Electrophilic Addition
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Electrophilic addition
electrons of pi bond are reactive as a Nu: and attracted to electrophilic reagents
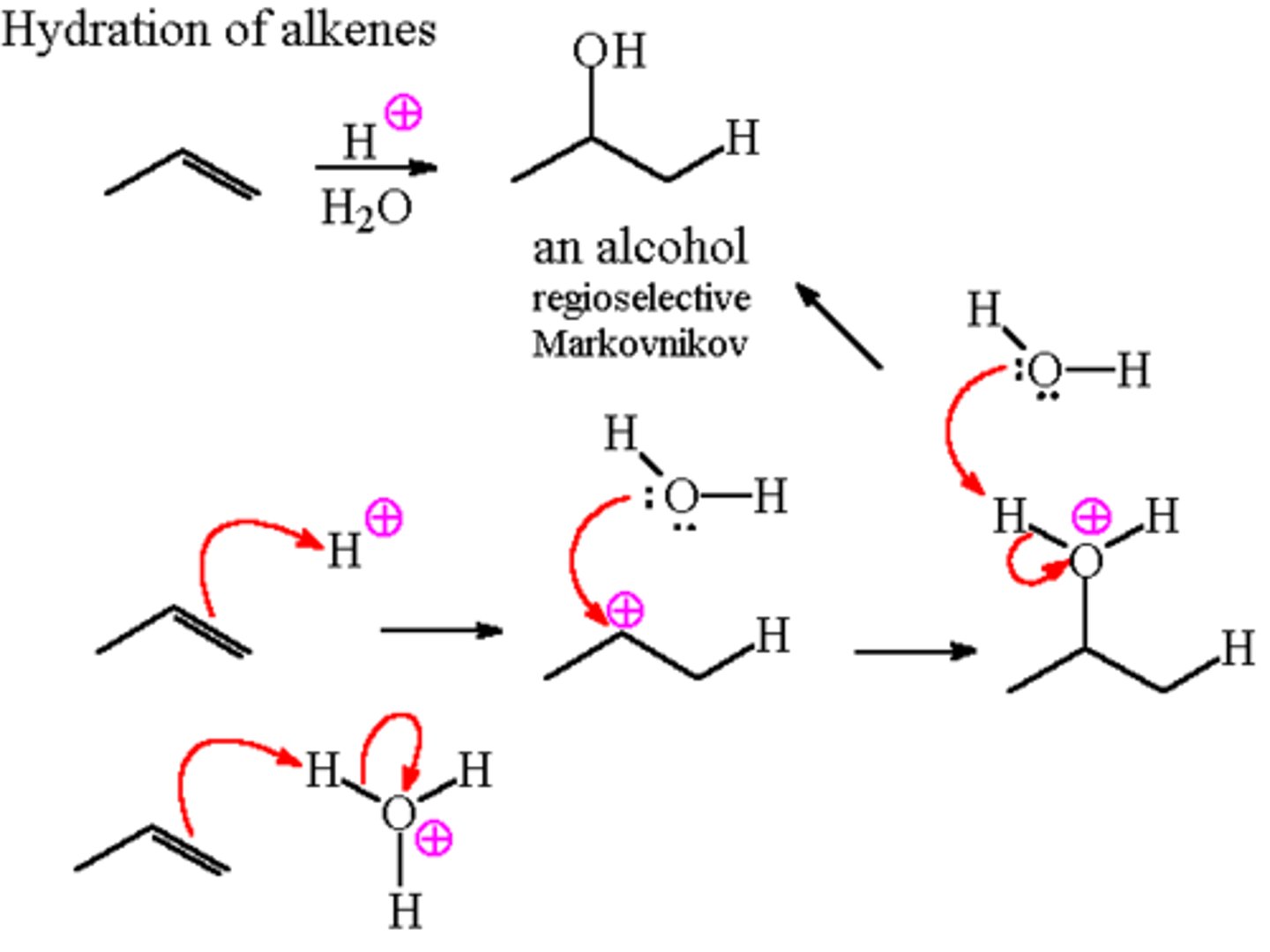
Acid Catalyzed Hydration
- converts alkenes to alcohols
- carbocation rearrangements are possible
