Chapter 6 Cranium Bones Flashcards
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
BIO 110 Chapter 6 Axial Skeleton (Skull) Flashcards
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms

Frontal Bone
-Forms the forehead and the roof of the orbits (eye sockets)
-Protects the anterior (front) of the brain
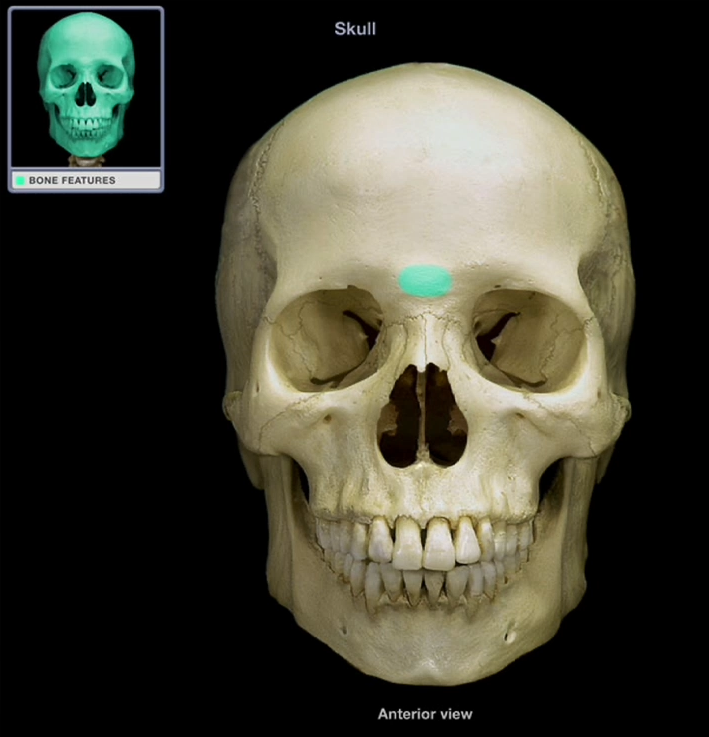
Glabella
-Smooth portion of the frontal bone between the superciliary arches (eyebrows)
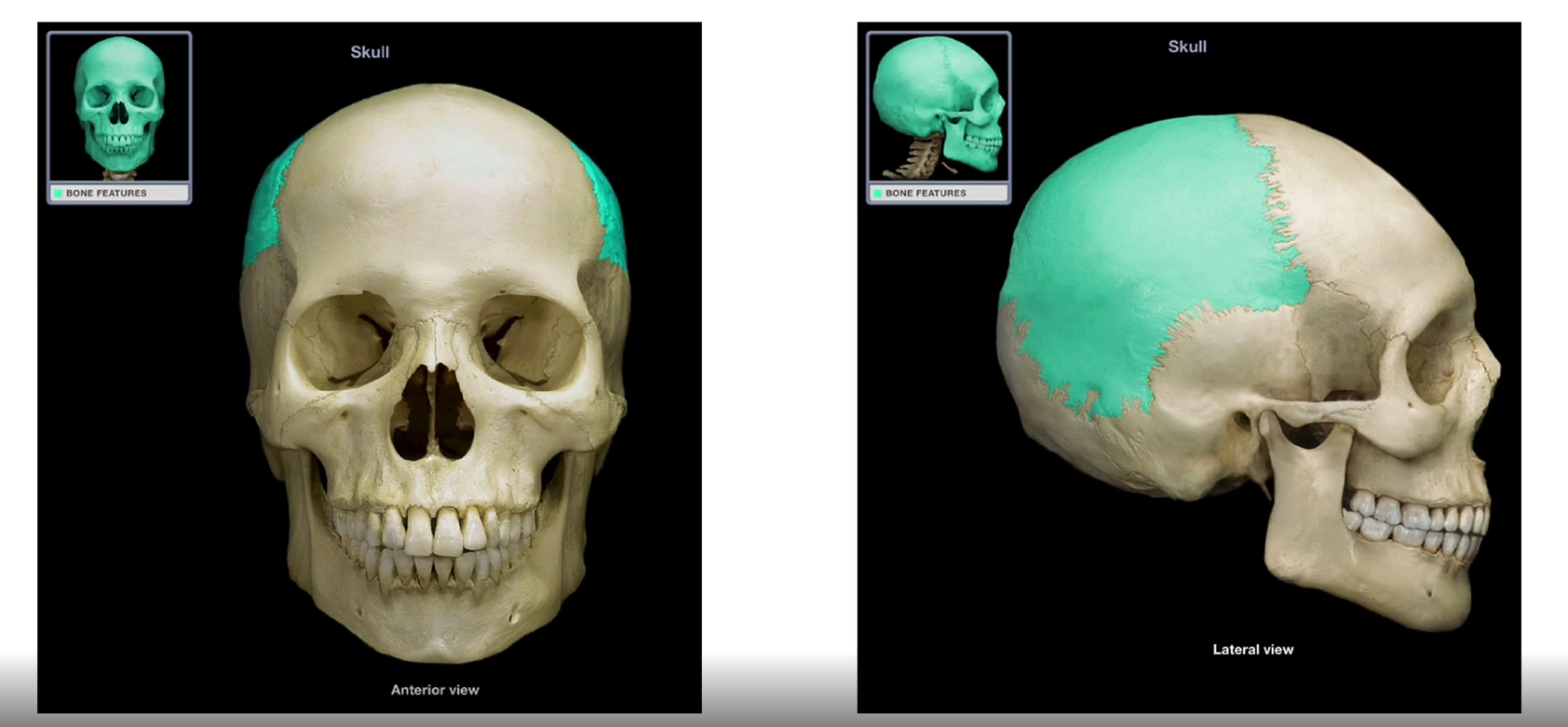
Parietal Bones
-Paired
-Right and left form the lateral walls and roof of the cranium
