Physics Electrostatics Vocab
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Electric charge
The property acquired by a material due to rubbing, causing objects to attract or repel each other.
Like charges
Repel each other.
Opposite charges
Attract each other.
Electric force
The force exerted between charged objects.
Magnetic vs. electric interactions
Not the same; atoms have a neutral charge unless they gain or lose electrons.
Ion
An atom or object that has gained or lost electrons.
Positive ion
An object that has lost an electron.
Negative ion
An object that has gained an electron.
Conductor
A material that contains free-moving charged particles, allowing charge transfer.
Insulator (Dielectric)
A material where charges cannot freely move but can shift through polarization.
Electric charge symbol
q or Q.
Electric charge unit
Coulombs (C).
Quantization of charge
Charge changes only in specific increments.
Conservation of charge
Charge cannot be created or destroyed, only transferred.
Coulomb's Law
Describes the force between two charges: \( F = k \frac{q_1 q_2}{r^2} \).
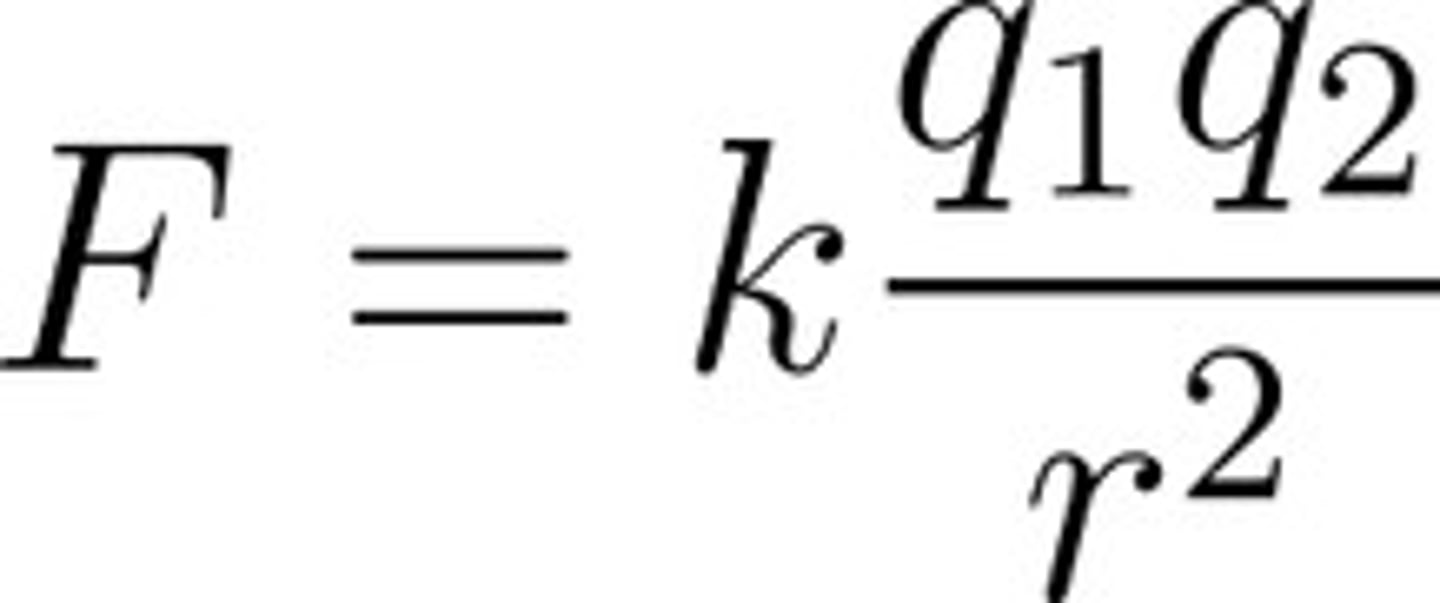
Charge of a proton
\( 1.6 \times 10^{-19} \) C.
Charge of an electron
\( -1.6 \times 10^{-19} \) C.
Newton's Law of Universal Gravitation
\( F = G \frac{m_1 m_2}{r^2} \), describing gravitational force.