- reagents: H20, H+, H2SO4 (aq)
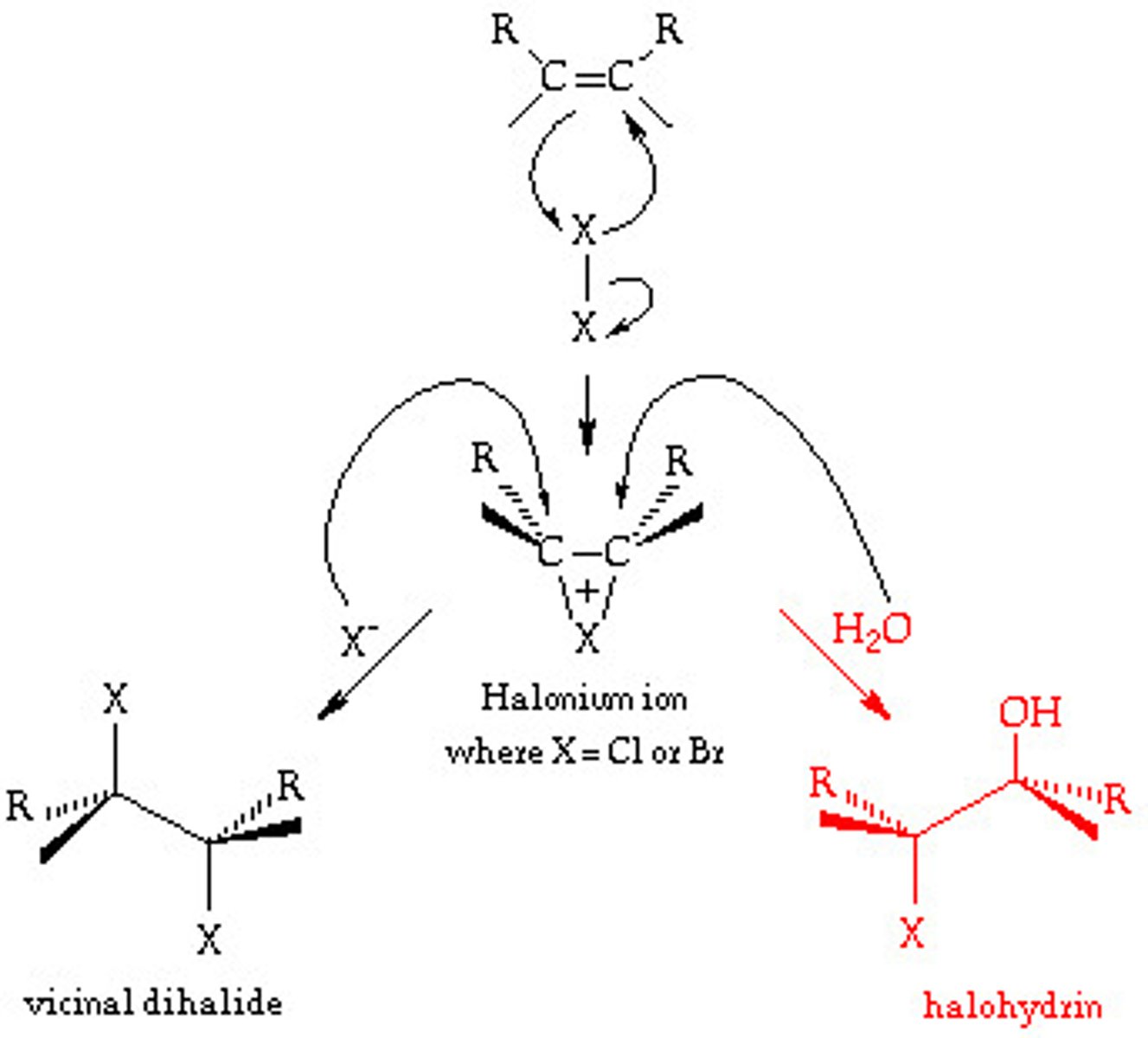
Halohydrin
-Reagents: Br2 or Cl2 in H2O
-Bromonium or chloronium ion intercepted by H2O
-Anti addition stereochemical preference
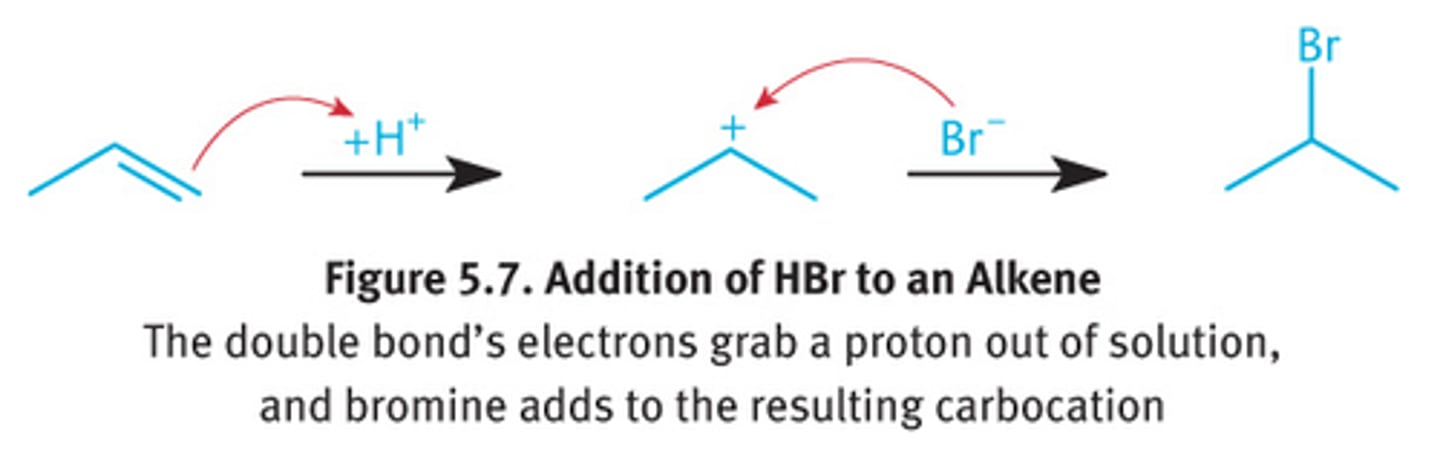
bromination of alkenes (mechanism and stereochemistry?)

