Strand 12- Hormones and Homeostasis
1/115
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
116 Terms
what are the main endocrine glands
hypothalamus/pituitary
thyroid
parathyroid
pancreas
adrenal
ovaries/testicles
hypothalamic-pituitary axis
brain:
hypothalamus
pituitary gland
pituitary gland
controls most (not all) glands in the body
most difficult part of endocrinology→ full attention is required
lobes of the pituitary gland
anterior pituitary→ produces various hormones
posterior pituitary→ stores various hormones
hormones produced in the anterior pituitary
growth hormone (GH)→ skeletal growth
Adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH)→ stimulates adrenals to produce steroids
gonatrotrophins (FSH and LH)→ stimulate testicles/ovaries to produce sex hormones
thyroid stimulating hormone/thyroptrophin (TSH)→ stimulates thryroid to produce thyroid hormones
Prolactin (PRL)→ stimulates breast milk production
posterior pituitary
stores hormones produced in hypothalamus
ADH→ stimulates water reabsorption by kidneys
Oxytocin→ helps uterine contractions during labour
How is pituitary controlled
Anterior PG under control of hypothalamus:
corticotrophin releasing hormone (CRH)→ stimulates ACTH secretion
growth hormone releasing hormone (GHRH)→ stimulates GH secretion
thyroptropin releasing hormone (TRH)→ stimulates TSH stimulation
Gonadotrophin releasing hormone (TRH)→ stimulates FSH and LH secretion
Prolactin release inhibited until childbirth
how are pituitary hormones switched off
negative feedback:
cortisol switches off ACTH and CRH
growth hormone switches off GH and GHRH
thyroid hormones switch off TSH and TRH
sex hormones switch off FSH/LH and GnRH
glands not controlled by the pituitary
adrenal medulla→ produces adrenaline and noradrenaline
parathyroid (PTH) → produces parathyroid hormone→ controls calcium levels
pancreas→ controls sugar levels
Gut hormones
thyroid gland structure
composed of:
midline isthmus (just below cricoid cartilage)
right lobe
left lobe
thyroid gland
thyroid cells are arranged in follicles and produce thyroid hormones
also contains C cells, producing calcitonin→ calcium metabolism
thyroid hormones interact with receptors in various organs→ regulate gene expression and aspects of organ function
control of thyroid hormone secretion
hypothalamus secretes TRH
Stimulates APG to secrete TSH
Stimulates thyroid to produce thyroid hormones
thyroid hormones inhibit TRH and TSH secretion
types of hyperthyroidism
primary hyperthyroidism→ thyroid pathology causing thyroid hormone production
secondary hyperthyroidism→ pituitary pathology causing increased TSH synthesis and consequently higher thyroid hormone production
calcium metabolism and organs involved
mainly controlled by 4 parathyroid glands sitting behind thyroid
kidneys→ calcium excretion and production of active vitamin D
gut→ absorption of calcium
bone→ storage of calcium
thyroid→ C cells
structure of adrenal glands
Adrenal cortex:
corticosteroids (cortisol)
androgens (male hormones)
