EXAM 2 PATHO
1/227
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
228 Terms
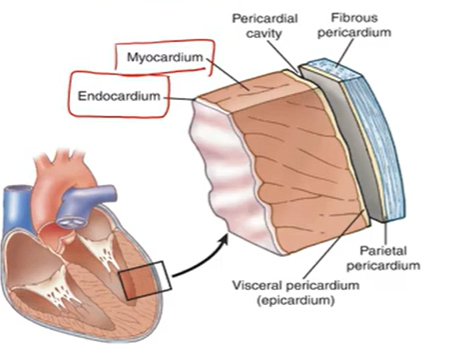
3 Layers of the Heart:
Pericardium: fibrous covering around heart; physical infection protection
Myocardium: Muscle; A & V
Endocardium: lines heart & valves
Diastole Cycle Steps:
Early: V. relaxes; semilunar cloves → AV valve opens → V. filled w/blood
Mid: A. & V. relaxed; continued blood filling
Late: SA nodes contract → A. contracts → V. + blood → AV node
Systole Steps:
AV node → Purkinje + ventricular cells → V. contracts
AV valve closes → Semilunar opens → blood (V. → arteries)
Preload & Afterload:
Volume of blood stretching V. muscles at end of diastole
Psi/tension L.V. generates to push blood → aorta; systematic + pulmonary resistance
^ = ^ Cardiac overload
Cardiac Contractility:
Heart change its contraction force
Inotropic drugs: influences cardiac contraction force
HR:
Regulates CO
Chronotropic drugs: effects HR control; can increase (+) or decrease (-)
CO & Stroke Volume:
CO: SV x HR
3.5-8 L/min
Stroke Volume: 50-100 ml/beat
Tests for Cardiovascular Function
Assessment:
Pulse= bounding & high= good psi
Capillary refill
Auscultate
Radiology: Size & contour of heart & structures
Chest X-ray
CT scan
MRI
Stress Testing:
Treadmill
Thallium & Cardiolite scans
ECG: HR & rhythm
Electrical activity
Echocardiogram:
US
Anatomic structures + functions
Ejection Fraction: 50-70% of blood pushed via L.V.
Cardiac Cathererization:
Fluoroscopy → light up vessels
Atherosclerosis:
fat deposit in the arteries; plaque buildup in lumen
Leading cause of coronary artery & cerebrovascular disease
Coronary arteries → blocked → heart ischemia → MI
Legs, carotid, brain
Based on atherosclerosis
Arteriosclerosis:
less elastic and stretchable
Thickening + hardening of vessel walls
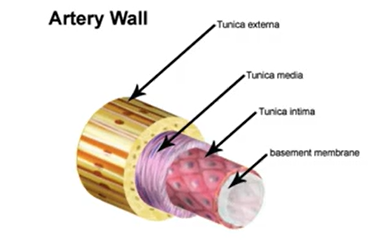
Artery Layers:
Intima: endothelium
Media: smooth & elastic tissue
Externa: Connective tissue
Ischemia from Atherosclerosis:
v O2 → Pain
Depend on which tissues affected + how long it lasts
Angina (Stable/Unstable)
Claudication: PVD
Subsequent thrombosis from unstable plaques → ischemia, infarction, stroke
Lipoproteins:
Water-soluble phospholipids & apoproteins
Transport ↓↓↓
Cholesterol & Triglycerides:
Hydrophobic, insoluble
for energy utilization, lipid deposition, steroid hormone, bile acid formation
Lipoproteins Density:
more protein = ^ density
more lipid (triglycerides) = v density
Types:
Chylomicrons
VLDL: carries large triglycerides #
IDL
LDL: carries cholesterol
HDL: 50% protein
Atherosclerosis steps:
1. Endothelial (intima) Cell Injury
HTN, smoking, hyperlipidemia, toxins, viruses, immune reactions, stress, hyperhomocystenimia
2. Migration of Inflammatory Cells and Formation of Fatty streak
From LDL entering inside → phagocytes eat LDL → foam cells formation → Fatty streak
3. Fibrous plaque (Fibrous Cap)
SMC
Fibroblasts
Ca
Elastin
Endothelium
4. Complicated lesion
Stable → platelets add up to “help” → thrombus (platelet + fibrin) → unstable plaque → angina
Atherosclerosis:
D/x:
pulses, bruits, check tissue perfusion
Doppler, angiography
T/x:
smoking cessation, lowering cholesterol
Restoring blood flow
Catheterization
Thrombus:
blood clot remaining and attached in vessel wall
Thromboembolism
detached thrombus
Embolism:
obstruction of vessel by embolus
Bolus of matter circulating in blood stream
Blood clot, fat, air
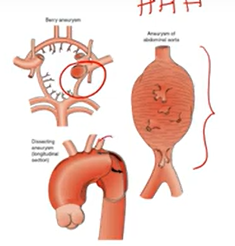
Aneurysm:
localized dilation of vessel/cardiac chamber
weakened artery via stretches
Ruptures & hemorrhage
clot formation
Hypertension:
90-95%: idiopathic; primary hypertension
5-10%: identifiable etiologic cause; secondary hypertension
HTN Risk Factors
Family history
Advanced age.
