S1.1.1-2: Introduction to the particulate nature of matter
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
plasma
An ionised gas mainly found in outer space.
Density
the ratio of its mass to its volume
kinetic molecular theory (KMT)
All matter is made up of small particles.
These particles all have kinetic energy (the energy of motion) which causes the particles to constantly move.
The amount of kinetic energy is proportional to the temperature of the substance; therefore, the particles have greater motion at higher temperatures (straight line motion) and lesser motion at lower temperatures (vibrational motion).
Collisions between particles are elastic, which means no loss in kinetic energy.
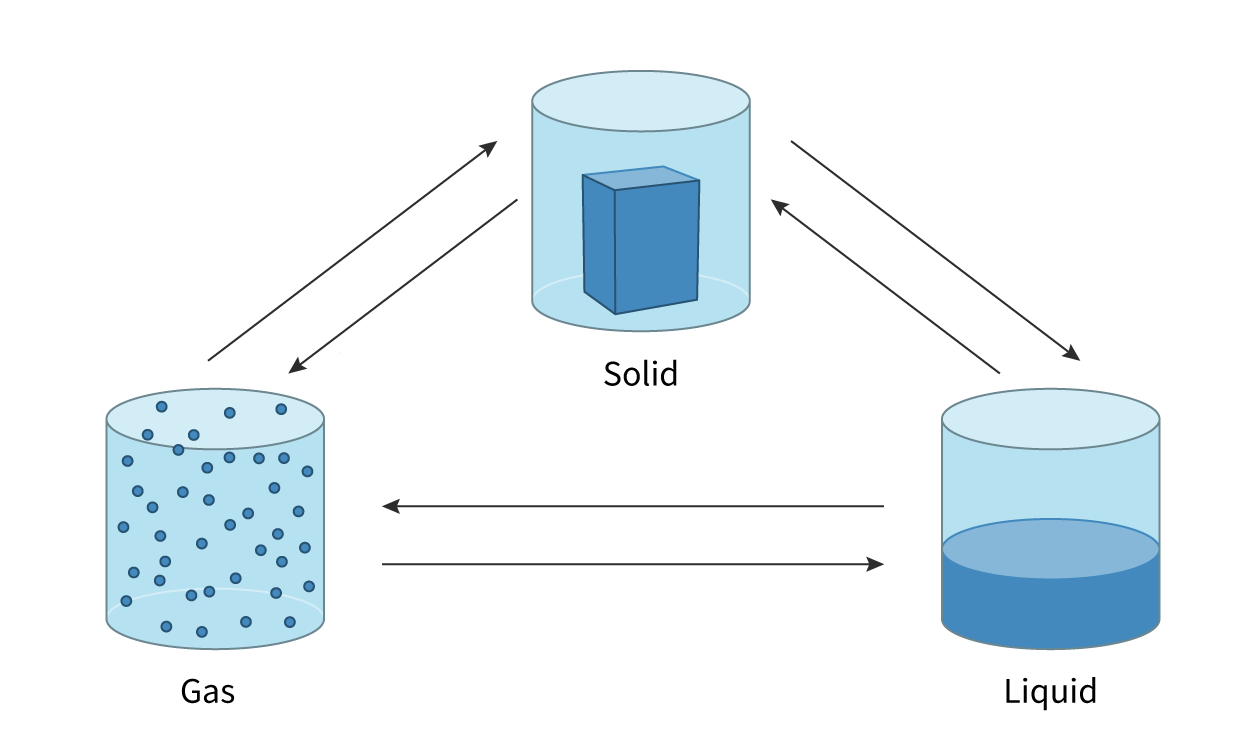
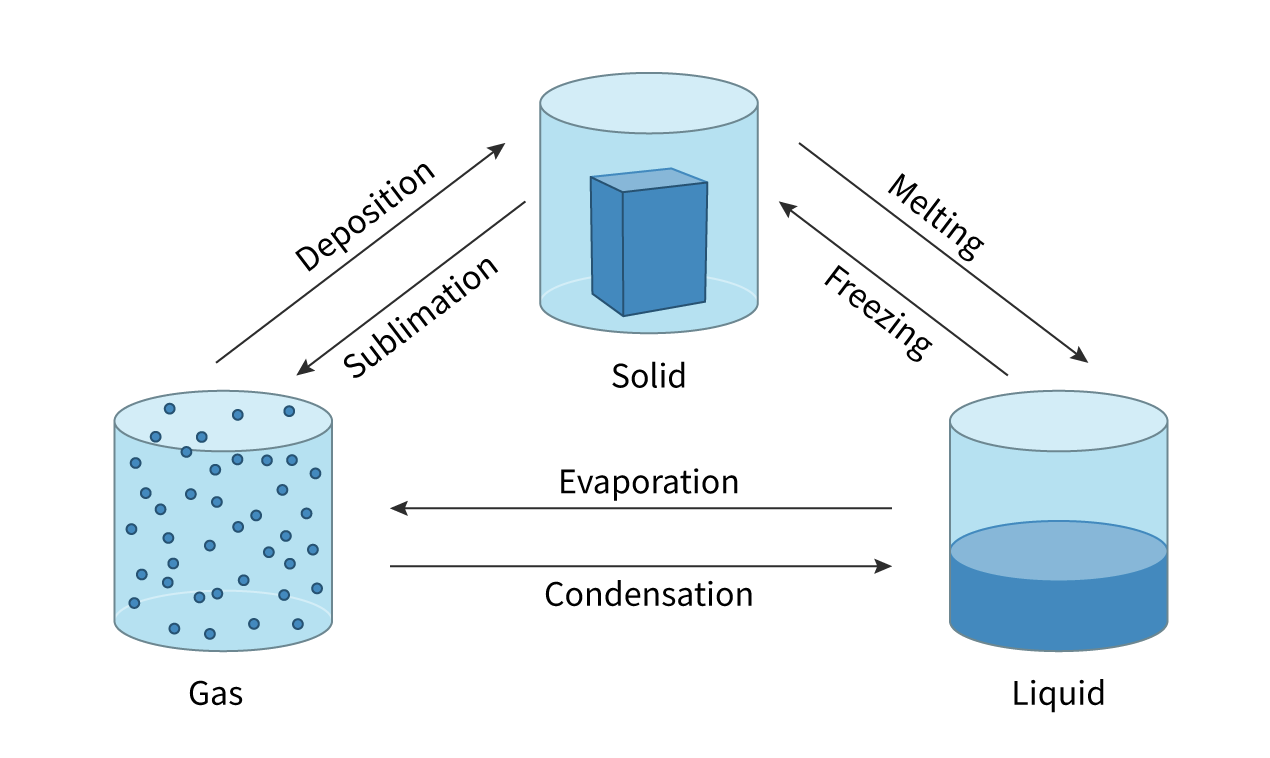
Sublimation
change of state directly from a solid to a gas with no liquid phase
Deposition
the direct change from a gas to solid with no liquid phase
Evaporation
change of state from liquid to gas and takes place only at the surface of the liquid. It can occur at temperatures below the boiling point of the liquid
Boiling
change of state from liquid to gas throughout the liquid. When the vapour pressure is equal to the external pressure (1 atm) the liquid boils
atom
The smallest particle of an element that retains the properties of said element.
matter
A substance that has both mass and volume; typically classified as solid, liquid or gas.
pure substance
Consist of only one type of substance: either an element or a compound. Fixed composition
mixtures
Composed of more than one element or compound not in a fixed ratio, which are not chemically bonded.
allotropes
Alternative forms of an elemental substance in the same physical state
Compounds
Compounds are pure substances composed of two or more different elements chemically combined in fixed ratios.
homogeneous
A type of mixture that a uniform composition and no visible phases or boundaries.
heterogeneous
A type of mixture with a non-uniform composition with visible phases or boundaries.
