A&P - Cells and Tissue (HS Junior Year)
1/33
Earn XP
Description and Tags
All of the paper flashcards I made for my Anatomy & Physiology class in my Junior year of High School but converted to a digital version :D
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Cells
Structural units of all living things
Cell Theory
All living things are made out of cells.
Cells are the basic structural and functional units of an organism.
All cells arise from pre-existing cells.
3 ways cells are bound together
Glycoproteins in glycocalyx act as adhesive or cellular glue.
Wavy contours of the membranes of adjacent cells fit together in a tongue-and-groove fashion.
Special cell membrane junctions formed (junctions vary structurally depending on roles).
Tight Junctions
Impermeable junctions that encircle the cells and bind them together into leak-proof sheets.
Adjacent plasma membranes fuse, forming a continuous belt around the cell.
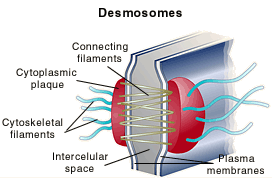
Desmosomes
Anchoring junctions scattered like rivets along sides of adjacent cells.
They prevent cells subjected to mechanical stress from being pulled apart.
What is the structure of a desmosome?
Junctions are button-like thickenings of adjacent plasma membranes that are connected by fine protein filaments.
Thicker protein filaments extend from plaques inside cells to plaques on cells’ opposite sides and forms “guy wires”
Gap Junctions
Function mainly to allow communication.
Commonly found in heart and between embryonic cells.
Neighboring cells connected by hollow cylinders composed of connexons that span the entire width of the abutting membranes.
Plasma Membrane/Cell Membrane/Cytoplasmic Membrane
Fragile, transparent barrier containing the cell contents and separates them from the surrounding environment.
Found in both plant and animal cells.
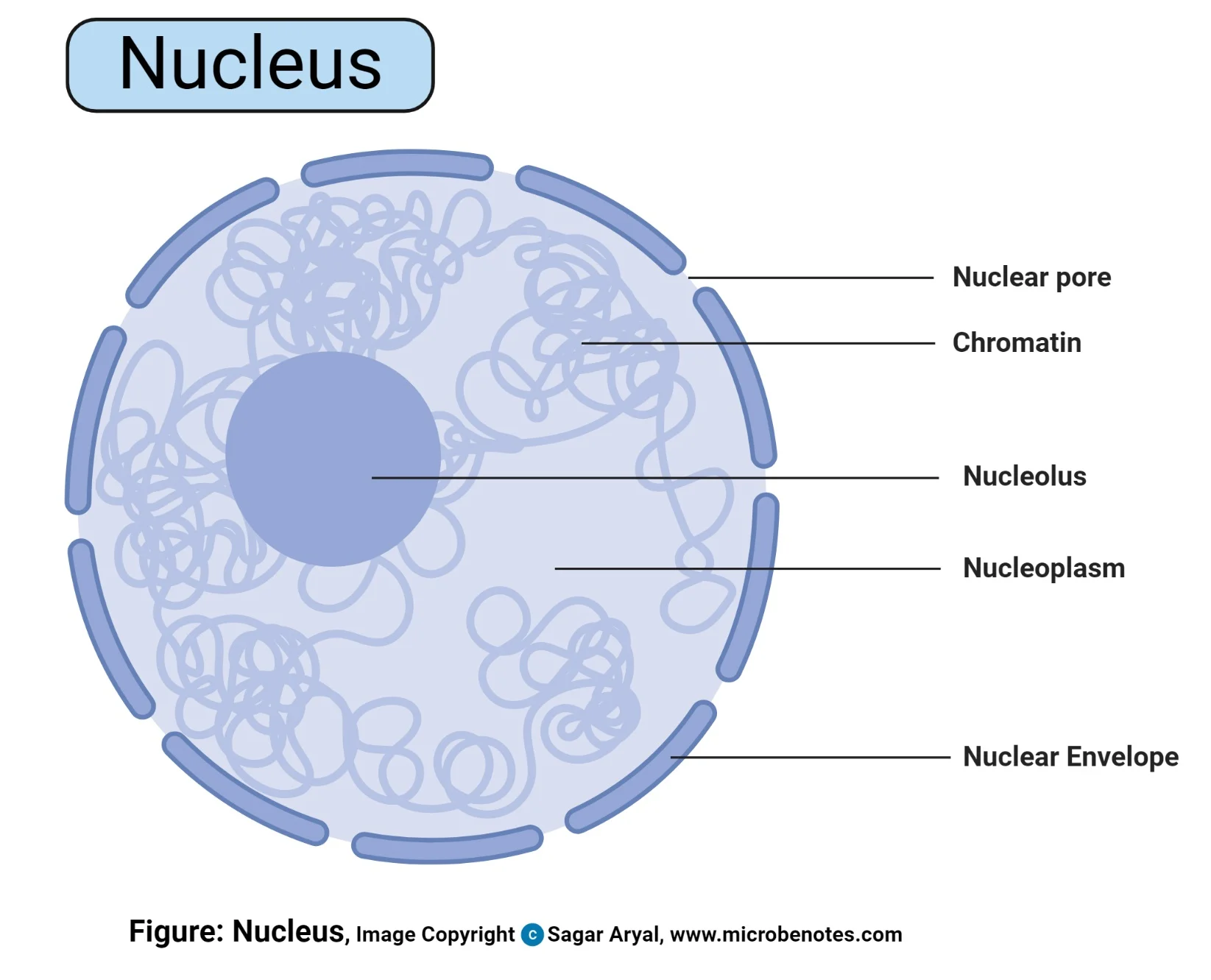
Nucleus
Control center of cells.