mineralocorticoid (aldosterone)
Adrenal medulla:
catecholamines (adrenaline, noradrenaline, dopamine)
extent of control of pituitary glands on adrenal hormones
catecholamine secretion not controlled by pituitary→ related to blood pressure
mineralocorticoid secretion not controlled by pituitary→ related to renin-angiotensin system→ controls blood pressure)
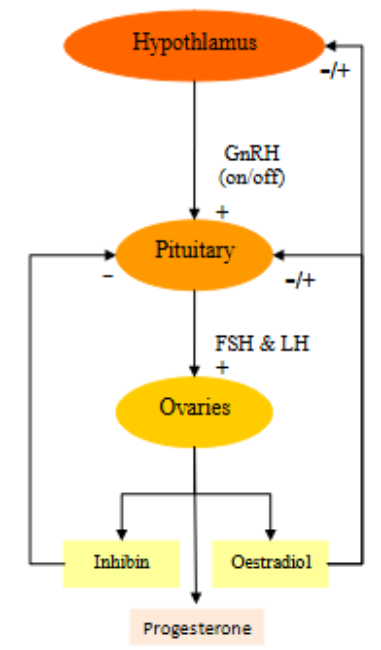
ovaries
situated on pelvis side of uterus
ovaries contain follicles (each contain oocyte) at different stage of maturation during reproductive life
control of female hormone secretion
hypothalamus secrets GnRH
Stimulates production of FSH and LH in pituitary
Stimulates ovaries to make inhibin, oestradiol, progesterone:
inhibin inhibits pituitary secretion→ FSH, LH
oestradiol inhibits FSH, LH and GnRH
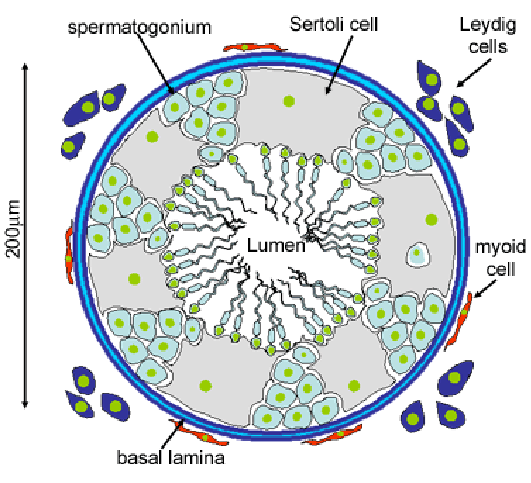
testes
composed of:
interstitial/ leydig cells→ produce testosterone
seminiferous tubules→ made of germ cells producing sperm
sertoli cells→ help in sperm production and produce inhibin
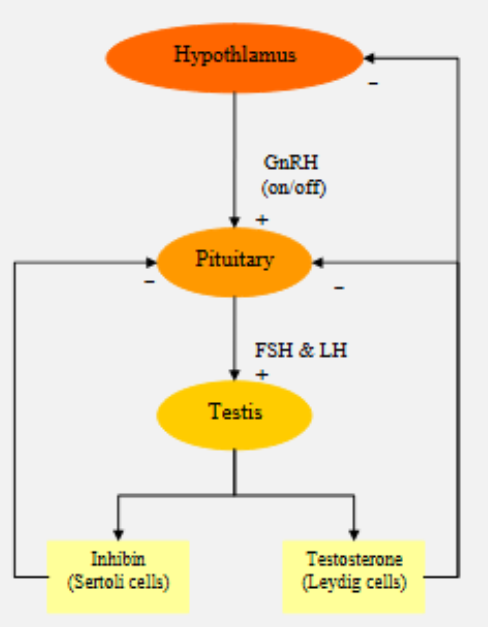
control of male hormone production
hypothalamus secretes GnRH
stimulates pituitary to produce FSH and LH
stimulates testis to produce inhibin and testerosterone:
inhibin inhibits pituitary secreting FSH and LH
testosterone inhibits hypothalamus and pituitary
clinical abnormalities of glands
hormonal over-secretion:
primary
secondary
hormonal under-secretion:
primary
secondary
tumour/nodules in glands without gland without affecting hormone secretion
types of tests for hormonal abnormalities
static tests
stimulation tests
suppression tests
static tests
diagnose abnormalities of thyroid and sex glands:
primary hyperthyroidism:
test for T4 and T4
TSH
Primary hyperthyroidism→ T3 and T4 elevated, TSH suppressed
stimulation tests
for suspected hormonal under-secretion where static test is not enough
e.g. giving ACTH to test for adrenal insufficiency (synacthen test):
if infividual fails to respond to stimulation test, gland failure is diagnosed
other e.g.s: glucagon stimulation and insulin stress test for pituitary failure
supression tests
for some hormonal over-secretion
e.g. giving steroids and testing for endogenous steroid production
giving glucose and testing GH secretion
diseases of the endocrine glands
over-secretion (usually benign tumours)
under-secretion gland destruction due to:
inflammation
infarction
tumours/nodules with normal hormone production
prolactin oversecretion
usually due to pituitary tumour secreting prolactin (prolactinoma)
clinical presentation:
galactorrhoea (breast milk production)
amenorrhoea in women, sexual dysfunction in men
large tumours→ headaches and visual field problems
diagnosis of prolactinoma
static test
pituitary MRI
causes of raised prolactin
sexual intercourse
nipple stimulation
stress
large number of drugs e.g. antipsychotics and antidepressants
non-functioning pituitary tumour→ compressing hypothalamus, interfering with inhibitory effect on prolactin secretion
growth hormone oversecretion
