Final Exam 519
1/157
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
158 Terms
Why is PROPER documentation important?
enhance our ability evaluate care, plan tx, monitor care over time
ensure effective communication and continuity of care among members of the health care team
improve quality of care
types of documentation
SOAP notes
FARM notes
pharmacy consult notes
anticoagulation consult - warfarin dosing
pharmacokinetic consult - abx dosing
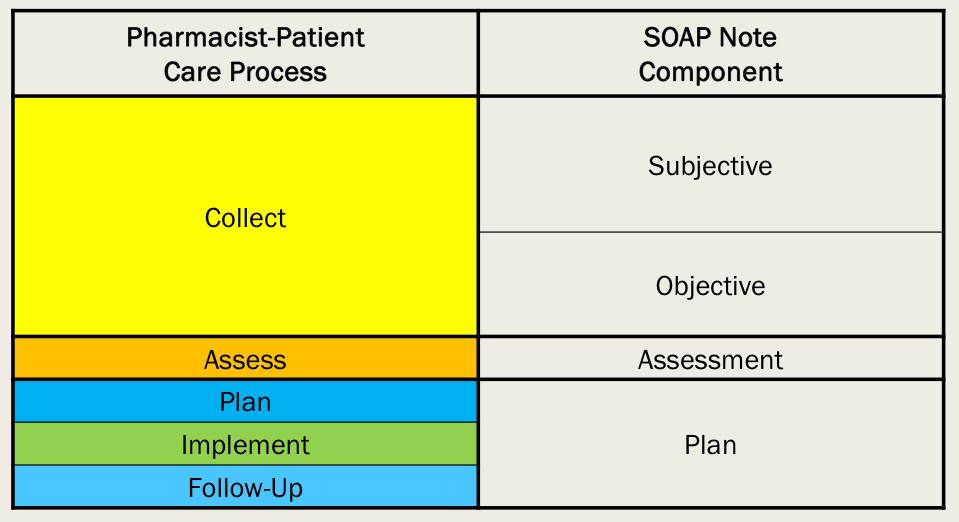
SOAP note = progress note
Subjective
Objective
Assessment
Plan
Most common method for documenting pt encounters systematically
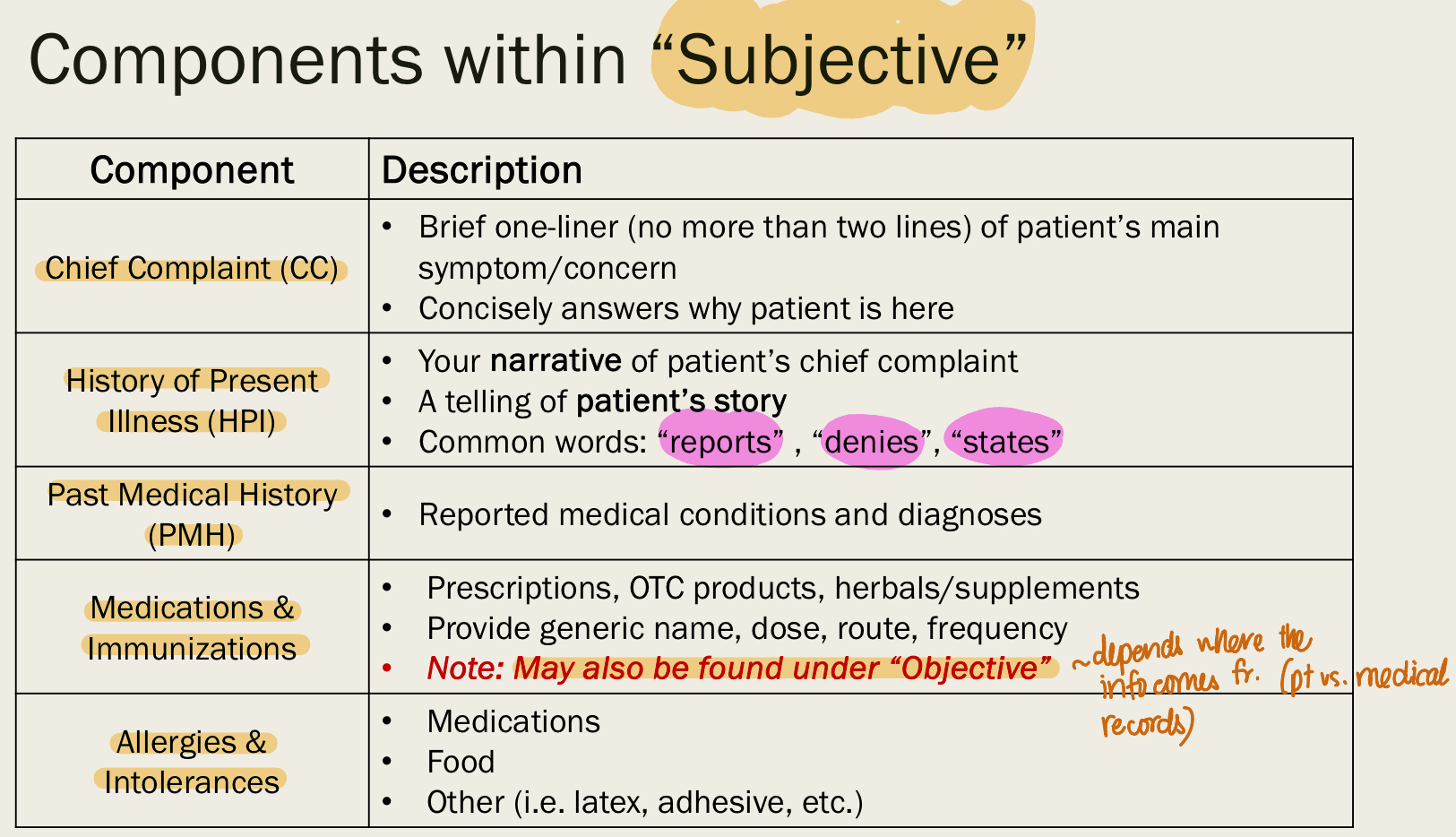
SUBJECTIVE DATA
data reported from pt/caregiver
second-hand info
include:
CC
HPI
PMH
medications and immunization
allergies
Family hx
social hx
ROS
ex:
pt says their sx are headache, CP…
pt says their BP is 130/90
OBJECTIVE DATA
facts, physical findings
data that is measurable and tangible
include:
Physical exam
VS
Labs
calculations
dx tests
ex: lab work, imaging, weight, VS
where do we get pt info?