Where all instructions for building the whole body are formed
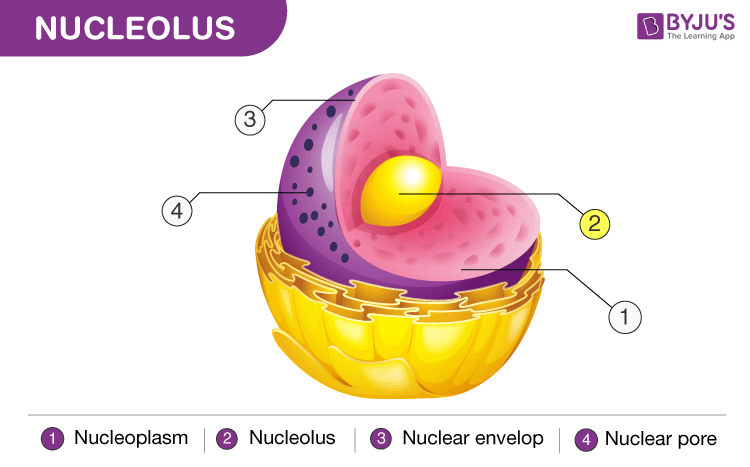
3 Recognizable regions/structures: Nuclear envelope, nucleolus, and chromatin
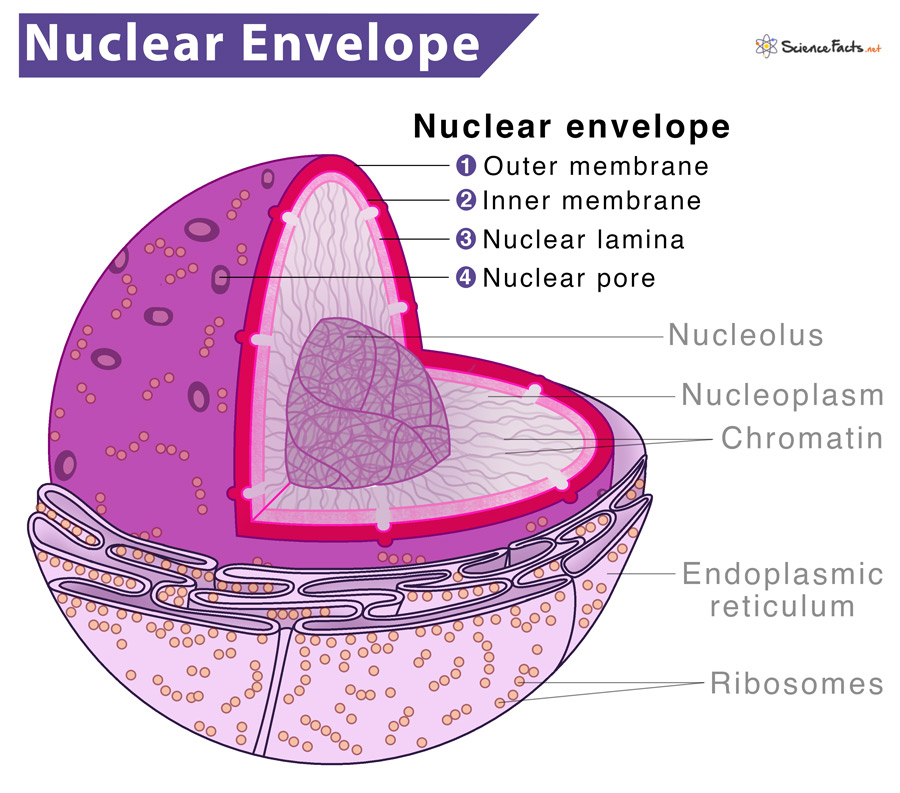
Nuclear Envelope
Double-membrane barrier.
Between the 2 membranes, there’s a fluid-filled space.
At various points, 2 layers of nuclear envelope fuse and generate openings called nuclear pores.
Nuclear envelope allows some but not all substances to pass through.
Encloses jelly-like fluid called nucleoplasm, where nuclear elements are suspended.
Nucleolus
Small, dark-staining, essentially round body found in nucleus.
Sites where ribosomes eventually migrate into cytoplasm and serve as actual sites of protein synthesis.