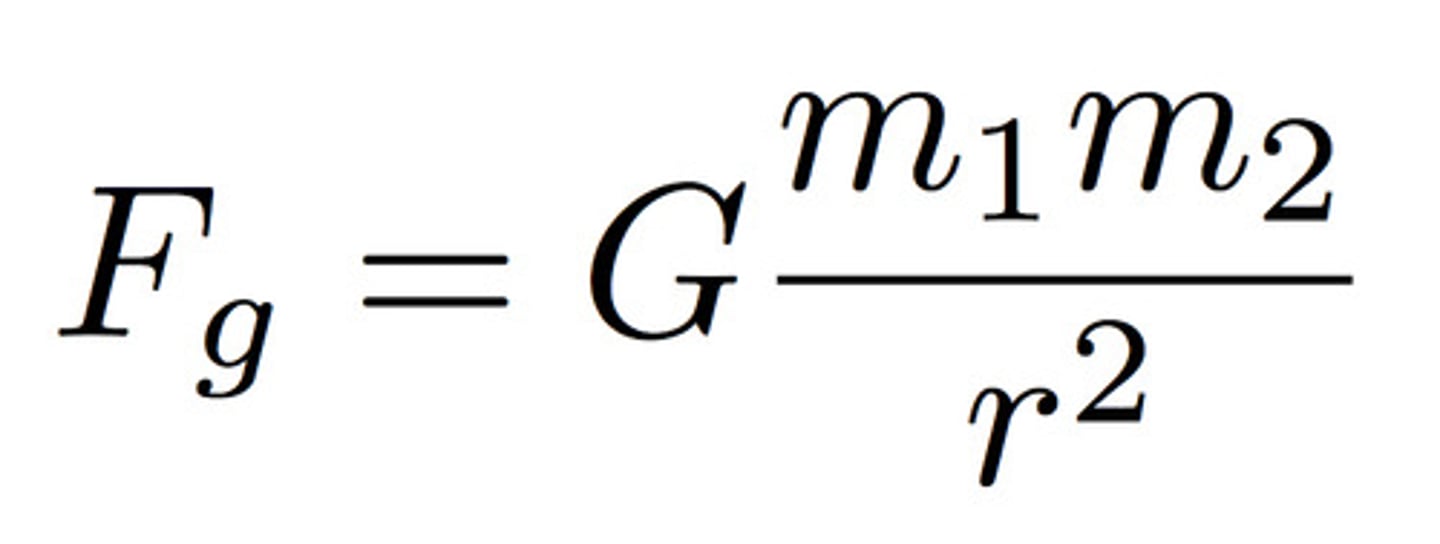
uninversal gravitational potential energy
mass (earth) mass (object) radius (E*O)
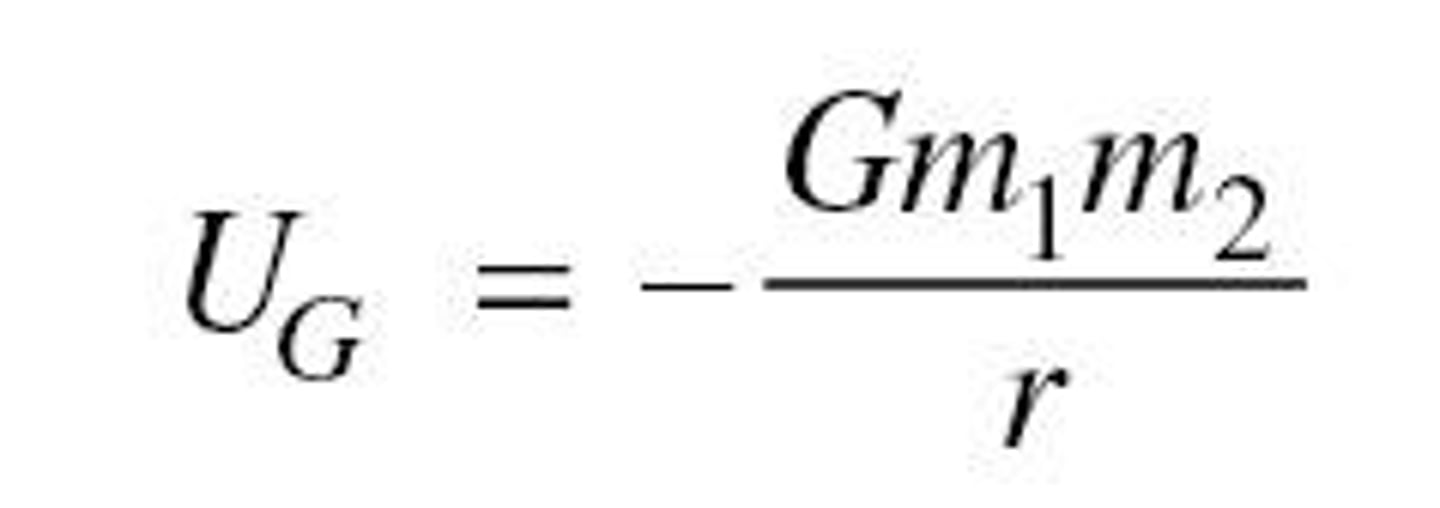
Potential energy bar charts
Show initial gravitational potential energy (\( U_g \)), work done, and final gravitational potential energy (\( U_g \)).