fr. pts and caregivers - subjective info
fr. medical/pharmacy record - objective info
fr. other health care professionals - objective info
chief complaint = CC
SUBJECTIVE data
brief 1-2 lines of pt’s main sx or concern
why is the pt here
history of present illness = HPI
SUBJECTIVE data
your narrative of pt’s CC
“reports” , “denies” , “states”
past medical history = PMH
SUBJECTIVE data
reported medical conditions and dx
medications and immunizations
SUBJECTIVE data but can also be found under OBJECTIVE
depends on where we get the info from (from pts vs. EMR)
including:
rx
OTC
herbals
including name, dose, route, frequency
allergies
SUBJECTIVE data
including:
medication allergies
food allergies
latex, adhesive…
family history = FH or FHx
SUBJECTIVE data
including medical hx of family members
deceased or alive
if not pertinent => noncontributory
social history = SH or SHx
SUBJECTIVE data
including:
diet, physical activity
tobacco, alcohol, drug use
occupation
living situation
support system
review of system = ROS
SUBJECTIVE data
including:
pt-reported answers to provided questionnaire
organized by organ system
physical exam
OBJECTIVE data
physical findings by organ system
VS
OBJECTIVE data
including:
temp
BP
HR
RR
SpO2
labs
OBJECTIVE data
including all the blood work
Calculations
OBJECTIVE data
including:
BMI
creatinine clearance (CrCI)
10-year ASCVD risk score
dx tests
OBJECTIVE data
include:
echo
EKG
PFT
CXR
Assessment
the WHY
provide rationale for our PLAN
include:
Prioritized problem list
Goals of therapy (short term vs. long term; disease-oriented vs. patient-oriented evidence)
Classifying problems (which stage? controlled or uncontrolled?)
Assessment of current therapy (AESA)
Changes to Medications (changes to current therapy, need to continue/discontinue/initiate regimen?)
Assess non-pharm/lifestyle factors (diet, exercise…)
Preventive health (immunization needs?)
Plan
the WHAT - what should be done
plan + implement + monitoring + f/u
state recs clearly + concisely
include:
pharmacologic recs (continue, increase, decrease, initiate, discontinue)
monitoring parameters
therapeutic - how do we know a med is working?
toxic - how do we know a med is causing harm?
non-pharm recs (lifestyle)
pt edu and pt counseling
f/u (when, what, who)
Continue, Initiate, Start, Discontinue, Increase, Decrease
adult immunization practice