in childhood/adolescent:
excessive growth spurt and increased feet and hand size
untreated→ gigantism
in adults:
affects skin, soft tissue and skeleton
acromegalic face
wide and large hands/feet
increased sweating
diagnosis of excess growth hormone
requires suppression test
glucose given, followed by GH measurements at different time points:
in healthy individuals, glucose suppresses GH production and plasma levels of hormones fall
imagine necessary to confirm presence of pituitary tumour
causes of cushing’s syndrome
pituitary secreting ACTH tumour (Cushing’s disease)
adrenal tumours secreting cortisol
cancers producing ACTH (such as lung cancers)
clinical presentation of Cushing’s
growth arrest in children
typical facial appearance:
round (moon-like) face
acne
hirsuitism
Fat redistribution:
truncal obesity
thin extremities
Skin abnormalities:
thin skin, easy bruising
striae on abdomen
complications:
hypertension
diabetes mellitus
high risk of infection
poor wound healing
tests for Cushing’s
static tests not enough→ suppression tests required
dexamethasone suppression test used to confirm failure of suppression of endogenous cortisol production
thyroid hormone overproduction
could be due to primary or secondary hyperthyroidism
primary→ very common
secondary→ very rare
causes of hyperthyroidism
graves disease→ autoimmune condition
toxic nodule or toxic MNG
thyroiditis
drug induced
rarities
symptoms of hyperthyroidism
hyperactivity, irritability, insomnia
heat intolerance and increased sweating
palpitations
weight loss despite overeating
signs of hyperthyroidism
signs of thyrotoxicosis:
hand tremor
increased sweating
fast pulse
enlarged thyroid:
smooth→ Grave’s disease
nodular→ toxic nodules
tender→ thyroid inflammation
extrathyroidal signs
thyroid eye disease
swelling around eyes
protrusion of eyeball→ proptosis
paralysis of eye muscles
investigations for hyperthyroidism
thyroid blood test:
raised thyroid hormone
supressed TSH
static test is enough
antibody testing (TSHR-Ab) confirms autoimmune nature of condition
growth hormone deficiency
children→ failure of growth
adults→ tiredness, depression
testing for growth hormone deficiency
stimulation test required
glucagon stimulation test
insulin stress test→ lowers blood glucose, stressing body and forcing growth hormone secretion
treatment of growth hormone deficiency
growth hormone replacement:
injections
expensive
steroid undersecretion
may be due to:
adrenal failure
pituitary failure
clinical presentation:
failure to grow in children
severe tiredness
dizziness due to low b.p
abdominal pain, vomiting, diarrhoea
testing for steroid undersecretion
stimulation test:
synacthen test (giving ACTH) if primary adrenal failure suspected
GST or IST if secondary adrenal insufficiency is suspected
for adrenal failure, cortisol should be given before results of investigations are available
hypothyroidism
very common in older ladies
primary hypothyroidism→ thyroid failure
usually autoimmune
can be drug induced
secondary hypothyroidism→ failure to produce TSH
