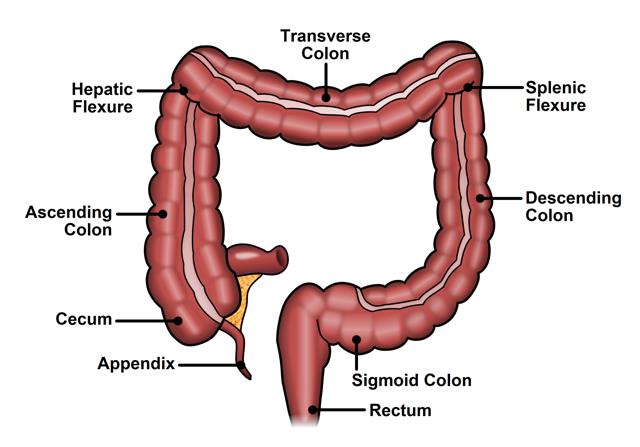
colon (large intestine)
- puckered/ ringed rather than smooth
- approx. 1.5m long
- lack villi
- approx. 1.5m long
- lack villi
5
New cards
digestion
the process of decomposing organic matter by bacteria or by chemical action or heat
6
New cards
3 digestive enzymes
1. Amylase (carbs- sugars)
2. Lipase (lipids- fatty acids + glycerol
3. Trypsin ( proteins - amino acids)
2. Lipase (lipids- fatty acids + glycerol
3. Trypsin ( proteins - amino acids)
7
New cards
Egestion
the act of excreting unusable or undigested material from a cel
8
New cards
fats
Composed of triglyceride= glycerol + 3 fatty acids
9
New cards
ingestion
the process of taking food, drink, or another substance into the body by swallowing or absorbing it
10
New cards
insulin
hormone secreted by the isles of Langerhans in the pancreas; regulates storage of glycogen in the liver and accelerates oxidation of sugar in cells
11
New cards
lipid
an oily organic compound insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents; essential structural component of living cells
12
New cards
mineral
solid homogeneous inorganic substances occurring in nature having a definite chemical composition
13
New cards
pancreatic juice
a fluid secreted into the duodenum by the pancreas; important for breaking down starches and proteins and fats
14
New cards
peristalsis
the process of wavelike muscle contractions of the alimentary tract that moves food along
15
New cards
phospholipid
any of various compounds composed of fatty acids and phosphoric acid and a nitrogenous base
16
New cards
saliva
a clear liquid secreted into the mouth by the salivary glands and mucous glands of the mouth
17
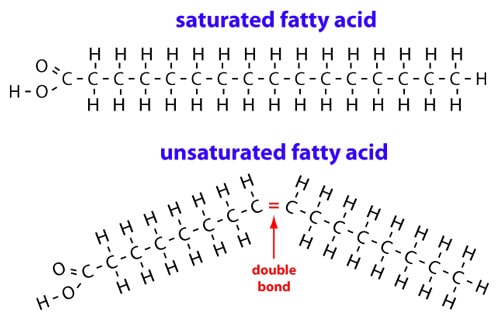
New cards
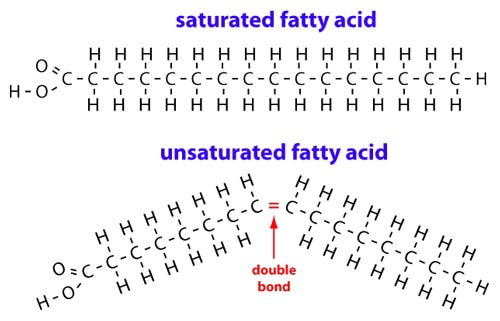
unsaturated fatty acid
a fatty acid whose carbon chain can absorb additional hydrogen atoms
18
New cards
steroids
- Type of lipid
- e.g cholesterol
- e.g sex hormones testosterone and estrogen
- e.g cholesterol
- e.g sex hormones testosterone and estrogen
19
New cards
vitamin
any of a group of organic substances essential in small quantities to normal metabolism
20
New cards
waxes
- type of lipid
- firm yet pliable
- e.g. cutin- waterproof coating for leaves
- e.g. beeswax- to make honeycombs
- firm yet pliable
- e.g. cutin- waterproof coating for leaves
- e.g. beeswax- to make honeycombs
21
New cards
BMR
Your Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR) is the number of calories you burn as your body performs basic (basal) life-sustaining function.