need to assess immunization status at every visit (age, health conditions, lifestyle, travel, occupation)
recommend vaccines
administer vaccines or refer to provider
document the vaccines
live vaccines
ONLY THESE
Dengue (DEN4CYD)
influenza (only LAIV4)
MMR
Rotavirus (RV1 and RV5)
Varicella (VAR)
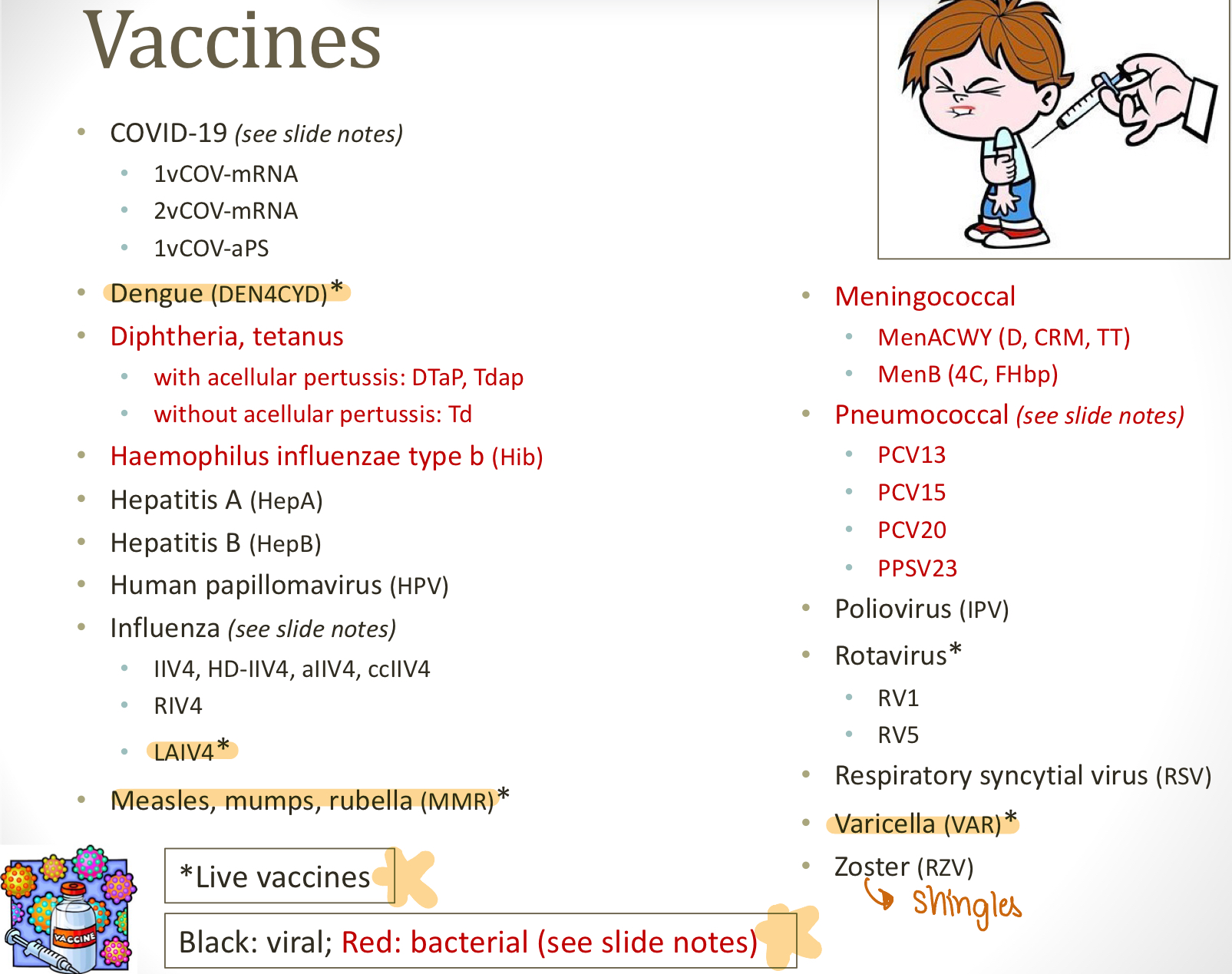
bacterial vaccines
ONLY THESE
diphtheria, tetanus
with acellular pertussis (DTaP, Tdap)
without acellular pertussis (Td
Haemophilus influenza type b (Hib)
Meningococcal
MenACWY (D, CRM, TT)
MenB (4C, FHbp)
Pneumococcal
PCV13
PCV15
PCV20
PPSV23
primary prevention
action taken to prevent the development of a disease/event
ex: pregnancy prevention
secondary prevention
action taken to reduce the recurrence of a disease/event that has already occurred
ex: screening pregnant women on depression risks
tertiary prevention
action taken to soften the impact of an ongoing disease/event that has lasting effects
ex: treat pregnant women with depression; treat babies?
HTN
2017 ACC/AHA guidelines - systolic >= 130mmHg or diastolic >= 80
screening criteria:
age 18 and up
age 18-39 + normal BP + no risk factors —> SCREEN EVERY 3-5 YRS
age 40 and up OR with risk factors —> SCREEN ANNUALLY
screening: 2 or more readings from different days >= 130/80
risk factors
age
African Ame
overweight or obese
pregnancy
smoking
poor diet
sedentary lifestyle
diabetes
Criteria
Testing for adults with OVERWEIGHT or OBESE and
1st degree relative with DM
high risk race/ethnicity
history of CVD
HTN
low HDL and/or high trig
women with polycystic ovary syndrome
physical inactivity
other clinical conditions a/w insulin
Pre-DM —> TEST ANNUALLY
Women with Gestational DM —> LIFELONG TESTING AT LEAST EVERY 3 YRS
>= 45 —> TEST ANNUALLY
HIV pts —> TEST ANNUALLY
DX screening:
fasting sugar >= 126 mg/dL (7 mmol/L)
2-h sugar >= 200 mg/dL (11mmol/L) during oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT)
dx requires 2 abn tests from same samples or in 2 separate samples
A1C >= 6.5% (48 mmol/mol)
fasting blood glucose = FBG
blood glucose levels after no eating/drinking for at least 8 hours
post prandial glucose = PPG
blood glucose levels after a meal, taken 2 hours after eating
hyperglycemia sx
polyuria
polydipsia = extremely thirsty
polyphagia = extremely hungry
ASCVD risk factors
age
race
total + HDL levels
LDL
sBP
smoking status
why do pharmacists need to know about nutritional assessment?
