LECOM MMS Immunology 2B Antibody and Antigens
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
What is an Antigen?
It is a substance that elicits an immune response
What are Antigens recognized by?
B cell receptor (BCR) and T cell receptor (TCR)
What is an Epitope (antigenic determinant)
It is the portion of an antigen that the B or T cell receptor recognizes
What is special about the BCR and the TCR?
They can recognize different epitopes on the same antigen
What are Linear epitopoes?
Several amino acids (aa) in a sequence
What are Discontinuous epitopes?
Two or more parts of the antigen separated by at lest 1 aa
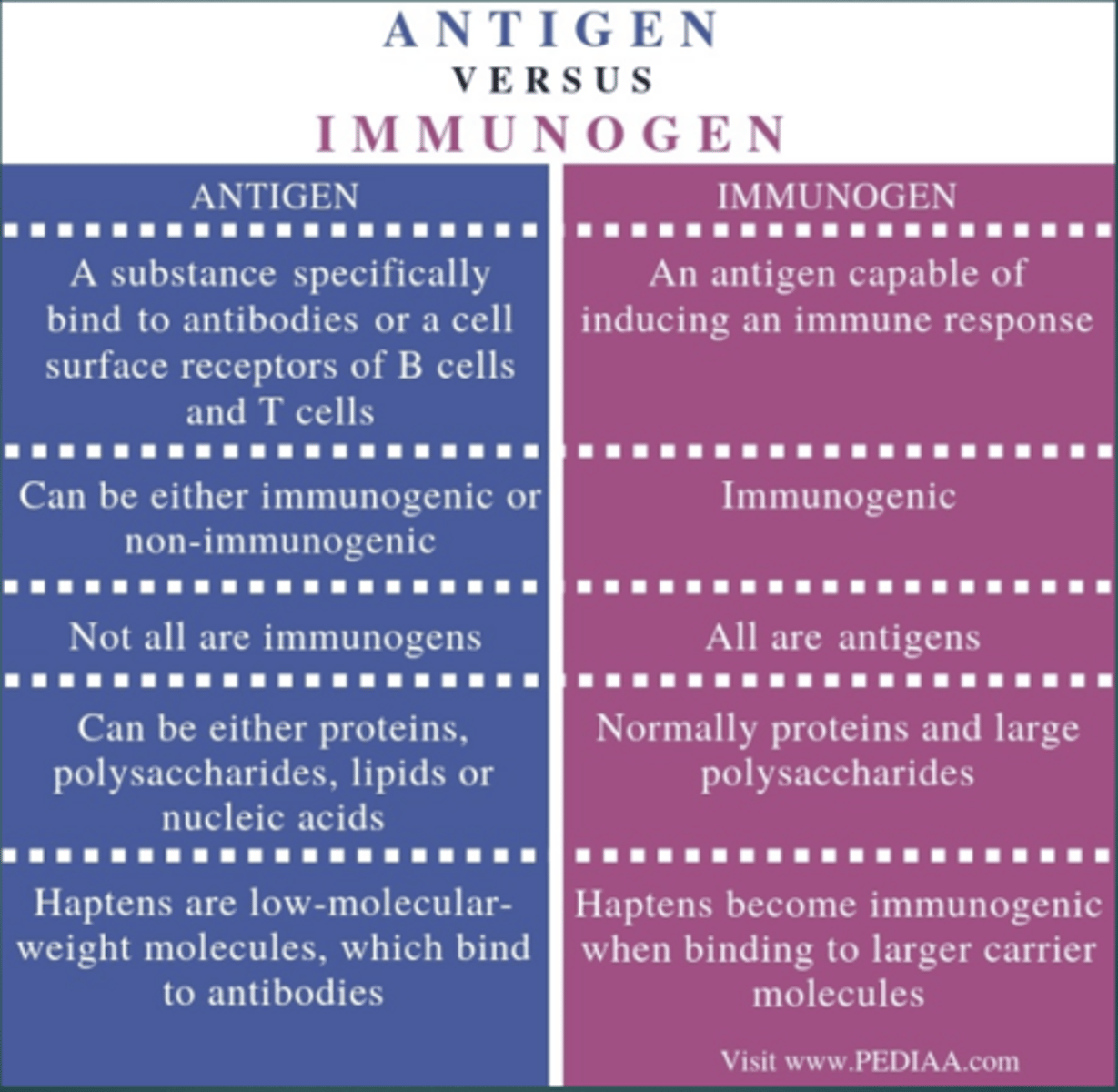
What is an Immunogen?
