A Level Edexcel Biology B Topic 9
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
104 Terms
Why must temperature and pH be regulated?
For optimum enzyme activity
Why must water potential be regulated?
To avoid negative osmotic effects which could damage a cell e.g lysis, shrinkage and disruption of metabolic reactions
What does negative feedback do?
Ensures that any departure from an ideal state results in a return to the ideal state
Counteracts changes in internal conditions to maintain dynamic equilibrium
What is the process of negative feedback?
1. Change occurs in internal environment
2. Change is detected by receptors
3. Receptors lead to activation of a mechanism that reverses the change
4. Conditions return to ideal and the mechanism is switched off
What is the process of positive feedback?
1. Change occurs in the internal environment
2. This change is detected by receptors
3. Receptors lead to activation of a mechanism that continues the change
What does positive feedback do?
Causes a departure from a starting condition to lead to further departure
What are the two main modes of action in hormones?
Hormones attach to receptor sites and trigger the release of a second messenger by a series of membrane bound reactions. The second messenger activates enzymes in the cell e.g. adrenaline
Hormones e.g. oestrogen pass through the cell membrane and binds to a receptor inside the cell. They form a hormone-receptor complex which passes into the nucleus and acts as a transcription factor to regulate gene expression.
What do endocrine glands do?
Secrete hormones directly into blood which signal proteins
What are cytokines?
Chemical messengers released by cells in the immune system that stimulate other cells in the immune system
What are neurotransmitters?
Chemicals released at the ends of neurones that stimulate their target cells
What are target cells?
Cells with receptor proteins on their cell surface membrane complimentary to the chemical
What are meristems?
Regions of actively dividing cells e.g. roots and shoots
What do cytokinins do?
promote cell division of stem and promote growth of lateral buds
How do auxins cause cell elongation?
Causes cell elongation by active transport of hydrogen ions into the cell walls, which lowers pH, making the cell walls flexible. Cells stretch to accommodate more water which leads to growth of the cell.
What is Apical Dominance?
The balance between auxins and cytokinins
Auxin inhibits cytokinins effect on lateral growth. As the shoot grows up, the concentration of auxin decreases lower and lateral buds form
What do auxins do?
Promote cell elongation
Promote growth of root laterally
Suppresses growth of lateral buds
What do gibberellins do?
Promote cell elongation when auxins are present
Reinforces the effect of auxins in apical dominance
Stimulates germination, growth of fruit and flowering
How do gibberellins stimulate seed germination?
1. Seed absorbs water and embryo is activated
2. The embryo secretes gibberellins which diffuse to the aleurone layer
3. The aleurone layer produces amylase
4. Amylase diffuses to the endosperm layer and breaks down to glucose
What happens when cytokinins work synergistically with ethene?
Promotes leaves falling off
What is a phytochrome?
Plant pigment that exists in two forms
What is Pr?
Absorbs red light (sunlight), the biologically inactive form
What is Pfr?
Absorbs far red light, the biologically active form
What happens when a phytochrome absorb red light?
It converts to Pfr
What happens when a phytochrome absorbs far red light?
It converts to Pr
What does Pfr do?
It is transported from the cytoplasm into the nucleus of the plant cells where it activates transcription factors that stimulate the transcription of genes affecting photomorphogenesis
Whats photomorphogenesis?
Effect of light of the growth of plants
What does Pfr do to long- day plants?
Stimulates flowering when there are short nights
What does Pfr do to short-day plants?
Inhibits flowering when nights are long
What is etiolation?
When plants are grown in the dark and become tall, thin, fragile, small and yellow leaved and short rooted
What happens if a plant is exposed to red light followed by far red light?
The plant is only effected by the last light exposed to it
What is the central nervous system?
The brain and spinal cord
What is the peripheral nervous system?
Automatic:
Sympathetic-ganglia close to CNS that coordinates flight or fight response
Parasympathetic-ganglia far from the CNS that coordinates the rest and digest response
Voluntary: Under conscious control/ somatic
How do the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems work together?
Antagonistically
What is the order of a reflex?
Receptor
Sensory neurone
Relay neurone
Motor neurone
Effector
What is in white matter?
Myelinated axons of motor neurones leaving the white matter and sensory neurones entering the white matter
Sensory neurones enter via a branch from a spinal nerve called the dorsal root at the back of the chord
Motor neurones leave by a spinal nerve at the front of the chord- the ventral root
What is in grey matter?
Un-myelinated neurones
Links sensory and motor neurones in reflex arcs
Runs up and down the spinal cord
What does the hypothalamus do?
temperature regulation and osmoregulation
Where is the pituitary gland?