22
New cards
amylase
any of a group of proteins found in saliva and pancreatic juice and parts of plants
23
New cards
carbohydrate
an essential structural component of living cells and source of energy for animals
24
New cards
disaccharide
any of a variety of carbohydrates that yield two monosaccharide molecules on complete hydrolysis
25
New cards
ER= M x EF x T
Energy required (kJ) = Mass x Energy factor x Time
26
New cards
lipase
an enzyme secreted in the digestive tract that catalyzes the breakdown of fats into individual fatty acids that can be absorbed into the bloodstream
27
New cards
pepsin
an enzyme produced in the stomach that splits proteins into peptones
28
New cards
polysaccharide
any of a class of carbohydrates whose molecules contain chains of monosaccharide molecules
29
New cards
protein
any of a large group of nitrogenous organic compounds that are essential constituents of living cells; consist of polymers of amino acids
30
New cards
trypsin
an enzyme of pancreatic origin; catalyzes the hydrolysis of proteins to smaller polypeptide units
31
New cards
saturated fatty acid
a fatty acid whose carbon chain cannot absorb any more hydrogen atoms; found chiefly in animal fats
32
New cards
4 functions of the colon
1. Absorbs water, minerals, and vitamins
2. House E- coli bacteria that use waste to make vitamins
3. Form feces
4. Moves feces for excretion
2. House E- coli bacteria that use waste to make vitamins
3. Form feces
4. Moves feces for excretion
33
New cards
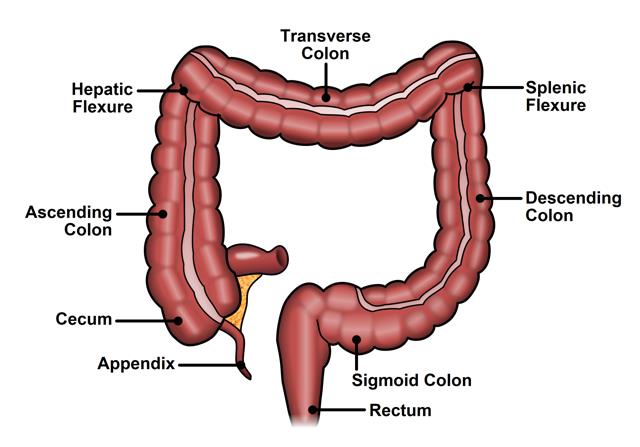
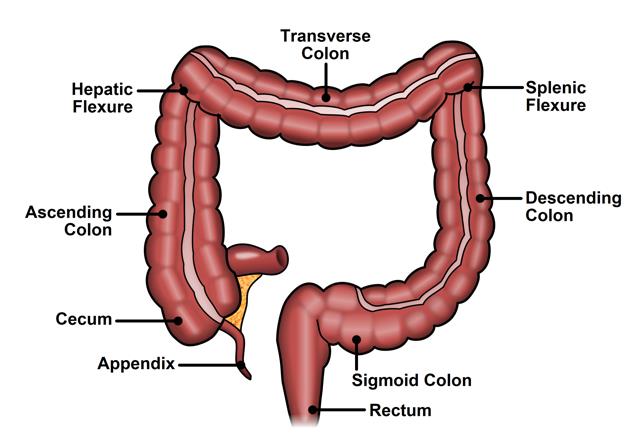