so they can refer
malnutrition and over nutrition are a/w negative clinical outcomes and increased morbidity/mortality
diet changes = 1st line therapy for dz
some drugs can alter nutrients levels and/or absorption in body
nutritional assessment
1) Anthropometric measurements
2) Biochemical and immune function studies
3) Clinical - specific nutrient deficiencies/clinical eval
4) Dietary - assessment of nutrient requirements
1) anthropometric measurements
physical measurement of size, weight, proportions of human body
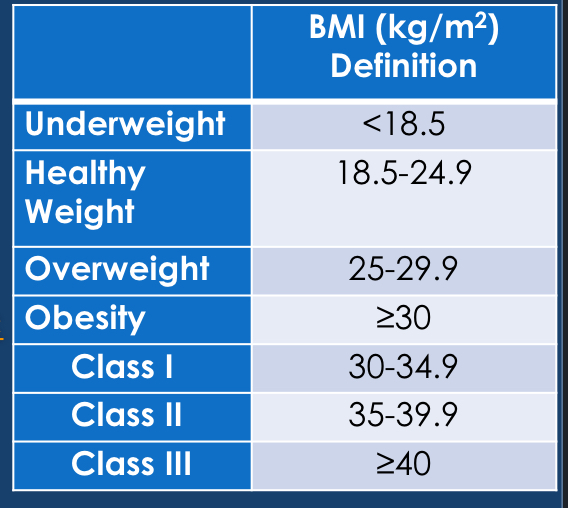
a) BMI
b) Waist circumference = WC
c) body composition
a) BMI (Anthropometric measurements)
kg/m²
pros: easy to obtain, inexpensive
cons: doesn’t show body composition or location of fat
b) waist circumference = WC (Anthropometric measurements)
measure around your middle (above hips)
pros: identify central/abdominal obesity; easy to get
cons:
doesn’t determine visceral vs. subcutaneous fat (visceral fat = fat around internal organs; subcutaneous fat = fat just below skin)
doesn’t describe body composition
c) body composition (anthropometric measurements)
Dual Energy Xray Absorptiometry (DXA/DEXA) for bone density - GOLD STANDARD
Bioelectrical analysis
use conduction of an alternating electrical current that passes thru tissues containing a lot of water and electrolytes (like blood and muscles)
does not pass as easily thru fat tissues, air, bone
ex: InBody scan (more accessible compared to DEXA scan but less accurate; check body fat vs. muscle of body - like at a fitness)
muscle mass is a predictor of longevity
b/c if we lose muscles = we fall
muscle is more metabolically active —> more muscles = the more it affects our metabolism
pros: most accurate, most detailed
cons: more expensive, not as accessible; DEXA scan has some radiation exposure
2) Biochemical and Immune Function Studies (lab)
visceral protein concentrations
serum proteins a/w nutrition risk (Albumin, Transferrin, Prealbumin or transthyretin)
can tell us about malnutrition, deficiency, dehydration, infxn…
immune function
nutrition status can affect immune function
total lymphocyte count and delayed cutaneous hypersensitivity rxns
—> any of these tests can tell malnutrition vs. over nutrition —> help create a clinical pic
3) Clinical: Specific Nutrient Deficiencies/Clinical Eval
in hospital or dr office
assessment of trace element, vit, essential fatty acid deficiencies
some vits from diet (zinc, copper, manganese, selenium, iodine, iron… —> deficiencies of these trace elements = clinical syndromes)
multiple vit deficiencies occur more commonly with malnutrition
essential fatty acid deficiency is rare, but can occur
pt clinical history
look at weight loss? GI sx? oral health? inability to chew/swallow? chronic/acute disease? psychiatric illness? loss of muscle mass?
physical exam
evaluate clinical signs and sx of nutritional deficiencies of vits and minerals
4) Dietary: Assessment of Nutrient Requirements
assess current food intake, diet hx, medications, supplements
consider dietary preferences, cultural and religious habits, food allergies, fluid intake, alcohol intake, age, physical activity
energy requirements and comparison btw food intake & energy expenditure —> can tell nutrition status
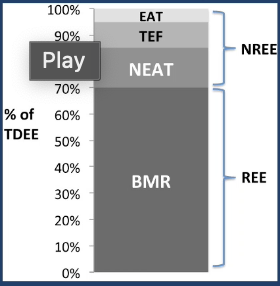
TDEE = total daily energy expenditure = most of it is made up of basal metabolic rate (BMR) = how much energy is needed to survive at rest
know relatives number only!!!