alkene with HBr
- alkyl halide on most substituted carbon
- carbocation intermediate
- rearrangements possible
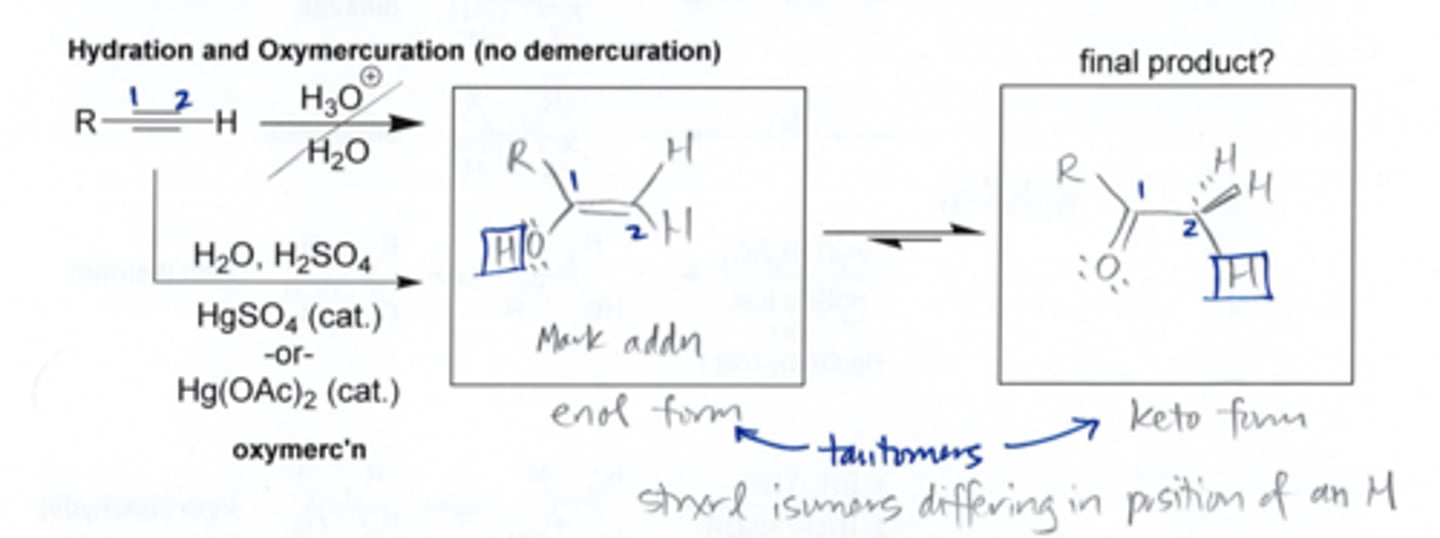
Oxymercuration-Demercuration Conditions
1) Hg(OAc)2, H2O
2) NaBH4
Oxymercuration-Demercuration mechanism
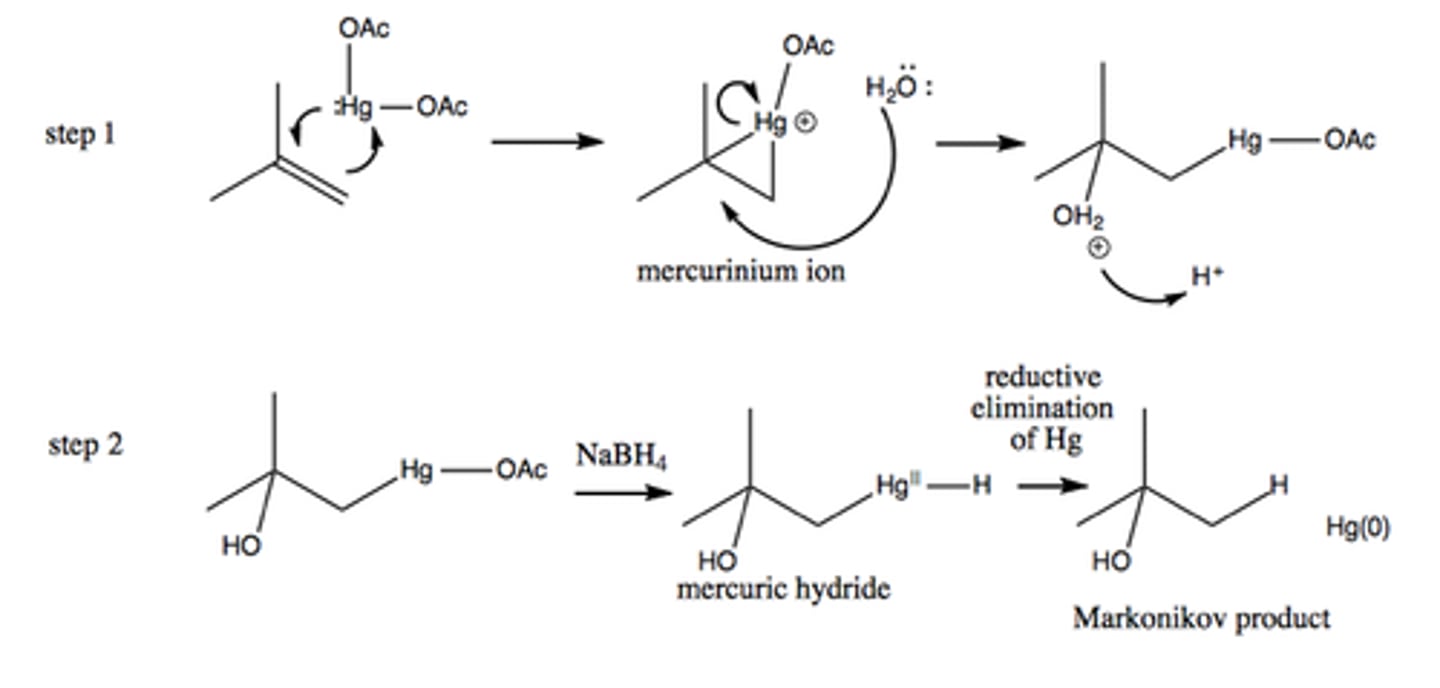
