P3.3 - Kinetic Theory
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
What are the assumptions of kinetic theory?
Volume of molecules is negligible compared to the size of the gas
Time between collisions is much longer than during
Collision between molecules are elastic
Forces of attraction between molecules are negligible
Gases consist a large number of molecules in rapid, random motion
What is an ideal gas?
A gas which strictly obeys the equation of state. With the exception of very high densities, a real gas approximates well to an ideal gas
What is ideal gas equation?
pV=nRT
pV=NkT
What are the 3 gas laws?
Pressure is inversely proportional to volume at constant T
Pressure is directly proportional to Temp at constant volume
Volume is directly proportional to T at constant pressure
What are the conditions for an ideal gas?
T and P aren’t too extreme
What are the assumptions of an ideal gas?
Collide with no loss of KE
Only exert forces on each other during collisions
Molecules are assumed to take up no space
What is the equation for the Boltzmann constant?
k=R/NA
What are the equations for moles?
n=N/NA
n=m/Mr
What is a mole?
The SI unit of an amount of substance. Amount containing as many particles as there are atoms in 12g of carbon-12
What is the avogadro constant?
Number of particles per mole
What is the equation for pressure exerted by a gas?
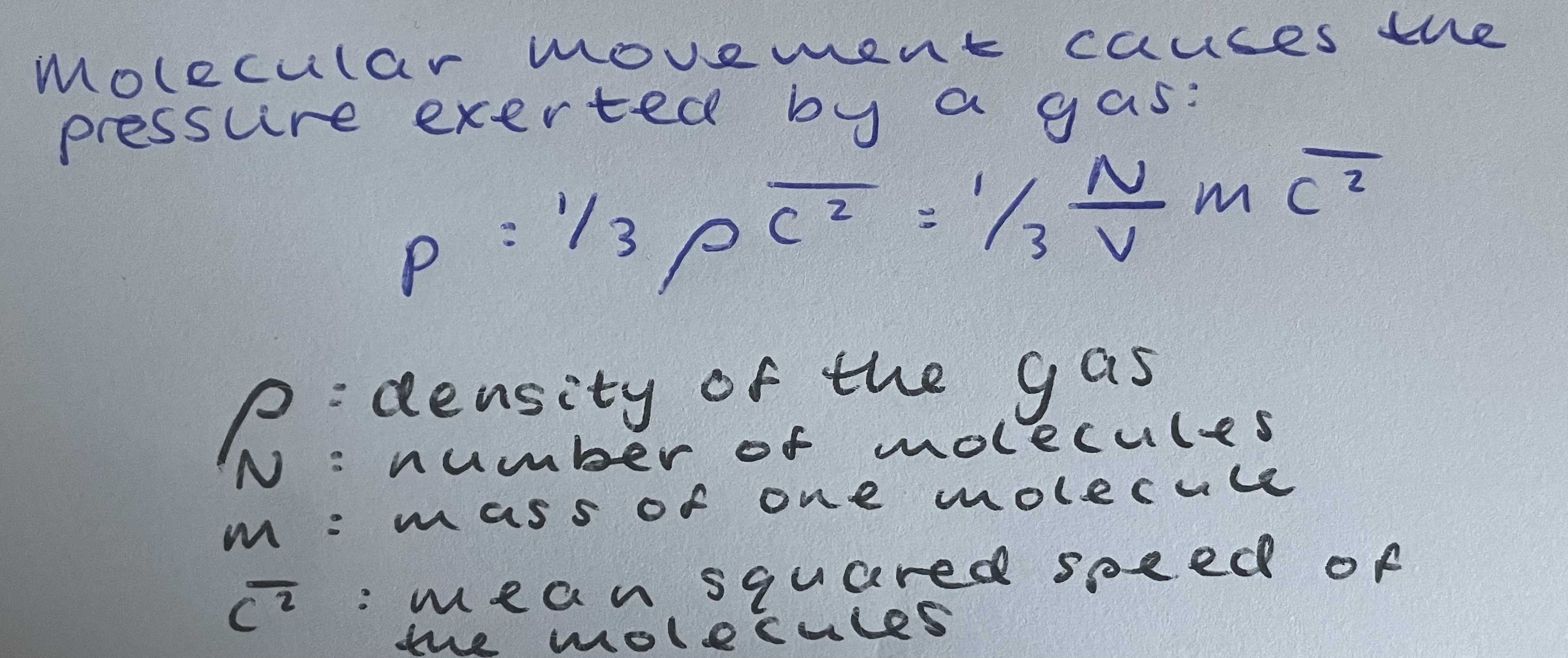
Why is mean squared speed used when calculating pressure?