a) RMR = resting metabolic rate or BMR = basal metabolic rate = 70% of TDEE (use predictive equations or measure)
b) Exercise activity thermogenesis = EAT = 5% of TDEE (ex: exercise, HIIT)
c) Thermic effect of food = TEF = 10% of TDEE (how much calories it takes to digest that food; depends on macronutrient content of food); proteins > carbs > dietary fat has the highest TEF
d) non-resting energy expenditure = NEAT = 15% of TDEE = daily movement if not sleeping (ex: walk to car, walk upstairs, work)
REE = resting energy expenditure
NREE = non-resting energy expenditure
—> keep a food journal for assessment of macronutrients (fats, carbs, proteins) and micronutrients (vits, trace elements)
fluid intake - daily adult requirement (30-40mL/kg)
drug-nutrient interactions
drug therapy can change serum concentrations of vits, minerals, electrolytes
some drug delivery vehicles contain nutrients (ex: most IV therapies include dextrose or sodium)
histamine-2 antagonists
Pepcid, Zantac
these drugs reduce acid —> can’t absorb vit B12 well —> vit B12 malabsorption
abx
cause vit K deficiency
aspirin
cause folic acid deficiency
increase vit C excretion
cathartics = laxatives
cause increased requirements for vit D, C, B6
loop diuretics
cause thiamine deficiency
thiazide diuretics
cause urinary zinc losses
phenobarbital
cause increased vit D metabolism
point of care (POC) testing
POCT has become a billion dollar business
pharmacists have work under collaborative practice for decades to manage cholesterol and glucose levels
exploded with COVID-19
allows a pharmacist to test for certain conditions and provide tx when appropriate
need collaborative agreements with providers
state protocols that grant autonomous authority
—> POCT needs to be FDA approved and CLIA waived (CLIA = Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments)
a cleared POCT test
test that has been cleared by FDA (not approved)
approved POCT test
test that has been approved by FDA
CLIA-waived test
classification of test that uses methodologies that are simple and accurate that
1) likelihood of results with errors are little to none
2) no risk of harm to pt if performed incorrectly
3) approved by FDA for home use
ex: glucometer
exempt test
low risk that the FDA does not require approval
POCT test
test that allow pt dx, screening, or monitoring in hospital/dr office/ambulance…
need to have results immediately (CAN’T SHIP TO LAB)
pharmacy-based lab testing
qualitative test
quantitative test
rapid diagnostic test
qualitative test
a test that gives results in terms of (-) and (+)
ex: COVID test, flu test, pregnancy test
quantitative test
a test that gives results in numbers
ex: blood sugar test, temp, BP, cholesterol monitor, INR
rapid diagnostic test
a test that is meant to provide immediate diagnostic results
can be quantitative or qualitative test
VA Test to Treat protocols
Pharmacists have the ability to imitate tx with/dispense/administer of controlled substances
dispense CII to CVI
for persons 18 and older
need a pharmacist-pt relationship
regulated by Board of Medicine and Department of Health and the Board
available protocols POCT
tobacco cessation
coronavirus testing
vaccines
TB
HIV PEP
HIV PrEP
hormonal contraception
Emergency contraception
prenatal vits
naloxone
epinephrine
tobacco cessation POCT
not testing, but tobacco screening and assessment process
can prescribe nicotine cessation therapy/non-nicotine cessation therapy for people 18 and older