usually part of complete pituitary failure
diagnosis and treatment of hypothyroidism
diagnosis→ static test
treatment→ thyroid hormone replacement
sex hormone deficiency
primary:
males→ testicular failure
females→ ovarian failure
secondary:
pituitary failure
presentation of sex hormone deficiency
males:
erectile dysfunction
reduced libido
females:
menstrual abnormalities (amenorrhoea)
diagnosis and treatment of sex hormone deficiency
diagnosis:
static tests for testosterone, oestradiol, FSH, LH
treatment:
hormone replacement therapy
pituitary hormone replacement
pituitary failure
may be due to:
large tumour
infarction
usually involves multiple hormones and combination of static and stimulatory tests required to make diagnosis
pituitary independent endocrine abnormalities
increased parathyroid hormone production may be due to:
primary hyperparathyroidism
cancers
drugs
homeostasis
state of steady internal physical and chemical conditions maintained by living systems
condition of optimal functioning for organism
negative feedback loop
mechanism that reduces effect of change and helps maintain balance in a system
occurs when the output of a system used to reduce or regulate its own activity
components of negative feedback loop
receptors/sensors→ detects change
control centres→ compares change to normal and initiates response
effectors→ acts to revert change back to normal
normal blood glucose levels
4-6nM
response to high blood sugar
blood sugar too high
beta cells release insulin:
glucose taken up by various tissues
liver reduces gluconeogenesis
blood sugar levels fall
repsonse to low blood sugar
alpha cells release glucagon
liver increases production of glucose
blood sugar levels rise
response to high body temperature
hypothalamus detects raise in temp of blood
signals to skin to vasodilate and sweat→ heat is lost
body temperature falls
response to low body temperature
hypothalamus detects fall in blood temperature
signals to skeletal muscles to shiver to generate heat
skin vasoconstricts to reduce heat loss
temperature rises
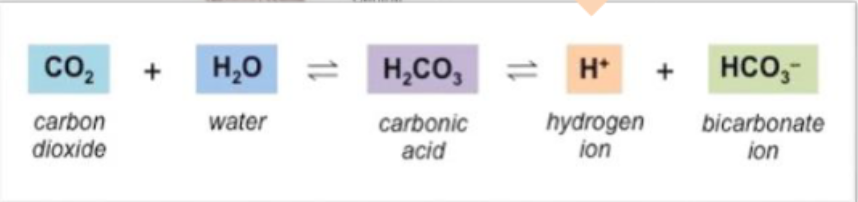
blood gases
O2 and CO2 have separate and different negative feedback loops
CO2levels control breathing:
if CO2 rises by 10%, resp. rate doubles
O2 levels don’t influence breathing until arterial O2 drops by 40%
response to hypercapnia (high CO2)
detected by central chemoreceptors
brain stem sends signals to diaphragm and intercostal muscles
person breathes deeper and more rapidly
more CO2 exhaled
CO2 levels fall
carbonic acid/bicarbonate system
more CO2 =more acidic blood
response to respiratory alkalosis
respiratory alkalosis caused by low CO2
Respiratory compensation:
inhibition of arterial and CSF chemoreceptors=decreased resp. rate
renal compensation:
H+ ions made and HCO3- ions secreted
other buffer systems release H+ ions
combined effects increase CO2, Increased H+, decreased HCO3-
plasma pH returns to normal
response to respiratory acidosis
respiratory acidosis due to increased CO2 conc.
