lf206 lecture 5 - eukaryotic genomes, transcriptional regulation
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
why is transcriptional regulation needed?
allows development of different tissues
transition from childhood to adult
allows reaction to environmental cues
deregulation can result in uncontrolled growth → cancers
what determines how/when genes are transcribed? [3]
chromatin structure
RNA polymerase binding specificity
additional binding and activation factors
facultative heterochromatin have H3K27me3 (__________) which is a histone modifaction.
H3K27me3 can bind to ________ proteins. these proteins remodel ________.
trimethylation of histone 3 at lysine 27
polycomb
chromatin
constitutive heterochromatin are regions that are consistently ________
silenced
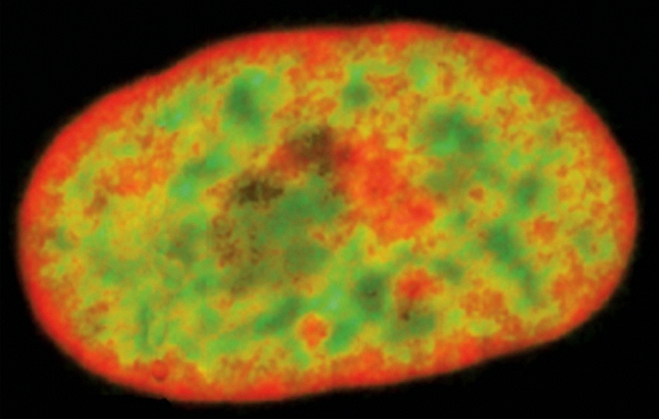
this is a eukaryotic nucleus. actively expressed genes (green) are central. heterochromatic regions (red) are close to the nuclear membrane.
what does this suggest?
DNA can be moved to the nuclear membrane for transcriptional inactivation
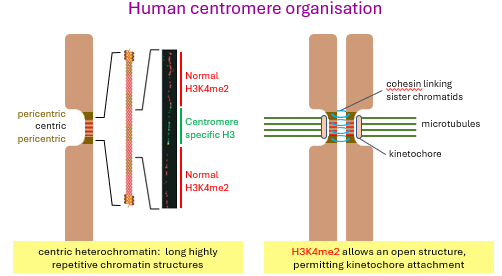
centric heterochromatin have long highly _________ chromatin structures.
_________ allows for an open structure, permitting kinetochore (define this) attachment
repetitive
H3K27me3
kinetochore binds chromosome to mitotic spindle aligning to metaphase plate
telomeres are a repeated ___ sequence on the ends of DNA
DNA
COMPENSATORY MECHANISM FOR TELOMERE SHORTENING
telomeres have a single-stranded ______-rich overhang
telomerase binds to the G-overhand
telomerase is a __________ (RNP) enzyme made of telomerase ___ (TER) and telomerase reverse ________ protein (TERT)
________ extends the __’ end of the parental strand using its own __ subunit as a template.
this is a reverse _______ process.
free 3’ unpaired end triggers repair __________
RNA-templated DNA synthesis by _______ extends the G-overhang 5’-3’, DNA _______ lays down RNA _____ on the extended G overhang
DNA-templated DNA synthesis by ___ ________ extends this primer 5’-3’, ___ ligase ligates the new _______ fragment to the old lagging strand 5’ end
guanine
ribonucleoprotein, RNA, transcriptase
telomerase, 3’, RNA
transcription
mechanisms
telomerase, primase, primer
DNA polymerase, DNA, Okazaki
3’ end of telomere extension needs to shelter from repair mechanisms.
why and how?
it resembles DNA damage
shelterin complex of TRF1 (telomeric repeat-binding factor 1), TRF2 and RAP1 (repressor/activator protein) stimulates t-loop formation.
this displaces a d-loop and results in base pairing on 3’ end.
if telomeres cannot be replicated what can this lead to?
Werner syndrome - premature aging symptoms
___ binds to the TATA box on RNA polymerase ___, and the strength of the binding regulates ________
TBP (TATA-binding protein)
II
transcription
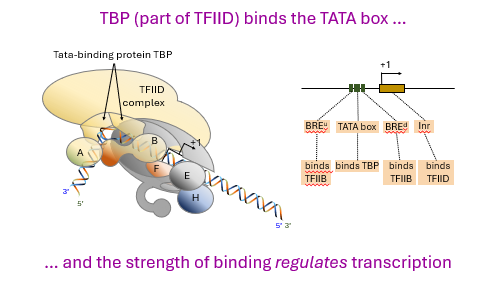
TATA box is a consensus sequence.
what does this mean?
TATA boxes have different ________ for TBP and so, some are more efficient at stimulating _________ than others.
a DNA sequence pattern that appears repeatedly in different places across genes
not identical but common pattern
affinities
transcription
G-less cassette transcription assay
a promoter is cloned upstream of a _-less cassette
add purified transcription factors, RNA Pol __, ATP, CTP and [alpha32P]-UTP (what is special about this?)
produces a radioactive ___ transcript which can be _________ through polyacrylamide gels and quantified following autoradiography
principle: because no ________ (GTP), RNA is truncated where _ should be
G
II
it is radioactive
RNA
electrophoresed
guanosine triphosphate