Bio H - Independent Unit Exam SG
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Ocean ecosystems
Ocean ecosystems are the most common and cover 70% of the Earth’s surface. The 3 basic types are: shallow ocean, deep ocean water, and deep ocean surfaces
Freshwater ecosystems
Freshwater ecosystems are the rarest, covering only 1.8% of the Earth’s surface. Lakes, rivers, streams, and springs are this type. They support a variety of fish, amphibians, reptiles, insects, phytoplankton, fungi, and bacteria
Terrestrial ecosystems
Terrestrial ecosystems are also known for their diverstiy. They are grouped into large categories called biomes, like rain forests, savannas, deserts, coniferous forests, deciduous forests, and tundra
Disturbance
Changes in an ecosystems enviornment that effect their compositions
Resistance
The ability of an ecosystem to remain at equilibrium after being disturbed
Resilience
The speed at which an ecosystem recovers equilibrium after being disturbed
Biomass
The total mass in an unit area at the time of measurement, of living or preioiusly living organisms within a trophic level
Net primary productivity
The energy that remains in the primary producers after accounting for the organisms’ respiration and heat loss
Trophic level
There’s a single path through a food chain, andeach organism in that food chain is assigned a level based on if theyre producers, consumers, species, or groups of species
Biomagnification
The increasing concentration of persistent, toxic substances in organisms at each trophic level
Biogenochemical cycle
The recycling of inorganic matter between living organisms and their enviornment
Hydrosphere
The area of the Earth where water movement and storage occurs
Residence time
The measure of the average time an individual water molecule stays in a particular reservoir
Surface runoff
The flow of fresh water either from rain or melting ice
Nonrenewable resource
A resource that is either regenerated very slowly or not at all, ex: fossil fuels
Symbiotic
Involving interaction between two different organisms living in close physical association, benefits both parties
Nitrogen fixation
The conversion of N2 into a usable form
Rhizobium
A type of bacteria that live symbiotically in the root nodules of legumes (peas, beans, nuts) and provide them with the organic nitrogen they need
Eutrophication
A process whereby nutrient runoff causes the excess growth of microorganisms, depleting dissolved oxygen levels and killing ecosystem fauna
Dead zone
An area within freshwater or marine ecosystem where large areas are depleted of their normal flora and fauna, these zones can be caused by eutrophication, oil spills, dumping of toxic chemicals, and other human activites
Acid rain
Caused by rainwater failling to the ground through mostly sulfur dioxide gas, turning it into weak sulfurous acid
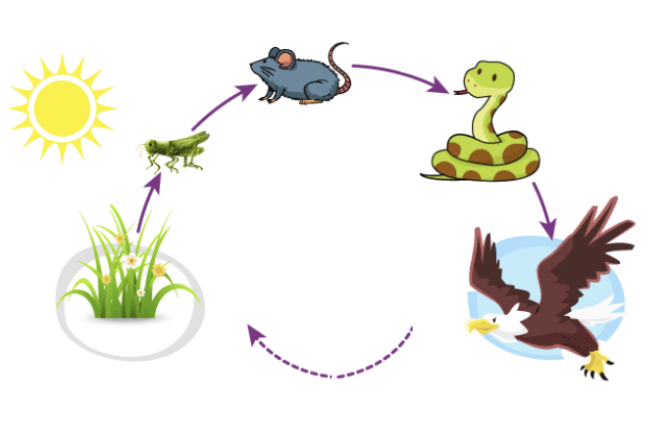
Grass | Primary producer |
Grasshopper | Primary consumers |
Mouse | Secondary consumers |
Snake | Teterairy Consumer |
Eagle | Apex Consumer |
Dotted line | The waste from the eagle gets absorbed by the earth and turned into nutrients to help the grass grow |