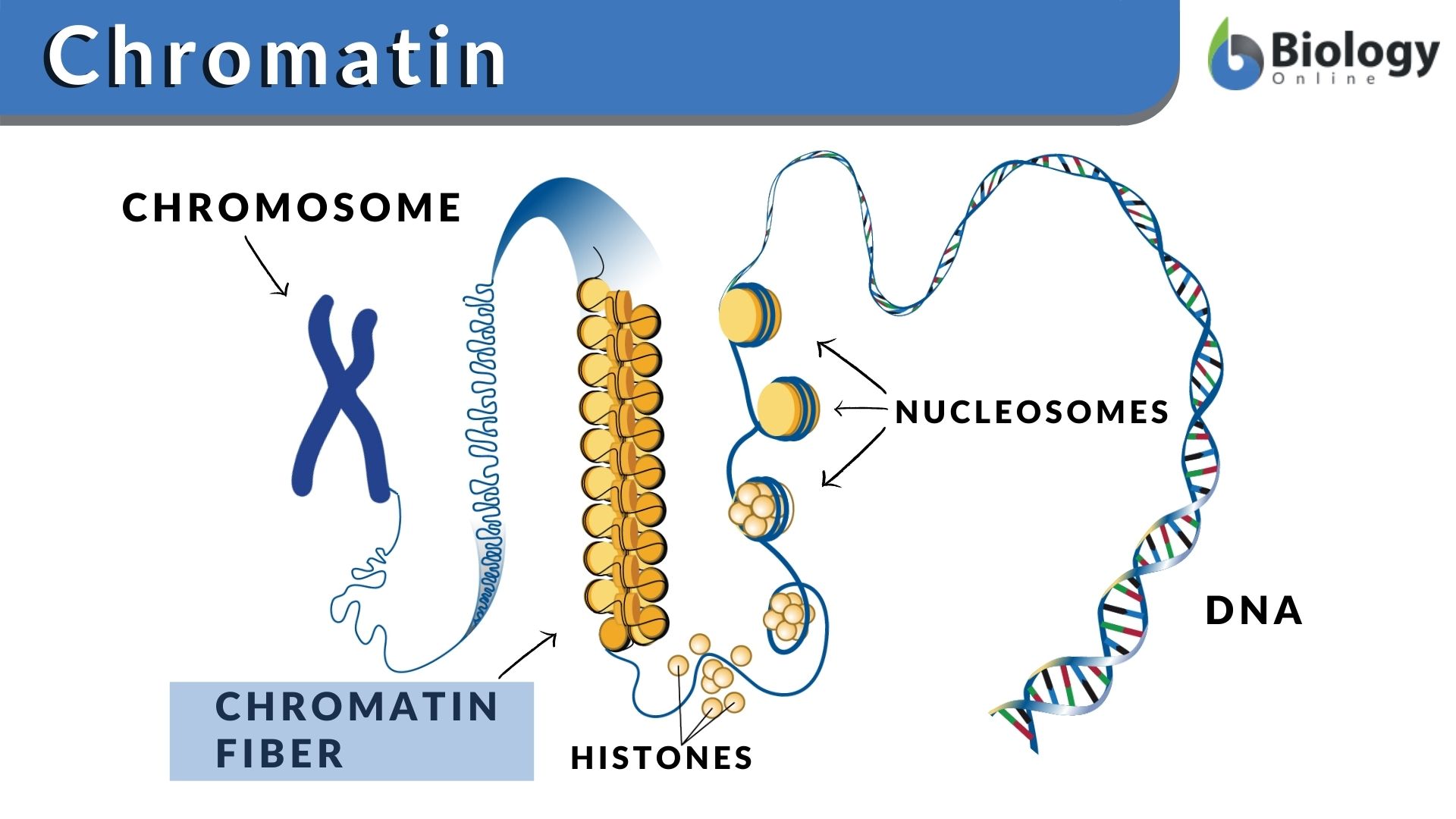
Chromatin
Composed of DNA wound around proteins called histones.
Looks like beads on a string
When a cell’s about to divide, chromatin threads coil and condense to form dense, rodlike bodies called chromosomes
Cytoplasm
Cellular material outside nucleus and inside plasma membrane.
Site of most cellular activities.
“Factory floor”
3 Major components: cytosol, inclusions, and organelles
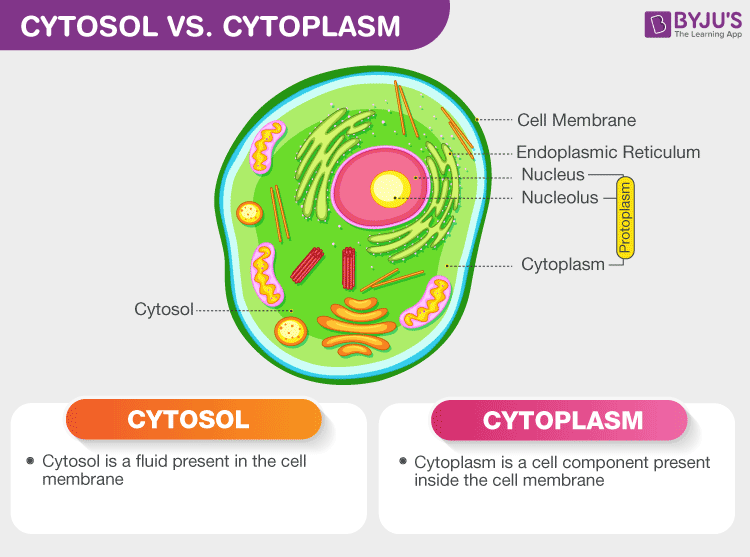
Cytosol
Semi-transparent fluid that suspends other elements
Inclusions
Chemical substances that may or may not be present depending on specific cell type.