Smoking
Obesity
Heavy alcohol consumption.
Gender (Male < 50 years, Female > 50 years)
Black race - higher renin producers-
High dietary sodium intake
Low dietary intake of potassium, magnesium, and calcium
Insulin resistance/glucose intolerance
Primary Hypertension
95% of cases of HTN
Unknown cause
Is usually of gradual onset
Peak age: 30-50
Asymptomatic for 10 to 20 years
Triggers include obesity, psychological stress, high-sodium intake, and alcohol intake over I ounce per day
Secondary Hypertension
Refers to sustained increases in blood pressure that result from identifiable underlying systemic diseases
Renal Vascular Disease
decreased flow to the kidney results in persistent increases in RAAS activity
Renal Parenchyma Disease
⚫ damage to glomeruli or tubules leads to increased RAAS activity
Adrenocortical Tumors
⚫ increased production of cortisol and mineralocorticoids (aldosterone) lead to sodium retention and potassium loss
Adrenomedullary tumors (non cancerous) (pheochromocytoma)
⚫ increased production of catecholamines with dramatic increases in heart rate and peripheral resistance
Check for tumor on adrenal gland
Secondary Hypertension Manifestations:
No symptoms till heart, brain, kidneys vascular changes
Brain → CVA, TIA
Retina → Blindness
Heart → MI
Kidneys → Proteinuria, edema, renal failure
Lifestyle changes for HTN:
Weight v
DASH diet
Sodium v
aerobic physical activity
Moderate alcohol consumption
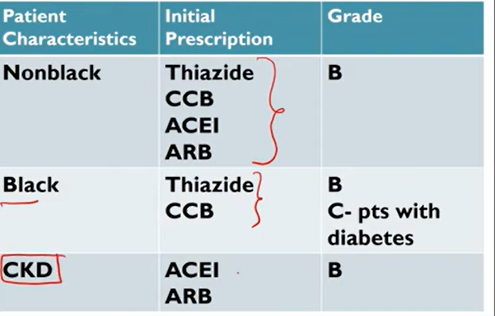
Meds for HTN:
“First line”
Thiazide-type diuretics
Calcium Channel Blockers (CCBs)
Working with RAAS:
Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEIs)
Angiotensin II receptor blocking agents (ARBs)
Later line meds for HTN:
Beta-blockers (BBs)
Alpha-blockers
Vasodilating BBs (nebivolol)
Direct vasodilators (hydralazine)
Loop diuretics
Aldosterone antagonists
Cultural changes in med administration for HTN:
Orthostatic/Postural HTN:
v sys & dia psi when standing
>20/>10
s/s: Dizziness, blurred vision, syncope
Causes: meds, prolonged immobility, starvation, exhausted
Heart failure (CHF):
Inability of heart to pump blood to meet needs
Right sided: inability of RV to provide enough blood → pulmonary circulation; from LHF
Left sided (LHF): inability of LV to produce enough stroke volume → v CO → blood backs into lungs; from HTN
Systole vs Diastolic CHF:
Sys: ventricles cannot empty properly; v muscle ability to contract
Dia: ventricles fail to fill properly
CHF Causes::
Primary: Defective malfunction
Cardiomyopathy
Coronary heart disease (CAD)
Valvular disorders
Secondary:
HTN → LHF
Renal failure
Pulmonary Disease → RHF
Anemia
CHF risk factors:
CAD
HTN
^ Cholesterol
Age
Smoking
Obese
Proteinuria
Diabetes
LHF vs RHF:
LHF:
shortness of breath
Difficulty breathing
Wheezing
Pink frothy/ blood sputum
v urine output
RHF:
Swollen ankles & feet → Edema
Hepatosplenomegaly
Weight gain
Abdominal pain
JVD
Nocturia
CHF compensation:
Ventricular dilation
Hypertrophy
^ Sympathetic N.S.
