Tissue Dynamics 2 Cell Migration Exam 2
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Chemotaxis
Unidirectional cell migration mediated by diffusible molecules in the fluid space
Chemotaxis chamber (Boyden chamber)
In the upper chamber: cells In the lower chamber: chemo attractant. Cells will migrate through the pores of the membrane filter.
Durotaxis
Directed motile response, Cell migration to stiffer surfaces
guidance by ECM fibers
Directed motile response, Cells tend to follow the “path of least resistance” along oriented matrix fibrils
avoid contact inhibition
Directed motile response, Cells cease to migrate in the same direction after colliding with another cell, Cells are directed away from dense cell populations, giving rise to the radial pattern of cell orientation commonly observed in tissue outgrowths.
The migratory path of each cell appears to be random
Migratory path and speed of cell migration is similar to particles in Brownian motion.
Cell migration in tissues
Macrophages and neutrophils crawl to sites of infection and engulf foreign invaders as a critical part of the innate immune response.
• Osteoclasts tunnel into bone, forming channels that are filled in by the osteoblasts that follow after them, in a continuous process of bone remodeling and renewal.
• Fibroblasts migrate through connective tissues and rebuild damaged structures at sites of injury
• Endothelial cells migrate during angiogenesis.
To migrate through the tissue, cells need to..
locally degrade the ECM (proteolysis)
Proteolytic enzymes:
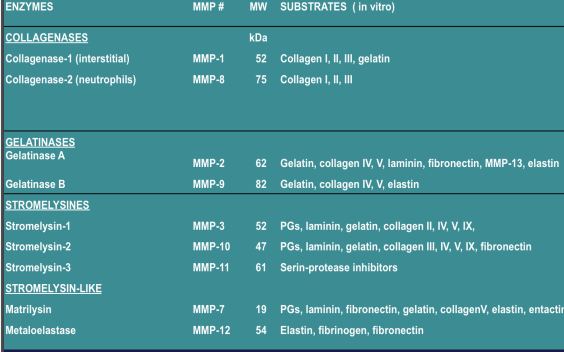
Matrix Metalloproteases (MMPs)
The MMP Family
Basement Membrane (Basal Lamina)
Secreted by the cells: -underlies all epithelial and endothelial cell sheets; -surrounds individual muscle cells, fat cells, and Schwann cells
Basement membrane components
Collagen type IV gives tensile strength. Laminin provides binding sites for cells. Perlecan - proteoglycan deposited in the ECM by vascular endothelial and smooth muscle cells
The basement membrane is part of the ECM. Role in tissue regeneration after injury: when muscles, nerves, or epithelia are damaged and the basement membrane survives, it provides a scaffold along which regenerating cells can migrate.
Endothelial cell migration and the generation of new capillaries:
ANGIOGENESIS, The majority of cells in the body need to be within 50-100 m of a blood supply to receive adequate oxygen and nutrients for survival.
Bone
highly vascularized tissue
Bone remodeling cycle
Osteoclasts - large multinucleated cells that continuously secrete acid and collagenase and degrade the mineralized collagen (bone resorption) Osteoblast - synthesize collagen and mediate new bone formation
Angiogenesis
- key component of bone generation after injury and in tissue engineering U.Saran, Arch. Biochem. Biophys. (2014) • New capillaries are needed to bring oxygen and nutrients for bone cell formation and function: • Monocytes fuse and form osteoclasts • Osteoblasts proliferate and secrete collagen • Angiogenic (VEGF) and osteogenic (BMP, PDGF, TGF) growth factors are involved
Angiogenesis: sprouting of an endothelial cell from an existing small blood vessel
Lack of oxygen in tissues (hypoxia) triggers the formation of HIF, a transcription factor that induces the secretion of VEGF. Endothelial cells are activated by VEGF (have receptors for VEGF) and would migrate towards the growth factor .
Formation of a capillary sprout
An endothelial tip cell, with many filopodia, leads the advance of each capillary sprout. The endothelial stalk cells trailing behind the tip cell divide and form a lumen. The tip cell does not divide.
A monolayer of endothelial cells lines the entire vascular system
Under the endothelium: basal lamina.
Steps in the process of angiogenesis (VEGF induced)
1. An activated endothelial cell secretes MMPs that will degrade the basal lamina
2. The endothelial cell migrates toward VEGF (chemotaxis)
3. The endothelial cells proliferate behind the leading front of migrating cells
4. Cells form a tubular structure with a lumen
5. Periendothelial cells are recruited to support the endothelial cells
Sequential release of angiogenic and osteogenic growth factors
VEGF released early (5 days) for vessel formation • BMP-2 released from 14-21 days for bone formation
Angiogenesis in vitro
Seeding endothelial cells onto a collagen-coated culture dish: after 20 days, capillary tubes begin to form and branches soon appear.
Vascularization:
breathing life into engineered tissue substitutes
1. Long-term function of tissue constructs depends on a vascular network connected to the host.
2. Biomimetic scaffolds are developed to provide signals and control cellular activity: • For migration: MMP degradable domains (specific sequences recognized by MMPs as substrates)
• For angiogenesis: immobilized VEGF
• For adhesion: RGD sequences
Integrins
Cells bind to ECM through INTEGRINS, expressed on on cell surfaces, bind to RGD-containing proteins from ECM Integrins are receptors for ECM proteins that contain the RGD = Arg–Gly–Asp
Fibronectin
protein closely associated with the basement membrane, Specific binding site recognized by cells: RGD= Arg–Gly–Asp
Bio-mimetic hydrogel scaffold with proangiogenic properties (1)
MMP-sensitive PEG hydrogel a. RGD induces cell adhesion b. Cells are attracted toward VEGF c. Protease substrate will be degraded by the MMP secreted by endothelial cells, creating migratory pathways
Bio-mimetic hydrogel scaffold with proangiogenic properties (2)
After 6 days, tubule-like structures are formed in hydrogels with intermediate polymer weight percentage (10%).
Bio-mimetic hydrogel with scaffold proangiogenic properties (3)
Cells produce ECM proteins (remodeling)
Bio-mimetic hydrogel scaffold with proangiogenic properties (4)
Cells cultured for 28 days in hydrogel: highly interconnected network of tubules