Muscle and Neural Tissue
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/22
Last updated 8:11 PM on 2/12/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
1
New cards
Actin and Myosin
Filaments within muscle fibers
2
New cards
Contraction
Function of muscle fibers
3
New cards
Skeletal Muscle Tissue
forms the flesh of the body, cells are long, cylindrical, striated (striped) and multi-nucleated (peripheral) with many mitochondria, have blunt ends
4
New cards
Location of Skeletal Muscle Tissue
\-Combined with connective tissues and neural tissue in skeletal muscles
\-Attached to skeleton or skin
\- tongue
\-Attached to skeleton or skin
\- tongue
5
New cards
Function of Skeletal Muscle Tissue
\-Moves or stabilizes the position of the skeleton
\-guards entrances and exits to the digestive, respiratory, and urinary tracts
\-generates heat
\-protects internal organs
\-Voluntary muscle
\-guards entrances and exits to the digestive, respiratory, and urinary tracts
\-generates heat
\-protects internal organs
\-Voluntary muscle
6
New cards
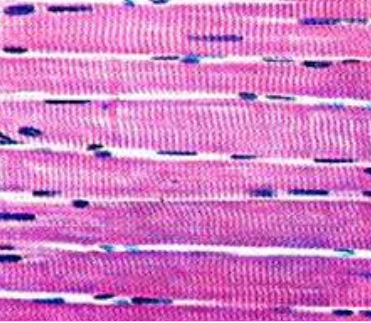
\
Skeletal Muscle Tissue
7
New cards
Cardiac Muscle Tissue
cells are short, branched, single nucleus, with some striations, cells connected by intercalated discs (joints between cells)
\-gap junctions allow ions to pass freely from cell to cell (rapid electrical impulse so cells beat in unison)
\-gap junctions allow ions to pass freely from cell to cell (rapid electrical impulse so cells beat in unison)
8
New cards
Location of cardiac muscle tissue
Heart
9
New cards
Function of cardiac muscle tissue
\-Circulates blood by causing the heart to pump
\-maintains blood pressure
\-involuntary muscle
\-maintains blood pressure
\-involuntary muscle
10
New cards
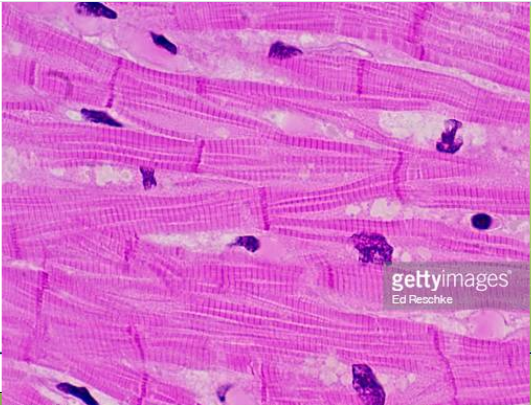
\
Cardiac Muscle Tissue
11
New cards
Smooth Muscle Tissue
\-Cells are short, spindle-shaped and nonstriated, single, central nucleus
\-When contracts, cavity becomes smaller, when relax they expand
\-Moves slower than other muscle types
\-When contracts, cavity becomes smaller, when relax they expand
\-Moves slower than other muscle types
12
New cards
Location of smooth muscle tissue
Found in the walls of hollow organs: digestive, respiratory, urinary and reproductive organs, blood vessels, skin (arrector pili)
13
New cards
Function of smooth muscle tissue
\-Moves food, urine and reproductive tract secretions
\-controls diameter of respiratory passageways
\- regulates diameter of blood vessels
\-Involuntary muscle
\-controls diameter of respiratory passageways
\- regulates diameter of blood vessels
\-Involuntary muscle
14
New cards
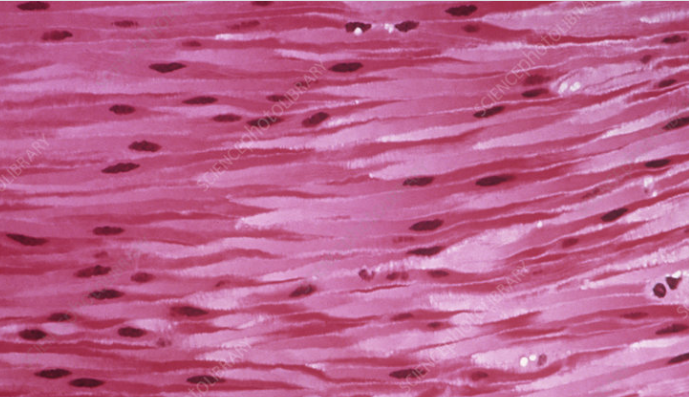
\
Smooth Muscle Tissue
15
New cards
Location of Neural Tissue
Brain, spinal cord, nerves
16
New cards
Function of Neural Tissue
Communicate through electrical impulses
17
New cards
Neuron
cell body with dendrites, long axon
18
New cards
Neuroglia
designed to insulate, support, and protect neurons
19
New cards
Neurons and Neuroglia
The 2 types of neural tissue
20
New cards
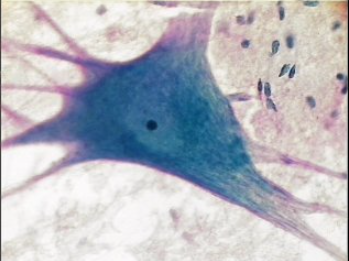
\
Neuron
21
New cards
\
Neuroglia
22
New cards
Intercalated discs
joins between cells
23
New cards
Gap junctions
allow ions to pass freely from cell to cell (rapid electrical impulse so cells beat in unison)