chapter 12: endomembrane system and protein sorting
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Trafficking
Movement of lipids and proteins b/w organelles
List all components of the endomembrane function and their function
*ER & golgi complex are sites for protein synthesis, processing, and sorting
*endosomes- carry and sort materials brought into cell
*Lysosomes- digest ingested materials and unneeded cellular components
What is the variation in amounts of smooth and rough ER?
Cells with synthesis of secretory proteins have prominent rough ER networks
Cells that produce steroid hormones have extensive networks of smooth ER
Rough ER is the site for:
adding carbs to glycoproteins
Folding polypeptides
Recognition and removal of misfolded proteins
Assembly of multimeric proteins
Proteasome
Protease complex made to carry out selective, efficient, and processive hydrolysis of proteins
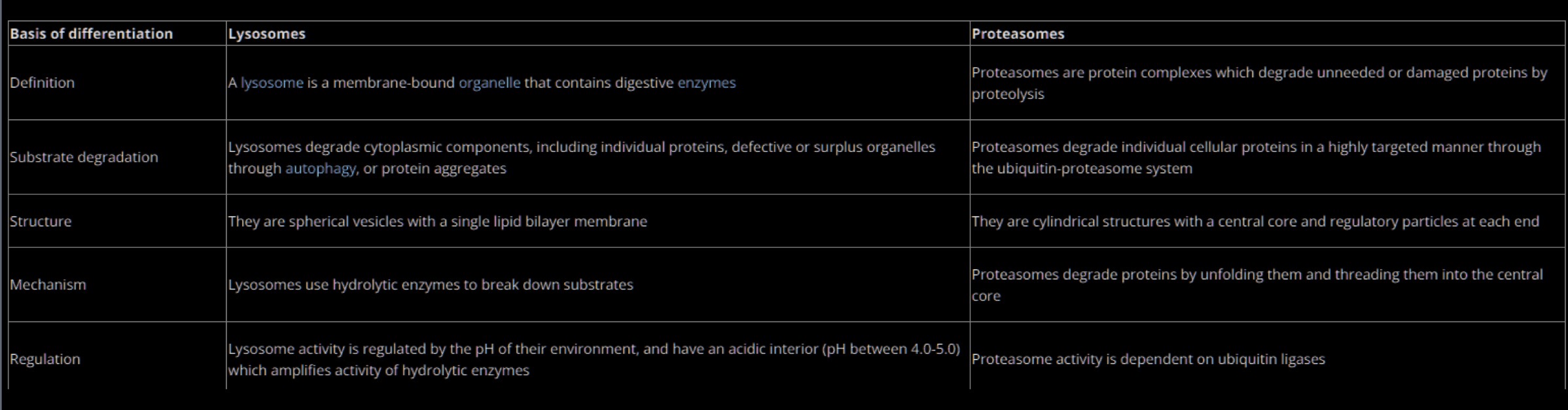
Proteasomes VS. Lysosomes
Smooth ER function
involved in drug detoxification, carb metabolism, calcium storage, and steroid biosynthesis
Golgi Apparatus
DON’T SAY FED-EX!!!!! plays a central role in membrane and protein trafficking in eukaryotes
What is the golgi a. comprised of?
Flattened membrane bounded cisternae. Usually 3-8 is called a Golgi stack
Name the 2 faces of the Golgi stack
Cis face- oriented towards the ER, called the cis-Golgi network.
Trans face- called the trans-Golgi network
What 2 models account for the flow of Lipids and proteins from the Golgi?
