Introduction to Pathophysiology: Disease Mechanisms and Cellular Changes
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
What does pathophysiology study?
Functional or physiologic changes in the body that result from a disease process.
What is homeostasis?
The maintenance of a relatively stable internal environment regardless of external changes.
What happens when homeostasis is not maintained?
Disease may develop.
How is health defined?
Physical, mental, and social well-being.
What is a disease?
A deviation from the normal state of homeostasis.
What factors can adjust health indicators?
Age, sex, genetics, environment, and activity level.
List one of the 7 Steps to Health.
Be a nonsmoker and avoid second-hand smoke.
What is the primary focus in health care regarding disease?
Prevention of disease.
What is the first stage of the research process?
Basic science, involving identification of technology and laboratory work.
What does HPI stand for in patient work-up?
History of Present Illness.
What is a biopsy?
Excision of small amounts of living tissue for examination.
What is the purpose of an autopsy?
Examination of the body and organs after death.
What does etiology refer to in the context of disease?
Causative factors in a particular disease.
What does idiopathic mean?
The cause of the disease is unknown.
What does iatrogenic mean?
A disease caused by an error, treatment, or procedure.
What are predisposing factors for disease?
Age, gender, inherited factors, environment, etc.
What are the two levels of changes studied in pathophysiology?
Anatomy (structure) and physiology (function).
What does the term 'disease process' encompass?
Diagnosis, evaluation of signs & symptoms, and laboratory tests.
What is the significance of the patient's story in the work-up?
It is the most vital/helpful part of understanding the current illness.
What are some new developments in pathophysiology?
Improved diagnostic tests, more effective drugs, and new technologies like 3D-printing.
What is the role of community health programs in disease prevention?
They help in maintaining public health and preventing disease spread.
What does ROS stand for in patient work-up?
Review of Systems.
What is prophylaxis?
Measures taken to preserve health and prevent the spread of disease.
What is pathogenesis?
The process by which a disease develops.
What is the difference between acute and chronic disease?
Acute disease develops quickly with significant symptoms, while chronic disease develops gradually with milder symptoms.
What is a subclinical state?
A state where there are pathologic changes but no obvious outward manifestations.
What is the incubation period?
The period from infection to the appearance of symptoms in infectious diseases.
What does the prodromal period refer to?
The early development of a disease where signs are nonspecific or absent.
What are signs in the context of disease?
Objective indicators of disease that are observable by someone other than the individual.
What are symptoms?
Subjective feelings that are only obvious to the affected individual.
What is a syndrome?
A collection of signs and symptoms that usually affect more than one organ and occur together.
What is the difference between remission and exacerbation?
Remission is a period where manifestations subside, while exacerbation is a worsening of severity.
What is morbidity?
Disease rates within a group.
What is mortality?
The relative number of deaths resulting from a disease.
