Lab 3: pH, Buffers, and Acid-Base Reactions
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
Acid
Substance donating hydrogen ions in water.
Base
Substance releasing hydroxide or absorbing hydrogen ions.
HCl
Strong acid donating protons in water.
Water (H2O)
Amphoteric substance acting as acid or base.
Conjugate Base
Species formed after an acid donates a proton.
Conjugate Acid
Species formed after a base accepts a proton.
Acid Dissociation Constant (Ka)
Equilibrium constant for acid ionization.
Strong Acid
Completely dissociates in solution, e.g., HCl. Acid with large Ka, equilibrium shifts right.
- Gastric Secretions
Weak Acid
Acid with small Ka, equilibrium shifts left. Partially dissociates in solution, fewer H+ ions.
- lemon juice: pH 2
Auto-ionization of Water
Water dissociating into H3O+ and OH-.
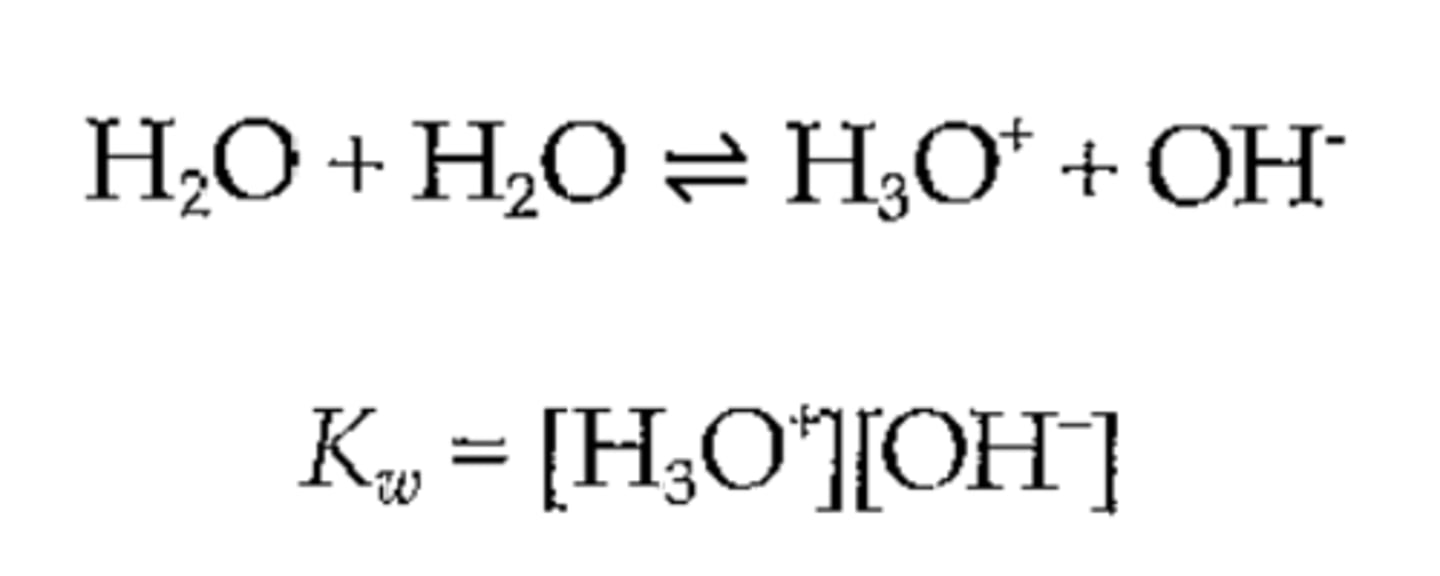
Dissociation Constant of Water (Kw)
Product of concentrations of H3O+ and OH-.