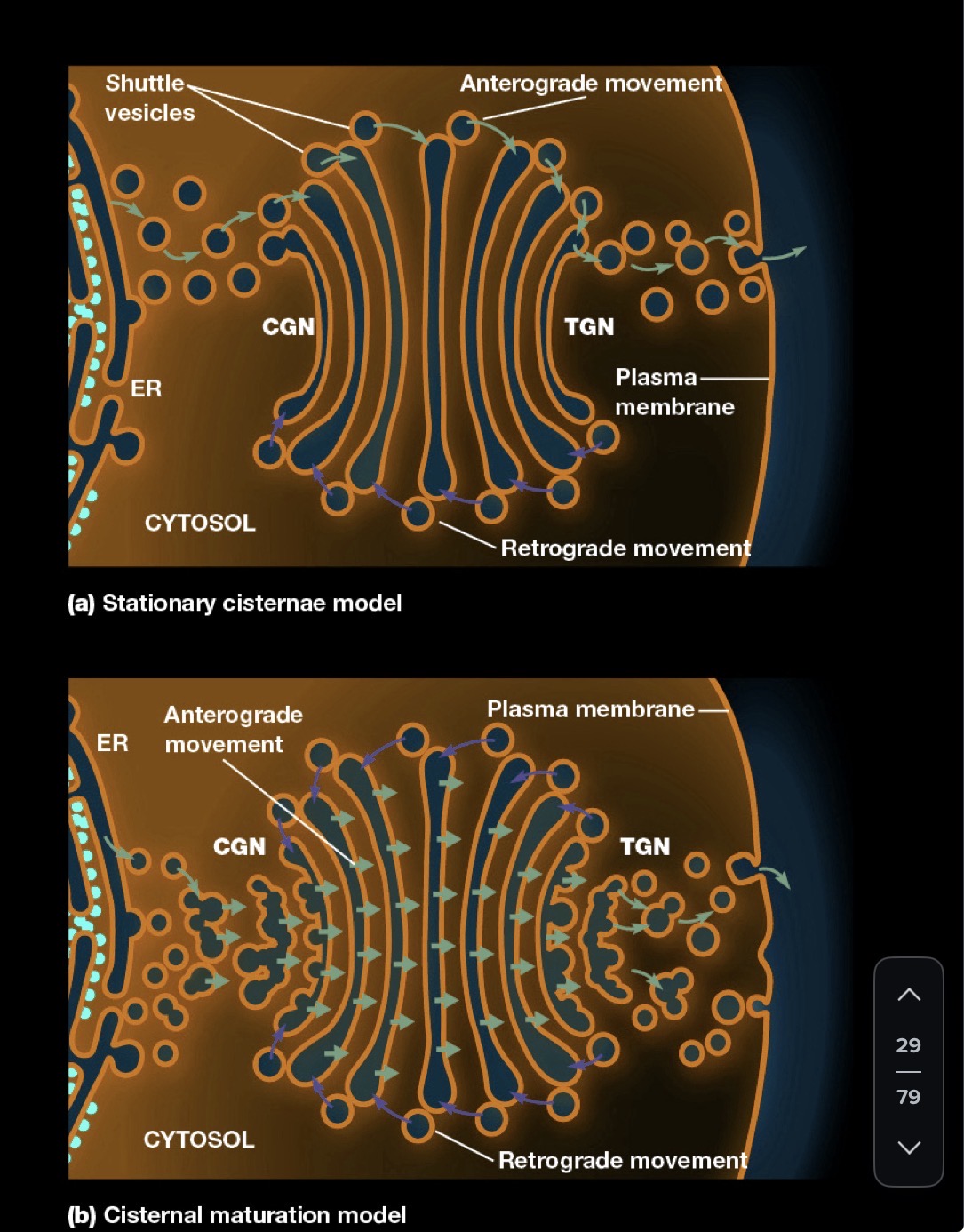
Anterograde vs. Retrograde transport
A-moving material toward the plasma membrane
R-flow of vesicles from Golgi cisternae back to the ER
define glycosylation and give the 2 general kinds nitrogen
• The addition of carbohydrate side chains to proteins to make glycoproteins.
N-linked: the addition of a oligosaccharide to the nitrogen atom of certain asparganine residues
O-linked: adding oligosaccharide to the oxygen atom on the hydroxyl group of some serine, threonine, and tyrosine residues
Molecular chaperones
Proteins that assist others to fold properly during or after synthesis, refold after partial denaturation, and to translocate to cellular locations
Explain what Bi P is and how it functions
an Hsp70 molecular chaperone
binds to the hydrophobic region of polypeptide to stop aggregation
Polypeptide is released, binding with ATP hydrolysis which helps the protein fold.
If folded correctly, hydrophobic regions are buried. If not, process is repeated
Protein disulfide isomerase
Enzyme that can either form or break disulfide bonds between cystenines until it reaches the most stable arrangement.
Unfolded protein response (up-r)
Detects misfolded proteins by way of sensor molecules in the ER membrane. Sensors activate signaling pathways that shut down protein production (except for folding and degradation).
ERAD
Gets rid of malfunctioning proteins by sending them to be degraded by proteasomes
define a protein “tag” and give examples
A target for proteins that ensure they go to the correct location
amino acid sequence
Hydrophobic domain
Oligosaccharide side chain
Something else
What are the 2 pathways for sorting tagged polypeptides
Endomembrane system- polypeptide is transferred the ER membrane as synthesis occurs. Cotranslational import
Organelle targeted- polypeptides transported to organelles after synthesis occurs. Post translational import
What are the 3 mechanisms by which membrane enclosed organelles import proteins?
-membrane transport (must be unfolded)
-nuclear pore transport (remains folded)
-Vesicle transport (remains unfolded)
ALL REQUIRE ENERGY
Describe nuclear transport
protein w/ localization signal binds to receptor
Complex enters the pore
RanGDP is phosphorylated by GEF to become ranGTP
Precursor protein
Inactive protein or peptide that can become active by post translational modification