Functions and Their Graphs - 1.2
1/13
Earn XP
Description and Tags
29/01/26
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
what is “e”?
euler’s constant (roughly equal to 2.17… functions like pi)
what is “ln”?
it represents a logarithm with base e. you’ll often see ln x
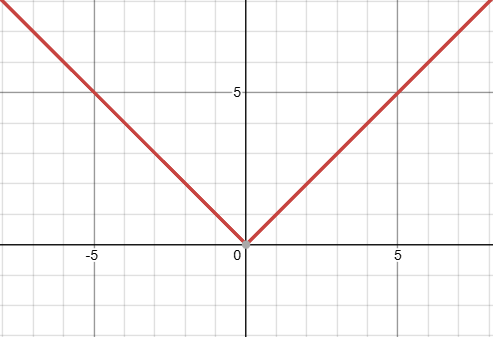
what kind of function is this, and what is it’s domain?
absolute value function, with infinite domain. also considered a piecewise function
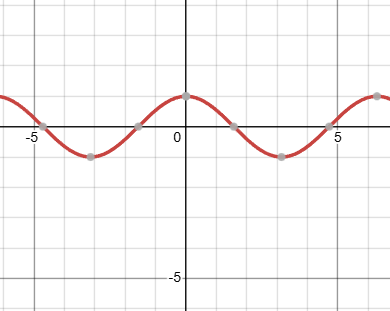
what kind of function is this, and what is it’s domain?
that’s a cos graph, with an infinite domain, and it starts at its peak of 1
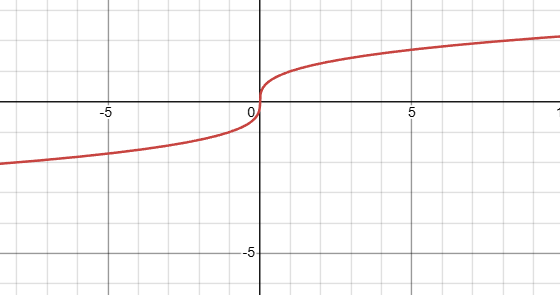
what kind of function is this, and what is it’s domain?
thats a cube root graph, with an infinite domain (cuz you can take negative roots with odd indexes)
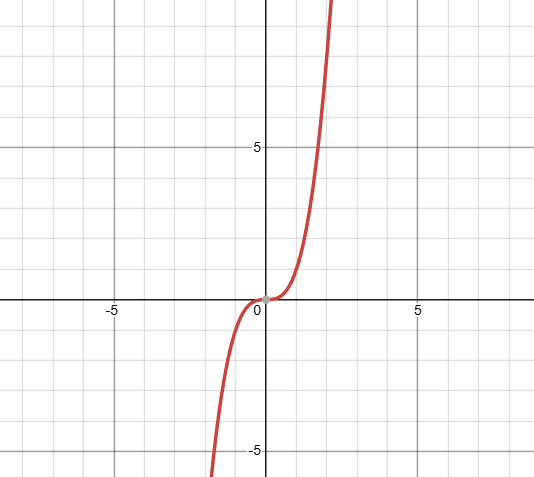
what kind of function is this, and what is it’s domain?
that’s a cubic graph, with an infinite domain.
what is the domain of ANY polynomial function?
inifinite
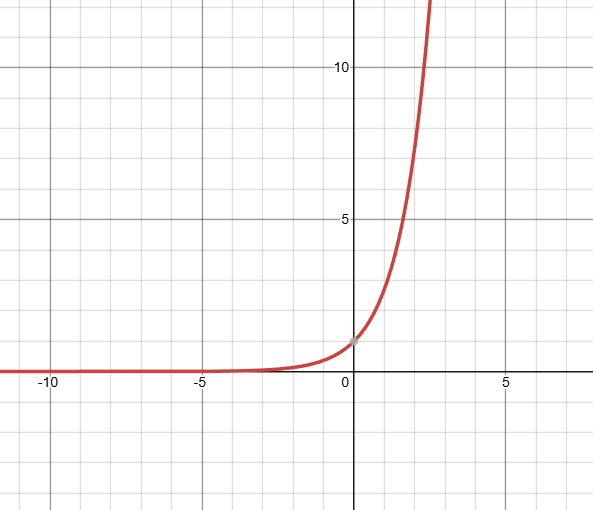
what kind of function is this, and what is it’s domain?
