Acid precipitation
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Pollutants involved in acid rain
- Sulfur dioxide
- Sulfur trioxide
- Ozone
- Hydrogen chloride
- Oxides of nitrogen
Sulfur dioxide dissolves in water to produce...
sulfurous acid
Sulfur dioxide may be oxidised in the atmosphere by gases, such as ozone to produce...
sulfur trioxide
Sulfur trioxide is dissolved to produce...
sulfuric acid, a much more powerful acid than sulfurous acid
Oxides of nitrogen dissolve to produce...
nitrous and nitric acids
What are primary and secondary pollutants?
Primary pollutants are directly emitted, secondary pollutants are primary pollutants that have reacted in air
Name the primary pollutants
• SOx : sulfurous and sulfuric acids
• NOx : nitric acid
Name the secondary pollutant
Ozone
Sources of Sulfur dioxide
• Smelting of sulphide ores.
Sources of oxides of nitrogen
High temperature combustion, mainly in power stations and car engines
Sources of ozone
A secondary pollutant produced by photochemical reactions involving oxides of nitrogen
Sources of hydrogen chloride
The combustion of coal and incineration of wastes containing chlorine (like PVC)
Sources of sulfur trioxide
Oxidation of sulfur dioxide by ozone
Impacts of acid rain on metal
Acid deposition corrodes metals, causing damage to railway lines, metal railings, water pipes, and overhead powerlines
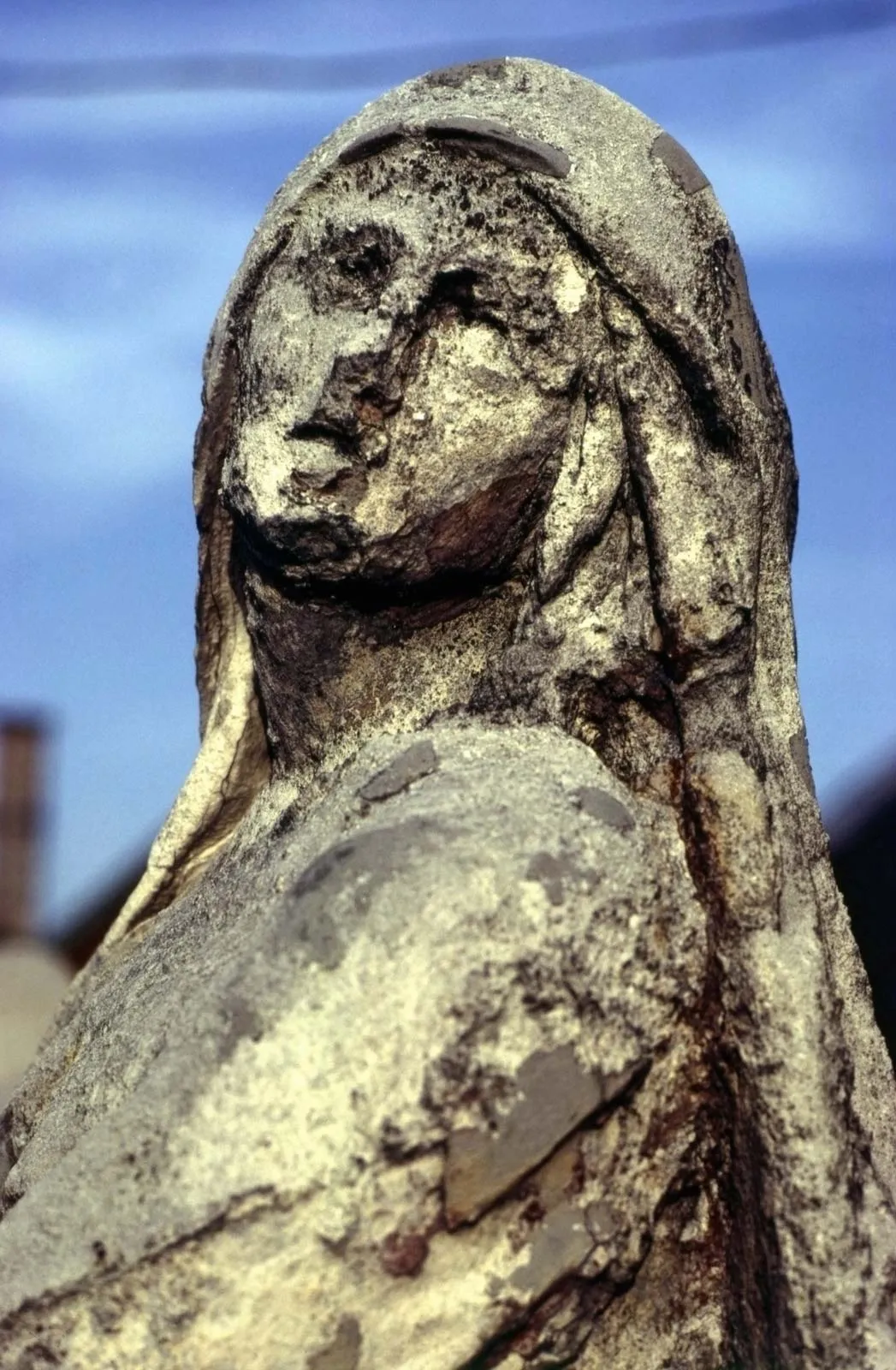
Impacts on limestone structures (like buildings and statues)
They are damaged as the acids dissolve the surface layers and weaken the stone structure of porous limestone

Impacts on cells
Low pHs denature proteins in cell membranes and can inhibit enzyme action
Tissues which have living cells exposed to the environment are most likely to be damaged by acid rain, like cells inside leaf stomata, plant root hairs, germinating seeds, fish eggs, fish gills
Impacts on exoskeletons
Invertebrates with exoskeletons may die as the acids dissolve the calcium compounds that form the skeleton

How can lichen be used to monitor acid rain?
They are very sensitive to acidic conditions and their size, state of health, abundance, and diversity, may be used in a biotic index to monitor acid rain pollution
Impacts on breathing
Sulfur dioxide can create breathing difficulties and increase the frequency of respiratory problems, like asthma attacks
What are the indirect impacts of acid rain on living organisms?
Many metal ions become more soluble at low pH.