Most inclusions are stored nutrients or cell products that are floating in cytosol.
Basically cellular “pantry” where items kept on hand until needed.
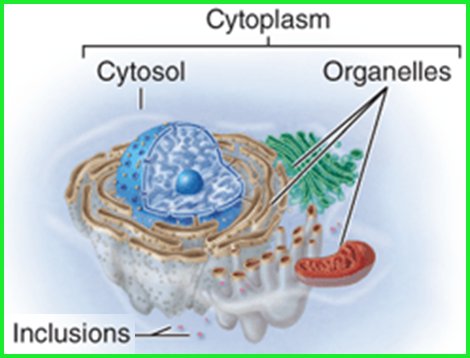
Organelles
Specialized cellular compartments that are the metabolic machinery of the cell.
Each organelle is specialized to carry out a specific function for the cell as a whole.
Mitochondria
Powerhouse of the cell. Produces energy (ATP) through cellular respiration.
Mitochondrial wall consists of a double membrane equal to 2 plasma membranes.

ATP
Provides energy for cellular work.
Every living cell requires constant supply of ATP for its many functions.
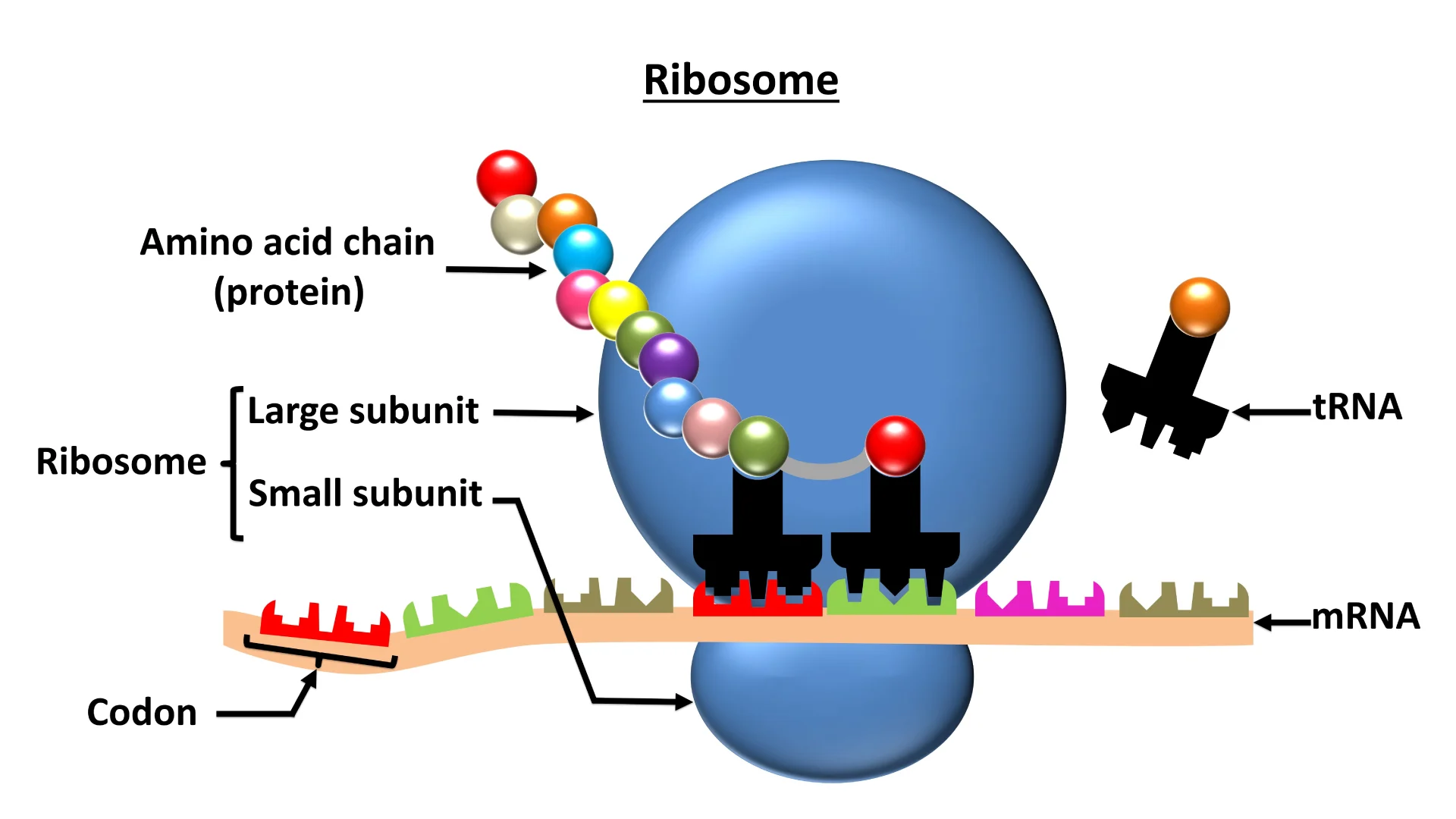
Ribosomes
Two globular subunits that fit together to create proteins.