Respiratory compensation:
stimulation of arterial and CSF chemoreceptors= increased resp. rate
renal compensation:
H+ secreted and HCO3- generated
other buffer systems accept H+ ions
combined effects decreased H+ and increased HCO3-
plasma pH returns to normal
responses to hypoxia
detected by peripheral (carotid body) chemoreceptors
brain stem sends signals to diaphragm and intercostal muscles
rapid, shallow breaths
more oxygen is breathed in absorbed into blood stream
O2 levels rise
ways of increasing blood pressure
vasoconstriction
increased cardiac output
RAAS activation
EPO production (bone marrow produces more rbc)
immediate response to low blood pressure
falling blood pressure=baroreceptors inhibited
vasomotor center stimulated→ vasoconstriction occurs
cardioacceleratory centers stimulated, cardioinhibitory centers inhibted→ increased cardiac output
blood pressure rises
renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system
blood flow through kidneys (renal perfusion) decreases→ renin released
renin causes angiotensin (made in liver) to be converted to angiotensin I
surface of pulmonary and renal endothelium releases ACE
ACE causes angiotensin I to be converted to angiotensin II
brings about effects raising blood pressure
effects of RASS
sympathetic activity
tubular Na+ and Cl- reabsorption and K+ excretion→ water retention
vasoconstriction
increased ADH secretion→ water retention
immediate response to high blood pressure
rising blood pressure= baroreceptors stimulated
cardioinhibitory centers stimulated cardioacceleratory centers inhibited→ decreased cardiac output
vasomotor centers inhibit→ vasodilation
homeostasis restored
blood pressure too high-long term response
natriuretic peptides released by the heart
responses to ANP and BNP cause effects which reduce blood volume
homeostasis is restored
responses to ANP and BNP
increased Na+ loss in urine
increased water loss in urine
reduced thirst
inhibition of ADH, aldosterone, epinephrine and norepinephrine release
peripheral vasodilation
ways to decrease blood pressure
vasodilation
decreased cardiac output
ANP/BNP release
response to high levels of calcium
parafollicular C cells of the thyroid release calcitonin:
calcium deposited in bones
more calcium excreted in urine
less calcium absorbed from food
calcium levels fall
response to low levels of calcium
parathyroid glands release parathyroid hormone:
calcium released from bones
more calcium reabsorbed by kidneys
kidneys activate vitamin D→ more calcium absorbed from gut
calcium levels rise
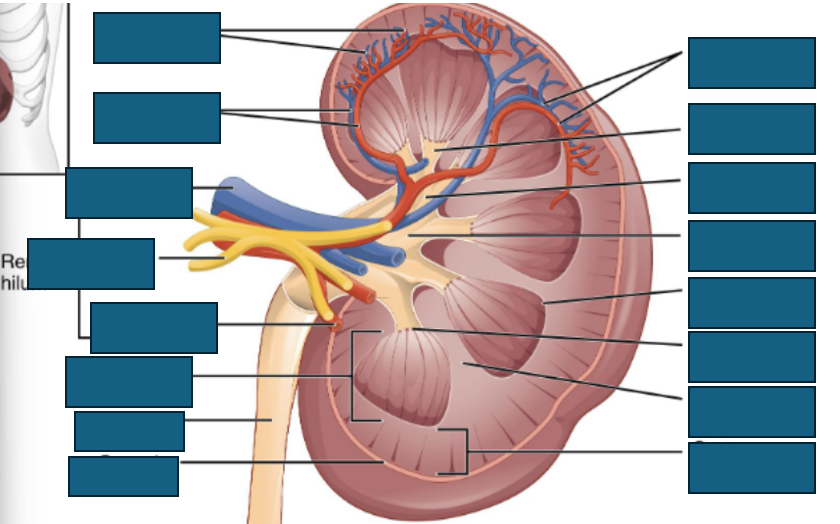
kidney anatomy

functions of the kidney
fluid balance
electrolyte homeostasis
endocrine functions:
EPO production
Vitamin D activation
pH regulation
Blood filtration
blood pressure control
glomerular filtration
blood enters glomerulus via afferent arteriole