The acidic solutions that percolate through soil can leach metal ions from the soil.
Now important plant nutrients like Mg2+ ions are lost
This leads to other toxic ions to be mobilised, like Al3+, when usually they are adsorbed onto the surface of clay particles to be immobilised.
What do the toxic metal ions do in plants?
They inhibit enzyme action in plant root hair cells and other soil organisms, such as detritivores and decomposers
What else do toxic metal ions do?
These mobilised ions can also be leached into rivers and lakes, where they can harm aquatic organisms
How can toxic metal ions affect human health?
Lead is a neurotoxin, and there is some evidence that aluminium ions may be a factor associated with some neurological disorders.
Controls of SOx
• Fuel (coal, crude oil) desulfurization
• Flue Gas Desulfurization (FGD)
• Dry FGD
• Wet FGD.
Fuel desulfurization
The removal of sulfur from the fuel before it is burnt

How is crude oil desulfurised?
Sulfur compounds are removed from crude oil during distillation, using molybdenum catalysts, in the process of hydrosylfurisation.
What form is sulfur present in coal?
Solid iron pyrites (FeS2)
How can FeS2 be removed?
By washing and streaming
Explain the washing and streaming process more.
The coal is crushed and put in a stream of flowing water, where the flow rate is fast enough to carry the coal away, but leaves behind the denser pyrites.
What are flue gases?
The exhaust gases containing SO₂
Flue Gas Desulfurization (FGD)
Processes to remove SO2 from the power station emissions released after fuel combustion
Wet FGD
These gases are passed through a tall tower (scrubber) where a liquid solution (sodium sulphite) is sprayed on to these gases.
This produces sodium hydrogen sulphite.
What can you do with calcium sulfate?
If the effluent gases have been cleaned to remove smoke particles, then the calcium sulfate produced may be pure enough to make gypsum building plaster
Dry FGD
Flue gases are passed through a bed of crushed calcium carbonate
Sulfur dioxide reacts with the calcium carbonate to produce solid calcium sulfur.
What happens with sodium hydrogen sulphite?
It is heated, which breaks down to produce sodium sulphite and water and concentrated pure sulfur dioxide.
Sodium sulphite and water are reused, and concentrated pure sulfur dioxide is a valuable raw industrial material, since it can be converted to solid sulfur or sulfuric acid.
