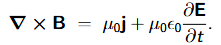Electromagnetism
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Scalar
a physical quantity that only depends on magnitude
Vector
an object which is described by both a magnitude and a direction
Scalar field
a map between an N-dimensional space and a scalar quantity
Vector field
a map between an N-dimensional space and an M-dimensional vector quantity.
What does the gradient of a scalar field represent
magnitude and direction of maximum increase of the scalar field
What is the gradient of a scalar field normal to?
lines (or surfaces) of constant field (contours) in direction of increasing field
What does (gradS) dotted with a unit vector of u represent?
the rate of change along the unit vector of u
What type of vector field is the result of the gradient on a scalar field?
A conservative field
What adjective describes any line integral over a conservative field?
path-independent
What value is given to any closed line integral in a conservative field?
Zero
What value is given to the curl of a conservative field?
Zero
What type of field is the divergence of a Vector field div V?
Scalar
What is the name of a vector field whose divergence is zero?
Solenoidal field
What type of field is the curl of a vector field?
Vector
What adjective is used to describe a vector field whose curl is zero?
Irrotational
What type of result is yielded from the Laplacian acting on a scalar field?
scalar
What type of result is yielded from the Laplacian acting on a Vector field?
Vector
The result of the curl of a gradient of a scalar field curl(gradS)?
Zero
The result of the divergence of the curl of a vector field div(curl(v))
Zero
Principle of Superposition
The total field, E( r ), due to the individual electric fields associated to different individual charged particles, E_i ( r ), is obtained by adding together (or superposing) all the fields
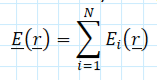
The electrostatic potential for a continuous charge distribution
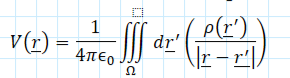
The electric field for a continuous charge distribution
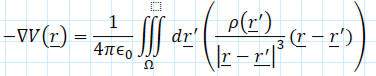
What are normal to the electric field lines?
The equipotential surfaces
In which direction to electric field lines point
From higher to lower potential
What equations of electrostatics relate potential to the charge densities?
Poisson Equation
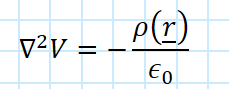
Gauss’ Law
The net electric flux through any closed surface equals the net electric charge within that surface, up to a factor
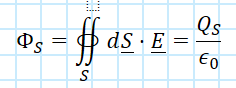
Divergence Theorem
The flux over a closed surface of a differentiable vector field equals the volume integral of the divergence of the field over the enclosed volume.
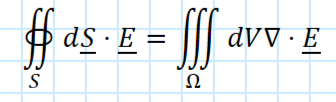
Stoke’s Theorem
The surface integral over an open bounded surface of the curl of a differentiable vector field equals the line integral of the curl of the field over the perimeter of the surface.
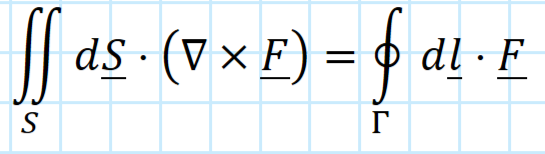
Force between charges q_1 and q_2
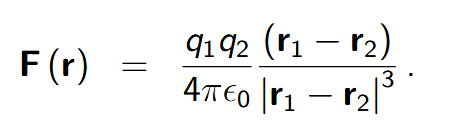
Electric field at any point due to charge q_1
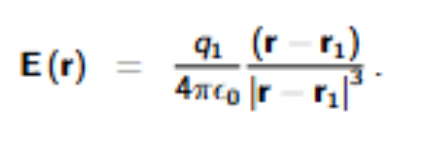
Relation between electric field and potential
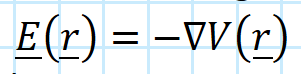
maxwells first equation
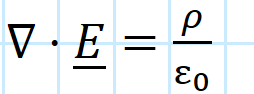
Maxwell 2
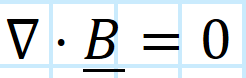
Maxwell 3
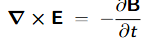
Maxwell 4