Unit 2 Biological molecules test/quiz
1/75
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
76 Terms
What are the monomers of Carbohydrates?
Monosaccharides
What atoms make up carbohydrates?
Carbon, oxygen, hydrogen
What is another name for simple sugars?
Monosaccharides
What are the three monosaccharides?
Glucose
Galactose
Fructose
What is another name for complex sugars?
Polysaccharides
What is two simple sugars together?
Disaccharides
What are the 3 disaccharides?
Sucrose
Maltose
Lactose
What 2 sugars make up sucrose?
Glucose + Fructose
What 2 sugars make up Maltose?
2 glucoses
What 2 sugars make up Lactose?
Glucose + Galactose
What is the main function of Carbohydrates?
To provide energy and structure to plants
Where can carbohydrates be found?
Plant cells and carb based foods
Examples of Carbohydrates?
Sugars
Starches
Cellulose
What is Cellulose?
Plant cell wall
Monomers of lipids?
Triglyceride
Glycerol
Fatty acids
What is another name for lipids?
Triglyceride
What is the function of lipids?
To provide energy (2x that of carbohydrates)
Where can lipids be found?
Fats and oils
Examples of Lipids?
Fats
Oils
Steroids
Cholesterol
What is the structure of lipids?
There is a hydrophilic head and a hydrophobic tail
What does hydrophilic mean?
Attracted to water
What does hydrophobic mean?
Repels water
What is a phospholipid bilayer?
2 sheets of triglycerides, the tails going together and the head facing out
What is Emulsification?
The process of blacking down lipids
What is an example of a emulsifier?
Soup is an example
What are the 2 types of cholesterol?
High-density lipoprotein (HDL)
Low-density lipoprotein (LDL)
Which type of cholesterol is bad?
Low-density lipoprotein (LDL)
What is atherosclerosis?
A disease that causes plaque to build up one the arteries and block blood flow.
What causes atherosclerosis?
Low-density lipoprotein (LDL)
What are the monomers of proteins?
Amino acids
What atoms make up proteins?
Carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen, sulfur (CHONS)
What is the main function of proteins?
To regulate chemical reactions
To transport materials
A. Oxygen (in blood)
B. CO2
Where can you find proteins?
In all cells
Proteins make up all cells
Where can you find proteins?
In all cells
Muscles
What do proteins control?
Muscles
What do proteins fight?
Diseases
Viruses
Bacterial infections
How many amino acids are there?
20
What are the 3 groups in an amino acid?
the Amino group (NHH)
The side chain (GHR)
The Carboxyl group (COOH
What makes the side chain special?
The side chain is what distinguishes the amino acid from the 20 different types
Structures of proteins from simple to complex.
Primary structure
Secondary structure
Tertiary structure
Quaternary structure
What is the primary structure?
The amino acid chain
What is the secondary structure?
Alpha-Helixes (made from amino acids)
What is the Tertiary structure?
Polypeptide chains
What is the Quaternary structure?
The complex of protein molecules
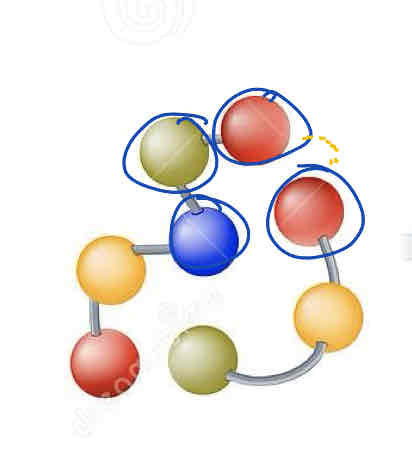
What is this in the protein structure?
The primary structure, amino acids
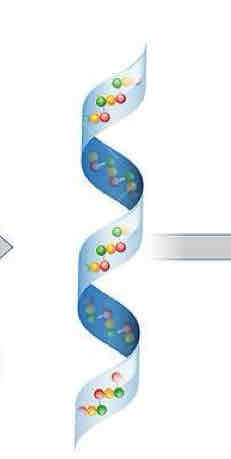
What is this in the protein structures?
