Chapter 13 + 14: Federal Reserve Monetary Policy Tools and Effects
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
What is the federal funds rate?
The interest rate at which banks lend reserves to each other overnight.
What does IORB stand for?
Interest (rate) on reserve balances.
What is ON RRP?
Overnight reverse repurchase agreement
Why doesn't the Fed have a specific target for the unemployment rate?
The level of maximum employment varies over time with business conditions, demographics, and other factors.
What is the federal funds market?
The market for interbank funds, where banks lend reserves to each other.
How are funds transferred in the federal funds market?
From the lender's reserve balance account at the Fed to the borrower's account.
What is the reservation rate?
The lowest interest rate at which a lender is willing to lend.
How is the reservation rate connected to IORB?
Banks should not lend at a lower rate than they can earn at IORB.
What is arbitrage?
The simultaneous buying and selling of the same commodity in different markets to profit from price differences.
How does arbitrage relate to IORB?
If the FFR falls below IORB, borrowers would borrow at FFR and deposit at IORB, increasing FFR.
Can all financial institutions have a reserve account at the Fed?
No, some are too small or not banks.
What could cause the FFR to fall below IORB?
A lack of arbitragers or banks authorized to borrow at FFR.
What is the purpose of the Overnight Reverse Repurchase Agreement Facility?
To keep the FFR close to IORB by allowing non-bank financial institutions to lend at ON RRP.
How do institutions use the ON RRP facility?
To deposit funds at the Fed and earn the ON RRP.
What is an administered rate?
A rate set directly by the Fed, not determined by the market.
Why can't the FFR fall below the ON RRP?
Lenders won't lend below ON RRP, and arbitrage would raise FFR to ON RRP.
Why does the discount rate act as a ceiling on the FFR?
Borrowers prefer to borrow at the discount window rather than pay a higher rate in the federal funds market.
What is the stigma associated with using the discount window?
It signals poor condition of the bank, as it is typically used in times of trouble.
What are open market operations (OMO)?
The Fed's sales or purchases of Treasury securities in the open market.
Why does the Fed conduct OMO?
To change the supply of reserves to ensure it intersects the demand for reserves.
How does the Fed conduct expansionary monetary policy?
By lowering all three administered rates.
How does the Fed conduct contractionary monetary policy?
By raising all three administered rates.
How does a change in the federal funds rate influence consumer and business decisions?
Lower rates decrease borrowing costs, encouraging spending and investment, which can decrease unemployment.
What happens when interest rates rise?
Increases borrowing costs, which can decrease spending and investment, potentially raising unemployment.
What was the primary goal of the Federal Reserve when it was created in 1913?
To make the American banking system more stable and reduce bank panics.
What was the major monetary tool of the Federal Reserve at its founding?
The discount rate.
When did open market operations become an important monetary tool of the Federal Reserve?
By the 1920s.
What does traditional monetary policy do?
Changes the money supply to change interest rates.
What monetary tools are included in traditional monetary policy?
Open market operations, reserve requirements, and the discount rate.
What initiated nontraditional monetary policy?
Interest rates were zero after the Great Recession.
What are some tools of nontraditional monetary policy?
Quantitatie easing, tightening, administer rates like IORB and ON RRP, forward guidance.
How can nominal interest rates be negative?
If banks pay zero interest on deposits and charge a fee to keep deposits.
What is the connection between negative nominal interest rates and nontraditional monetary policy?
Negative interest rates encourage banks to increase lending to stimulate the economy.
What is a repurchase agreement?
An agreement where the Federal Reserve buys short-term securities from a bank with a promise to resell them later.
What is a reverse repurchase agreement?
An agreement where the Federal Reserve sells short-term securities to a bank with a promise to buy them back later.
Why is the federal funds rate important?
It influences other market interest rates and lending activity.