Antigen that can induce an immune response
Are all immunogens antigens?
Yes
Are all antigens immunogens?
No
What Factors influence Immunogenicity?
- Foreignness
* Recognized as non-self
- Molecular size
* Larger the better. Best > 100,000 Daltons
- Complexity
* Increase complexity = better immunogen
Antigen bvs. Immunogen Chart
What are Antibodies also known as?
Immunoglobulin/gamma globulin
What are Antibodies a part of?
Humoral immune system
What will Antibodies focus on?
Extracellular pathogens
- Intracellular agents
- Toxins
What are Antibodies membrane bound by?
B Cells (BCR)
What are Antibodies secreted by?
Plasma Cells
What does a Resting B cell encounter?
An antigen
What happens after a Resting B cell encounters an antigen?
The stimulated B cell gives rise to antibody-secreting plasma cells
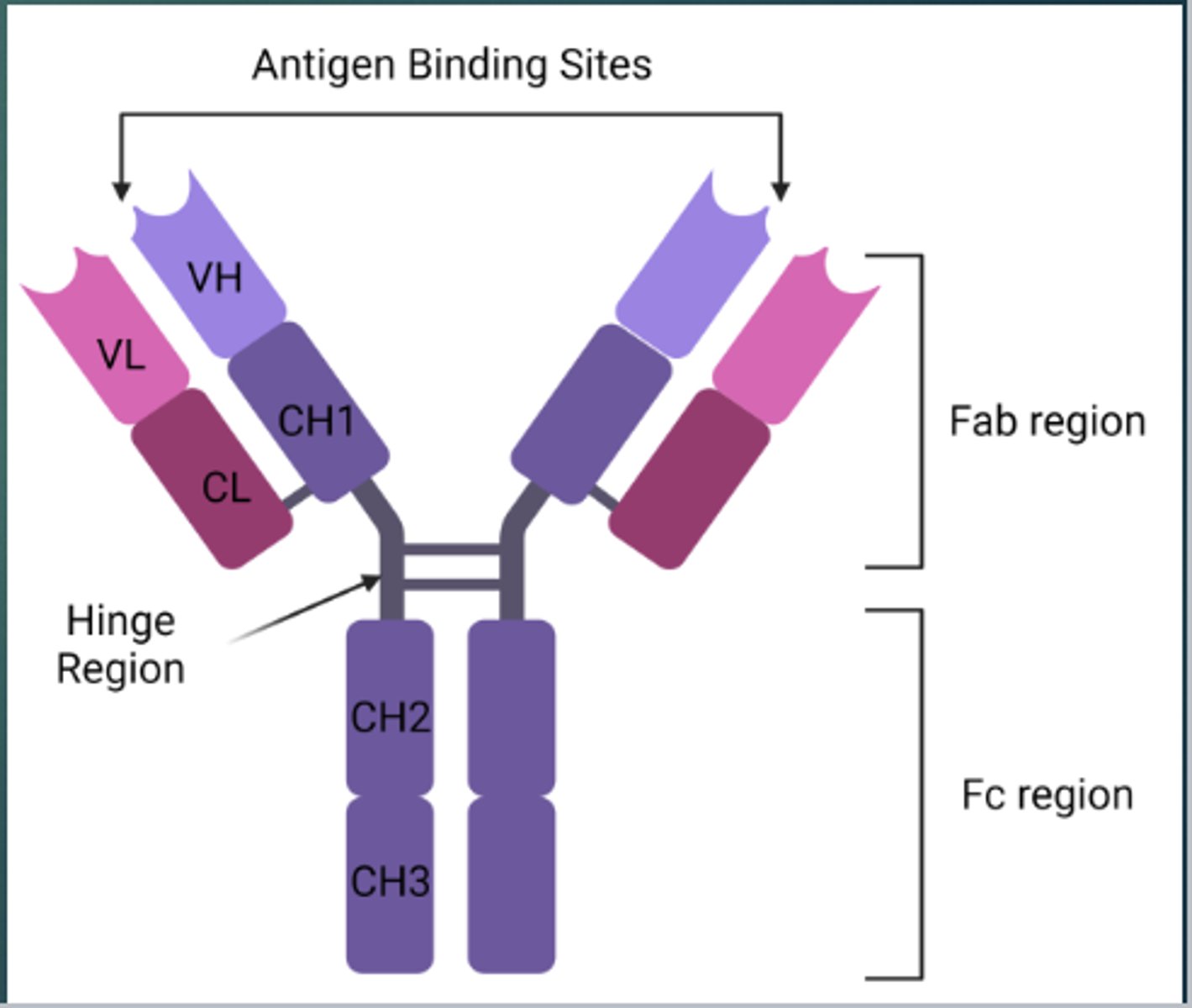
What is the Basic Structure of Antibodies?
