2025 Nationals Review Notes
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering key vocabulary terms and concepts from the CMU 2025 Invitational Notes.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Fire Interval
The time between fires in a given ecosystem.
Permian-Triassic Extinction
Major extinction event approximately 252 million years ago, resulting in a loss of 90-96% of species, caused by volcanic eruptions leading to global warming, ocean acidification, and anoxia.
Cretaceous-Paleogene Extinction
Extinction event approximately 66 million years ago, resulting in a loss of 75% of species and the extinction of dinosaurs, caused by an asteroid impact and volcanism.
Holocene Extinction
The current extinction event.
Scopes Monkey Trial
A court case where teacher John Scopes was accused of violating the Butler Act that prohibited teaching evolution in schools. He was found guilty.
Buffelgrass (Cenchrus ciliaris)
An invasive species in deserts that increases fire risk and displaces native species like the Saguaro cactus, particularly problematic in the Sonoran Desert.

Tamarisk/Saltcedar (Tamarix spp.)
An invasive species found in desert riparian zones across the American West that outcompetes native cottonwoods and willows, uses a lot of water, and alters soil salinity; exacerbated by dams.

Red Brome (Bromus rubens)
An invasive species found in the Mojave & Sonoran deserts. The mature plant is highly flammable, exacerbating wildfire risk, and its sharp awns harm wildlife.

Cheatgrass (Bromus tectorum)
An invasive species originating in Europe/Eurasia, introduced to the US in the late 1800s. It increases fire risk and affects western US sagebrush steppe & Great Plains.

Sericea Lespedeza (Lespedeza cuneata)
An invasive species that affects central US prairies, growing very densely in monocultures.

Yellow Star-Thistle (Centaurea solstitalis)
An invasive species that affects western US grasslands and is toxic to horses.

Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs)
Harmful pollutants that don’t break down, are likely to bioaccumulate & biomagnify.
Stockholm Convention on POPs (2001)
An international treaty to combat Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs), targeting the initial 12 POPs known as the 'Dirty Dozen.'
Autecology
The study of individual organisms.
Synecology
Treats a group of organisms as one unit.
Nuclear Fission
The process where a nucleus of uranium-235 or plutonium-239 is bombarded with neutrons, releasing a large amount of heat.
Boiling Water Reactor (BWR)
A type of nuclear reactor with only one loop, where water is boiled directly from fission producing steam. Simpler design, but turbines and steam generator must be radiation shielded and less efficient at higher power levels.
Pressurized Water Reactor (PWR)
The most common type overall of nuclear reactor. A primary loop of pressurized water absorbs heat from fission but stays liquid, transferring heat to a secondary loop with clean water to create steam.
Fast Breeder Reactor (FBR)
A type of nuclear reactor that generates more fissile material than it consumes. It uses U-238 as a blanket for neutrons released by the fission of U-235, and contact w/ neutrons creates plutonium-239. It uses liquid Na as a coolant. Very complex design & expensive with proliferation risk.
Photovoltaic
Energy from light absorbed in PV cells that excites electrons that move in an internal electric field. Uses inverters to convert DC to AC current.
Concentrated Solar-thermal Power
Mirrors reflect and concentrate light onto a water source which creates steam that spins turbines.
Run of river systems
Force of river’s current moves the turbines. These facilities might have a weir to divert the water flow to the turbines
Storage systems
Water accumulates in reservoirs & its released as needed; most common in US
Pumped-storage (Hydro)
Water is pumped from a source up to a storage reservoir at a higher elevation to be released when electricity prices are high.
Geothermal Electricity Generation
Using natural or anthropogenic fractures, the fluid absorbs heat from the rocks and is drawn up toe surface, where its used for turbines that produce electricity
Geothermal Heat Pumps
When the ground has a constant-ish temp it can act as a heat sink during hot temps and can provide heat during cold temps
Anaerobic Digestion
Anaerobic bacteria break down organic waste and produce gas that can be burned.
Gasification
Biomass exposed to high temps w/ very little oxygen so it turns into gas of CO and H2, which can be burned
Pyrolysis
Biomass is heated at a lower temp but in complete absence of hydrogen, which results in a crude bio-oil
Primary / Definitive Host
Final host for a parasite, where it reaches adulthood and reproduces if possible
Secondary / Intermediate Host
organism that harbors sexually immature parasite and is required for the parasite to develop. This is usually the vector for a parasite to reach the primary host.
population diversity
refers to variety within a population (i.e. same species), encompassing genetic variation, morpho differences, and demographic variations (age, sex, density).
community diversity
refers to the number and relative abundance of different species (or subspecies) within a particular area or ecosystem
organism diversity
diversity in morphology specifically of organisms in the same species
landscape diversity
variations in land cover, landforms, or environmental conditions within an area (kind of like beta diversity).
genetic diversity
variety of genotypes within a species
species diversity
variety of types of species
state w/ highest solar capability
california
minimum capacity for utility-grade solar plant
1 megawatt
reintroduction
moves captive born animals into their natural historical range
translocation
moving wild-caught animals from one location to another
What do Biden’s 2023 regulations to reduce CO2 emissions over next 10 years aim to address?
strict tailpipe emissions for cars and light trucks
Inflation Reduction Act (2022)
Passed in 2022, has been described as the most significant climate legislation in U.S. history. It includes major investments in clean energy, emissions reduction, and incentives to support the transition to a green economy.
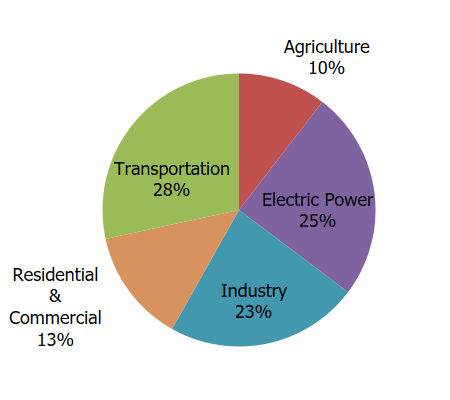
Order of worst sources of GH gas emissions (worse to less worse)
Transportation, electricity, industry, residential/commercial buildings, agriculture