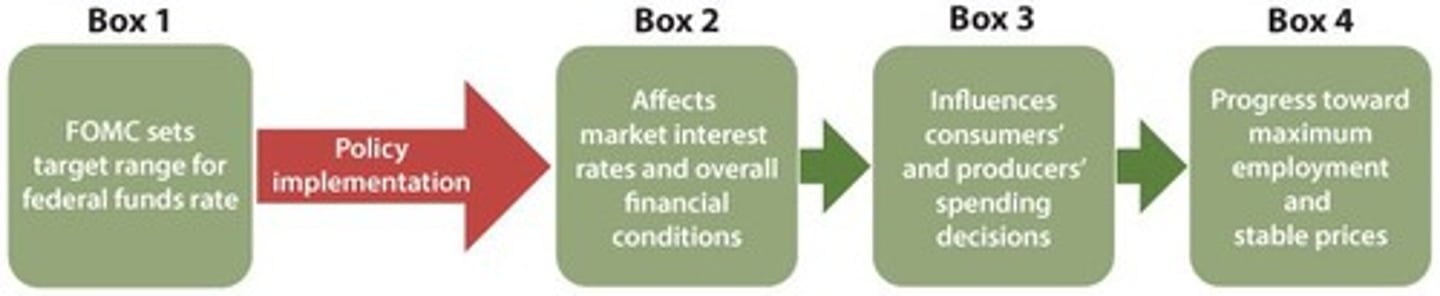
How does the Federal Reserve influence the federal funds rate?
By using interest on reserve balances and ON RRP as a floor for the FFR.
What is the effect of expansionary monetary policy on the economy?
It reduces the federal funds rate, lowers interest rates, increases aggregate spending, output, and employment.
What is the effect of contractionary monetary policy on the economy?
It increases the federal funds rate, reduces spending, output, and employment.
How did Paul Volcker tame the Great Inflation of the 1970s?
By adopting a restrictive monetary policy that raised short-term interest rates to about 20 percent.
What was the cost of Volcker's success in taming inflation?
The worst recession for the U.S. since the Great Depression.
What did the Federal Reserve do during the Great Recession of 2007-2009?
Enacted an expansionary monetary policy, purchased short-term government securities, and cut the discount rate.
What was one method the Federal Reserve used to lower long-term interest rates during the Great Recession?
Quantitative easing.
What did the Federal Reserve do to stabilize the economy during the COVID-19 pandemic?
The Fed cut lowered the FFR to 0-25% and kept it there for 2 years
What monetary policy did the Federal Reserve adopt during the COVID-19 pandemic?
An expansionary monetary policy by slashing the federal funds rate, reestablishing quantitative easing, and providing forward guidance.
What was the target federal funds rate set by the Federal Reserve in March 2020?
0-25%.
When were zero interest rates lifted by the Federal Reserve?
March 2022.
What led to the Biden administration's decision to stimulate the economy?
Fears that low interest rates were insufficient to avert a long recession.
What was the initial response of the Federal Reserve to rising inflation during the pandemic?
They insisted that inflation was temporary and referred to it as transitory.
What was the inflation rate in July 2022?
9.1%.
What actions did the Federal Reserve take from March 2022 to September 2023 regarding the federal funds rate?
Increased the rate from 0.25-0.5 percent to 5.25-5.5 percent.
What is quantitative tightening?
The process of shrinking the Federal Reserve's balance sheet by reducing holdings of Treasury and mortgage-backed securities.
What are the major strengths of monetary policy?
Speed of implementation, flexibility, and insulation from political pressure.
What are the weaknesses of monetary policy?
Timing lags, asymmetry of the business cycle, and negative supply shocks.
What is inflation targeting?
A rules-based approach where the Federal Reserve forecasts inflation and adjusts monetary policy based on the difference from the target rate.
How does the Federal Reserve modify monetary policy under inflation targeting?
By adopting contractionary policy if forecasted inflation exceeds the target.
What must the Federal Reserve do to retain the ample reserves framework?
Increase the amount of reserves in the system using expansionary open market operations.
What is the initial margin requirement set by the Federal Reserve?
The percentage of the purchase price of securities that must be covered by the investor's own money.
How can the initial margin requirement be used as a tool of monetary policy?
By increasing it to offset a stock market bubble.