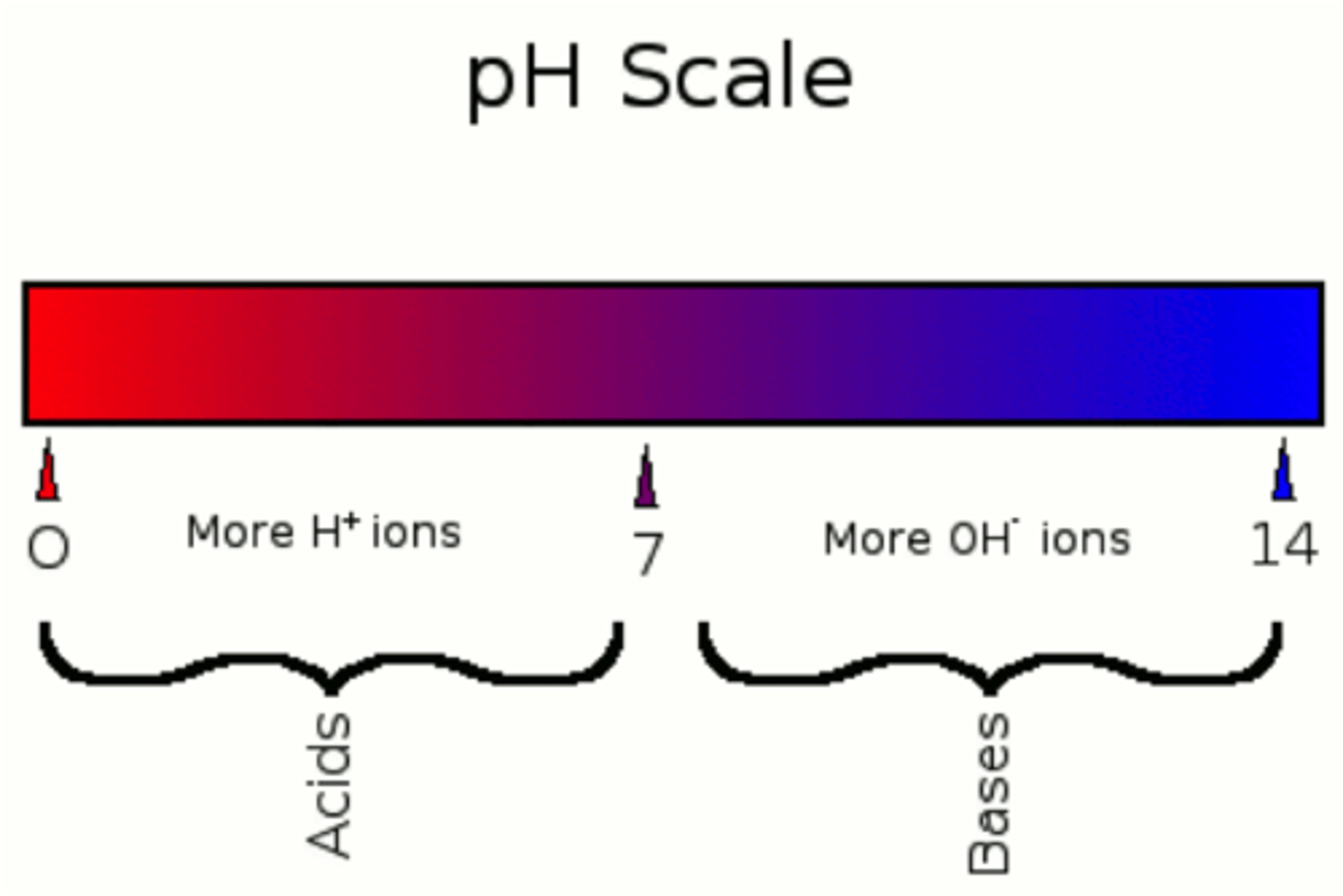
pH Scale
Logarithmic scale measuring hydrogen ion concentration.
pH Formula
pH = -log10[H+].
![<p>pH = -log10[H+].</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/54b0941d-d7fb-451d-a056-f4ec63c72872.jpg)
Neutral pH
pH of 7, equal concentrations of H+ and OH-.
pH 0
Indicates 1 M concentration of H+ ions.
pH 14
Indicates very low concentration of H+ ions.
Equilibrium Expression
[H+][OH-] = 1 x 10^-14 M.
Organic Acids
Typically weak acids found in biological systems.
