Nature of Economics (Economic Problem)
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
What are the 4 factors of production?
Labour, Land, Capital & Enterprise
What is the definition of a social science?
The scientific study of societies and social interaction.
One key difference between economics and the natural sciences is?
Theories are harder to test in economics, because other variables can change.
How can you argue economics is not a science?
Since it the study of human behaviour, of which cannot be reduced down to scientific laws.
What is enterprise?
The willingness to take risk to make profit
(Usually undertaken by entrepreneurs)
What is the purpose of any economic activity?
Increase people’s economic welfare by creating outputs that satisfy their various wants and needs.
What is economic welfare?
The level of prosperity and quality of living standards in an economy.
3 examples of economic activity?
(Making of) Goods
(Provision of) Services
Consumption
What 3 questions are asked when deciding what to produce, given limited resources?
What to produce? (What products firms can make profits from)
How to produce it? (Most efficient to maximise profits)
Who to produce it for? (Consumers who are willing to pay)
These questions are answered by figuring out agents incentives
What are the 3 main types of economic agents?
Producers, consumers, government
How do Producers, Consumers and Government all make decisions that affect how resources are allocated?
Producers decide what to make, and how much they’re willing to sell it for.
• Consumers have to decide what they want to buy, and how much they’re willing to pay for it.
• Governments have to decide how much to intervene in the way producers and consumers act.
What are all economic agents assumed to be?
Rational - meaning that they all make decisions that are best for themselves.
What do PPFs show?
The maximum possible output available when you consider the production of just 2 goods/services
What property do all points on the PPF have?
They are all productively efficient. (producing the maximum output with the minimum possible cost, using all resources optimally at the lowest point of the average cost curve)
They are not all allocatively efficient (resources are distributed to produce the mix of goods and services that society most desires, maximizing overall welfare where the Price (P) consumers are willing to pay equals the Marginal Cost (MC) of producing it (P=MC))
What are points outside & inside the PPF respectively?
Outside = Not possible to achieve using the current level of resources in the economy.
Inside = Possible, but productively inefficient. (e.g you could make more of B, without having to make more of A)
What is opportunity cost?
The next best alternative that you are forced to give up.
What are some problems with the concept of opportunity cost?
Not all alternatives are known, or there is a lack of information on the alternatives and their costs.
Some factors don’t have alternatives or are very difficult.
The true opportunity cost may only be known after the decision.
How would increased resources affect a PPF?
PPF shifts outwards - since total possible output of the economy would increase.
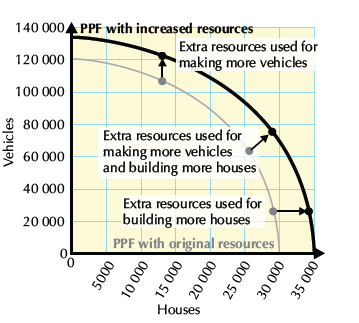
How can a PPF shift outwards?
Improvement in technology and labour, both leading to an increase in productivity.
Also, if there is a total increase in resources.
Explain what a PPF shows
A production possibility frontier (PPF) shows the maximum possible combinations of two goods or services that an economy can produce using its given resources and level of technology, assuming resources are used fully and efficiently.
What is meant by a trade-off?
A trade-off is the situation where choosing more of one option requires giving up some of another, because resources are limited.
How does a free market allocate resources?
Supply and demand as well as price mechanisms
What is price signalling?
Price signalling is the way prices convey information to consumers and producers about scarcity, demand, and resource allocation in a market economy.
Pros and cons of free market economy

What is a mixed economy?
Combination of free market and government interventions.
What is a command (or planned) economy?
The government decides how resources should be allocated - NOT MARKETS.
Pros and cons of a command economy?

What is market failure?
Market failure happens when the price mechanism fails to allocate scarce resources efficiently or when the operation of market forces lead to a net social welfare loss
Happens when free markets result in undesirable outcomes
(Traffic congestion is considered a market failure)
What are demerit goods?
Products or services that are overconsumed in a free market because individuals underestimate their long-term negative consequences, leading to market failure. (e.g drugs)
How do governments intervene when there is a market failure?
Change the law (Banning smoking in enclosed public spaces to reduce negative externalities)
Offer tax breaks (Subsidies for renewable energy (solar panels, wind power)
Create other incentive to influence people’s behaviours )Taxes on cigarettes or alcohol to discourage consumption (sin taxes).)
Buy or provide goods and services
(Government supplies goods the market would underprovide or not provide at all. - e.g hospitals)
What is the Public Sector and Private Sector in a mixed economy?
Public Sector = Government
Private = Privately owned businesses
In a pure free market economy there would be no public sector and in a pure command economy there would be no private sector.
What are economic agents?
Anybody who makes an economic decision
What does it mean for an agent to act rationally?
They will make decisions based solely on maximising utility. Nothing else affects decision making.
What is marginal utility?
The benefit gained by consuming one addition unit of a good.
What is total utility?
OVERALL benefit of consuming a good
What is the law of diminishing marginal utility?
The marginal utility gained by each additional unit of a good decreases.)
(this is why the demand curve is 1/x (x>0))
What are the 2 things firms may choose to do with their profits?
Reward their shareholders &/or staff
Reinvest into business in aim of even more profits later. This is done by expanding.
What are some quantities firms may choose to maximise?
Profits, market share, total share, ethical objectives

What are the 2 things agents are assumed to have by traditional economic theories in regards to being rational?
They have symmetric information about the alternatives
They have the ability to make informed decisions based on this information.
Difference between imperfect information and asymmetric information?
Imperfect information = information is incomplete.
Asymmetric information = information is incomplete and unevenly distributed.
Why do people not act rationally (4 things)?
Habitual behaviour
Weakness at computation
Consumer inertia
Social norms

What type of rationality is it when an agent cannot act fully rationally?
Bounded rationality
What is bounded rationality?
Agents tend to satisfice (decide on and pursue a course of action that will satisfy the minimum requirements necessary to achieve a particular goal.) rather than spend ages trying to make a rational decision that maximises utility.
What is the latin term for perfect rational agent?
Homo economicus
What is bounded self control
Individuals have bounded self control if they intend to act rationally in the long term, however do not do so due to self-control problems (e.g giving into short term interests)
How can biases prevent individuals acting rationally?

How can fairness affect decision making?

What is choice architecture?
Where an individual’s choice is influenced by adapting the way the choice is presented.