General overview (light and the electromagnetic spectrum)
1/44
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
What is total internal reflection?
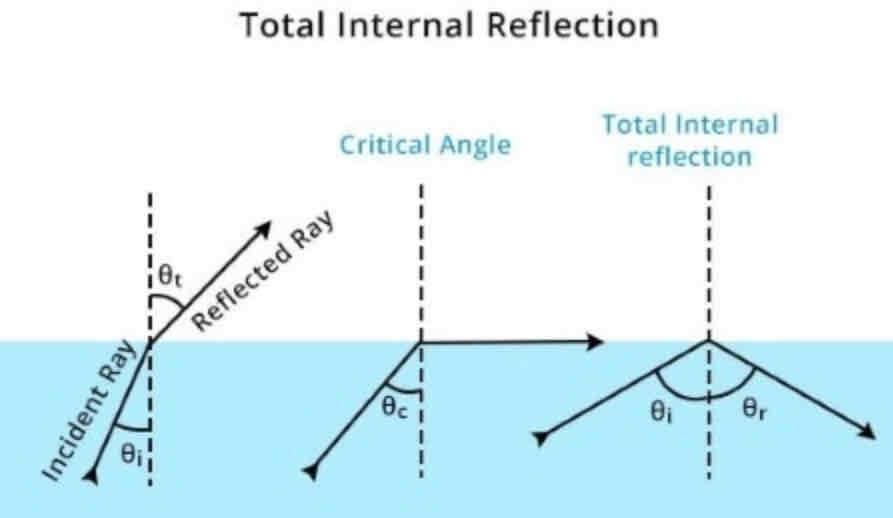
Light is completely reflected back at a boundary between two mediums. It occurs when light meets a less dense medium at an angle of incidence larger than the critical angle
What is the law of reflection?
Angle of incidence=angle of reflection
What is a critical angle?
The angle of incidence in the denser medium which causes the angle of refraction to be 90 degrees
What is speculation reflection?
Rays are reflected from a smooth surface in a single direction
What is diffuse reflection?
Reflection from a rough surface which causes scattering
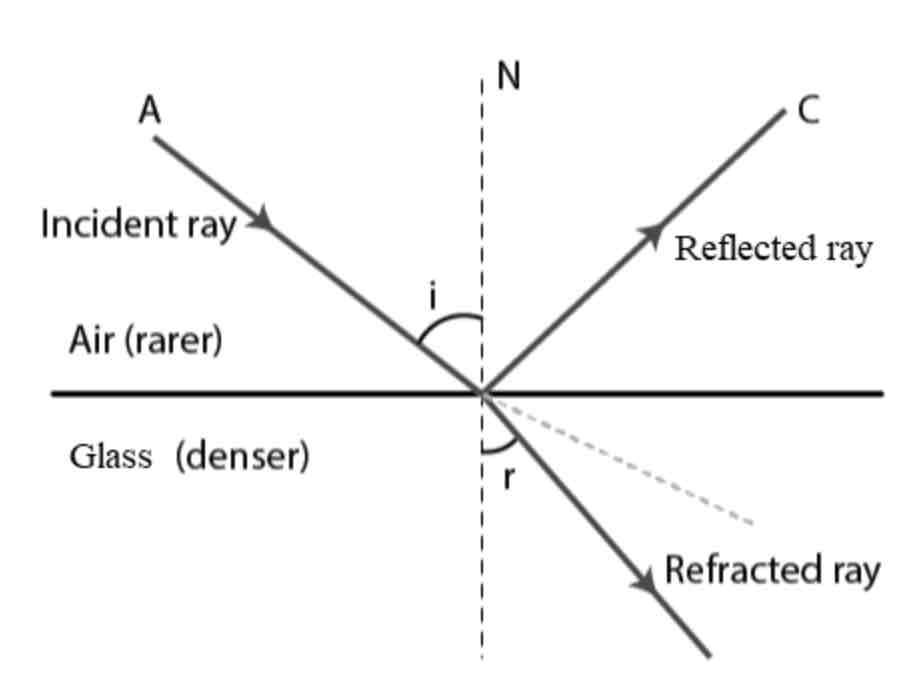
Draw a labelled diagram showing refraction of a ray from air into glass
Labels should include: normal (dotted line), incident ray (first line), refracted ray (second line), angle of incidence (first angle), angle of reflection (second angle)
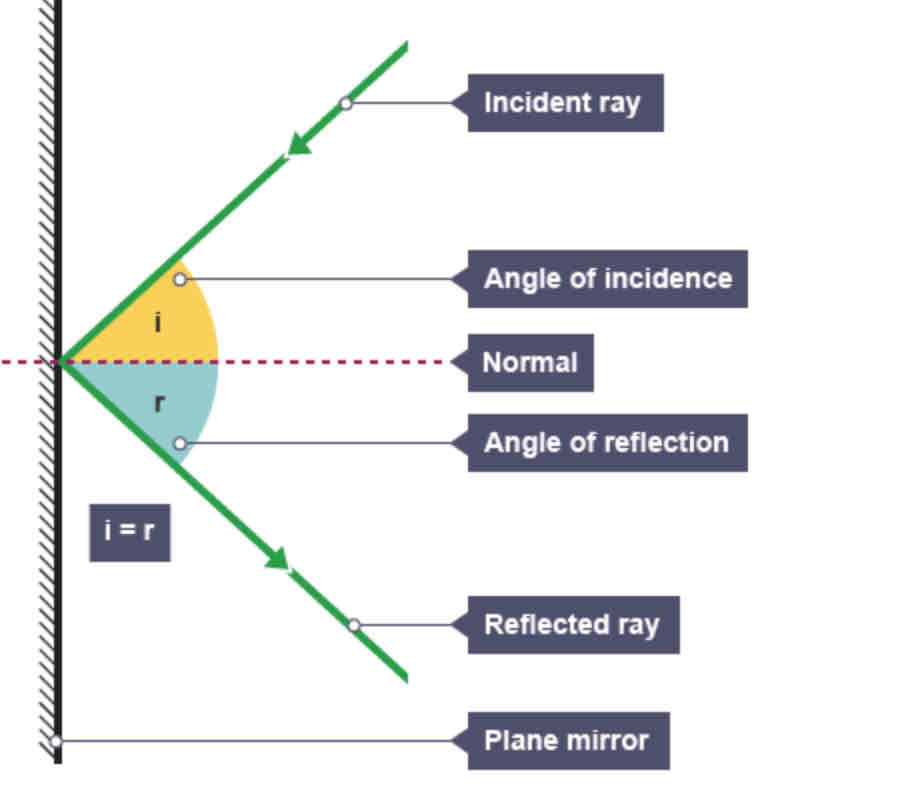
Draw a labelled diagram to show reflection against a plane mirror
Labels should include: incident ray, reflected ray, plane mirror, normal, angle of incidence, angle of reflection
Draw diagrams to show total internal reflection from water to air
Why do some objects appear certain colours?
Opaque objects only reflect a specific wavelength, causing the object to appear that colour - all other wavelengths are absorbed
How do filters work?
Only a certain colour is transmitted through the filter - all other colours are absorbed
What is the focal length of a lens?
Distance between the lens and the focal point
What is a focal point?
The point where all horizontal rays meet after passing through the lens
How is the focal length of a lens related to its power?
Power is the inverse of the focal length. The shorter the focal length, the greater the power
What is a concave lens?
Also called a diverging lens, it is thinner at the centre than the edges (hourglass-like)
How do concave lenses refract light?
Parallel rays are caused to diverge. They separate, but come to form a principle focus on the other side of the lens
What type of image does a concave lens produce?
A virtual image only
What is a convex lens?
Also called a converging lens, it is thicker in the middle than at the edges
How do convex lenses refract light?
Parallel light rays converge
What type of image does a convex lens produce?
Can produce both real and virtual images