that is an exponential graph, with a base of e. it has an infinite domain, and a y-int at y=1
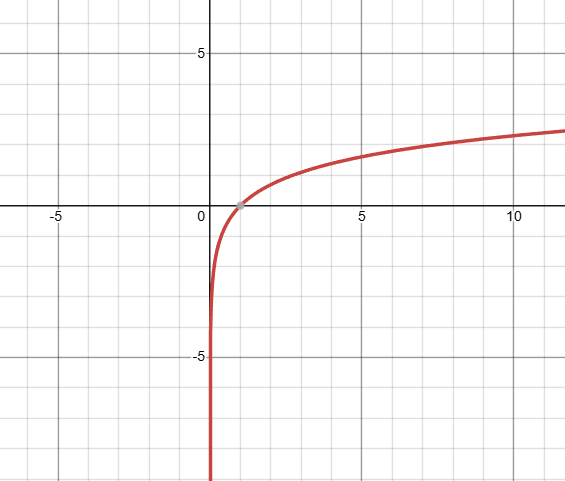
what kind of function is this, and what is it’s domain?
that is a logarithmic graph, with a base of e. it has a restricted domain (can’t have negative arguments for logs) of zero to infinity. note that the zero is not expressed, and that there is an x-int at 1. (the inverse of an e exponential graph)
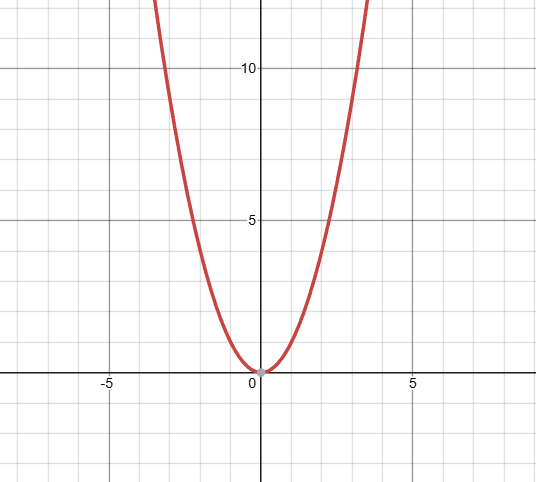
what kind of function is this, and what is it’s domain?
that’s a quadratic, with an infinite domain.
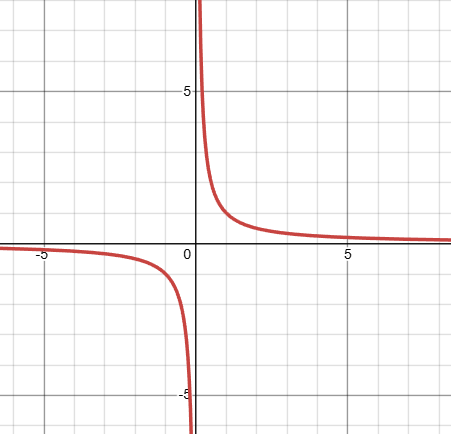
what kind of function is this, and what is it’s domain?
that is a rational function, with a restricted domain (-infinity, 0) U (0, infinity), due to a vertical asymptote at x = 0 (and a horizontal asymptote at y = 0). it is the inverse of a y = x graph
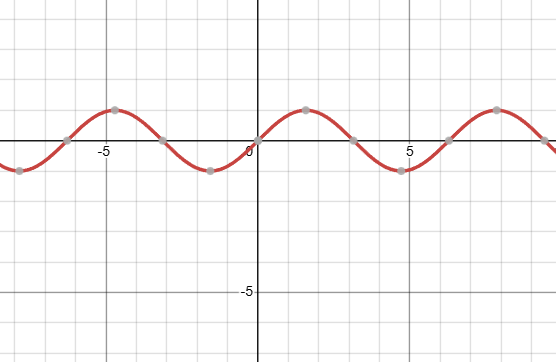
what kind of function is this, and what is it’s domain?
thats a sin graph, with an infinite domain. note how it starts at the origin, at the midline of its wave
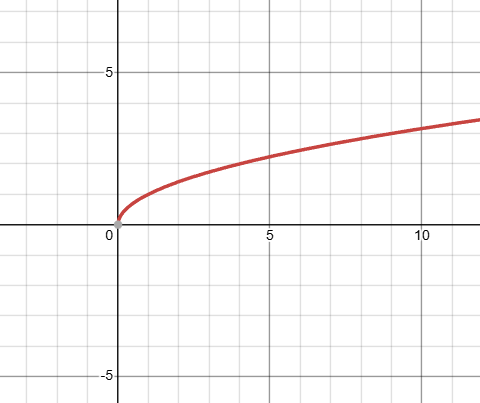
what kind of function is this, and what is it’s domain?
that is a square root function, with a restricted domain. you cannot take the square root of a negative, so there are no values there. note, zedro is expressed.
for quadratic functions, the constant term will always be the what….
the y-int