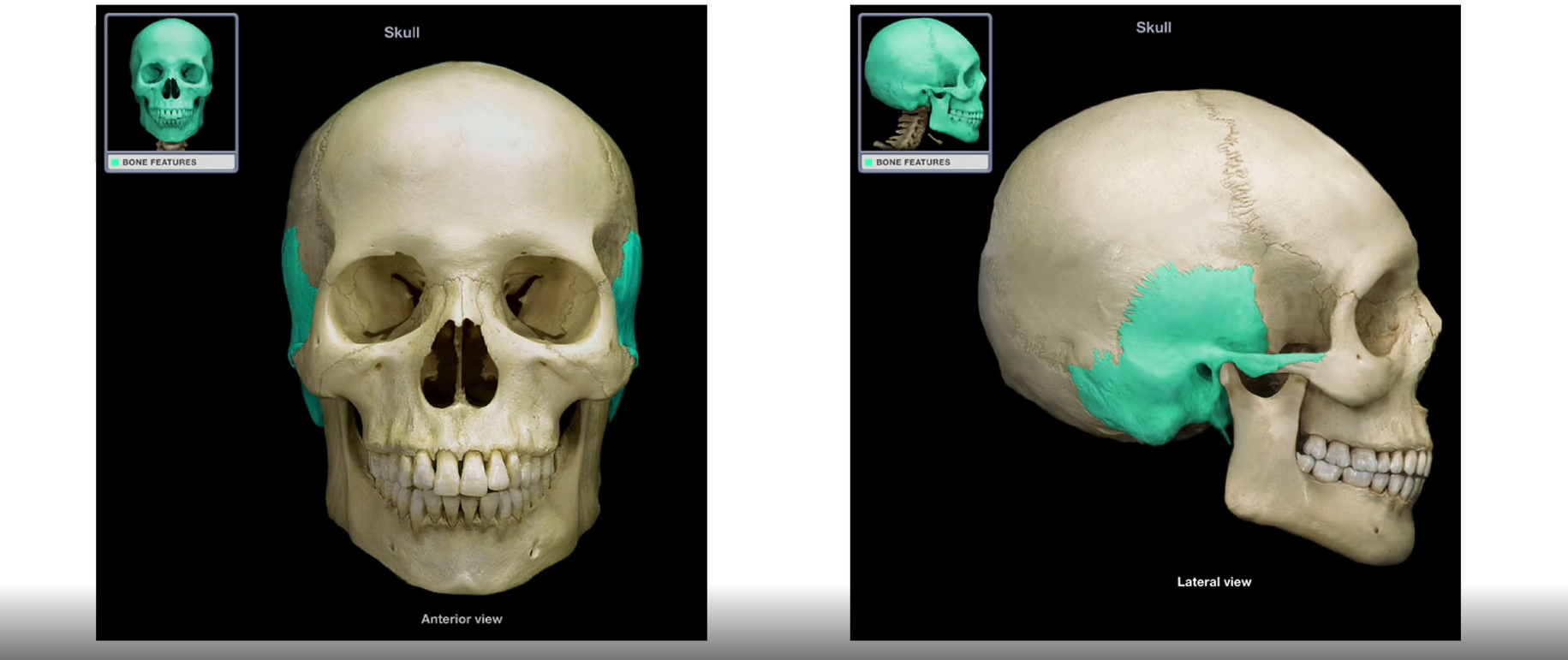
Temporal Bones
-Paired
-form the inferior lateral walls and part of the floor of the cranium
-irregular bone

Carotid Canal
-located within the temporal region
-medial to the styloid processes
-How the carotid artery reaches the brain
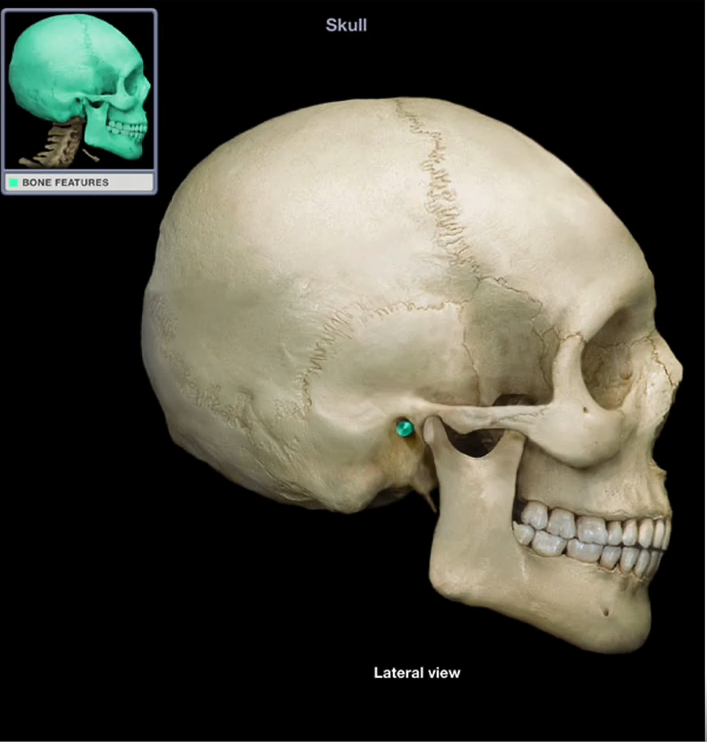
External Auditory Canal
-Also known as the external acoustic meatus
-Acts as a passageway between the outer and middle/inner ear
-How we transmit sound between outer and inner ear

Mandibular Fossa