RAAS cascade
In the end, these mechanisms are gonna make the heart work harder → CHF worse
CHF compensation diagram
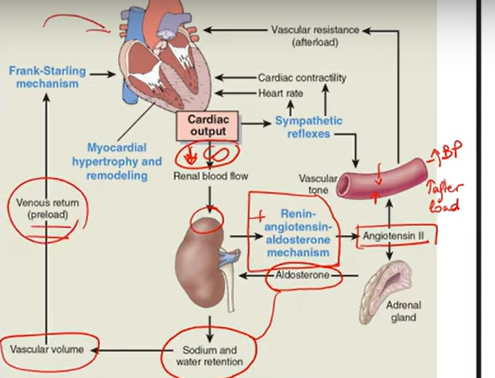
CHF diagnosis:
CXR
ECHO
EKG
Blood work
Electrolytes
Serum osmolarity
BNP
CHF t/x:
Improve pumping
Ionotropics
Lowering preload
Diuretics
Lowering after load:
ACEI, ARBs, aldosterone inhibitors
Peripheral Vascular Disease (PVD)
PAD
Vein disease
Claudication: PAD, low O2 → ischemia, plaque formation
intermitent: only when pt walks feels pain
Severe: pain anytime
PAD:
Atherosclorosis
Thromboangiitis
Raynnud Phenomenon Disease
Thromboangiitis/ Buerger Disease
Inflammatory Disease of peripheral arteries of hands & feet
Young men that smoke
s/s:
Pain, tenderness, gangrenes, malformed nails
t/x: stop smoking bro
Raynud Phenomenon:
Vasospasm of small arteries/oles in fingers & feet (less common)
cold environments
s/s: ischemia
Numb, tingling, rubor, gangrene
Vein Disease:
Varicose Veins
DVT
Chronic Venous Insufficiency
Varicose Veins:
veins in which blood has pooled → distended, palpable veins; open vein valves
Causes:
Trauma
Clots
Gradual Venous distention: from standing
Chronic Venous Insufficiencies:
Inadequate venous return; worse than Varicose & DVTs
s/s: pooling of blood in veins in lower extremity edema
LE circulation becomes sluggish
Necrosis from venous stasis ulcers
DVT:
s/s: pain to site, warm to touch
risk factors:
Circulatory stasis
Vascular wall injury
Hypercoagulable state
Pregnancy
Surgery
Estrogen Therapy
d/x: doppler
t/x: anticoagulants
Heparin
Enoxaparin
(TPA dissolves thrombus)
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD):
Plaques; chest pain from low O2
CAD risk factors:
Dyslipidemia
HTN
Smoke
Diabetes
Obesity
Sedentary
CAD d/x:
Ischemic disease → dyspnea
MI → syncope, dyspnea, nause
Resting EKG
CAD t/x:
Life long care
Angioplasty & bypass surgery not a cure
Reducing risk factors
Percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty
Drugs
Antiplatelts
Statins → v cholesterol
Coronary Bypass Surgery
Angina:
chest pain from reduced blood flow to heart
CAD symptom
Prinzmetal: from vasospasms of vessels; no atherosclerosis
Stable: ischemia during exercise
Nitroglycerin → dilates arteries → less pain
Unstable: complicated plaque; pain at rest
MI: necrosis; prolonged ischemia in myocardium
STEMI (elevated ST) or non
Angina Steps
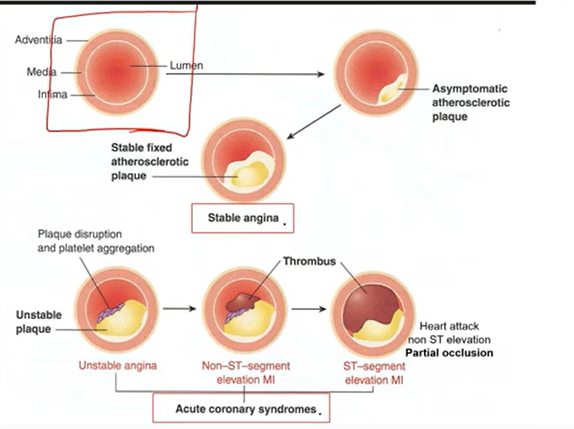
Stable Plaques:
Thick fibrous cap
Partially blocked vessels
No clots/emboli
Unstable Plaques:
Thin Fibrous caps
Rupture & form blood clots:
Thrombosis
Embolization
Ischemia, Scars, MI:
lack of oxygen
20-40 mins = cell death
__________________
Scars replace muscle but loses function
__________________
Hypertrophy → loss of contractility
MI remodeling
MI manifestations:
Bad pain
Referred
Tightness
15-20 mins
nor relieved by NTG & rest
Tachycardia/pnea & Dyspnea
Diaphoresis
Elderly, women, diabetes: atypical presentation of MI
Feeling of impending doom
EKG changes:
Ischemia: inverted T wave & ST depression
Injury, MI: ST elevated
Q wave formation (infarction/necrosis)
Cardiac Biomakers:
Enzymes released by heart when damaged (Myocyte Necrosis)
Myoglobin
CK-MB: detected after 2-3 hrs
Troponin I & T: detected after 3-4 hours
Creatine Kinase
bold means its specific to MN
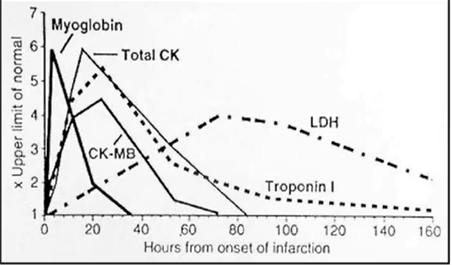
MI diagnosis:
Blood work for Biomarkers, electrolytes (K), blood gases
EKG, CXR, ECHO, stress test
MI t/x:
O2
Meds:
Antianginals: Nitrates
Antiplatelet: ASA, aspirin
Analgesics
Thrombolytics
Antiarrhythmics
Heart Wall Disorders
Disorders of the Pericardium
Acute pericarditis
Pericardial effusion - tamponade
Constrictive pericarditis
Disorders of the Myocardium
Cardiomyopathies
Disorders of the Endocardium
Valvular dysfunctions
Acute rheumatic fever
Infective endocarditis
Acute Pericarditis:
Inflamed and roughened
90% from viruses
Bacteria
Autoimmune diseases
s/s:
Chest Pain worsening w/ respirations or movement
When lying down
Dysphagia
Restlessness
D/x:
Friction rub
Sinus Tachycardia
Low grade fever
Echocardiogram
Complications:
Hypotension
Pulse paradoxus: v BP when inspirating (deep breath)
Normal drop is 10
Abnormal is 20 mmHg
t/x:
NSAIDs
Pericardial effusion:
Fluid accumulation in cavity
Serous effusion
Serosanguineous
Blood
Leads to Cardiac Tamponade:
Cardiac Temponde:
Fluid/blood in pericardial sac compresses heart
from trauma, Mi, med, bleeding
s/s:
Muffled heart sounds
BECK’s triad: low arterial BP and distended neck veins
d/x:
ECHO, CT, chest
t/x:
Pericardial window
Pericar
Cardiomyopathy:
Myocardium
three types:
Dilated: Dilated heart → big floppy heart → unable to pump
Hypertrophic: thickening of myocardium
Restrictive: cannot fill diastolic the heart with blood; heart is ridged
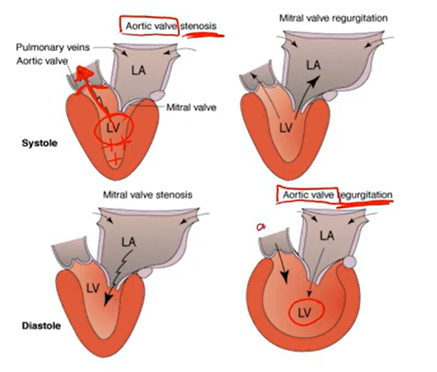
Valvular Defects:
Stenosis: valve does not open all the way; harder to force blood out → narrow
Regurgitation: valve does not close all the way → leaks
Mitral Valve Prolapse:
Congenitive Disease; mitral valve cups billow upward → LA during systole
Women
Asymptomatic
Heart Murmurs
Prevent Infective Endocarditis
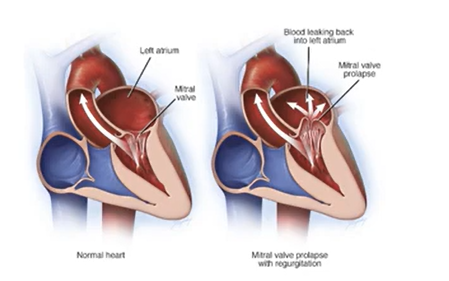
Infective Endocarditis:
May include 1+ valves