pharmacists can notify pt’s PCP and if don’t have PCP, pharmacists can counsel on the benefits of establishing care with PCP
non nicotine therapy = bupropion or varenicline
Pharmacists need at least 2 hours of CE training related to prescribing tobacco cessation products
coronavirus testing
pharmacists may initiate tx/dispense/administer COVID test for pts 18 and older
require to:
have appropriate training on this
obtain a history
maintain records and report (+) to local/state health dept
notify PCP
vaccines
pharmacists must have knowledge about immunization
trained in basic CPR
can issue rx and dispense/administer vaccines for pts 3 and older
exclusions
less than 3 yrs old
vaccine is not recommended by CDC
pts had received all CDC recommended vaccines
counsel, record keeping, notify PCP
TB testing
pharmacists can initiate dispensing/administration/interpretation of TB test for pts 18 and older for
those who are at increased risk for latent or active tuberculosis
need it for documentation for school, work…
need required training (must be kept for 6 yrs following last pt)
counsel and notify (+) to health dept and refer
HIV PEP and PrEP
PEP = post exposure prophylaxis (after unprotected sex, needle stick…)
PrEP = pre exposure prophylaxis
pharmacists can initiate tx/dispense/administer tx for pts 18 and older under FDA regulations
need to complete training related to prescribing/dispense HIV prevention meds
training include trauma-informed care (pts may not go to pharmacy to talk about this, trauma related, rape…)
counsel, record keeping, notify PCP
hormonal contraception
pharmacists can prescribe birth control for pts 18 and older
need to complete Accreditation Council for Pharmacy Edu (ACPE) CE training
approved for:
injectable medroxyprogesterone acetate
transdermal patches
vaginal rings
oral pills
pharmacists can’t prescribe/dispense to pts beyond 3 yrs from the initial prescription without being seen clinically
females need pap smear (also preventive care)
counsel, record keeping, notify PCP
emergency contraception
pharmacists can dispense/administer for pts 18 and older
need at least 1 hour of CE training
can prescribe approved emergency contraception or OCP for emergency contraception with additional options for management of anti-nausea tx
prenatal vitamins
can dispense/administer prenatal vitamins for pts 18 and older
prenatal vitamins approved by FDA
sometimes insurance will cover if have a rx for this
naloxone
can write rx/dispense/administer for pts 18 and older (intranasal + intramuscular + injection)
can be dispensed to those at risk for overdose or to those unable to administer the drugs
can’t prescribe to:
under 18
those receiving tx for acute/chronic pain like cancer, sickle cell, in hospice, in palliative care, in clinical trial
pharmacists must provide a copy of the rEVIVE! Pharmacy dispensing brochure to pts
epinephrine
to pts 18 and older experiencing anaphylaxis or at risk for experiencing anaphylaxis
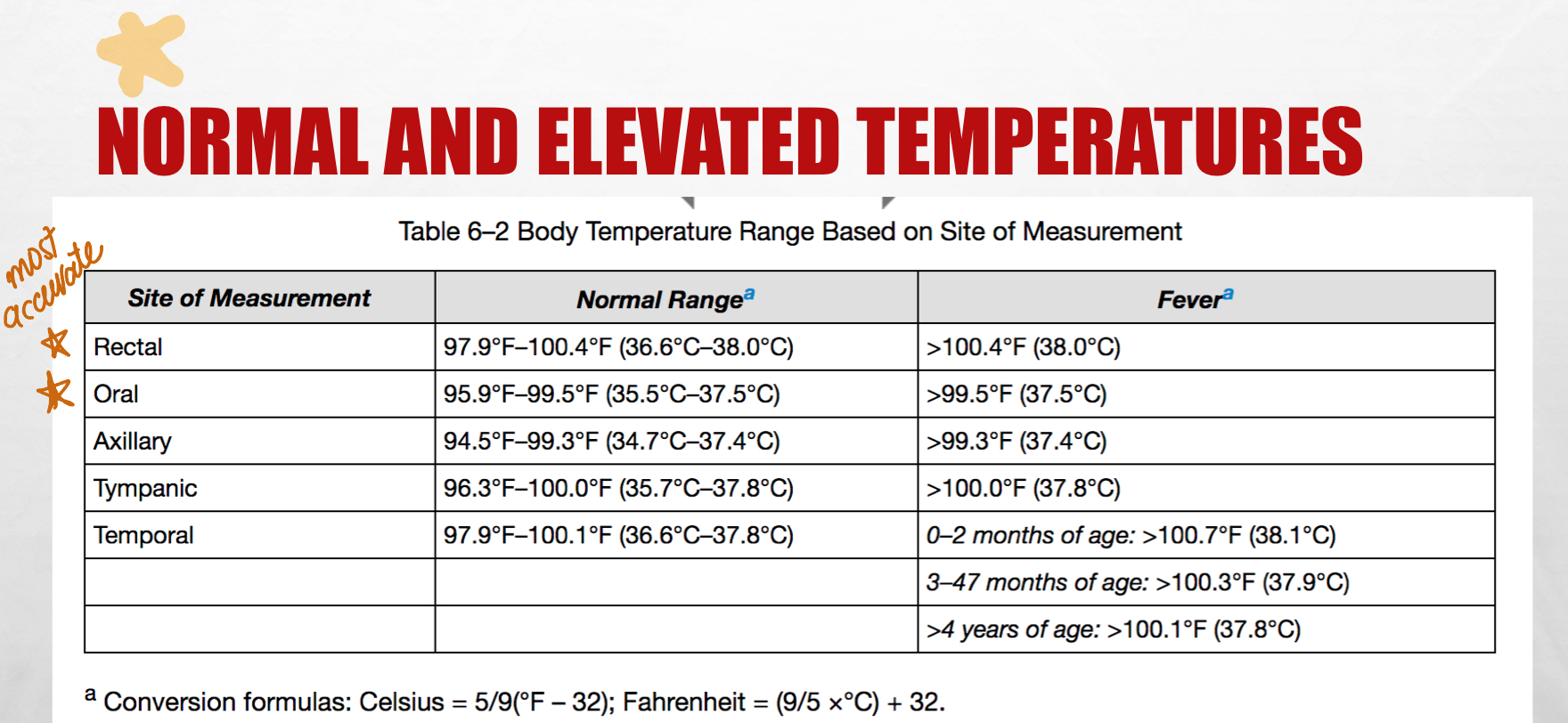
most accurate temp tests
rectal test (rectal is the STANDARD for infants less than 3 months)
oral test
thermometer characteristics
age
preference
what is available
accuracy/reliability
What to do with thermometer
need to disinfect the thermometer after use (use probe cover)
rectal - for infants less than 1
oral
axillary - remain still
tympanic
temporal - when we don’t want to wake pts up
What to not do with thermometer
don’t use a rectal thermometer orally
don’t use an oral thermometer in pts
hyperventilating
recent oral surgery
lethargic
uncooperative
<3 y.o.