Oxymercuration-Demercuration to make ethers
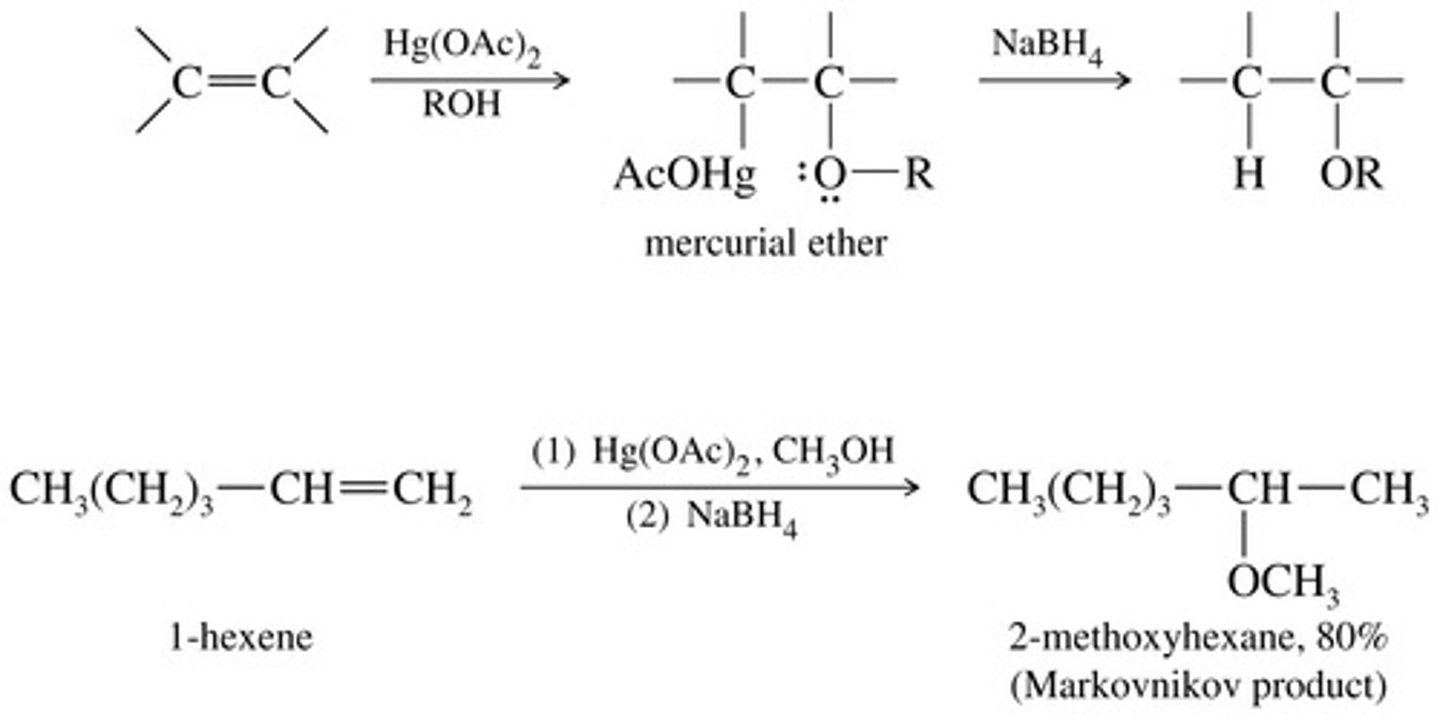
Oxymercuration-Demercuration of alkynes
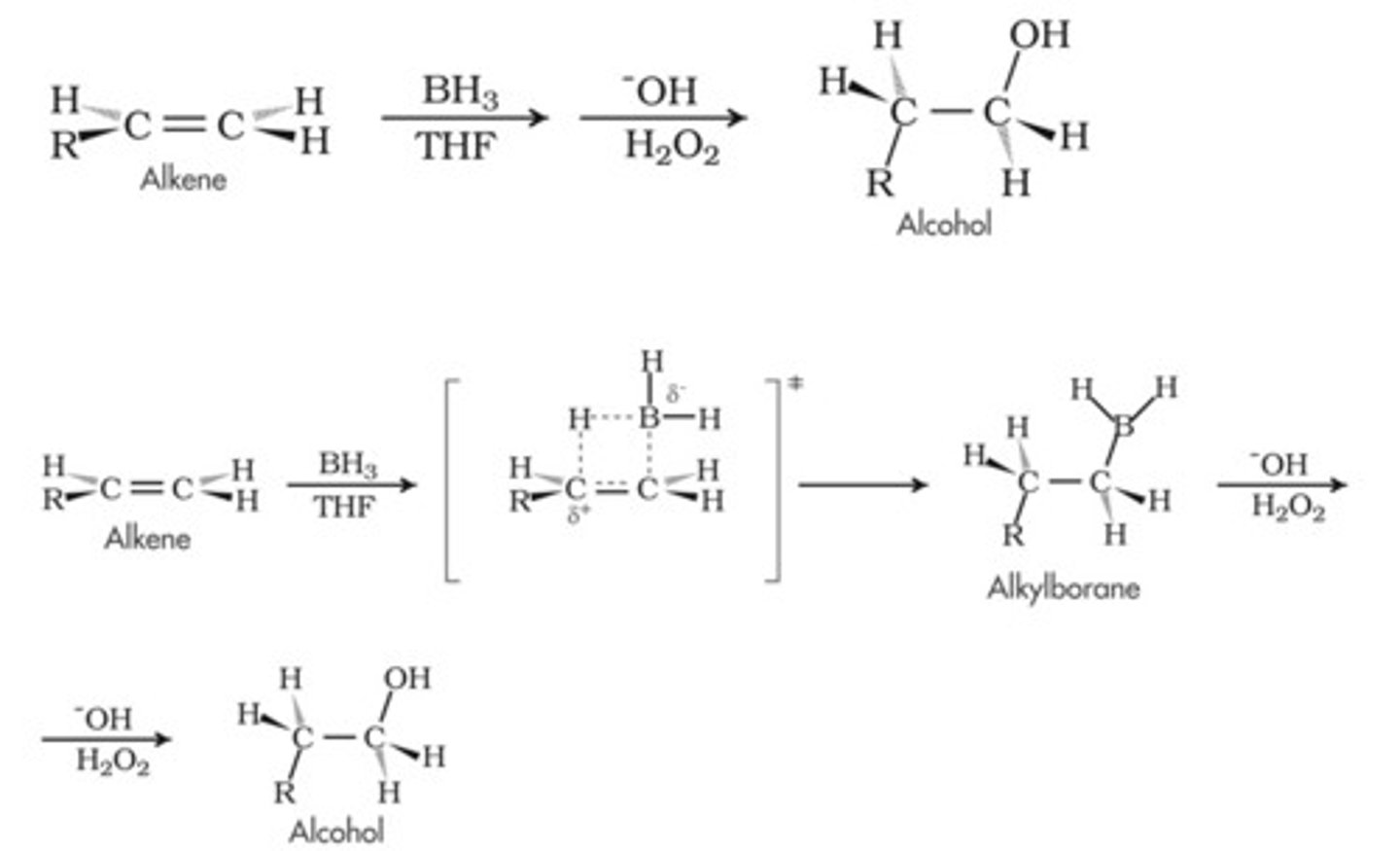
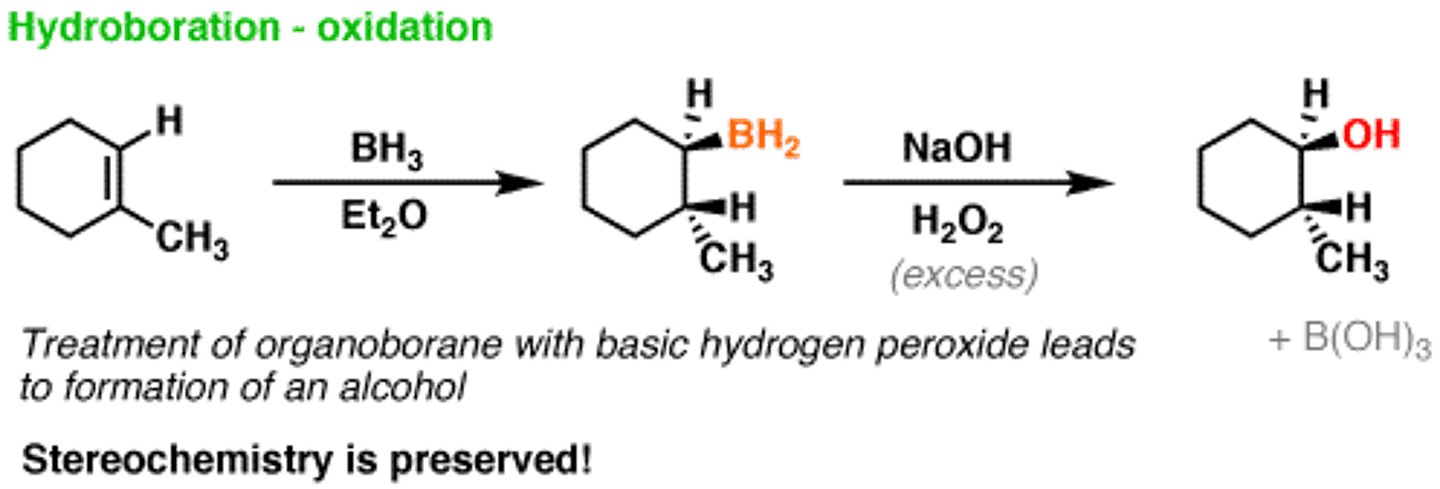
Hydroboration-Oxidation conditions
1. BH3, THF
2. H2O2, NaOH
