3.4.2 Perfect competition
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
PERFECT COMPETITION
market where there’s high degree of competition
few industries which fit this type of market structure
e.g. may be agriculture but gov interferences may prevent it from being so
assumptions made rarely hold and no market is completely perfectly competitive
PC CHARACTERISTICS
mean that demand for firm’s goods is perfectly elastic, and prices are solely determined by interaction of demand and supply; the firms are price takers
many buyer and sellers
freedom of entry and exit from industry
perfect knowledge
homogenous goods
MANY BUYERS AND SELLERS
means that one firm or customer won’t be able to influence market
e.g. decision of one firm to double their output will have no effect
if firm did manage to have an effect, this would mean the market was no longer perfectly competitive as there would be one large firm and other smaller firms, or one large buyer and other smaller buyers
FREEDOM OF ENTRY AND EXIT FROM INDUSTRY
important as it means that when a business is making profits anyone can enter that market and start producing that product for themselves
as a result, business are unable to make huge profits in long run and if they are making losses they are able to leave
in long run, they make normal profits
PERFECT KNOWLEDGE
enables firms to know when other firms are making profits which will attract them to join market
all firms also have same costs as they can use same production techniques
also means that any attempt to raise prices above level determined by market will lead to no sales, as customers will be aware they can buy the same good for a lower price
HOMOGENOUS GOODS
important because it means if a firm raises it price above competitors’ no one will buy it and they won’t gain from lowering their price because they can sell all of your product at the same price as everyone else
PROFIT MAX EQULIBRIUM
firms assumed to SR profit maximise- MC=MR
SR- possible for firm to make a normal profit, a supernormal profit or a loss.
LR- only normal profit for perfect comp
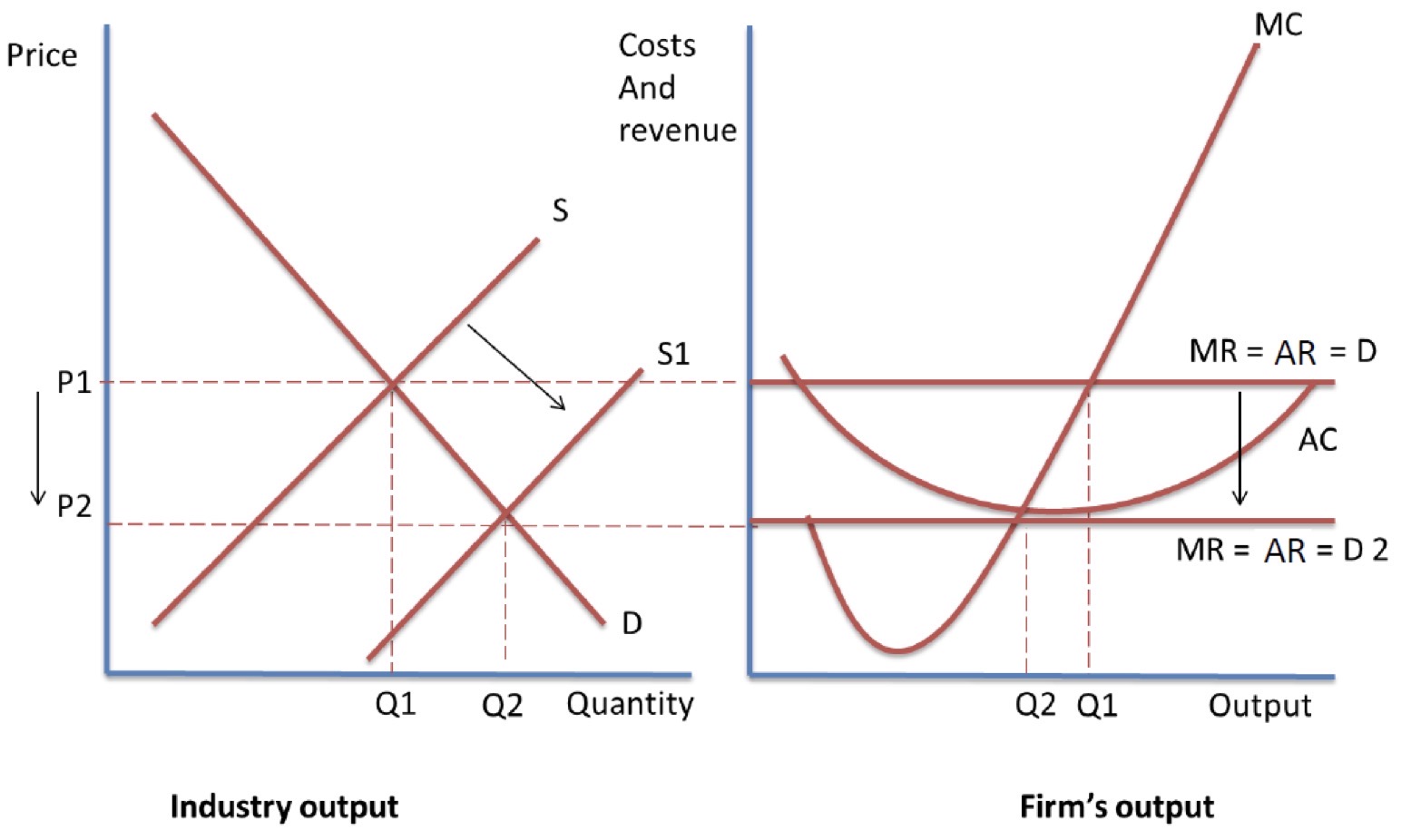
PROFIT MAX SR EQUILIBRIUM- DIAGRAM
firm is a price taker- accepts industry price of P1
firm produces an output of Q1
yellow shaded rectangle shows area of SNP earned in SR

PROFIT MAX LR EQUILIBRIUM- DIAGRAM
SNP made by existing firms means that new firms have an incentive to enter industry and no barriers allow them
causes supply to increase- shown by right shift in supply from S to S1
price level falls
since firms are price takers- accept this new price
SNP competed away, so firms only make normal profits
new equilibrium at P=MC means firms produce at the new output of Q2 in the long run
ADVANTAGES OF PROFIT MAX
LR- P=MC- allocative efficiency
LR- produce at the bottom of AC curve- productive efficiency
DISADVANTAGES OF PROFIT MAX
competition should keep costs and prices low- but firms unable to benefit from EoS so costs may be higher
dynamic efficiency limited due to perfect info- means one firms’ invention will be adopted by another firm so investment will give the firm no competitive benefit