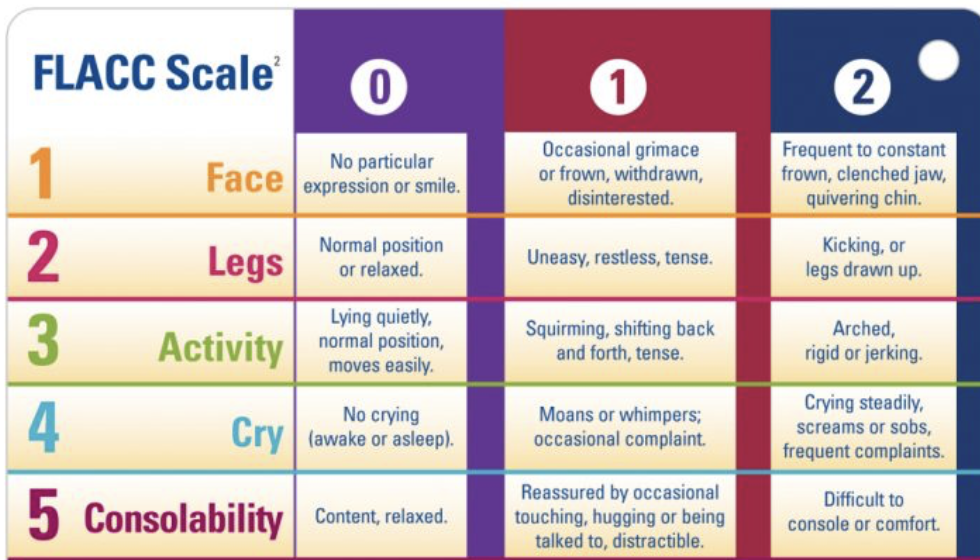
different types of pain scale
Wong-Baker FACES pain rating scale
FLACC scale
numeric 1-10 pain scale
Wong-Baker FACES pain rating scale
mostly for kids

FLACC pain scale
for
infants
nonverbal pts (intubated…)
neurocognitive deficits
common errors in height
incorrectly placed stadiometer
improper positioning
garments not removed
inaccurate reading/documentation
common errors in length
improper equipment use
improper positioning of pts
head not in correct position
both legs are not straightened with heels flat
garments not removed
inaccurate reading/documentation
weight tools
infant scale
bathroom scale
balance
wheelchair scale
bed scale
important notes regarding measuring weight
need to calibrate scale
need to weight same time
need to PEE + remove garments/walker/cane/prosthesis
safety precautions!
BMI = kg/ (m²)
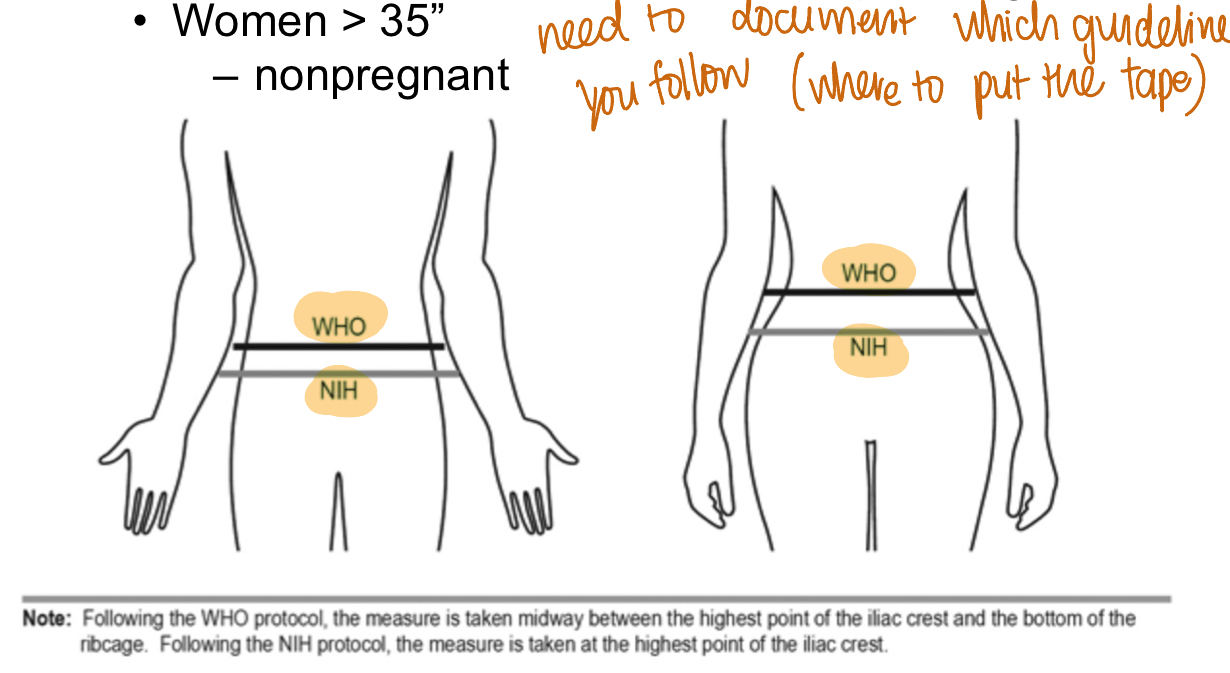
waist circumference screening
screening tool for excessive abdominal fat —> CV risk
higher risks:
men >40”
non-pregnant women >35”
need to put measuring tape horizontally around abdomen
tape is snug, parallel to floor, not compressing the skin
need to document which guideline you follow (WHO vs. NIH)
common errors in getting weight
moving on scale
improper positioning
garments not removed
inaccurate reading/documentation
BP
if repeat BP, wait 1-2 mins before repeating on the same arm
common errors in getting BP
white coat HTN
overestimation of BP = HIGHER BP