Actual sites of protein synthesis in the cell.
Ribosomes that float freely in cytoplasm manufacture proteins that function inside the cell, while others attach to membranes.
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Serves as a mini circulatory system for carrying substances from one part of the cell to another.
System of fluid-filled tunnels that coil and twist through the cytoplasm.
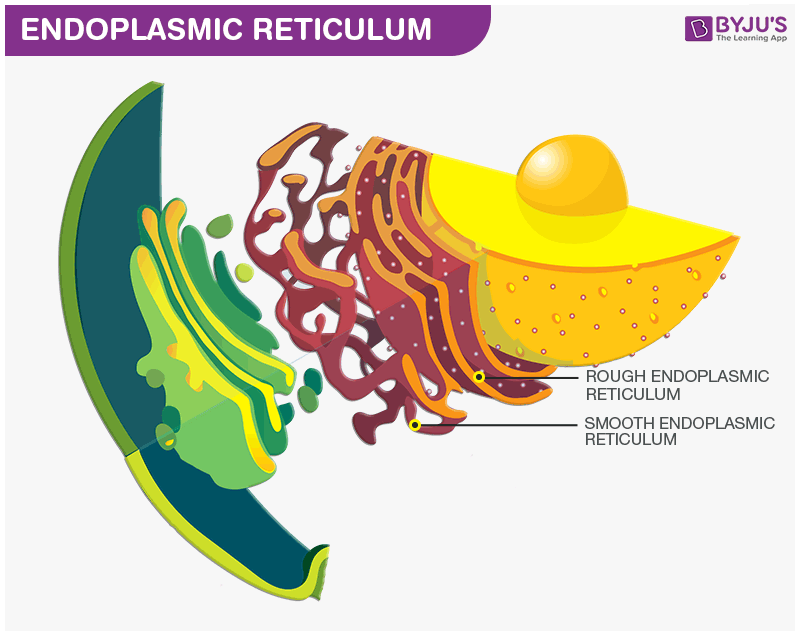
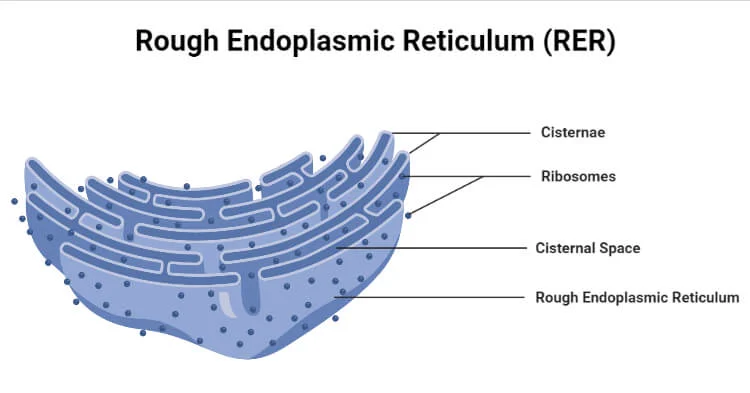
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
“Cell membrane’s factory'“
Studded with ribosomes, it plays a crucial role in the synthesis, folding, modification, and transport of proteins that are destined for secretion, insertion into cell membranes, or delivery to other organelles.
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
No role in protein synthesis because it has no ribosomes.
Functions in lipid metabolism and detoxification of drugs and pesticides.
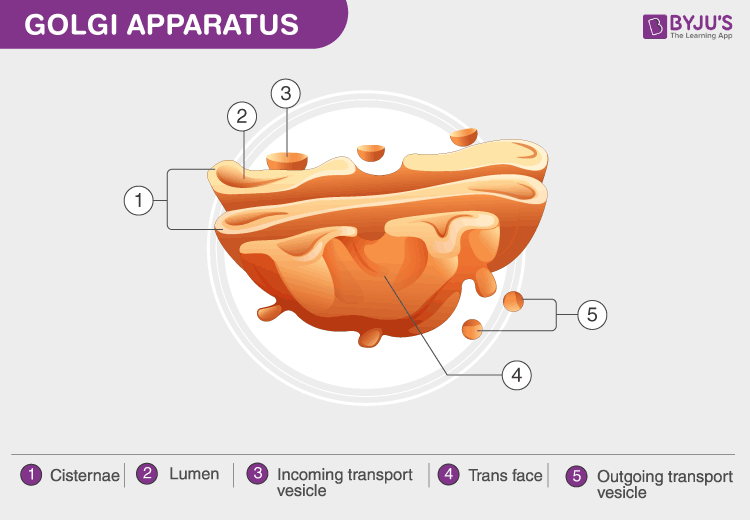
Golgi Apparatus
Series of flattened, membrane-bound sacs that process, package, and sort proteins and lipids synthesized in the endoplasmic reticulum.
Modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and lipids for secretion or delivery to other organelles.
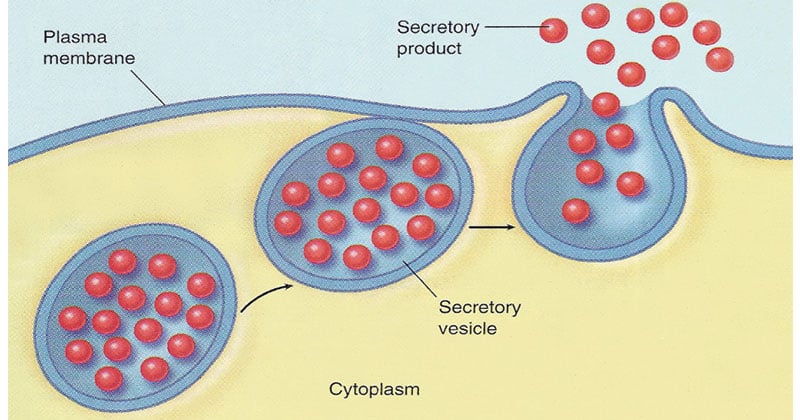
Secretory Vesicles
Small, membrane-bound sacs that bud off from the Golgi apparatus and contain proteins or lipids for secretion outside the cell or delivery to other organelles.
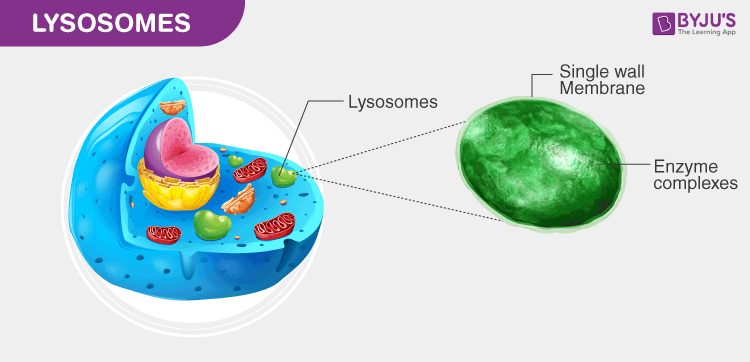
Lysosomes
Membranous organelles that contain powerful digestive enzymes and function as the cellular “stomach” by breaking down damaged organelles, cellular debris, and ingested material to recycle components or eliminate waste.
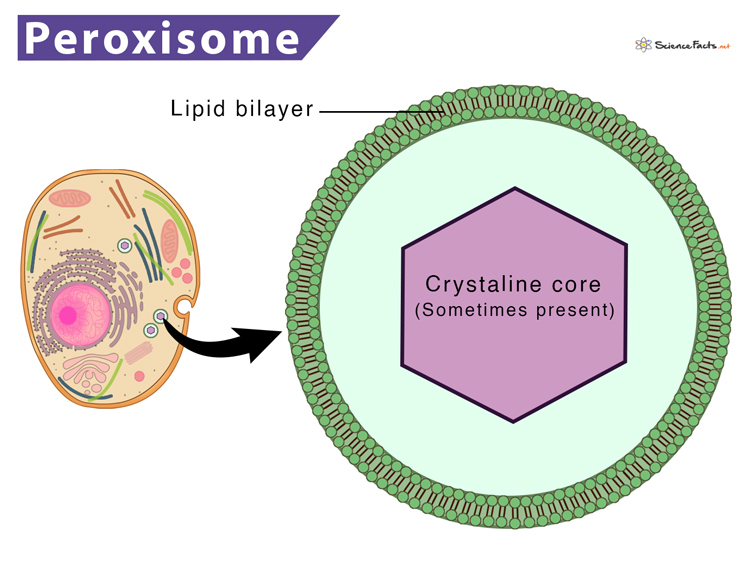
Peroxisomes
Membranous sacs of oxidase enzymes that detoxify harmful or toxic substances using molecular oxygen, such as alcohol and formaldehyde.
Especially abundant in liver and kidney cells.
Most important function is to disarm dangerous free radicals
Free Radicals
Highly reactive chemicals with unpaired electrons that can damage structure of proteins and nucleic acids.
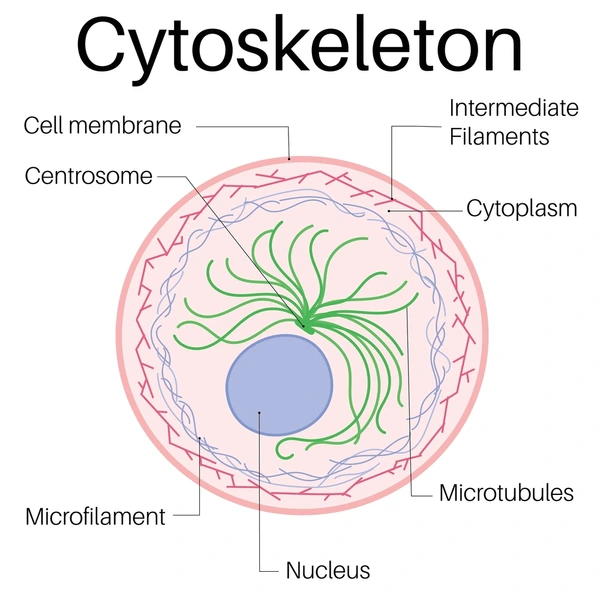
Cytoskeleton
Elaborate network of protein structure that extends throughout the cytoplasm and acts as the cell’s “bones and muscles” by furnishing an internal framework that determines cell shape, supports other organelles, and provides machinery for intracellular transport and various types of cellular movements.