Hydrogen Ion Concentration
Measured in molarity, affects pH value.
pH Decrease
Increased [H+] relative to [OH-].
pH Increase
Decreased [H+] relative to [OH-].
Dissociation
Process of an acid breaking into ions.
Ka
Equilibrium constant for weak acid dissociation.
pKa
Negative logarithm of the acid dissociation constant.
Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation
pH = pKa + log10([A-]/[HA]).
![<p>pH = pKa + log10([A-]/[HA]).</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/381a3b64-f9d1-4f92-a7ba-225966f3e0f3.jpg)
Buffer
Solution that resists pH changes upon acid/base addition.
Buffer Pair
Combination of weak acid and its conjugate base.
Acetic Acid
Common weak organic acid, CH3COOH. Used in buffer solutions.
Acetate
Conjugate base of acetic acid, CH3COO-.
Equilibrium
State where reactants and products remain constant.
Ionization
Process of forming ions from molecules.
Buffer Capacity
Amount of acid/base a buffer can neutralize.
pH Regulation
Maintaining constant H+ concentration in cells.
Enzyme Inactivation
Loss of enzyme function due to pH extremes.
HI
Hydroiodic acid, a strong acid indicator.
H+
Proton that influences acid-base balance.
OH-
Hydroxide ion that raises pH level.
pH Meter
Device for accurate pH measurement using electrodes.
Electrometric Method
Technique using voltage difference to measure pH.
Thymol Blue
Dibasic acid indicator, changes color at pH 1.2-9.6.
Brom Phenol Blue
Indicator changing from yellow (pH 3.0) to blue (pH 4.6).
Brom Cresol Green
Indicator changing from yellow (pH 4.0) to blue (pH 5.6).
Methyl Red
Indicator changing from red (pH 4.4) to yellow (pH 6.0).
Chlor Phenol Red
Indicator changing from yellow (pH 4.8) to red/purple (pH 6.0).
Brom Cresol Purple
Indicator changing from yellow (pH 5.2) to blue/purple (pH 6.8).
Brom Thymol Blue
Indicator changing from yellow (pH 6.0) to blue (pH 7.6).
Neutral Red
Indicator changing from red (pH 6.8) to orange (pH 8.0).
Phenol Red
Indicator changing from yellow/orange (pH 6.8) to red/pink (pH 8.4).
Cresol Red
Indicator changing from pink/orange (pH 7.2) to red/purple (pH 8.8).
Phenolphthalein
Indicator changing from colorless (pH 8.3) to red/pink (pH 10.0).
Buffer System
Solution that resists pH changes upon acid/base addition.
Hydrochloric acid solution used for titration.
0.1 M HCl
Sodium hydroxide solution used for titration.
0.1 M NaOH
In what increments should either acid/base be added to the water/buffer at a time?
5 drop increments
HAc
Acetic acid, a weak acid in solutions.
NaAc
Sodium acetate, a conjugate base of acetic acid.
Acid precipitation
Rain or snow with pH lower than 5.6.
Carbonic acid (H₂CO₃)
Weak acid formed from CO2 and water.
Natural acidity level of rainwater.
pH 5.8
SO2
Sulfur dioxide, contributes to acid rain formation.
Nitrogen oxides
Gases that form nitric acid in rain.
Environmental degradation, Acid rain
Damage to ecosystems from acid precipitation.
Acid rain - pH: 2.4
Buffering capacity
Ability to neutralize acidity.
Limestone soils
Soils that can buffer acid rain effects.
Acid-base response
Change in pH upon adding acid or base.
pH
Measure of hydrogen ion concentration in solution.
pH Indicator
Substance that changes color at specific pH.
Titration
Technique to determine concentration of a solution.
Sodium Acetate
Salt that acts as a buffer component.
NaOH
Strong base, fully dissociates in water.
Buffer Saturation
Point where buffer can no longer maintain pH.
pH Curve
Graph showing pH changes during titration.
pH of Water
Neutral pH is typically 7.
pH of AcH-NaAc
Buffer solution maintains pH around 4.76.
Acidic Solution
Solution with pH less than 7.
Basic Solution
Solution with pH greater than 7.