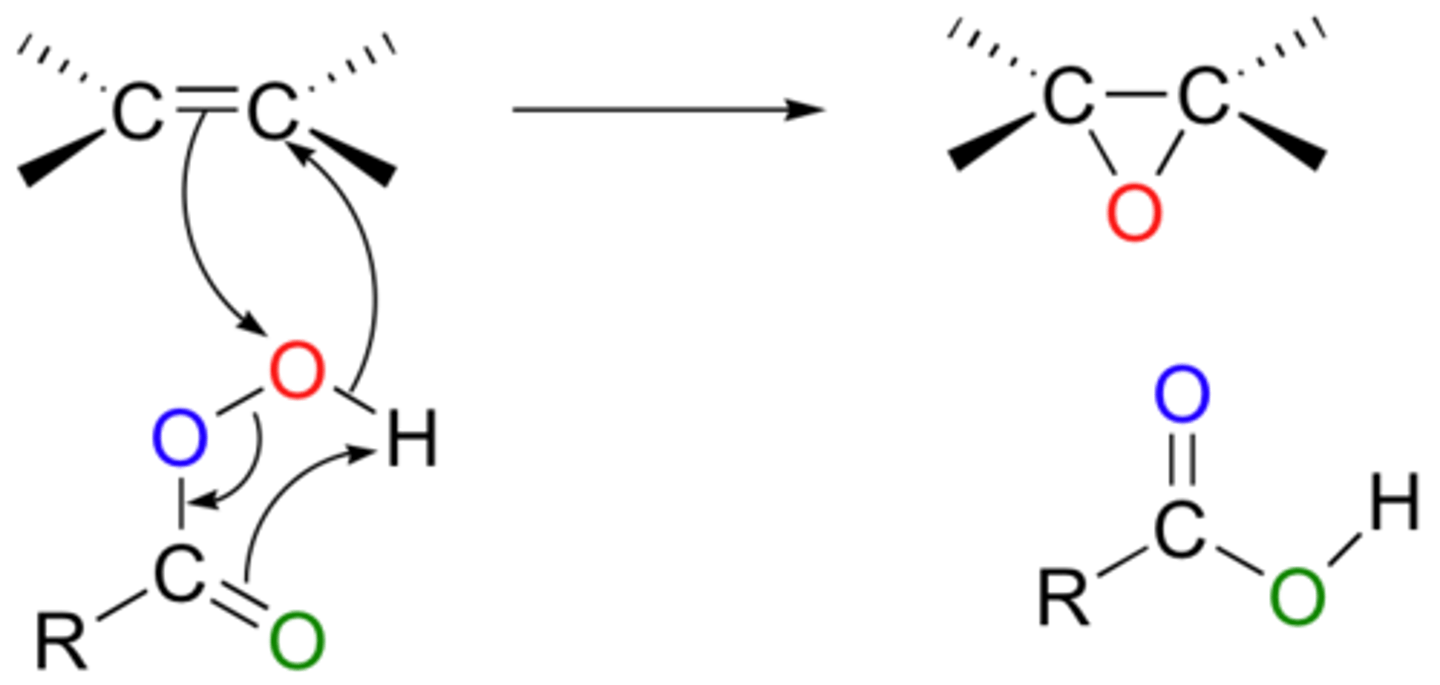
Hydroboration-Oxidation mechanism
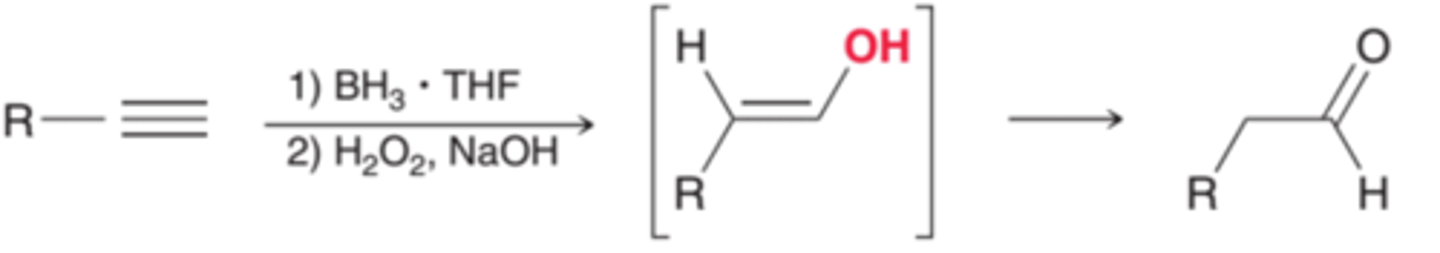
Hydroboration-Oxidation of Alkynes
1. BH3, THF / H2O2
2. Hydroboration of terminal alkyne gives an aldehyde.
3. Hydroboration of internal alkyne gives a ketone.
Hydroboration-Oxidation stereochemistry
Markovnikov's Rule
hydrogen will add to the least substituted carbon of the double bond
Anti-Markovnikov Addition
An addition reaction in which a hydrogen atom is installed at the more substituted position and another group (such as a oxygen) is installed at the less substituted position.