-Depression where the mandible articulates with the temporal bone to form the temporomandibular joint (TMJ)
-helps to move the jaw
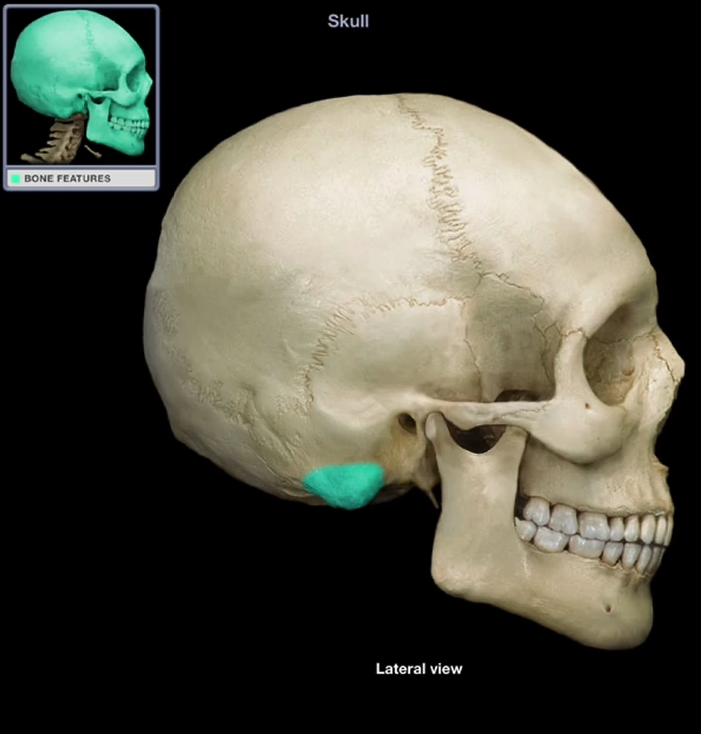
Mastoid Process
Prominent bulge on the inferior surface that acts as an anchoring site for muscles that move the neck
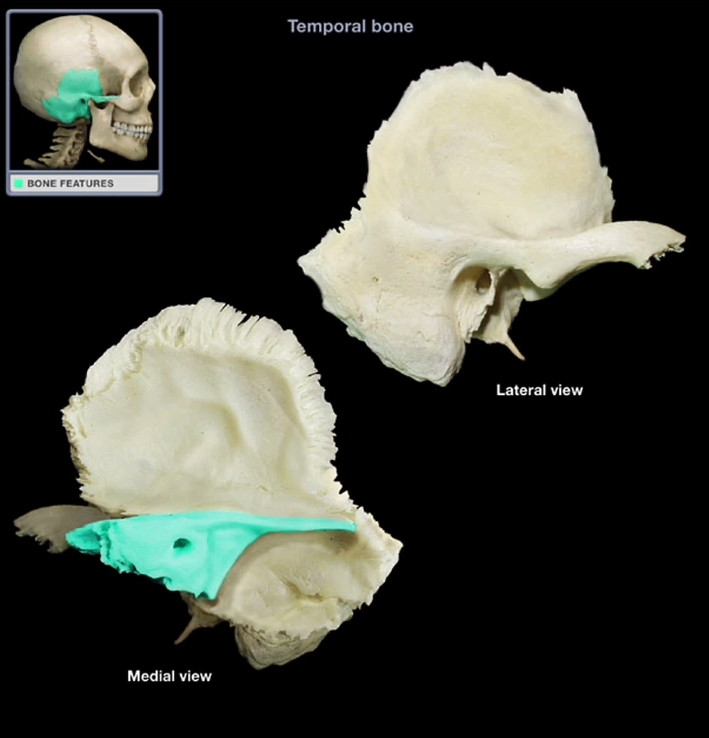
Petrous Region
-One of the strongest/thickest portions of the skull
-Lots of blood vessels and nerves
-Houses sensory structures of the inner ear that provide information about hearing and balance
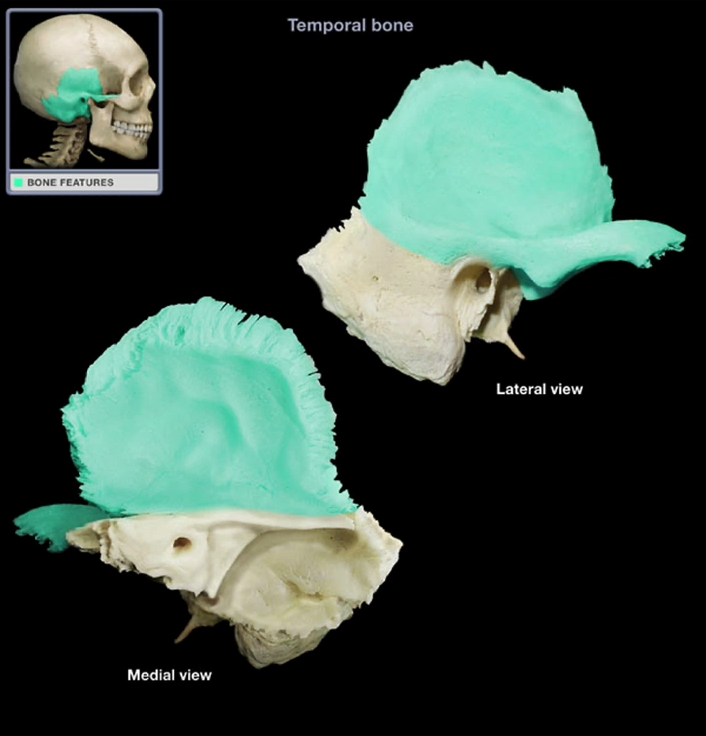
Squamous Region