Filtration
Separates insoluble solid from liquid or solution
Evaporation
Separates mixture with solute dissolved in solvent
Solvation
Separates heterogeneous mixture of solids based on solubility
Distillation
Separates liquid mixture by boiling point differences
Paper Chromatography
Separates a mixture of solutes in a solvent.
Mixture is dissolved in a solvent (mobile phase) and placed on chromatography paper (stationary phase).
Chromatography is a separation technique based on the different affinities of substances for a mobile phase vs a stationary phase.
Substances that interact more strongly with the stationary phase move slower.
Substances that interact more strongly with the mobile phase move faster.
Recrystallisation
Removes impurities from a solid using solubility differences
Absolute Zero
Lowest possible temperature, 0 K or -273°C
Freezing Point of Water
Temperature at which water freezes, 0°C or 273 K
Temperature During Melting
Remains constant to overcome intermolecular forces
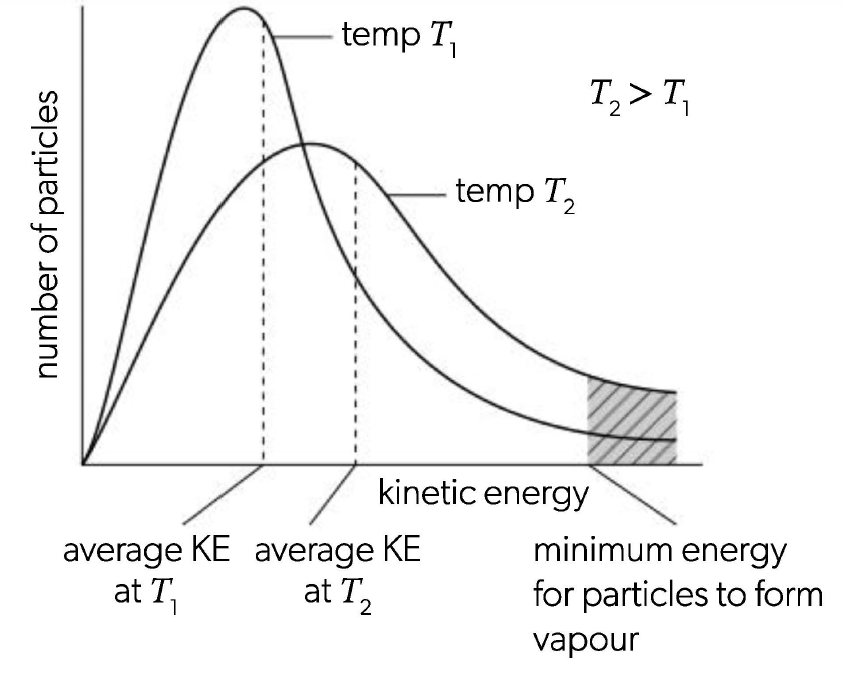
Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution
moving particles in a gas or liquid do not all travel with the same velocity — The distribution of kinetic energies is shown by a Maxwell-Boltzmann curve
since number of particles will stay the same the area under the graph does not change
plasma
An ionised gas mainly found in outer space.
Density
the ratio of its mass to its volume
kinetic molecular theory (KMT)
All matter is made up of small particles.
These particles all have kinetic energy (the energy of motion) which causes the particles to constantly move.
The amount of kinetic energy is proportional to the temperature of the substance; therefore, the particles have greater motion at higher temperatures (straight line motion) and lesser motion at lower temperatures (vibrational motion).
Collisions between particles are elastic, which means no loss in kinetic energy.
Sublimation
change of state directly from a solid to a gas with no liquid phase
Deposition
the direct change from a gas to solid with no liquid phase
Evaporation
change of state from liquid to gas and takes place only at the surface of the liquid. It can occur at temperatures below the boiling point of the liquid
Boiling
change of state from liquid to gas throughout the liquid. When the vapour pressure is equal to the
external pressure (1 atm) the liquid boils


immiscible
not forming a homogeneous mixture when mixed
physical properties of the components that affect seperation method
boiling point, solubility, polarity, particle size, magnetism