CIE IGCSE Physics Formula Sheet
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Average speed
Distance (m) / time (s); formula: s = d/t.
Average velocity
Displacement (m) / by time (s); formula: v = x/t.
Acceleration
Change in velocity (final - initial) / by time; formula: a = (v - u)/t.
Weight
Mass (kg) x gravitational field strength (ms−2); formula: W = mg.
Force
Mass (kg) x acceleration (ms−2); formula: F = ma.
Density
Mass (kg) / volume (m³); formula: ρ = m/V.
Hooke’s law
Force (N) is proportional to extension (m); formula: F = kx.
Pressure
Force (N) / area (m²); formula: P = F/A.
Fluide pressure (Pa)
density x gravitational field strength x height formula: P = ρgh.
Work
Force (N) x distance moved (m); formula: W = Fd.
Power (work)
Work (J) / time (s); formula: P = W/t.
Kinetic Energy
Half the mass (kg) x velocity squared (ms−1); formula: KE = 1/2 mv².
Gravitational potential energy
Mass (kg) x gravitational field strength (ms−2) and height (m); formula: GPE = mgh.
Efficiency
Useful power output / total power input x 100%; formula: η = Pout/Pin × 100%.
Moment (Nm)
Force (N) x perpendicular distance from pivot; formula M = Fd
sum of clockwise moments (Nm)
sum of anticlockwise moments (Nm); formula F1d1 = F2d2
Momentum (kgms-1)
Mass (kg) x velocity (ms−1); formula: p = mv.
Impulsive Force (N)
change in momentum (kgms-1) / time (s); Formula F = change in p / t
Impulse
Change in momentum (kgms−1); formula: Δp = mv - mu.
Boyle’s Law
Pressure1 (Pa) x Volume1 (m³) = Pressure2 (Pa) x Volume2 (m³); formula: P1V1 = P2V2.
Specific heat capacity
Energy (J) is mass (kg) x specific heat capacity (Jkg⁻¹°C⁻¹) times temperature change (°C); formula: Q = mcθ.
Temperature in celsius (C)
temperature in kelvin - 273.15; formula C = K - 273.15
Wave speed
Frequency (Hz) x wavelength (m); formula: V = fλ.
Frequency (Hz)
1 / period (s); formula 1/T
Refractive index (angles)
Ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence to the sine of the angle of refraction; formula: n = sin i/sin r.
Refractive Index (speed)
speed of light in vacuum / speed of light in material; formula n = c/v
Refractive index (critical angle)
1 / sine of critical angle; formula n= 1/sinc
Current
Charge (C) / time (s); formula: I = Q/t.
Voltage (charge)
Energy transferred (J) / charge (C); formula: V = W/Q.
Voltage (V)
current (A) x resistance (Ω); formula: V = IR
Power (electricity)
Current (A) x voltage (V); formula: P = IV.
Power Loss (W)
current2 (A) x resistance (Ω); formula P = I2R
energy transferred (J) current
current (A) x voltage (V) x time (s); formula W = IVt
Energy transferred (J) power
power (W) x time (s); formula W = Pt
resistors in series; total resistance
sum of individual resistors
resistors in parallel
1/total resistance = 1/sum of individual resistors
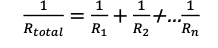
resistance with wires
resistivity (ohm m) x length (m) / area (m2); formula R = pl / A
Transformers voltage and coil ratio
Ratio of voltage in secondary coil to voltage in primary coil equals ratio of turns on secondary to turns on primary; formula: Vs/Vp = Ns/Np.
transformers voltage and current ratio
voltage in secondary coil/voltage in primary coil = current in primary coil / current in secondary coil; formula Vs/Vp = Ip/Is
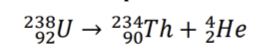
Alpha decay
Nuclear reaction where an atom emits an alpha particle; formula: ZX_A → Z-2Y + A-4He.
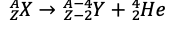
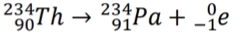
Beta decay
Nuclear reaction where an atom emits a beta particle; formula: ZX_A → Z+1Y_A + -1e_0.
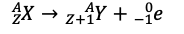
Gamma Decay
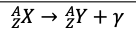
average orbital speed (ms-1)
2 x pi x average radius of the orbit (m) / orbital period (s); formula v = 2 pi r/T
Hubble's Law/ Hubble Constant
Distance of a far galaxy / speed away from us = 1/Hubble constant; formula: d/v = 1/H₀.
Hubble constant 2.2 × 10-18 s-1
speed of light
3.0 × 108 m/s
1 light year
9.5 x 10^15 km