-Lateral, flat surface of the temporal bone
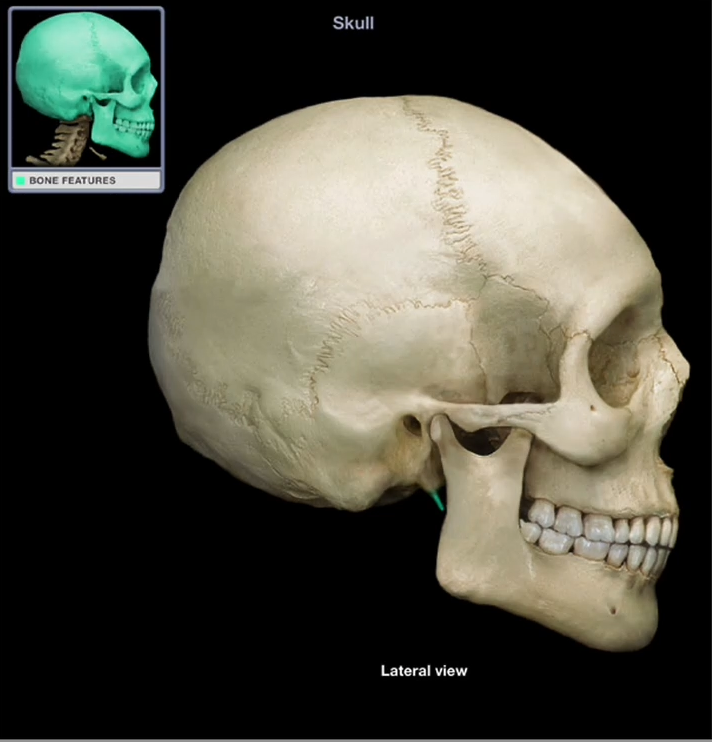
Styloid Process of the Temporal Bone
-Thin, pointed projection that serves as an attachment for several hyloid and tongue muscles
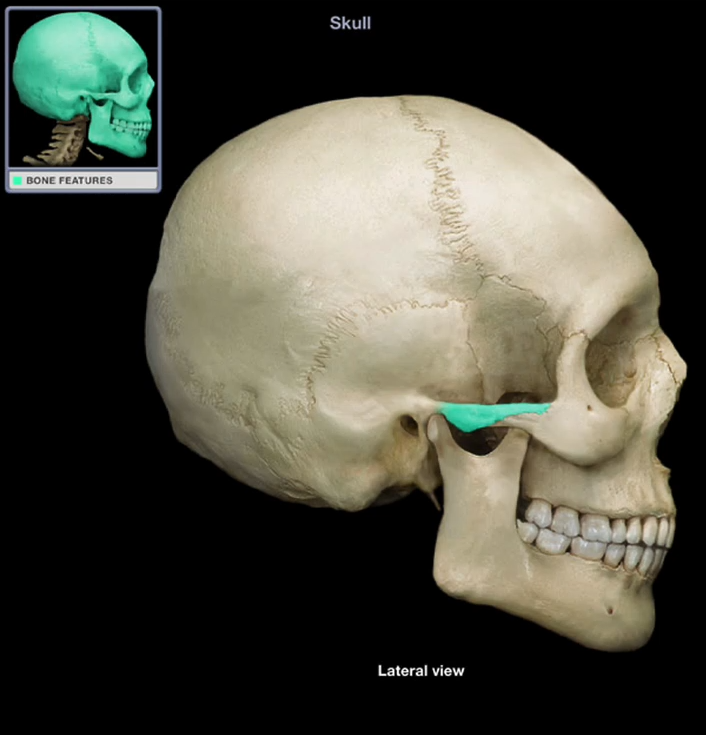
Zygomatic Process of the Temporal Bone
-Projection that curves laterally and anteriorly to articulate with the zygomatic bone to form the zygomatic arch
-forms arch for your cheekbones
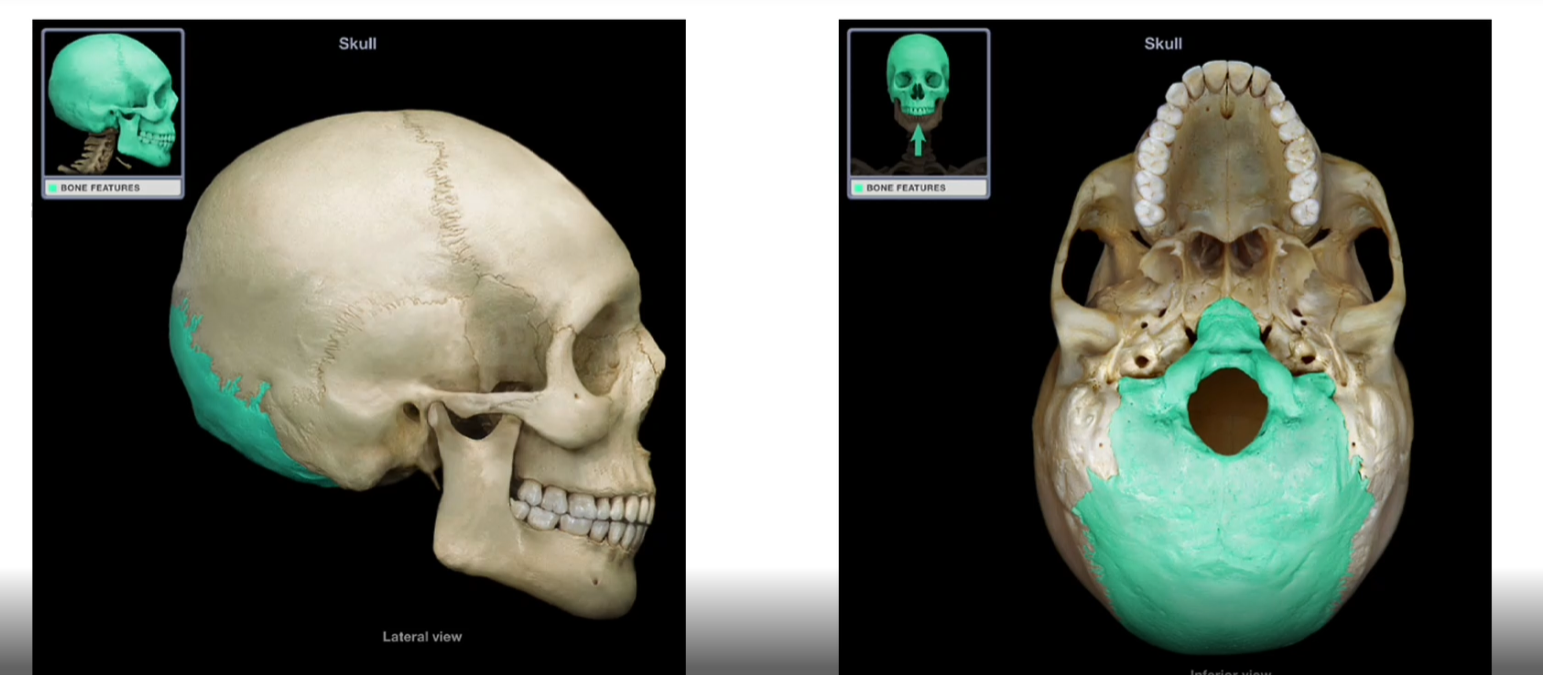
Occipital Bone
-Forms the inferior wall of the cranium
-where the brain sits