2 identical heavy chains (HC) and 2 identical light chains (LC)
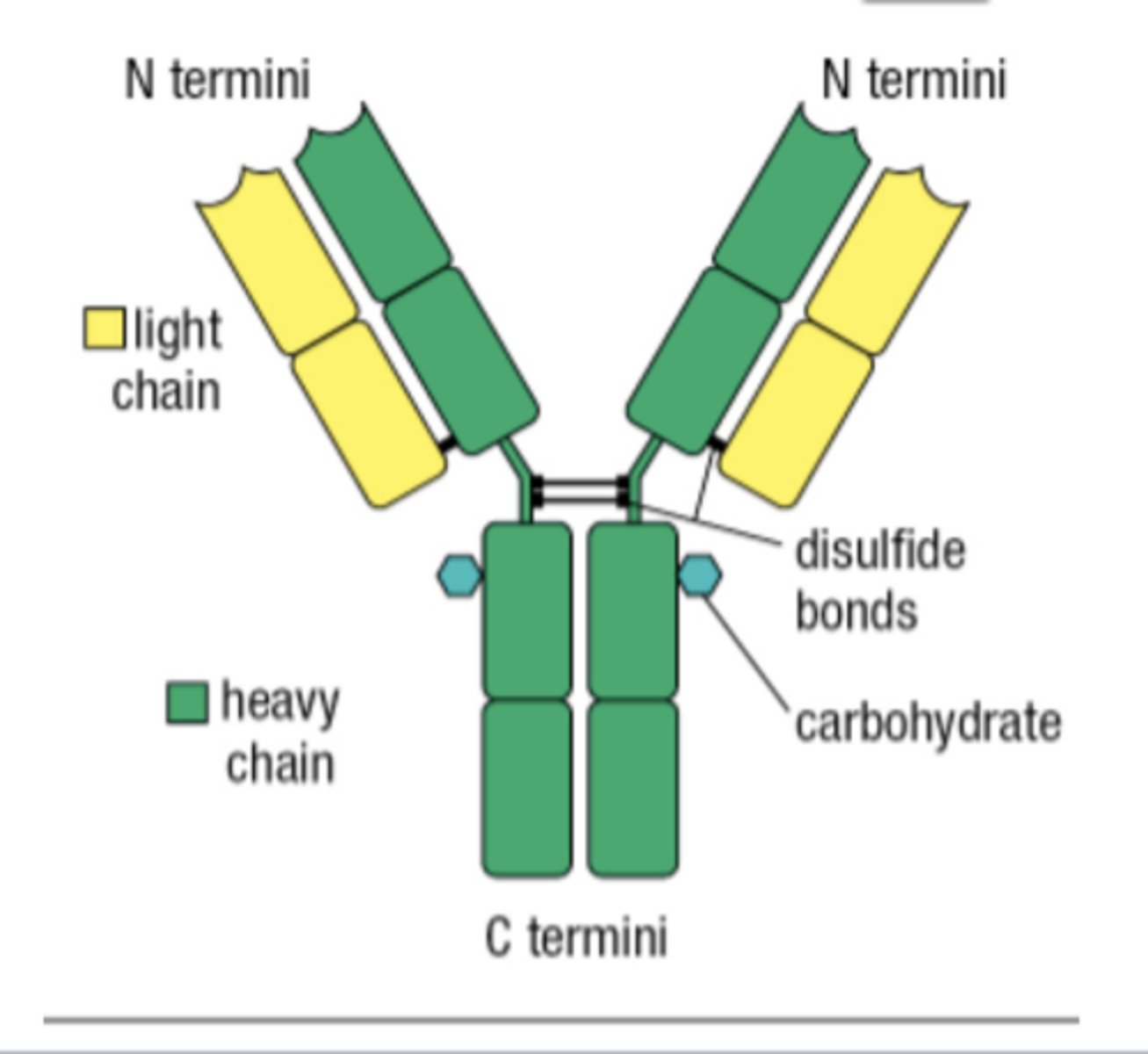
What are Antibody chains held together by?