6 sections of the large intestine
1. Caecum
2. Ascending
3. Sigmoid
4. Transverse
5. Descending
6. Rectum
2. Ascending
3. Sigmoid
4. Transverse
5. Descending
6. Rectum
34
New cards
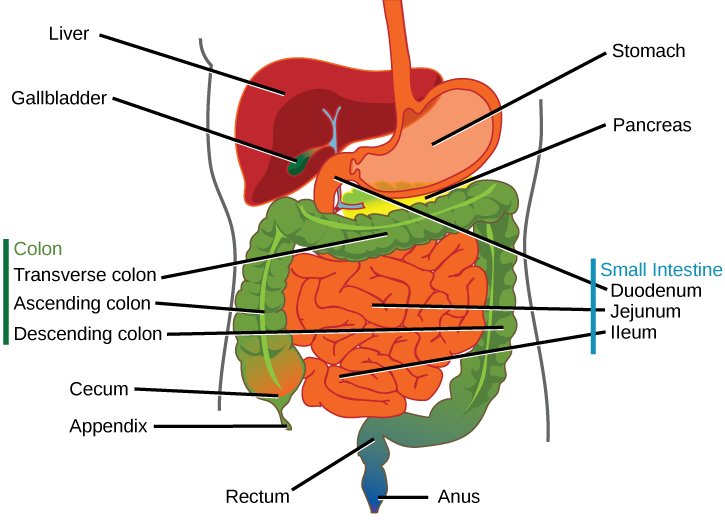
Accessory organs
- Aid in digestion and are outside of the alimentary canal
- secrete their contents into the canal via ducts
- secrete their contents into the canal via ducts
35
New cards
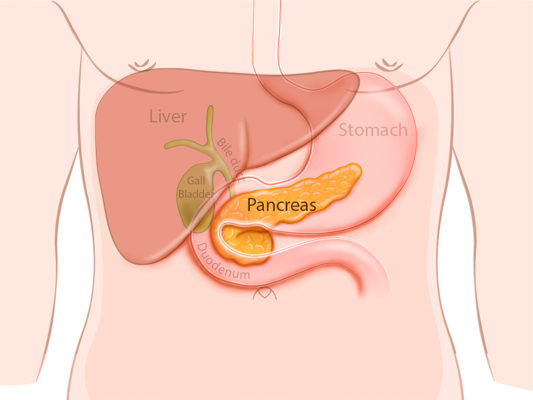
Pancreas
Secretes 2 products:
1. Pancreatic juice
2. Basic, neutralizes stomach acid
3. Contains digestive enzymes
1. Pancreatic juice
2. Basic, neutralizes stomach acid
3. Contains digestive enzymes
36
New cards
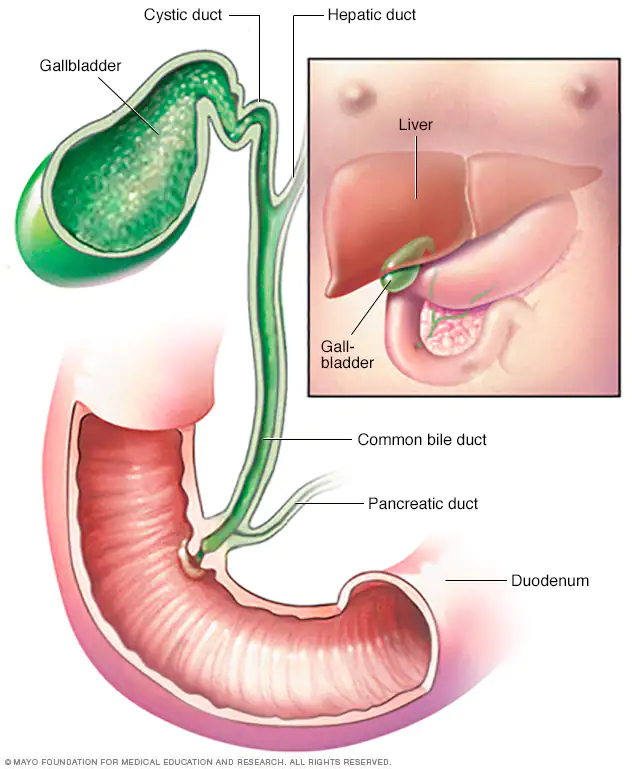
Gall bladder
- small as a finger
- stores bile when stomach is empty
- stores bile when stomach is empty
37
New cards
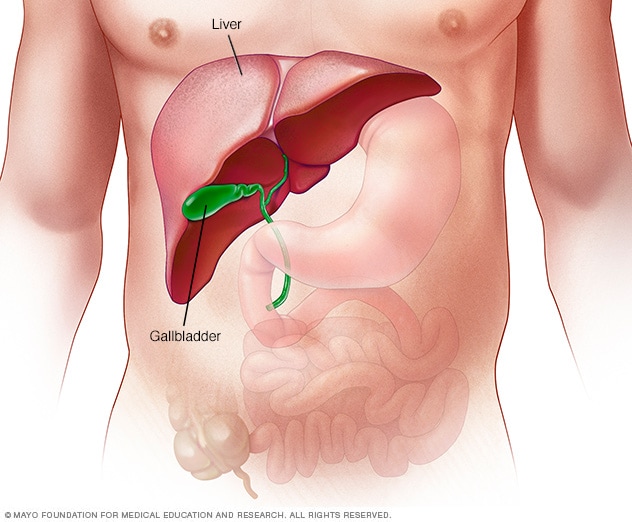
4 main functions of the liver
1. Forms bile
2. Converts glucose - glycogen (stored form)
3. Detoxifies blood
4. Breaks down hemoglobin from RBCs - brown feces
2. Converts glucose - glycogen (stored form)
3. Detoxifies blood
4. Breaks down hemoglobin from RBCs - brown feces
38
New cards
Emulsification of fat by bile
- Physical process
- smaller fat droplets increase surface area for lipase action
- smaller fat droplets increase surface area for lipase action
39
New cards
3 stages of fat emulsification
1. Fats present in small intestine
2. Gall bladder releases bladder
3. Bile salts break down large globs of fat
2. Gall bladder releases bladder
3. Bile salts break down large globs of fat