What type of waves are electromagnetic waves?
Transverse
What do electromagnetic waves transfer?
Energy only
What are the main groups in the magnetic spectrum?
Radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, x-rays, gamma rays
What type of spectrum is the electromagnetic spectrum?
Continuous (each group goes into the next)
What trends are there in the electromagnetic spectrum?
As wavelength increases, frequency decreases
Danger also increases (gamma rays can cause cancer while radio waves aren’t dangerous at all)
What can happen when radiation hits an object?
It can be transmitted, reflected or absorbed
What do all objects emit and absorb?
Infrared radiation
How does the quantity of infracted radiation increase?
If temperature increases
What happens to the type of radiation emitted by an object as temperature increases?
Wavelength decreases
What is required for a body to be at a constant temperature?
It should emit radiation at the same rate it absorbs it on average
What happens to the body if the average power it radiates is less than the power it absorbs?
The temperature of the body decreases
What happens to the body if the average power it radiates is more than the power it absorbs?
The body increases in temperature
What factors control the temperature of the earth?
The rate of absorption and emission of radiation, and the amount of reflection of radiation into space
What happens to how dangerous an electromagnetic wave is as frequency increases?
It increases
What is the danger of microwaves?
Internal heating of body cells
What is the danger of infrared waves?
Skin burns
What are the dangers of visible light waves?
Blindness
What are the dangers of ultraviolet waves?
Damage to surface cells and eyes, which can lead to skin cancer
What are the dangers of x-rays and gamma waves?
Mutation to cells and cell damage
What are radio waves used for?
Broadcasting, communications, satellite transmissions
What are infrared waves used for?
Thermal imaging, optical fibres, security systems
What is visible light used for?
Photography, vision, illumination
What are gamma rays used for?
Sterilising food, detection and treatment of cancer, sterilising medical equipment
How are radio waves and electrical circuits linked?
They can be produced by oscillations in electrical circuits, and they can induce oscillations in electrical circuits
What can changes in atoms and nuclei do?
Generate radiations over wide frequency ranges
What can cause a change in atoms and nuclei?
Absorption of a range of radiations