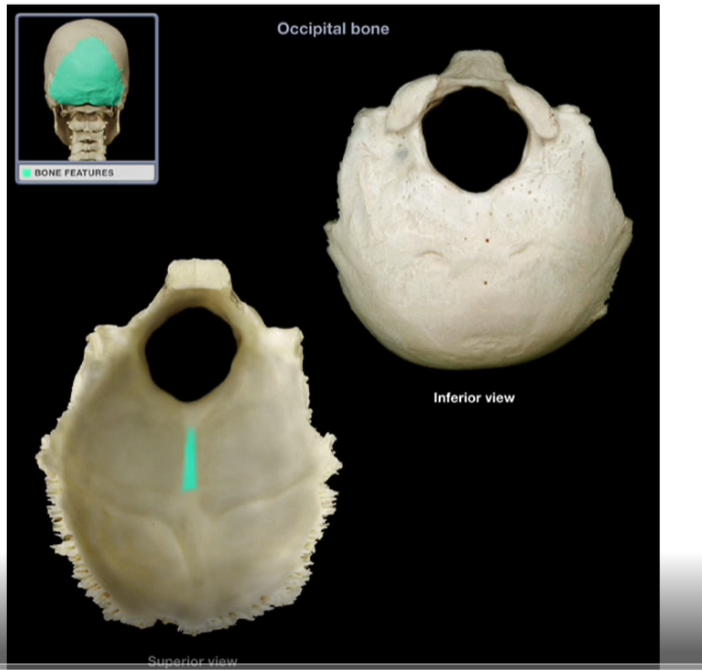
External Occipital Crest
-Prominent ridge that projects posteriorly from the foramen magnum

External Occipital Protuberance
-Projection that marks the end of the external occipital crest and acts as an attachment site for muscles that extend the head and neck
-”bump on the back of your head”

Foramen Magnum
-Large, circular opening that allows for the passage of the brainstem and spinal cord into the spinal column
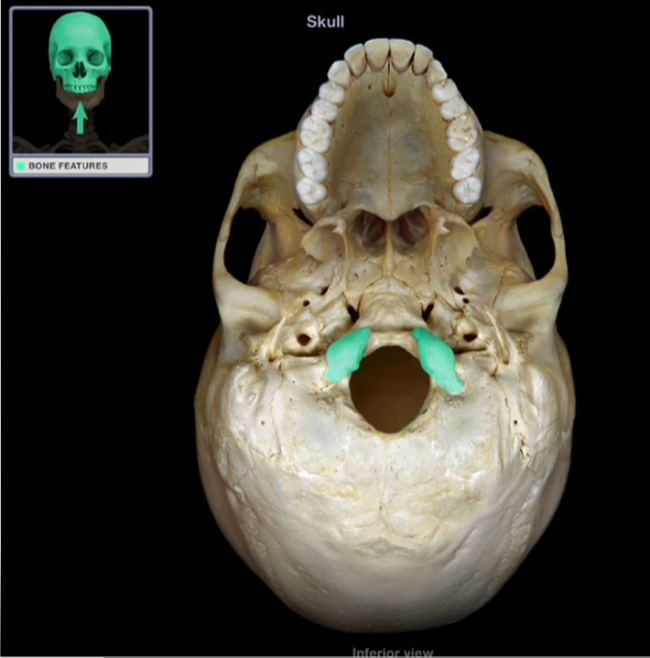
Occipital Condyles