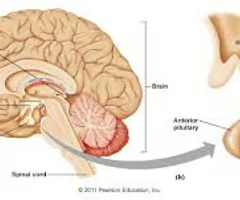
Where is the hypothalamus?
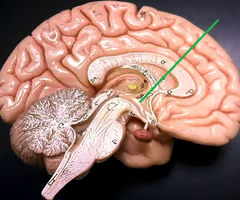
Where is the cerebrum?
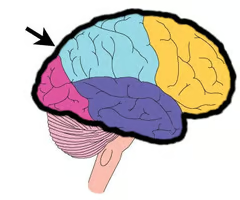
Where is the medulla oblongata?
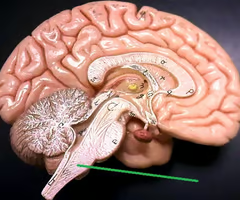
Where is the cerebellum?
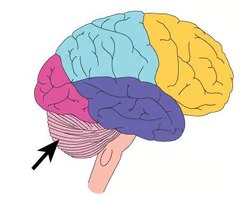
What does the cerebrum do?
Initiates movement
What does the cerebellum do?
Controls balance and coordination of movement
What does the medulla oblongata do?
Controls breathing and heart rate
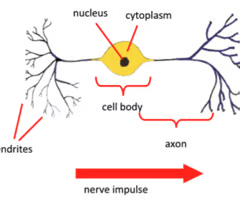
What's in the cell body of a neurone?
Nucleus and cell organelles
What are dendrons?
at the end of axons and stimulated by neurotransmitters released by an adjacent neurone
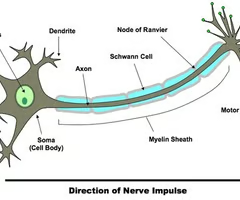
What is an axon?
Long extension from cell body that transmits impulses
What is a myelin sheath?
Insulates axon, restricting movement of a charge jumping as it is impermeable
What are Schwann cells and Nodes of Ranvier?
cells wrapped around axons and the gaps between them
What do synaptic bulbs do?
release neurotransmitter onto cell
What does a motor neurone look like?
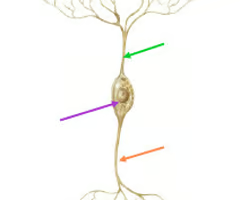
What does a sensory neurone look like?
What does a relay neurone look like?
What speeds up the speed of transmission in a neurone?
Myelination-prevents electrical impulses jumping
Thicker diameter of nerve fibre
Saltatory conduction
What is saltatory conduction?
Rapid conduction of action potentials in myelinated axons as they jump between nodes of Ranvier as they are impermeable to myelin sheath
What is a resting potential?
When an axon is polarised when it is not transmitting an impulse
There is a difference in charge between cytoplasm and external medium
The membrane potential is -70mV
How is a resting potential maintained?
1. Na+ is actively transported out of the neurone
2. K+ is transported into the neurone
3. For every 3 Na+ ions pumped out, 2 K+ ions are pumped in (by a sodium-potassium pump) so cytoplasm is more negative
4. K+ also diffuses out of the cell by facilitated diffusion through open K+ channels
5. Na+ diffuses into the cell through open Na+ channels
What is an action potential?
When a receptor or neurone secretes neurotransmitter across an excretory synapse it causes the membrane potential of the receiving cell to change momentarily to about +40mV
What are the steps of depolarisation and repolarisation?
1. All the voltage-gated Na+ channels and voltage-gated K+ channels are closed
2. Some voltage-gated Na+ channels open allowing Na+ ions to diffuse into the axon. This makes the membrane potential less negative
3. The membrane potential reaches -55mV which is the threshold level and more voltage-gated Na+ channels open and Na+ ions rapidly diffuse into the axon
4. The membrane potential reaches +40mV and two events are stimulated:
-voltage-gated Na+ channels close
-voltage-gated K+ channels open to let K+ ions diffuse out of the axon and resting potential is restored
5. Often too many K+ ions diffuse out causing hyperpolarisation of about -80mV
What does an action potential graph look like?
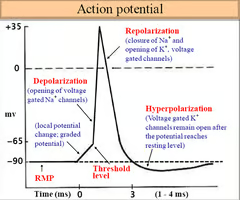
What is the refractory period of an action potential?
The period of time after an action potential where another action potential can't take place
What is the absolute refractory period?
Periods of depolarisation and repolarisation
What is relative refractory period?
Period of hyperpolarisation and time when resting potential is restored
What is a synapse?