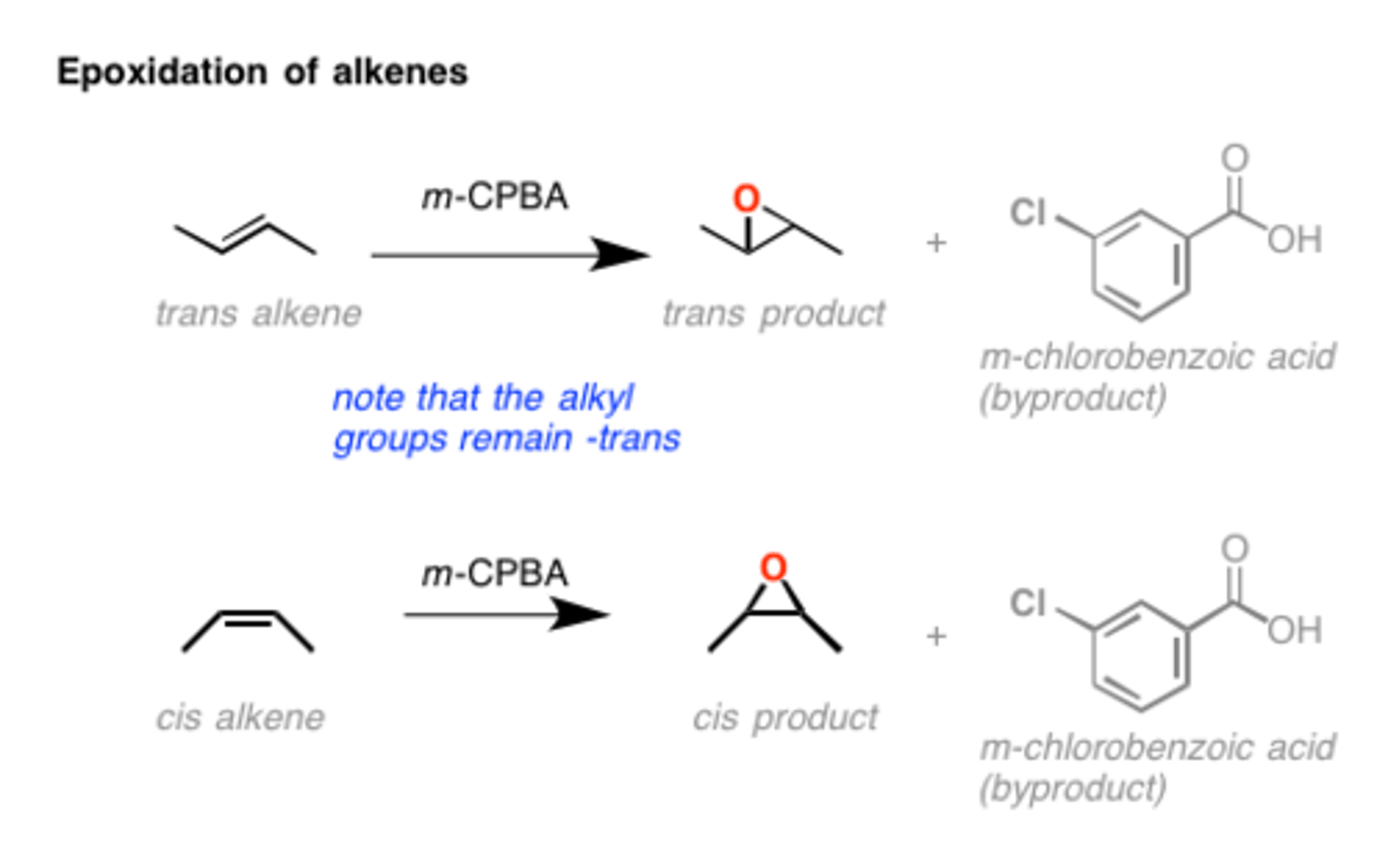
Epoxidation of Alkenes
MCPBA, CH2Cl2
stereochemistry of epoxidation
the alkyl substituents stay trans or cis but cyclopropane could add to either face
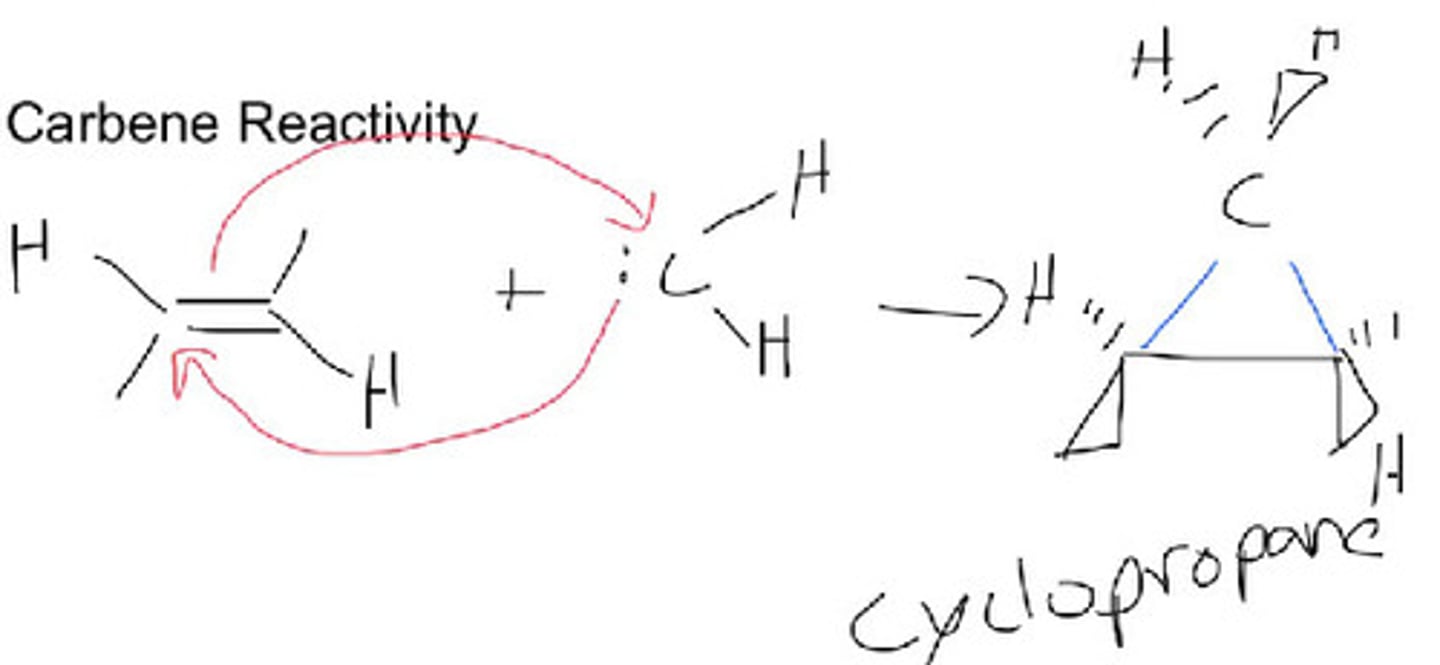
Simmons-Smith Reaction
A cyclopropanation of an alkene using the carbenoid reagent generated from diiodomethane and the zinc-copper couple.