passes through glomerulus, where it is filtered due to blood pressure→ plasma forced through barrier
blood exits through efferent arteriole
serum and urine osmolality
osmolality→ concentration of dissolved particles in a fluid
normal serum osmolality→ 275-295 mOsm/kg
mostly determined by sodium, glucose and urea
fluctuates based on hydrations status and is tightly regulated by ADH and other homeostatic mechanisms
anatomy of a nephron
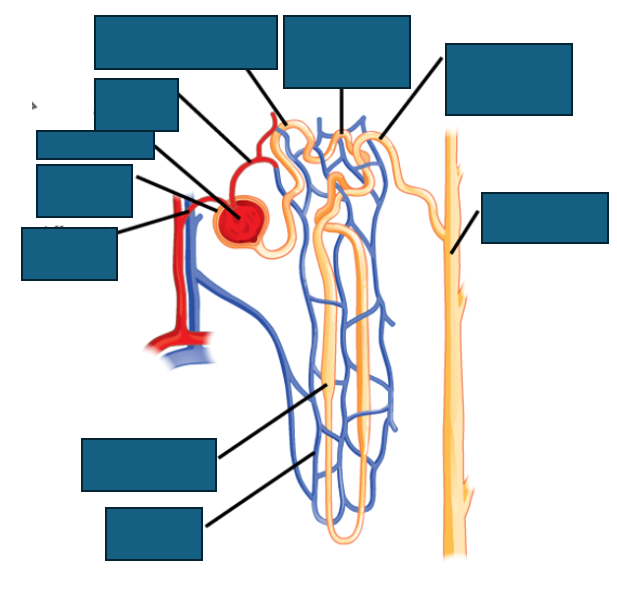
sodium reabsorption
hormones acting on the kidney
antidiuretic hormone→ increases water reabsorption via aquaporins in collecting ducts
aldosterone→ influences retention of sodium, excretion of potassium: controls BP and water retention
EPO
erythroppoietin
hormone produced in kidney
stimulates erythropoiesis→ RBC production
vitamin D
important role in calcium homeostasis
step in metabolic activity occurs in kidney
components of the U&E
sodium
potassium
urea
creatinine
chloride
bicarbonate
sodium
main extracellular cations and determines effective extracellular fluid osmolality
osmolality/tonicity gradients→ osmotic pressure gradients
serum sodium→ concentration determined by total body water
potassium
primarily intracellular cation
cellular uptake mediated by sodium/potassium ATPase
excretion is mostly renal
urea
produce din liver as waste product of protein breakdown
serum urea raised in:
kidney failure
upper GI bleeding
dehydration
uraemic symptoms:
pruritus
encephalopathy
gout
creatinine
waste product of muscle metabolism
higher in those with greater skeletal muscle mass
excreted almost entirely by kidney
serum creatinine can be used as proxy for kidney’s ability to filter creatinine from blood
bicarbonate
determined by CO2, bicarbonate and other factors
bicarbonate is basic
kidney can adjust bicarbonate to maintain normal pH
GFR
sum of filtration in all glomeruli
inulin clearance is gold standard way of measuring GFR:
inulin freely filtered, not reabsorbed and not secreted by kidneys
issues with GFR
impractical due to injection/infusion and multiple measurements
expensive
time consuming
not widely available
eGFR
estimated glomerular filtration rate
creatinine used as surrogate marker of renal function
can be used to calculate eGFR using factors e.g. age, gender, ethnicity
normal eGFR >90mL/min/1.73m2
muscle mass and eGFR
high muscle mass→ high baseline Cr→ false low eGFR
low muscle mass→ low baseline Cr→ false high eGFR
diet and eGFR
creatinine found in meat/supplements
can transiently raise serum creatinine
tubular secretion and eGFR
some drugs block tubular secretion of creatinine
creatinine rises→ eGFR falls, but actual GFR is unchanged
acute kidney injury
decrease in renal excretory function
occurs over hours to days
can result in failure to maintain fluid, electrolyte and acid-base balance
oliguria
decreased urine output
<0.5ml/kg/hour (<20/30ml/hour for most adults)
anuria
absence of urine output