Non-covalent bonds and Disulfide bonds
What type of regions do Antibodies consist of?
A variable region and a constant region
What is the Variable region of an Antibody made up of?
One heavy chain and one light chain
What does the Variable region of an Antibody create?
The antigen binding region
What is the Constant region of an Antibody?
It is the portion that varies between antibody classes (isotypes)
e.g. IgM, IgG, IgA, IgE, and IgD
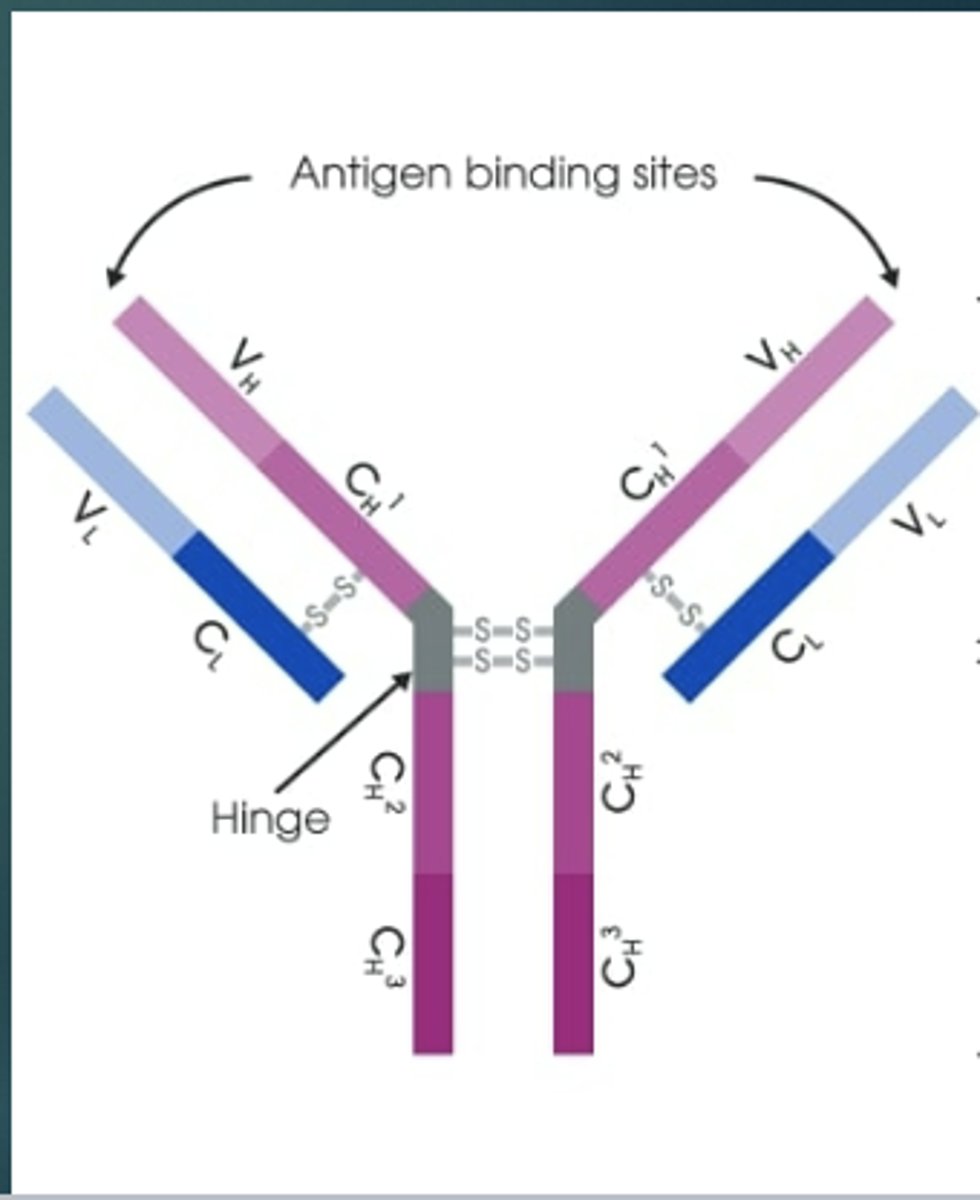
What are Antibody Light Chains made up of?
1 Variable domain and 1 Constant domain
What does each antibody have?