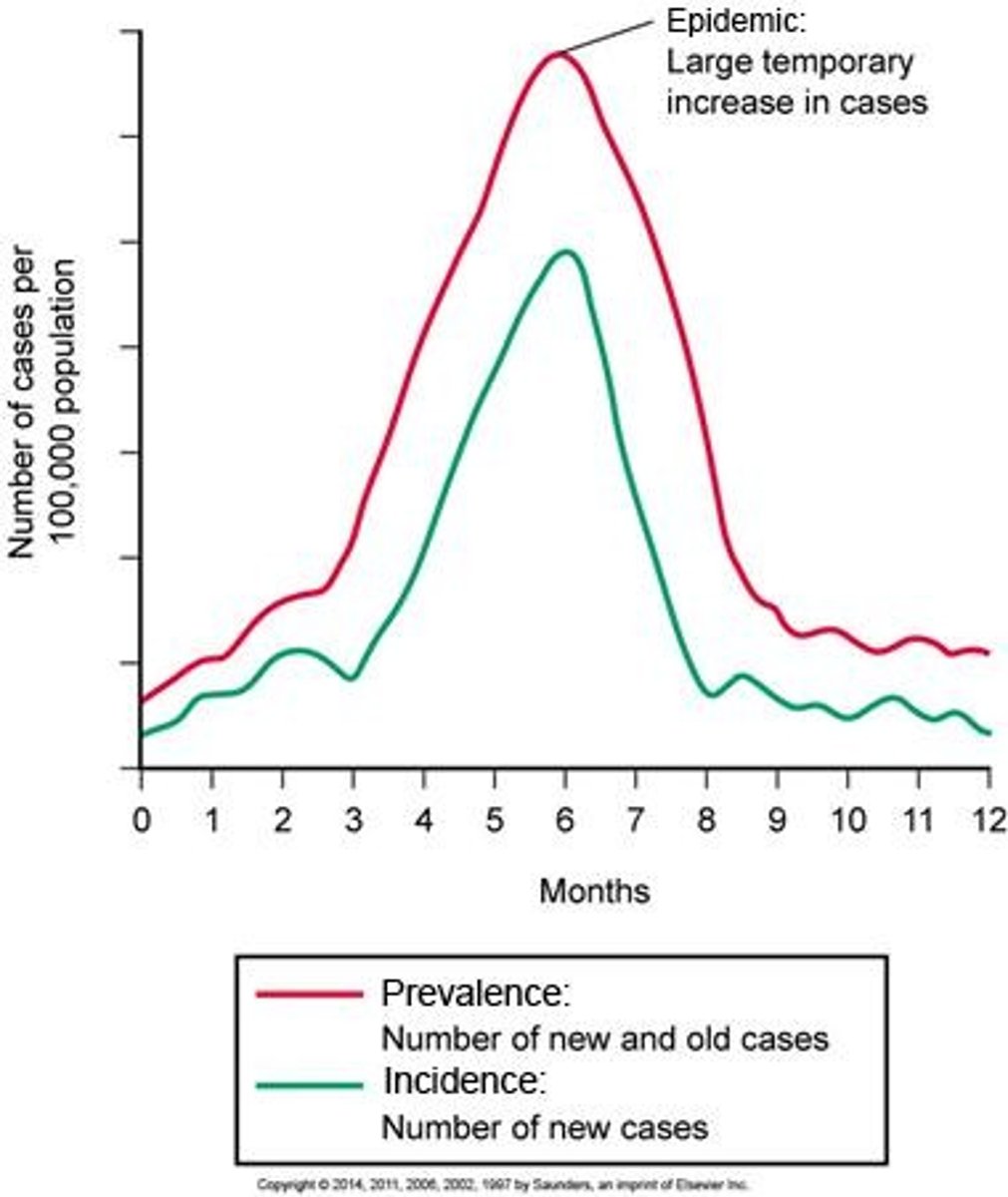
What is the incidence of a disease?
The number of new cases in a given population within a specific time period.
What is prevalence?
The number of new, old, or existing cases within a given population and time period.
What defines an epidemic?
A higher number of expected cases of an infectious disease occurring within an area.
What is a pandemic?
A higher number of infectious diseases occurring in many regions of the globe.
What are communicable diseases?
Infectious diseases that can spread from one person to another.
What is apoptosis?
Programmed (controlled) cell death that is a normal occurrence in the body.
What is ischemia?
A deficit of oxygen to tissues or organs due to circulatory obstruction.
What is necrosis?
Uncontrolled cell death where dying cells cause further damage due to cellular disintegration.
What is liquefaction necrosis?
A type of necrosis where dead cells liquefy due to the release of cell enzymes.
What is gangrene?
An area of necrotic tissue that has been invaded by bacteria.