cuff size
temp
arm position - below
anxiety, pain, discomfort, strenuous activity
deflating too slowly/too early/halting deflation
underestimation of BP = LOWER BP
underinflation
deflating the cup too quickly
cuff size
arm position - above
hypertensive crisis
sBP >180 OR dBP >110
emergency
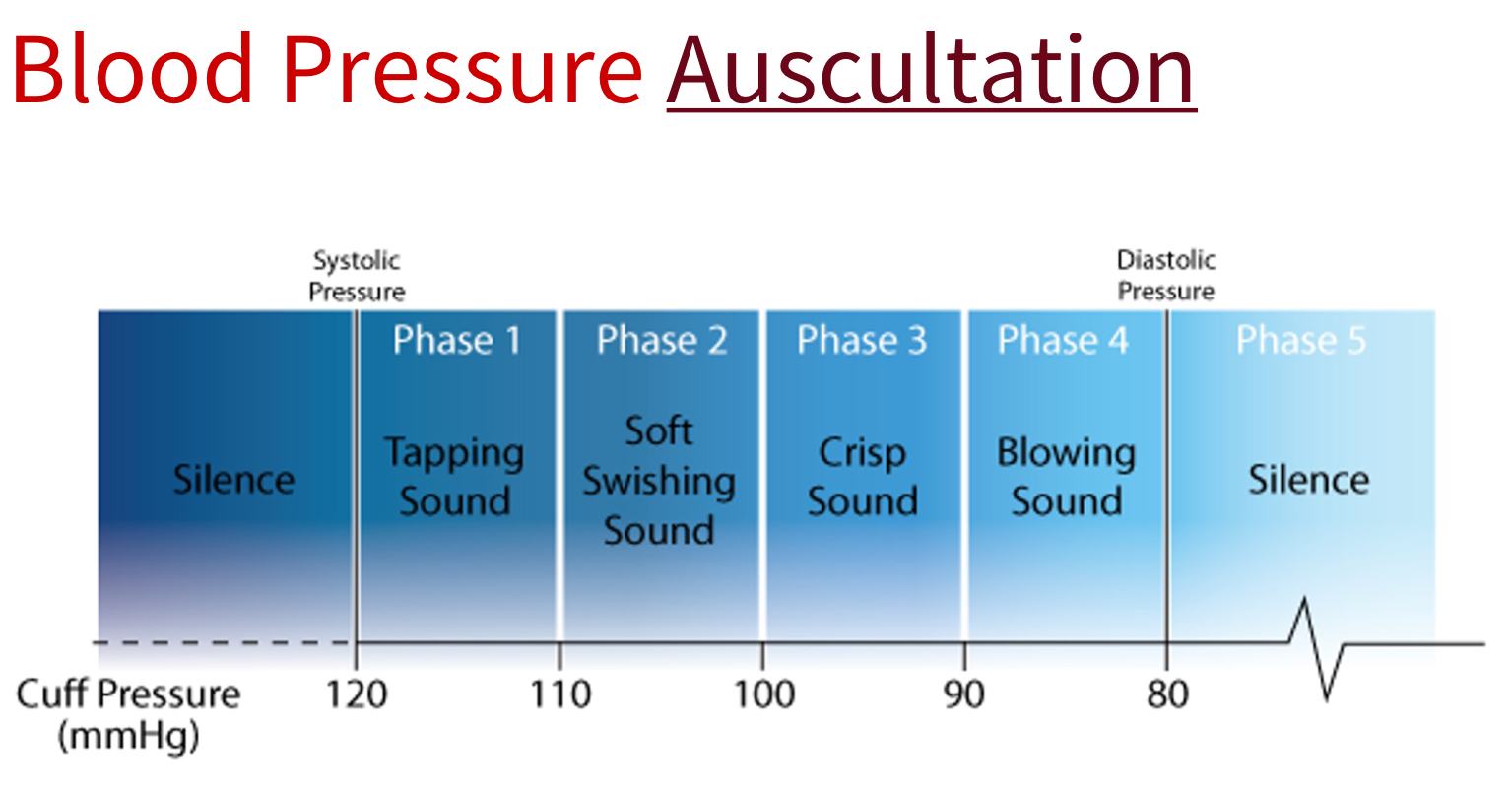
ascultatory gap
silent interval between sBP and dBP
document completely
Collaborative Practice Agreements (CPA)
allows for prescriptive authority under supervision of a physician according to a protocol
1) pharmacist licensure
2) signed CPA/Protocol with a specific provider based on a Standard of Care (pharmacists are more than just dispensing)
Laws vary by state
provide culturally competent care
Listen
Explain
Acknowledge
Recommend
Negotiate
physical exam process
in COLLECT of the PPCP
1) inspection
2) palpation - assess vibration, swelling, rigidity, lumps/masses, pain/tenderness
—> document: SIZE, CONSISTENCY, MOBILITY, NORMAL vs. ABN
3) percussion - assess position, size, density (gas vs. fluid)
4) auscultation
diaphragm of stethoscope
used for high pitched sounds
breath sounds
bowel sounds
regular heart sounds
bell of stethoscope
used for low pitched sounds
heart murmurs
bruits
venous turbulence
extra heart sounds
Korotkoff sounds
-ic
-al
pertaining to
para-
beside
eu-
normal
rhinitis
inflammation of the nasal membrane
rhin/o
aphonia
absence of voice
can be caused by laryngitis
dysphonia
difficulty in speaking or weak voice