5: IMMUNITY: cytokines and inflammation
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
Cytokines?
Protein molecules secreted by cells of the immune system
Bind to receptors onto target cell
How are cytokines produced?
More than 1 type of cell and in different tissues
Effects of cytokines upon target cells?
Cell proliferation
Cell differentiation
Haematopoiesis
Give example cytokine xe
interleukin 1
interleukin 6
TNF alpha
Describe effects of interferon on target cell
Cells activate factors that interfere with viral replication
Cells produce Rnase enzymes
Cells downregulate protein translation
Cells upregulate pro apoptotic proteins
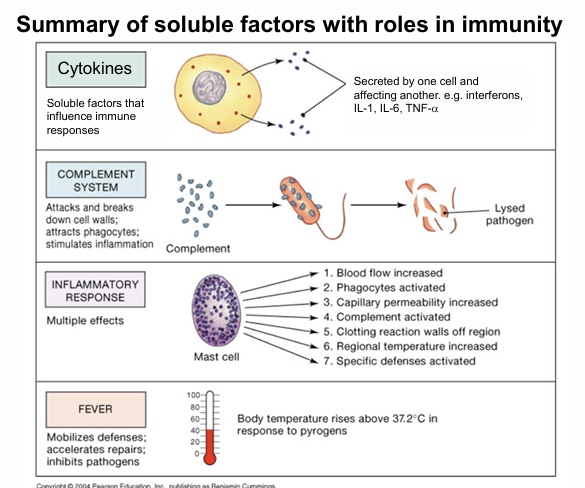
Give 3 triggers of inflammation
infections
trauma
foreign bodies
physical and chemical agents
Function cytokines released during inflammation
increase white blood cells numbers
vasodilation
increase capillary permeability
Name 2 cells that cause inflammation
mast cells
macrophages
mast cells?
respond to tissue damage and release histamine
macrophages?
produce cytokines in response to pathogens
give 3 benefits inflammation
isolation damaged area
mobilisation effector cells
healing
give 2 disadvantages of inflammation
allergy
autoimmunity
Extravasation?
During inflammation, endothelial cells act as a gate-keeper by increasing adhesion molecules that let white blood cells stick, cross the vessel wall, and enter tissue
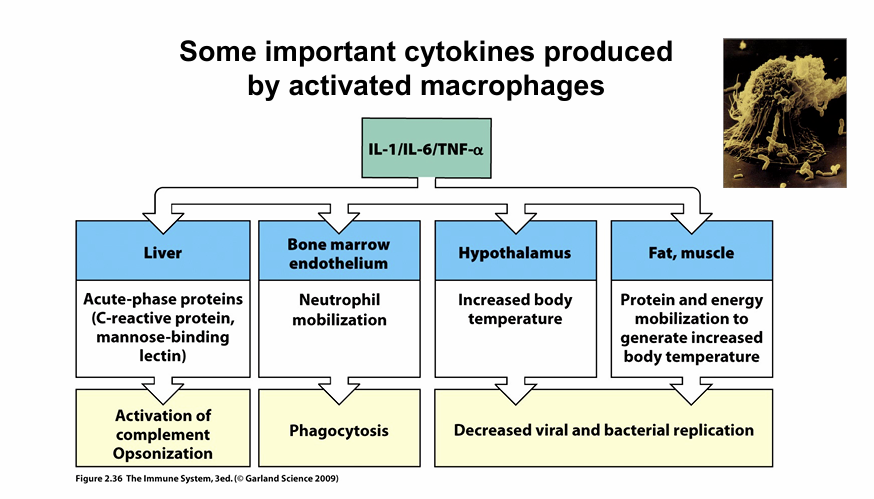
Describe the acute phase response (livers reaction to inflammation due to cytokinesis)
Local inflammation triggers macrophages to release IL-6.
IL-6 stimulates the liver to produce acute phase proteins (e.g., complement, C-reactive protein).
Positive acute phase reactants ↑ increase in level.
Negative acute phase reactants ↓ decrease in level.
Describe fever
Part of the acute phase response
White blood cells (e.g., macrophages) release pyrogens: IL-1, TNF-α, IL-6
Pyrogens act on the hypothalamus
Hypothalamus increases body temperature