- Each antibody has 2 identical Light Chains
- Each antibody has 2 identical Heavy Chains
What are Antibody Heavy Chains made up of?
1 Variable domain and 3-4 Constant domains
What does the Constant region in Antibody Heavy Chains consist of?
5 sequences
- IgG is gamma (γ)
- IgM is mu (μ)
- IgA is alpha (α)
- IgE is epsilon (ε)
- IgD is delta (δ)
What is the Fab fragment?
It is the location of the antigen binding site
- Fragment, antigen-binding region
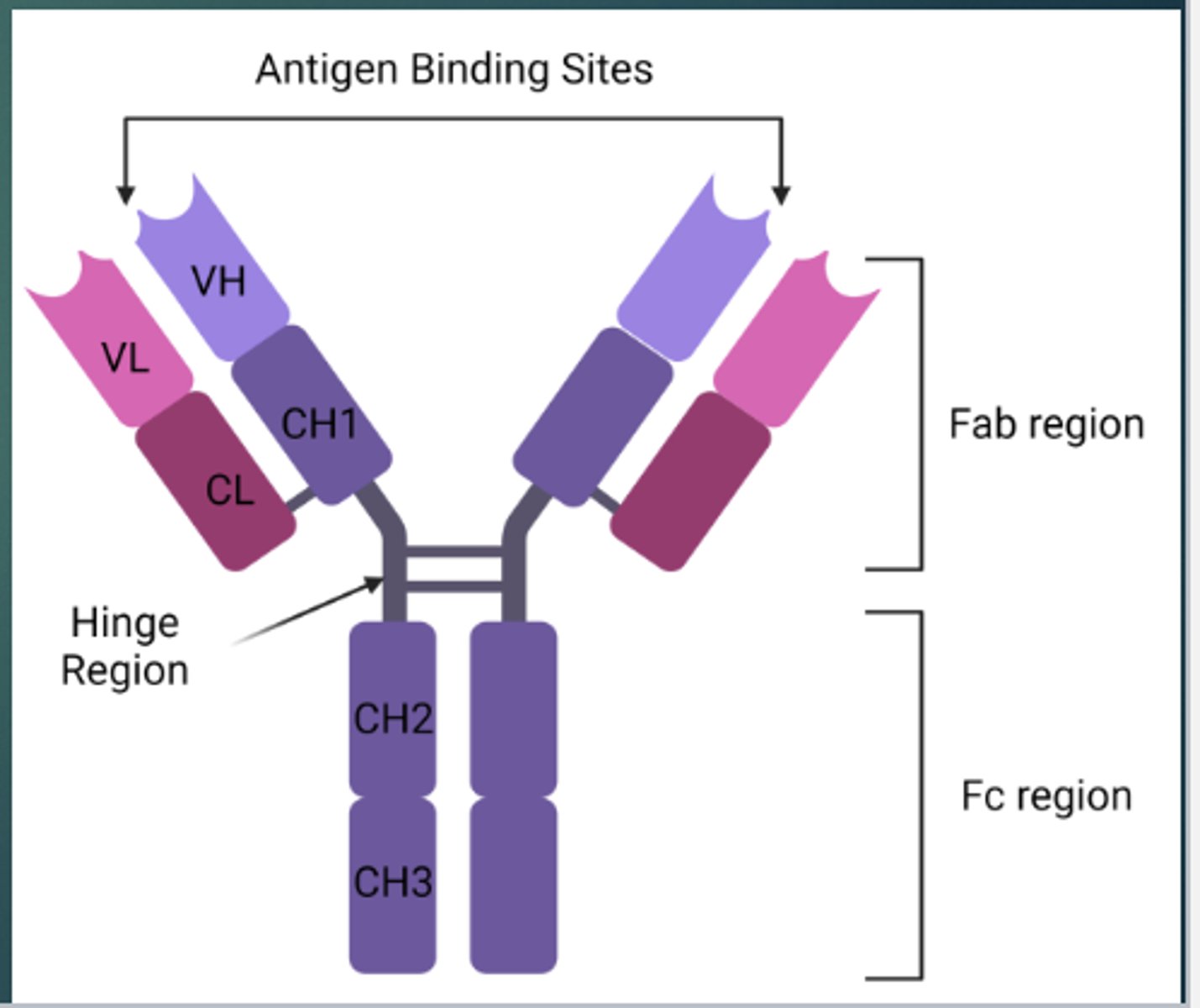
What does the Fab fragment include?