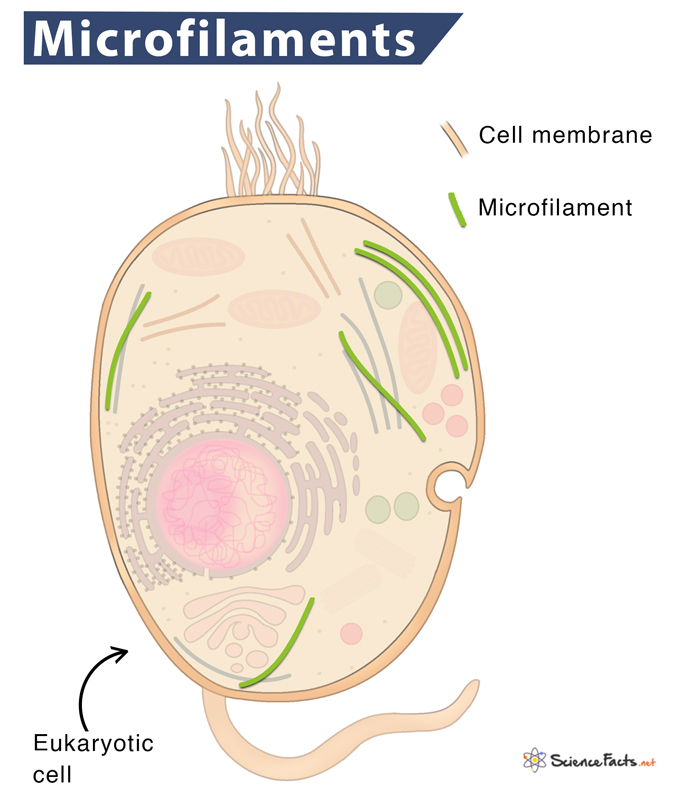
Microfilaments
Most involved in cell motility and producing changes in cell shape
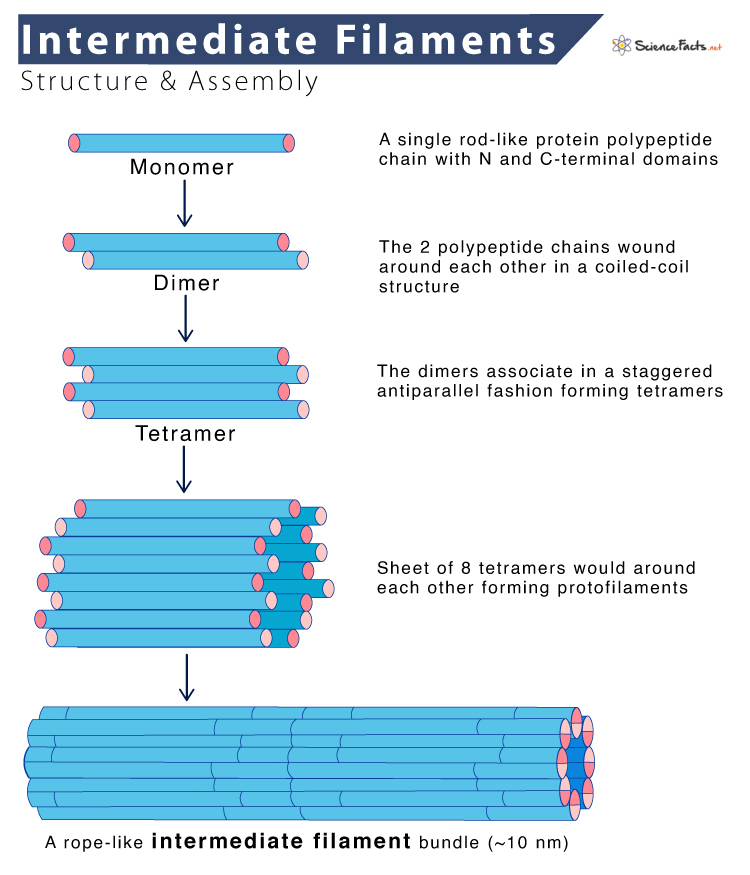
Intermediate Filaments
Strong, stable, rope-like.
Made up of fibrous subunits and help form desmosomes and provide internal guy wires to resist pulling forces on cell.