The secondary structure, Alpha-Helixes

What is this in the protein structures?
The Tertiary structure, polypeptide chains
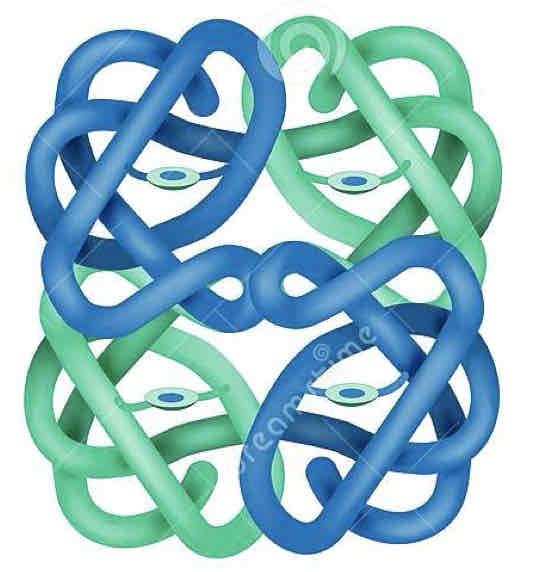
What is this in the protein structures?
The quaternary structure, complex protein molecules
Where is the hemoglobin?
In red blood cells
What does the hemoglobin do?
Transports oxygen from the lungs to other parts of the body
How does oxygen, iron, and the hemoglobin work together?
The oxygen bonds with the iron (together called the Heme), the iron is connected to the polypeptide chains
How is the hemoglobin relate to a bus
Red blood cells = The bus
Polypeptide chains = the row of seats
Iron = the seats on a bus
Oxygen molecule = the passenger
What is Sickle Cell Anemia?
Cockle cell anemia is a mutation of the blood cell where the cell is misshapen and the hemoglobin is deformed. Causing it to not be able to hold oxygen, and blocks blood flow.
What does having an iron deficiency do?
There is no heme in the hemoglobin so it can not hold oxygen and you get faint.
What is denaturation?
When the protein unravels and losses its shape therefore it stops working.
What things cause denaturation?
High temperature
High salt levels
High acidity
What are the monomers of Nucleic acids?
Nucleotides
What is the main job of Nucleic Acids?
Holds genetic information
regulates protein synthesis
Where can you find Nucleic Acids?
In the nucleus
What are examples of Nucleic Acids?
Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA)
Ribonucleic Acid (RNA)
What are the differences between DNA and RNA?
DNA = double-stranded. RNA = single-stranded
DNA = double helix. RNA = single helix
DNA = has thymine. RNA = has Uracil
What are the three parts of the nucleotides?
The phosphate group
The nitrogenous Base (A,C,G,T/U)
Pentose sugar (5-carbon sugar)
What are the differences between the DNA and RNA nucleotides?
DNA’s nitrogenous base has thymine (T). RNA’s nitrogenous base has Uracil (U)
DNA does not have oxygen just hydrogen. RNA has both hydrogen and oxygen
DNA’s sugar is Deoxyribose. RNA’s sugar is Ribose
What is the A base?
Adenine
What is the C base?
Cytosine
What is the G base?
Guanine
What is the T base?
Thymine
What base does RNA have instead of the one in DNA?
U
What is the U base?
Uracil
What are the bases pairings?
A with T/U
C with G
What is a catalyst?
Speeds up chemical reactions and make them require less energy to do.
What are enzymes?
They provide activation energy
What is activation energy?
The amount of energy needed to start a chemical reaction
What do enzymes do?
Make chemical reactions go faster and happen
Act as a catalyst in a chemical reaction
Lowers the amount of activation energy needed to make the chemical reaction happen
Why is it important that enzymes retain their shapes?
Because without the right shape it would not work
What does the enzyme lactase break up?
The disaccharide Lactose → into Glucose and Galactose