It includes the variable heavy and light regions
Where are the antigen binding sites located on an antibody?
On the Fab region
What is the Fc region?
It is the location of the Constant heavy regions
- Fragment, crystalline region
Where do Fc receptors bind?
The Fc region
What is the Hinge region?
It allows the two antigen binding sites to move
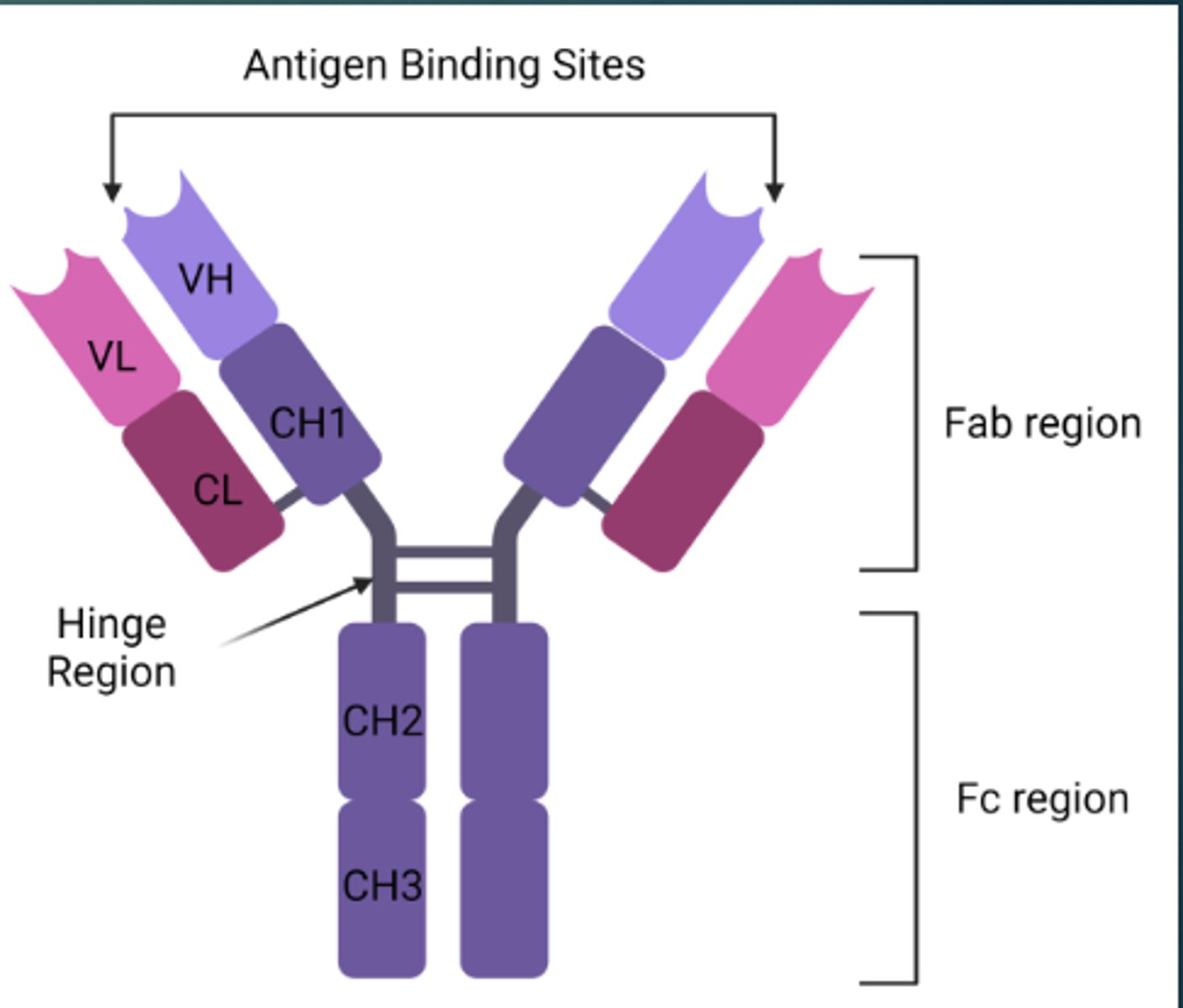
During a helminth infection, a B cell is signaled to isotype switch from IgM to IgE. Which of the following structures is changed during this process?