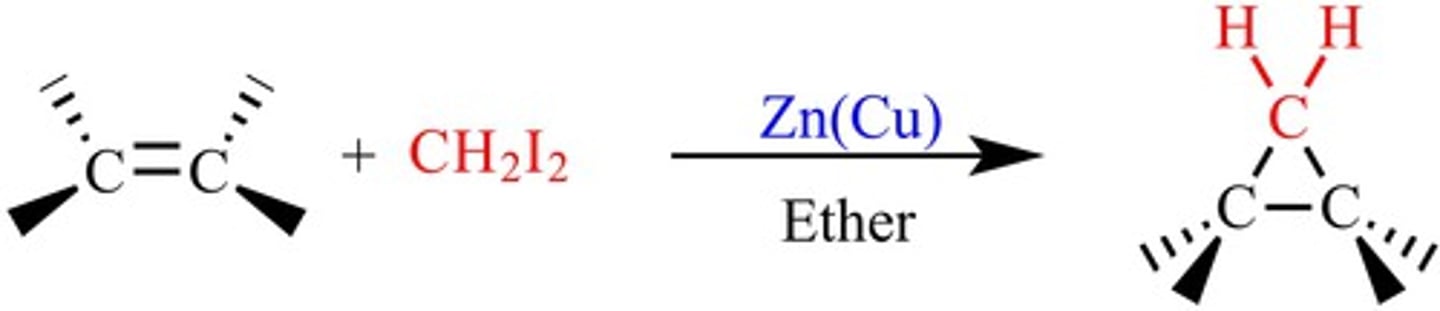
Simmons-Smith Reaction mechanism
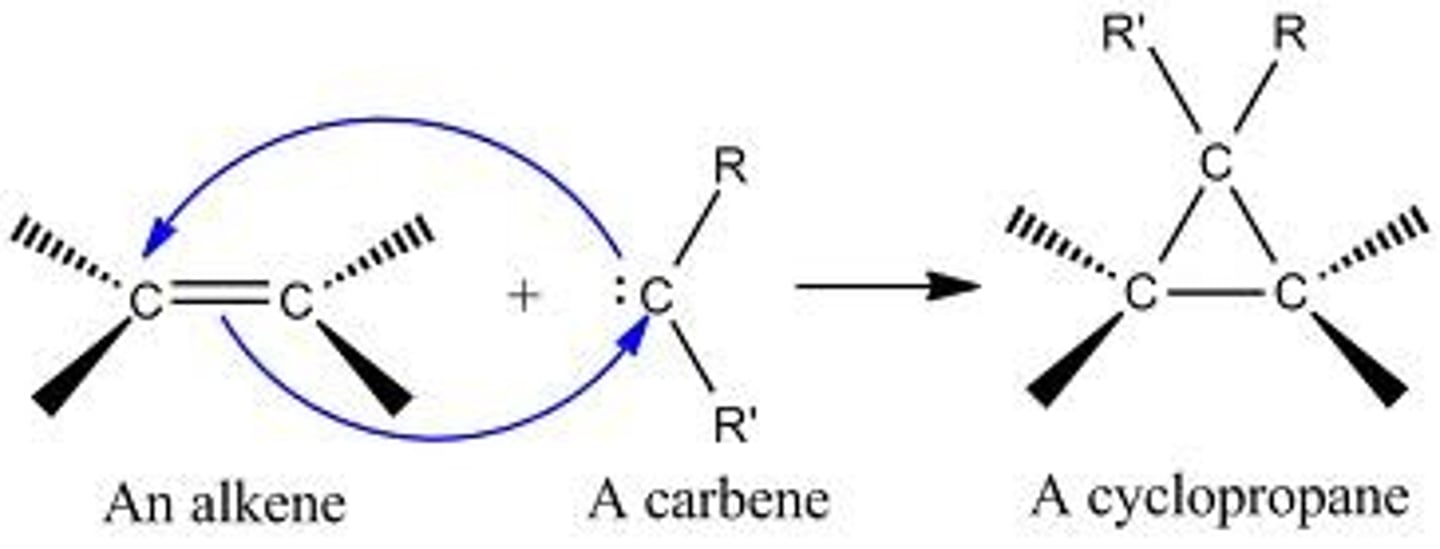
Simmons-Smith Reaction trans alkene (stereochemistry?)
the alkyl substituents stay trans but cyclopropane could add to either face