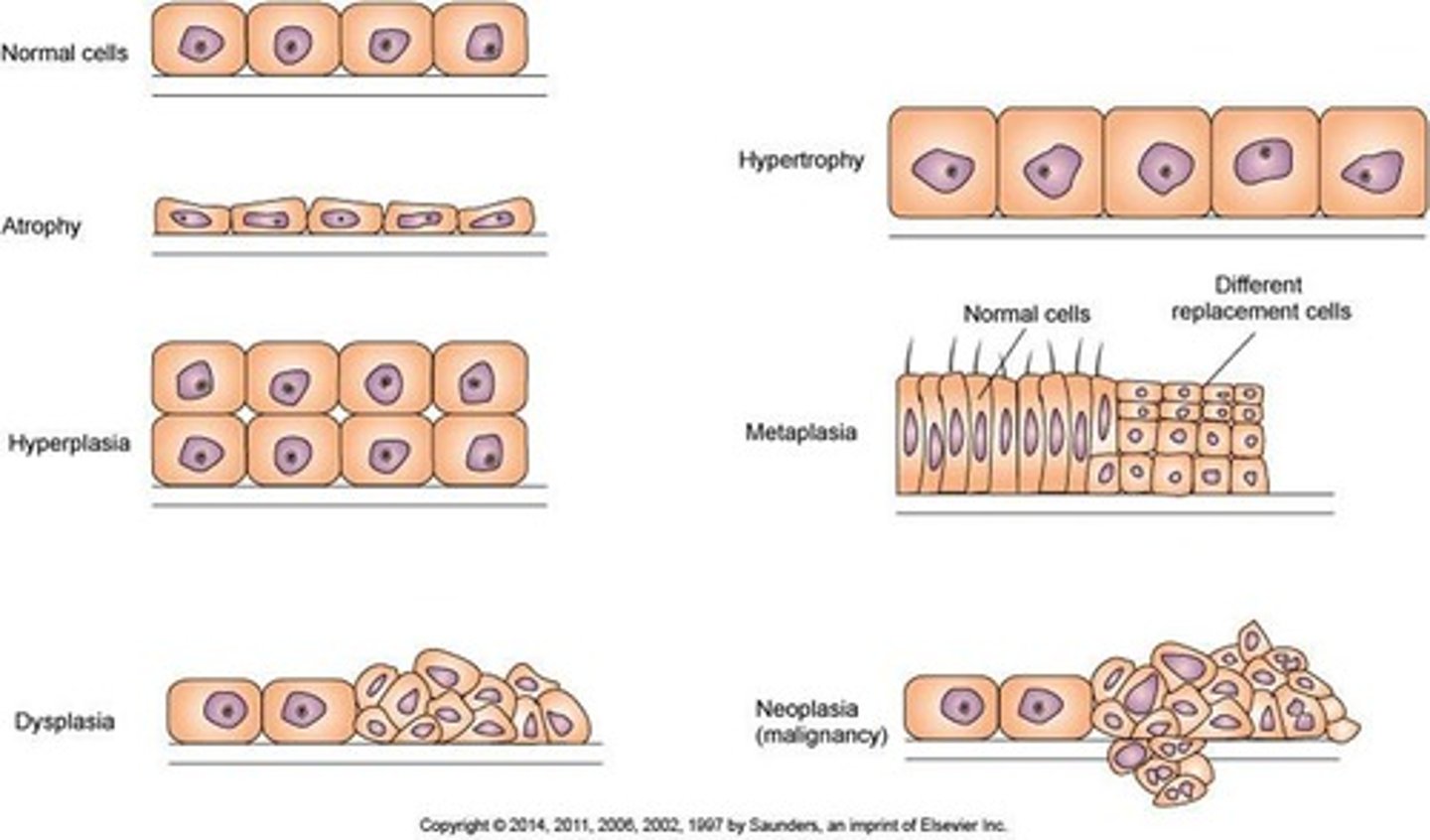
What is hypertrophy?
An increase in cell size that results in enlarged tissue mass.
What is dysplasia?
Cells vary in size and shape within a tissue, often resulting from chronic irritation.
What is neoplasia?
New growth commonly referred to as a tumor, which may be benign or malignant.
What are precipitating factors?
Conditions that trigger an acute episode, such as a viral illness or pollution for asthma.
What are complications in disease context?
New secondary or additional problems that arise, such as secondary bacterial pneumonia due to a viral URI.