-Smooth knobs that articulate with the first cervical vertebrae (C1-Atlas) forming the atlantooccipital joint
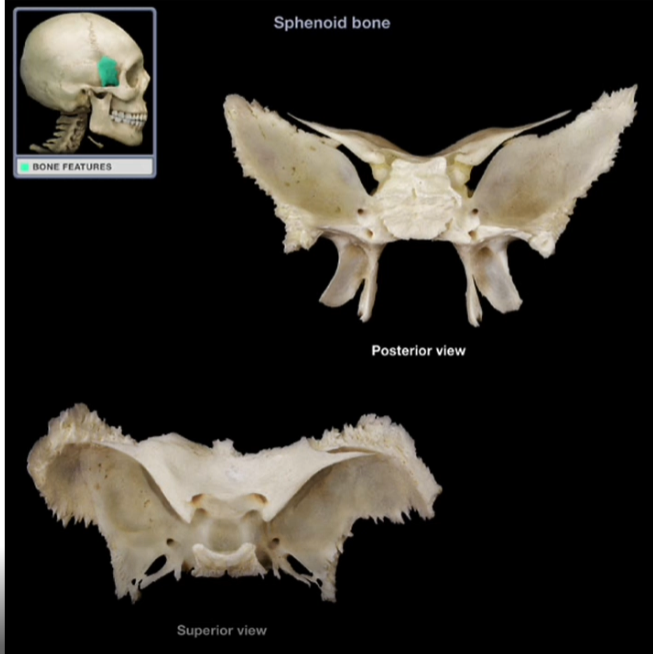
Sphenoid Bone
-”keystone” of the skull
-Comes in contact/ articulates with almost every other bone in the skull
-Complex-shaped bone that unites the cranial and facial bones
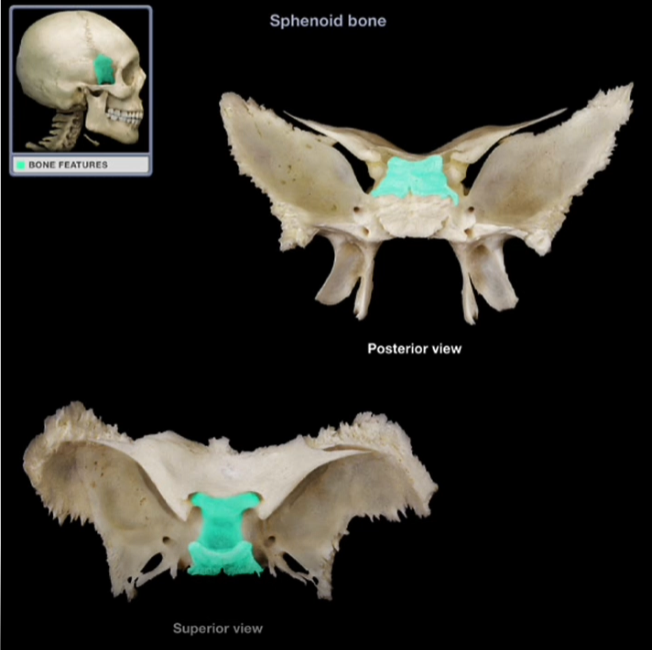
Body of the Sphenoid Bone
-Thick, medial portion of the sphenoid bone
-Contains the sella turcica
Sella Turcica
-”sella” = “saddle”
-Houses and protects the pituitary gland

Hypophyseal Fossa
-Pit where the pituitary gland sits