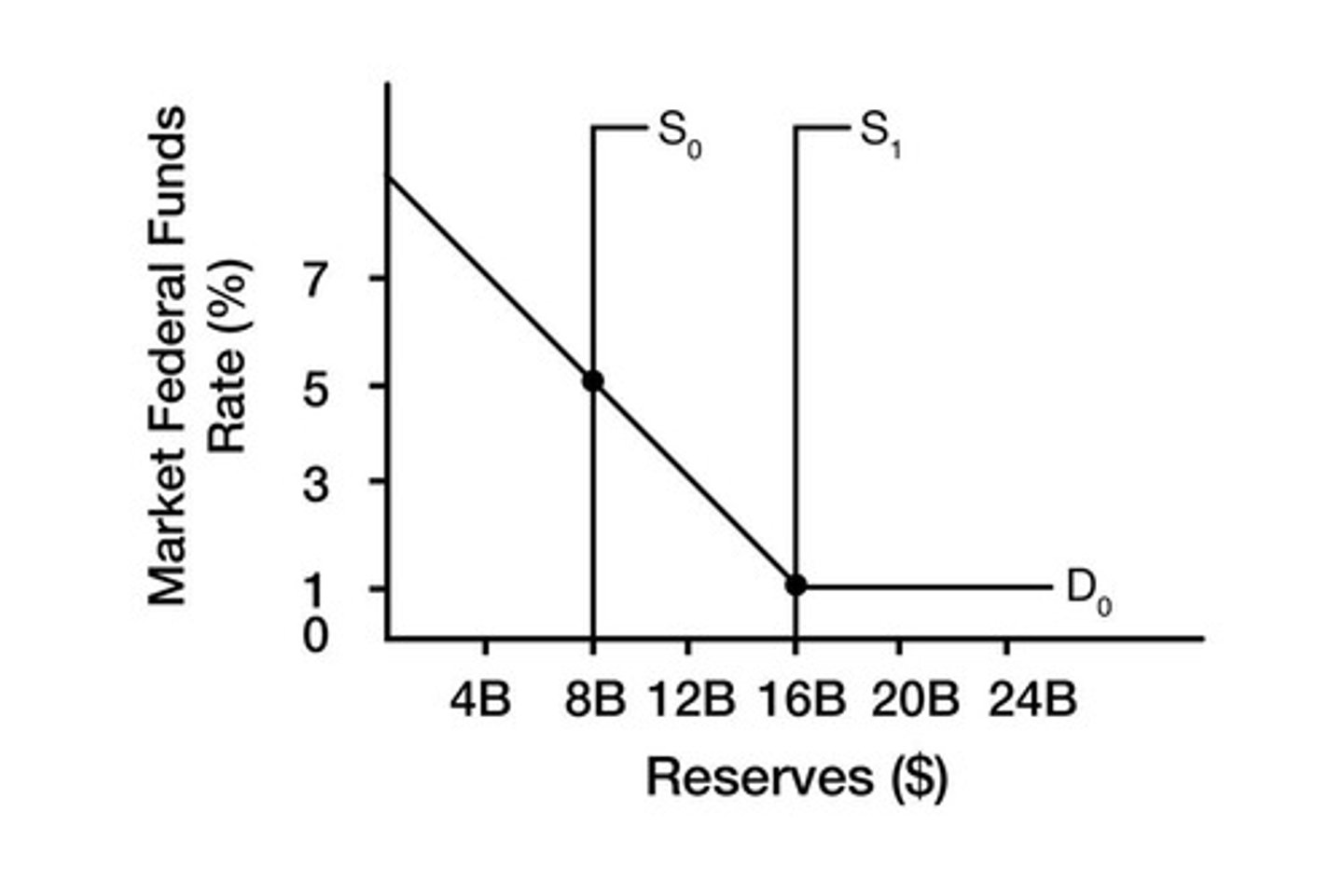
What is the equilibrium federal funds rate if the supply curve intersects the demand curve at its lowest point?
1 percent.
If the demand for reserves rises, where does the new equilibrium intersect the demand curve?
At its downward-sloping portion.
What challenges did the Federal Reserve face in addressing inflation without triggering a recession?
How to slow down the economy and reduce inflation without causing a hard landing.
What economic factors contributed to the inflation during the COVID-19 pandemic?
Supply shortages, new COVID variants, Russia's invasion of Ukraine, and China's lockdowns.
What was the Federal Reserve's expectation regarding inflation during the pandemic?
That it would dissipate once structural imbalances were resolved.
What was the Federal Reserve's approach to interest rates during the recession of March-April 2020?
They lowered the interest rate to stimulate the economy.
What did the Trump administration do in 2020 to stimulate the economy?
Sent out $1,200 individual checks.
What is the significance of the term 'transitory' in the context of inflation?
It refers to the belief that inflation would be temporary.
What is the role of the Federal Reserve in setting the initial margin requirement?
To regulate the percentage of securities purchases that must be financed by the investor's own funds.