40
New cards
Water
-Makes up 2/3 of human body mass
- transports nutrients to cells
- lubricates tissues and joints
- regulates body temperature
- transports waste
- major component of blood and mucus
- transports nutrients to cells
- lubricates tissues and joints
- regulates body temperature
- transports waste
- major component of blood and mucus
41
New cards
Mono saccharides
42
New cards
disaccharide
any of a variety of carbohydrates that yield two monosaccharide molecules
a) sucrose
b) maltose
c) lactose
a) sucrose
b) maltose
c) lactose
43
New cards
polysaccharide
Long chains of monosaccharide molecules
a) starch
b) cellulose
c) glycogen
d) chitin
a) starch
b) cellulose
c) glycogen
d) chitin
44
New cards
proteins
any of a large group of nitrogenous organic compounds that are essential constituents of living cells; consist of polymers of amino acids
45
New cards
amino acid
-organic compounds containing an amino group and a carboxylic acid group
- 8/20 are “essential” in diet
- 12/20 made by human body
- 8/20 are “essential” in diet
- 12/20 made by human body
46
New cards
mouth
- Where digestion begins
- food chewed and formed into bolus by the tongue
- food chewed and formed into bolus by the tongue
47
New cards
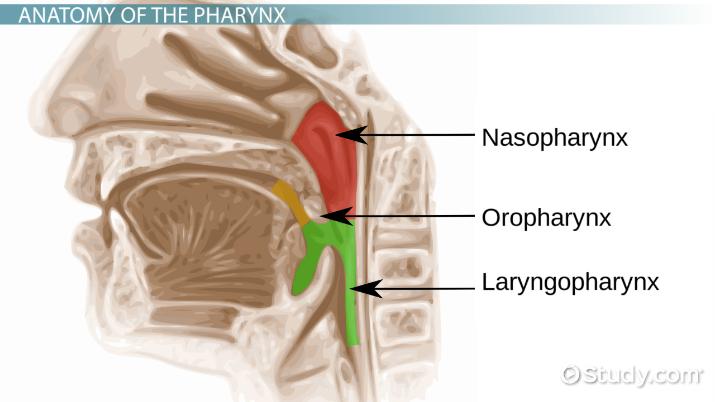
Pharynx
- short tube shared by digestive glands and respiratory system
- passageway for food between mouth and esophagus
- passageway for food between mouth and esophagus
48
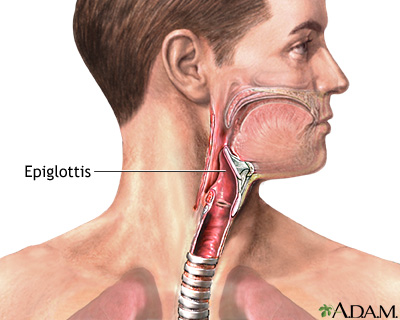
New cards
epiglottis
a flap of cartilage that covers the windpipe while swallowing