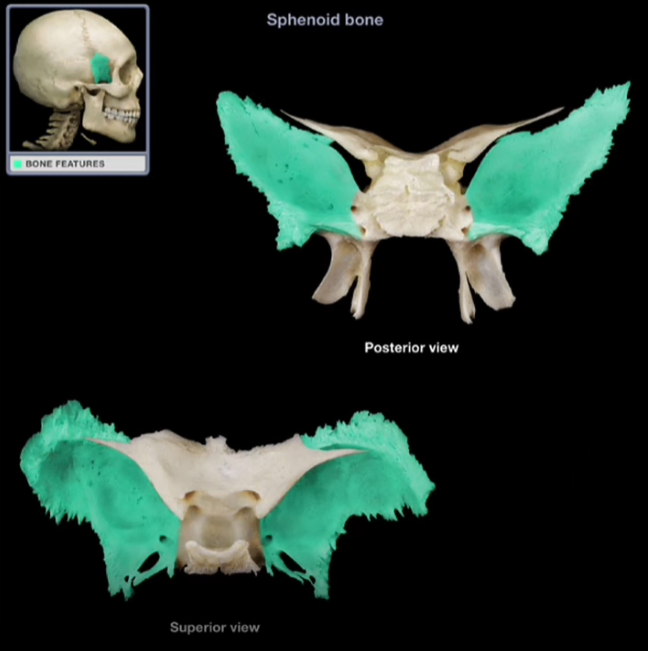
Greater Wings
-Larger, lateral projections from the body of the sphenoid bone
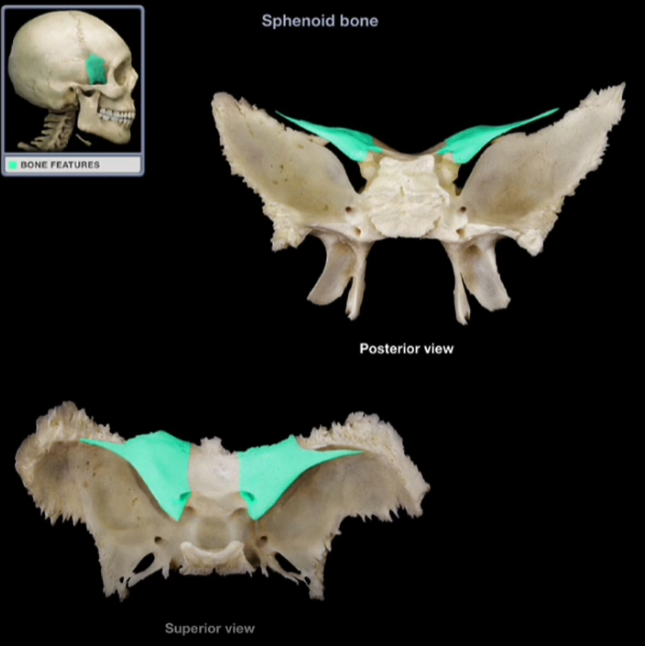
Lesser Wings
-Smaller, lateral projections from the body of the sphenoid bone
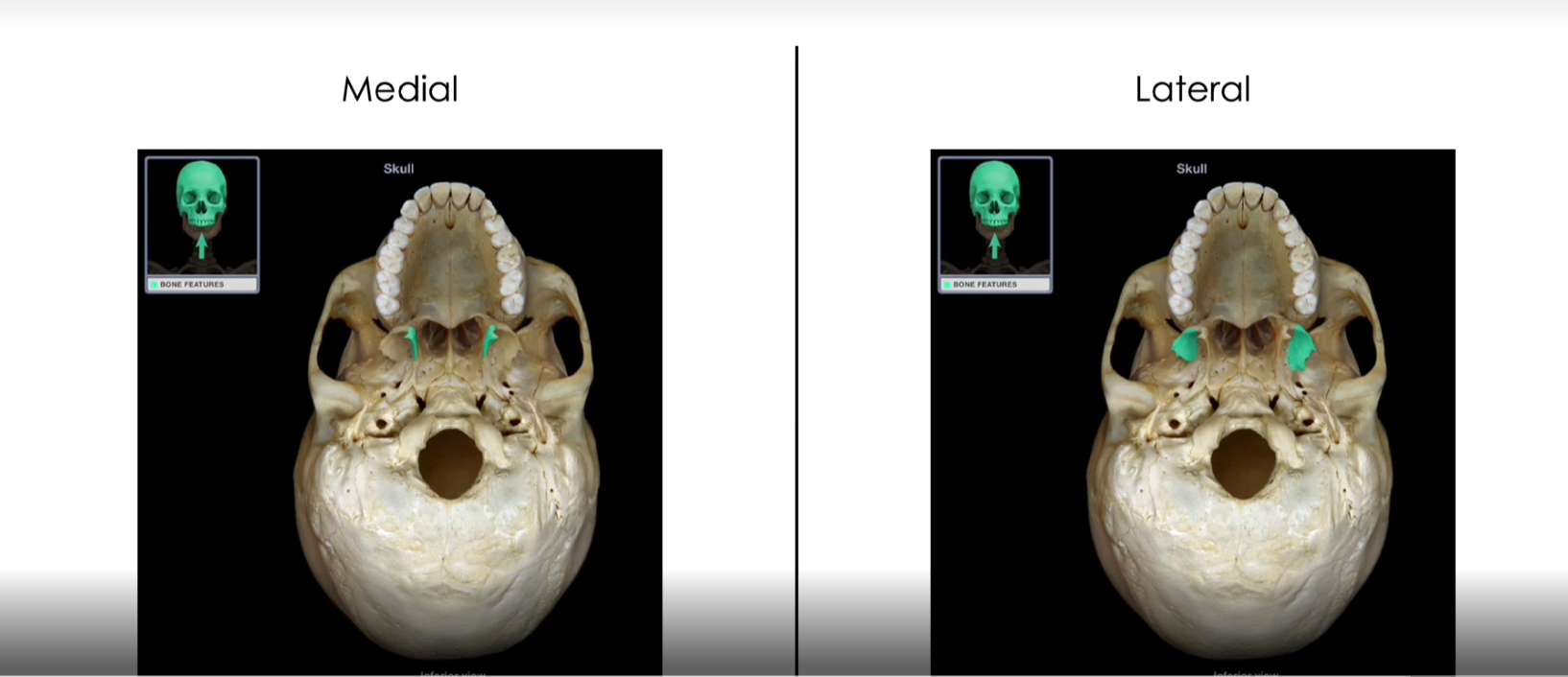
Medial and Lateral Pterygoid Processes
-Vertical projections that provide the attachment surfaces for some muscles that move the lower jaw and soft palate
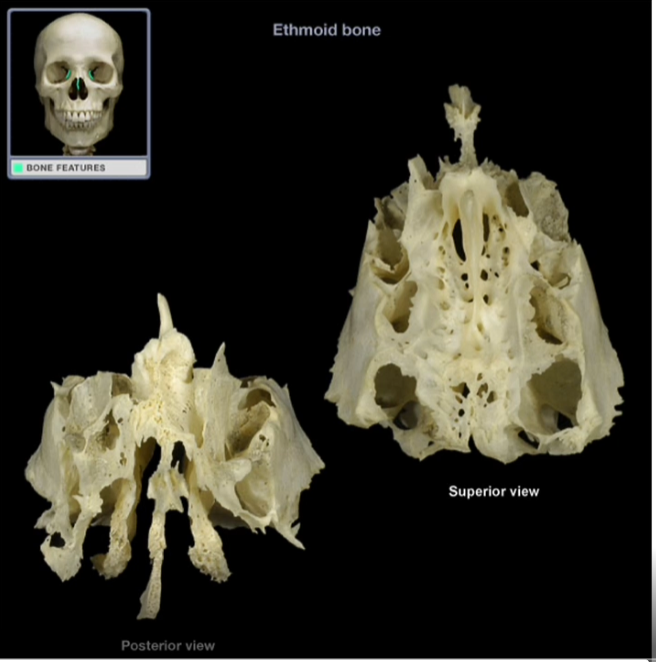
Ethmoid Bone