E
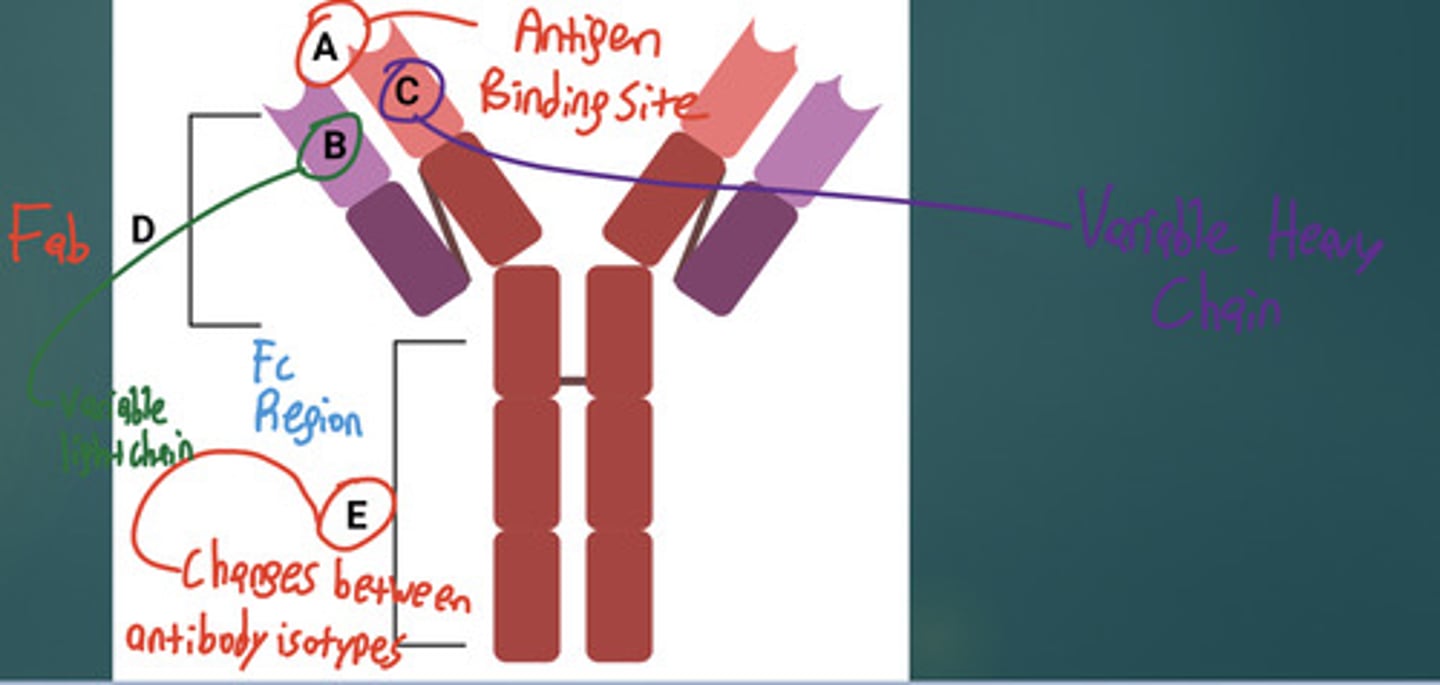
A patient suffering from a Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection produces and antibody that interacts with a bacterial antigen. Which of the following regions of an antibody directly interacts with the antigen?
A. Fab region
B. Fc region
C. Hinge region
D. Heavy chain
E. Light chain
A. Fab region
A patient suffering from a Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection produces and antibody that interacts with a bacterial antigen. Which region of an
antibody does a phagocyte recognize?
A. Fab region
B. Fc region
C. Hinge region
D. Heavy chain
E. Light chain
B. Fc region
What do phagocytes contain?
Phagocytes (like macrophages and neutrophils) have Fc receptors on their surface.
A new bacteria strain can create and release a protease that can cleave antibodies. If this protease cleaves antibodies at the hinge region, which of the following would be generated?
A. 2 Fab fragments and 1 Fc fragment
B. 2 Fab fragments and 2 Fc fragments
C. 1 Fab fragment and 1 Fc fragment
D. 1 Fab fragment and 2 Fc fragments
E. 1 Fab fragment and 3-4 Fc fragments
A. 2 Fab fragments and 1 Fc fragment
Good luck to whoever is reading this!!!
You got this!!!