Junction between two neurones
What is in the synaptic knob?
Surface membrane with gated Ca2+ channels
Cytoplasm with many mitochondria
Vesicles containing a neurotransmitter
e.g. acetylcholine or noradrenaline
What is the synaptic cleft?
The gap between two cells
What does the dendrite on the post-synaptic neurone have?
A cell surface membrane with neurotransmitter receptors that act as gated Na+ and K+ channels
What does an excitory synapse do?
Stimulates an impulse in the post-synaptic cell
What does the inhibitory synapse do?
Inhibits an impulse in the post-synaptic cell
What happens at an excitory synapse?
1. Action potential arrives at the pre-synaptic membrane
2. The pre-synaptic membrane depolarises so the Ca2+ channels open and Ca2+ rapidly diffuses from the synaptic cleft into the pre-synaptic neurone
3. Entry of Ca2+ ions cause vesicles to fuse with the pre-synaptic membrane and release a neurotransmitter into the synaptic cleft
4. The neurotransmitter diffuses across the synaptic cleft and fuses with receptors in the post-synaptic membrane
5. Gated Na+ channels open in the membrane and Na+ rapidly diffuse into the post-synaptic cell
6. The cytoplasm of the post-synaptic cell becomes more positively charged and the action potential continues
What happens at an inhibitory synapse?
1. Action potential arrives at the pre-synaptic membrane
2. The pre-synaptic membrane depolarises so the Ca2+ channels open and Ca2+ rapidly diffuses from the synaptic cleft into the pre-synaptic neurone
3. Entry of Ca2+ ions cause vesicles to fuse with the pre-synaptic membrane and release a neurotransmitter into the synaptic cleft
4. The neurotransmitter diffuses across the synaptic cleft and fuses with receptors in the post-synaptic membrane
5. Gated K+ channels and gated Cl- channels open in the membrane letting K+ and Cl- to rapidly diffuse into the post-synaptic cell
6. The cytoplasm of the post-synaptic cell is more negatively charged, preventing an action potential
What is the effect of nicotine?
Mimics the effect of acetylcholine and triggers the release of dopamine
What is the effect of lidocaine?
Blocks voltage gated Na+ channels in post-synaptic membranes
Used as anaesthetic
What is the effect of cobra venom?
Blocks acetylcholine receptors in post-synaptic membranes
Deadly
What is the structure of the retina?
Outer segment-light sensitive and contains flattened membranous vesicles with photosensitive pigments
Constriction- a narrow region between segments
Inner segment- packed with mitochondria and ribosomes
Synaptic region
What is the difference between rod and cone cells?
Cone found at centre, rod found at periphery
Cone has iodopsin, rod has rhodopsin
Iodopsin degrades with high intensity light, rhodopsin degrades with any light
Cone sensitive to red, green or blue light, rod is insensitive to coloured light (only picks up black and white light)
What happens when Rhodopsin is stimulated by light?
1. The pigment within rods is degraded into opsin and retinal
2. Opsin stimulates a series of enzyme-catalysed reactions that cause the cell surface membrane of the rod cell to become hyperpolarised
3. Rod cells no longer release neurotransmitters
4. The cell surface membrane of the bipolar cell becomes depolarised and release neurotransmitters
5. The ganglion cell becomes depolarised and transmits an impulse to the optic nerve
6. Rhodopsin is resynthesised in the dark
What happens when Rhodopsin is not stimulated by light?
1. Cell surface membrane is depolarised
2. Rod cells release glutamate onto the bipolar cell
3. This has an inhibitory synapse so a neurotransmitter is not released to the ganglion cell
4. No impulses are sent from the ganglion cell to the optic nerve
What changes in the blood does the heart respond to?
CO2 concentration -detected by chemoreceptors in the aorta and carotid arteries
Blood pressure -detected by baroreceptors in aorta and carotid arteries
Where do receptors for heart rate send impulses to?
The medulla oblongata where the cardiac centre is located
What happens when blood pH decreases (high CO2)?
Impulses are passed down sympathetic nerves from the acceleratory centre of the cardiac centre to the SAN causes an increase in heart rate by releasing noradrenaline
How is heart rate decreased?
Impulses are passed down parasympathetic nerves and release acetylcholine at the SAN
What is the structure of the kidneys?