Controls of NOx
• catalytic converters
• urea sprays
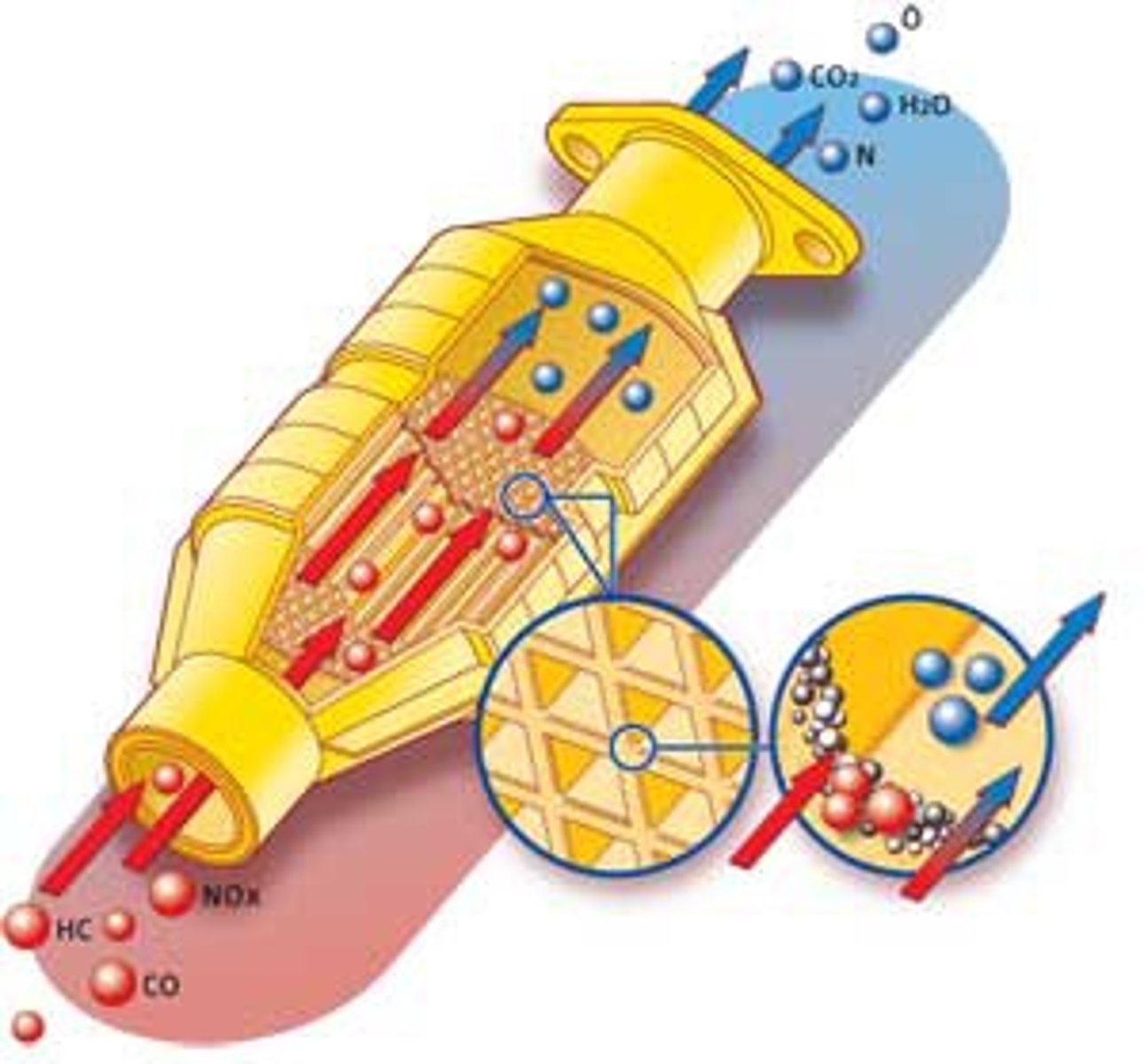
Catalytic converters
A chamber in the exhaust pipes containing a catalyst, such as platinum, which chemically reduces NOx back to nitrogen and oxygen gases.
Urea Sprays
NOx can be removed by reacting it with urea
Control of ozone
Control of NOx reduces ozone formation.