Bacteria infection most common
Risk factors: IV drug uses, Valvular heart disease
s/s:
Fever
Infection signs
Murmurs
Lesions
Micro embolism
d/x:
Blood cultures
ECHO
t/x:
Antibiotics
Valve replacement
Rheumatic Heart Disease:
Rheumatic fever: inflammatory diseases affecting heart, joints, skin, brain, valves
Group A streptococcal throat infection
Risk Factors: Sore throat, H/A, fever, abd. pain, swollen pain
T/x: ABX, fever
EKG:
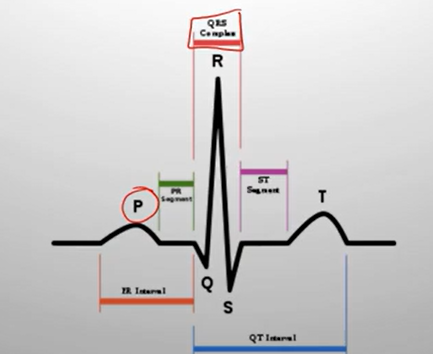
P wave → Atrial depolarization (atria activated → contract).
PR interval → Signal travels through AV node → to ventricles.
QRS complex → Ventricular depolarization (ventricles activated → contract).
Atrial repolarization happens here too, but it’s hidden inside the QRS.
ST segment → Early part of ventricular repolarization (should be flat).
T wave → Ventricular repolarization (ventricles reset/relax).
U wave (sometimes seen) → Final phase of ventricular repolarization (extra reset, not always visible).
Electrical pathway of the heart:
Sinoatrial node
AV node: connects between A. & V.; impulse is slowed → allow atria to contract & empty blood before stimulating the ventricles → depolarization
Bundle of his
Bundle Branches
Purkinje Fibers
Mechanical Activity:
Must have electrical impulse
Muscle contraction + pulse
“Lub Dub” → S1 & S2
S1: close AV valve
S2: close Seminular valves
Electrical Activity:
Prepares heart for contraction
Precedes mechanical activity
Not always followed by mechanical activity
EKG/ECG
PACEMAKERS:
SA: 60-100 bts/min
AV: “back up” 40-60 bts/min
Ventricular cells: back up too; 20-45 bts/min
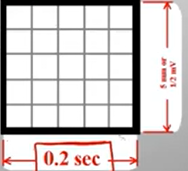
EKG Paper
Horizontal:
Small box - 0.04 s
Large box - 0.2 s
Vertically:
Large box - 0.5 mV
Every 3 seconds (15 large boxes) marked by a vertical line; 60 seconds would be 90 HR
Helps when calculating HR
Determining PR interval:
Normal: 0.12-0.2 secs
(3-5 small boxes)
If 4 small boxes = 0.16 secs
QRS duration:
Normal: 0.04-0.12 secs
(1-3 small boxes)
If 2 small boxes = 0.08 secs
Normal Sinus Rhythm (NSR):
Electrical impulse formed in SA node & conducted normally
Arrhythmias if irregular
Dysrhythmia Formation:
Arise from:
Sinus mode
Atrial Cells
AV junction
Ventricular cells
SA node problems:
fire too slow → Sinus Bradycardia
fire too fast → Sinus Tachycardia
Sinus Bradycardia:
<60 bpm
regular
Normal P wavers
Normal PR & QRS
Sinus Tachycardia":
>100 bpm; from stress
regular
Normal P wavers
Normal PR & QRS
Atrial cells problem:
Atrial Flutter
Atrial Fibrillation
Atrial Flutter:
fires continuously due to a looping re-entrant pathway; makes F (flutter) waves 250-350 bpm
Only some impulses conducted through AV node
W/every 2nd, 3rd, 4th impulse → QRS → AV node
Irregular P waves, No PR interval, (QRS, regularity, rate) normal
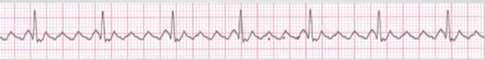
Atrial Fibrillation
No organized atrial depolarization → no normal P wave; not originating from sinus node
Chaotic atrial activity → irregular rate
2-4%
8-10% in pt older than 80 yrs
No P waves & PR intervals, irregular
Rate, QRS normal
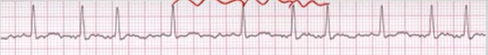
Ventricular cell problems:
Ventricular Tachycardia
Ventricular Fibrillation
Ventricular Tachycardia
fire continuously due to looping re-entrant pathways in ventricles (most common)
can create or not create pulse at times
Faster rate, no P waves & PR, wide (>0.12) QRS
Regular
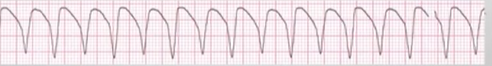
Ventricular Fibrillation
COMPLETETLY ABNORMAL; NO PULSE → CPR; from multiple foci
No rate, irregular, no P & PR, wide & irrecognizable QRS
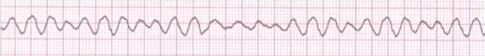
ST elevation:
J point is higher; elevated ST segment

ST elevation infarction:
Normal EKG → Ischemia → ST depression → Infarction → ST elevation
Depression: peaked T waves → T inversion
Elevation: Q waves appearance
Innate/Natural Immunity:
nonspecific; rapid
Only to group of microbes
Phagocytes, nk, dendritic cells
Monocytes → macrophages
1st line:
Skin
Mucous
Flora (stomach, i.s.)
2nd line:
Innate immune cells
Inflammation *
Complement
Antimicrobials
Adaptive/Acquired Immunity:
specific; slower
for each unique antigen
3rd line:
Lymphocytes
B cells
T cells vvv
Helper & Killer t cells
B Lymphocytes:
Memory cells: efficient; antibody response to subsequent antigen recognition
Plasma: Secretes antibodies/iG
T Lymphocytes:
Cytotoxic T cells: specific cellular antigen destruction
Helper T cells: Activates antigen-specific T cells
Mucus & Cilia:
lysozymes → destroy bacteria cell wall
moves mucus out to keep antigens out
Inflammatory Response:
2nd line; from many problems
Trauma, infection, chemical injury, foreign bodies, ischemia
s/s: Redness, swelling, heat, pain, function loss
WBCs abundance
Neutrophils > Lymphocytes > Monocytes > Eosinophils > Basophils
“Never let monkeys eat bananas”
Leukocytes (WBCs):
Granulocytes: N, E, B
Monocytes → Macrophages & Dendritic
Initiate adaptive response
Dendrites turn on lymphocytes
NK cells, lymphocytes
Mast cells: histamine; located in tissues
Allergies, asthma, inflammation
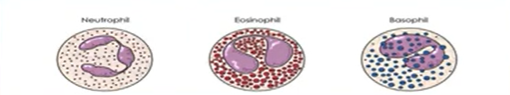
Neutrophils:
Most abundant granulocytes (55% WBC)
Early responder of innate immunity