-Irregularly shaped bone that forms the anteromedial floor of the cranium, the roof of the nasal cavity, part of the medial wall of each orbit, and part of the nasal septum
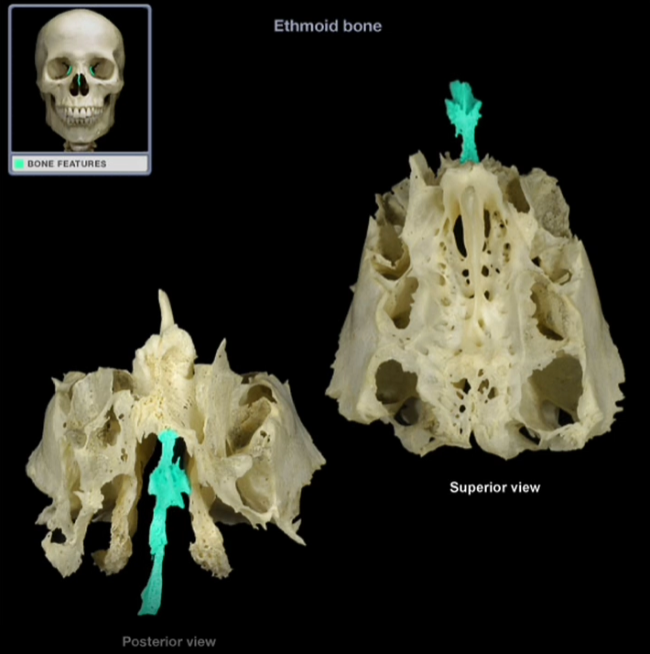
Perpendicular Plate
-Inferior, midline projection that forms the superior part of the nasal septum
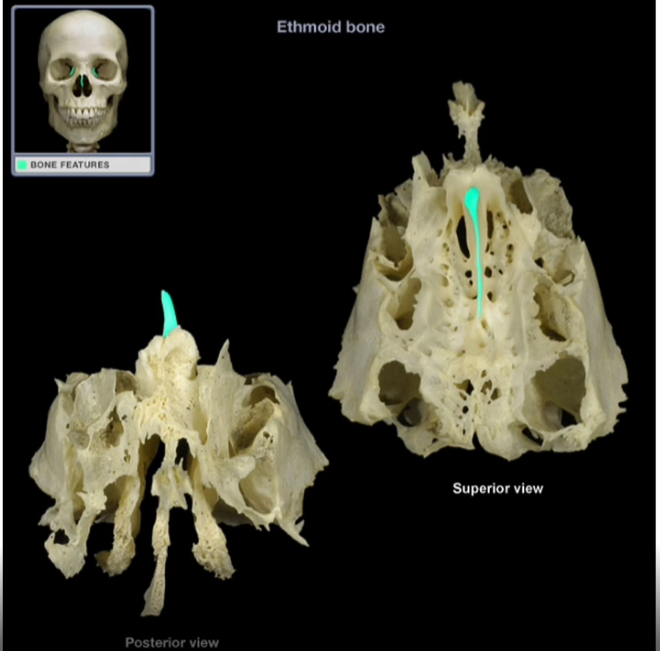
Crista Galli
-Thin, midsaggital elevation
-Acts as a point of attachment for a membranous sheet that helps support the brain
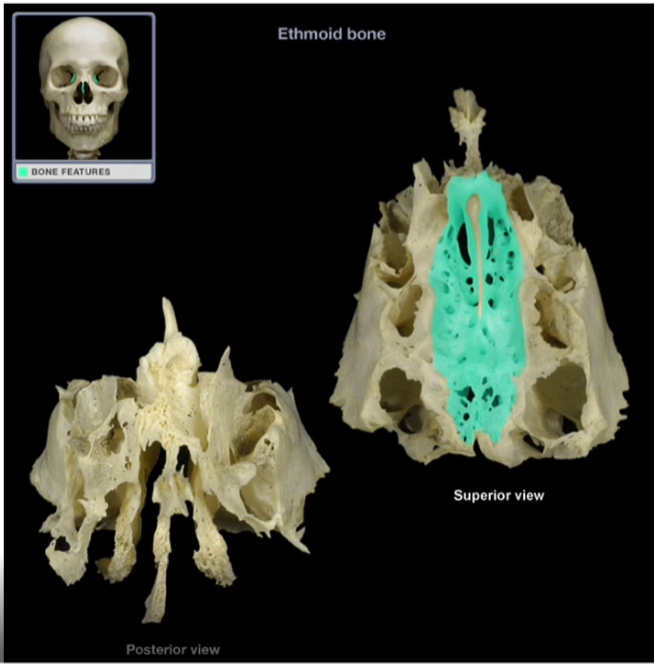
Cribiform Plate
-Horizontal structure that contains foramina that provide passageways for the olfactory nerves