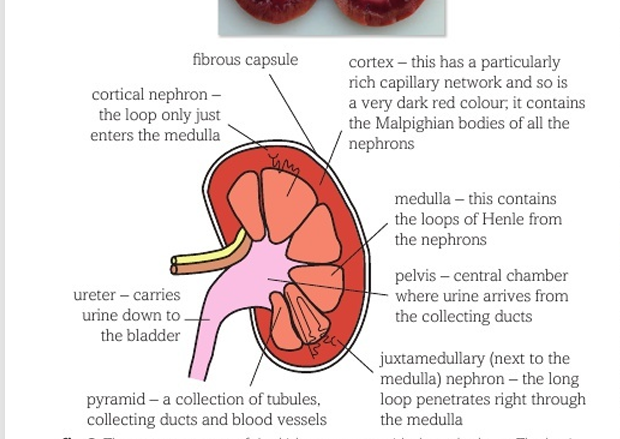
What is the structure of a nephron?
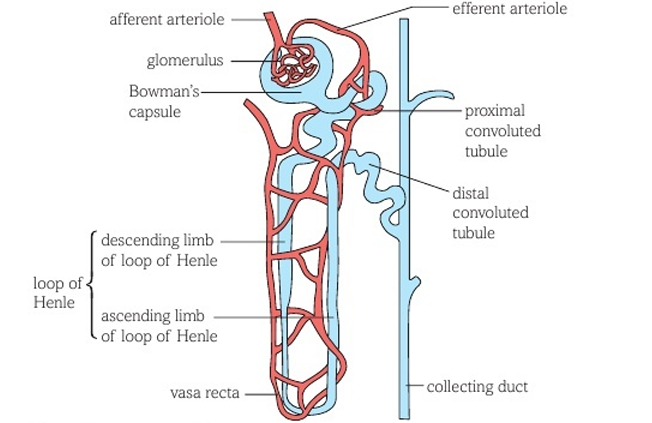
What happens at the Bowman's capsule and glomerulus?
Ultrafiltration
What happens in the proximal convoluted tubule?
Selective reabsorption of filtrate
What happens in the loop of Henle?
Water conservation
What happens in the distal convoluted tubule?
pH adjustment and ion reabsorption
What happens in the collecting duct?
Water reabsorption
What is ultrafiltration?
Water, ions and small molecules are forced out of capillaries of the glomerulus and into the Bowman's capsule
(in a similar process to tissue fluid being forced out of capillaries)
What happens in the first process of selective reabsorption?
Some water, all glucose and amino enzymes (co-transported with Na+ ions), ions and some urea is reabsorbed into the blood
How does the loop of Henle conserve water?
1. Cells in the upper part of each ascending limb actively secretes Na+ ions and Cl- ions from the ultra filtrate into the tissues of the medulla
2. Cells in the upper part of the descending limb, are permeable to these ions and diffuse in from the ascending limb
3. This greatly increases the concentration of Na+ and Cl- in the tissues of the medulla
4. This results in the tissues of the medulla having the negative water potential
5. Water passes from the collecting ducts into the medulla and into the vasa recta capillaries around the loop of Henle
6. The ultra filtrate is more concentrated than the blood and therefore urine is more concentrated
What happens in the second process of selective reabsorption?
Some ions and some water diffuse back into the blood
Controlled by hormones
What happens during water reabsorption?
ADH regulates water diffusing back into the blood
How is urea produced?
By deamination:
1. Hepatocytes (liver cells) deaminate excess amino acids
2. Amino acids are removed and converted into ammonia
3. This is further converted to urea which is less toxic
4. Urea is secreted by the kidneys
What is osmoregulation?
Maintenance of a constant osmotic pressure in tissues of a living organism by controlling water and salt concentrations
How does ADH effect the amount of urine produced?
(negative feedback mechanism)
1. When water is in short supply, the concentration of inorganic ions in the blood rises and the water potential becomes more negative
2. The change is detected by osmoreceptors in the hypothalamus and nerve impulses are sent to to the posterior pituitary which releases ADH
3. ADH binds to receptors in the kidney as triggers a series of membrane-bound reactions which lead to cAMP being produced.
4. cAMP is a second messenger that causes vesicles containing water channels to fuse with cell membranes making the DCT and collecting duct more permeable to water.
More ADH released causes urine to be concentrated.
No ADH released causes urine to be dilute.
What makes kangaroo rats special?
They never drink as they live in the desert. They do this by:
Staying cool in burrows
Generating water by oxidative reactions
Get water from their food
Producing very concentrated urine -have many juxtamedullary nephrons, long loops of Henle, high concentrations of ions in the medulla and more infoldings in cell membranes of epithelial cells lining tubules to increase diffusion
What is an ectotherm?
A cold-blooded animal that relies entirely on behavioural methods to gain or lose heat