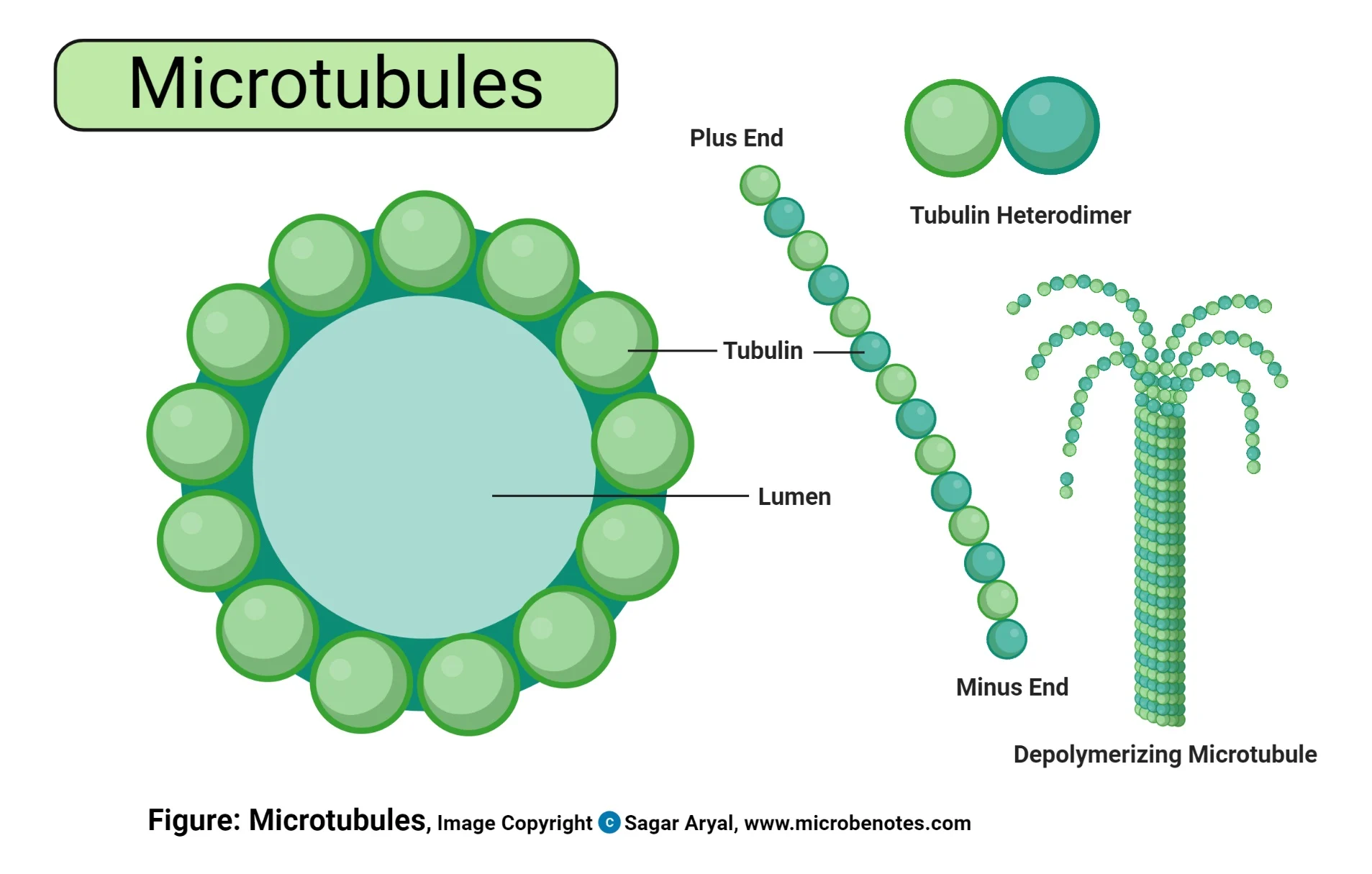
Microtubules
Made up of repeating subunits of tubulin and determine the overall shape of a cell and the distribution of organelles.
Crucial in cell division.
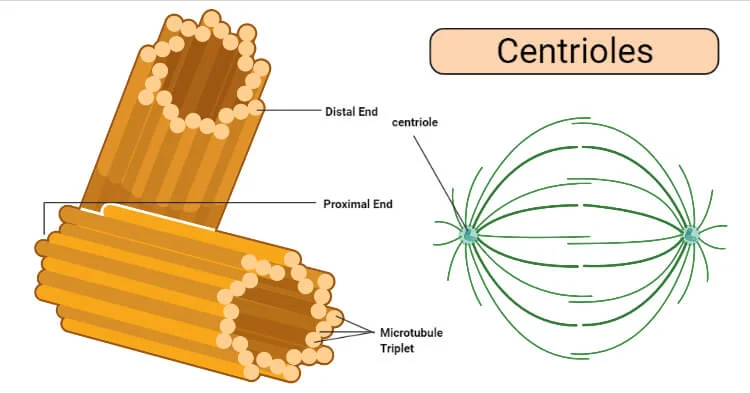
Centrioles
Rod-shaped bodies that lie at right angles to each other.
Best known for their role in generating microtubules and directing formation of mitotic spindle during cell division.
Cilia and Flagella