Energy of the particles is distributed randomly. This is a way of representing the speed squared of an average molecule
What is relative molecular mass?
Mr
Mass of a molecule relative to the mass of Carbon-12
What is molar mass?
M
Mass of 1 mole of a substance
What is the equation for Molar Mass?
M/kg = Mr/1000
What causes the pressure exerted by a gas?
Molecular movement
What is the equation for total translational Kinetic Energy?
Total tKE= 3/2RT
What is the equation for the mean Kinetic Energy of a molecule?
Mean KE of a molecule = 3/2kT
What is the derivation for the equation for total translational kinetic energy?
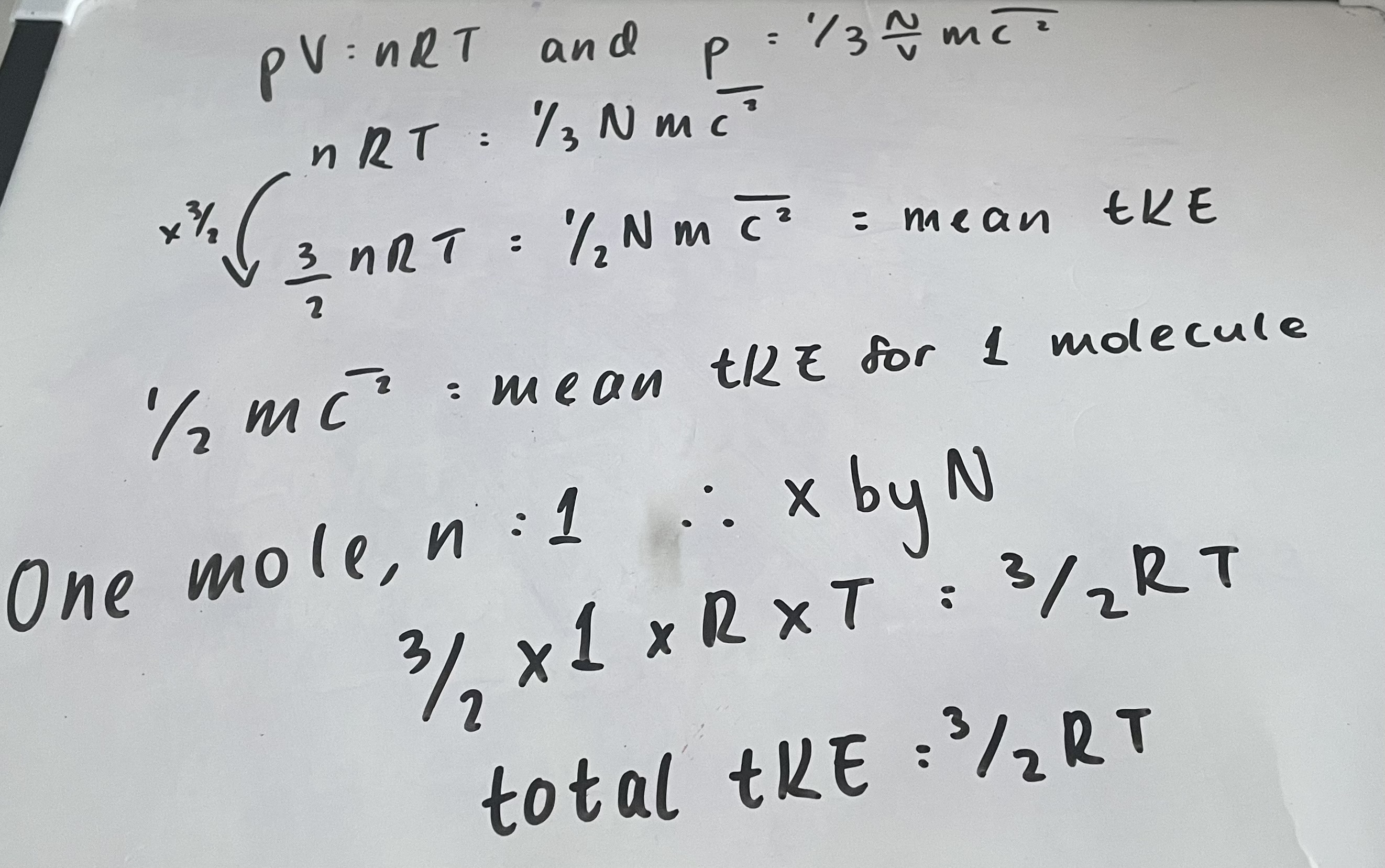
What is the derivation for the equation for the mean KE of a molecule?
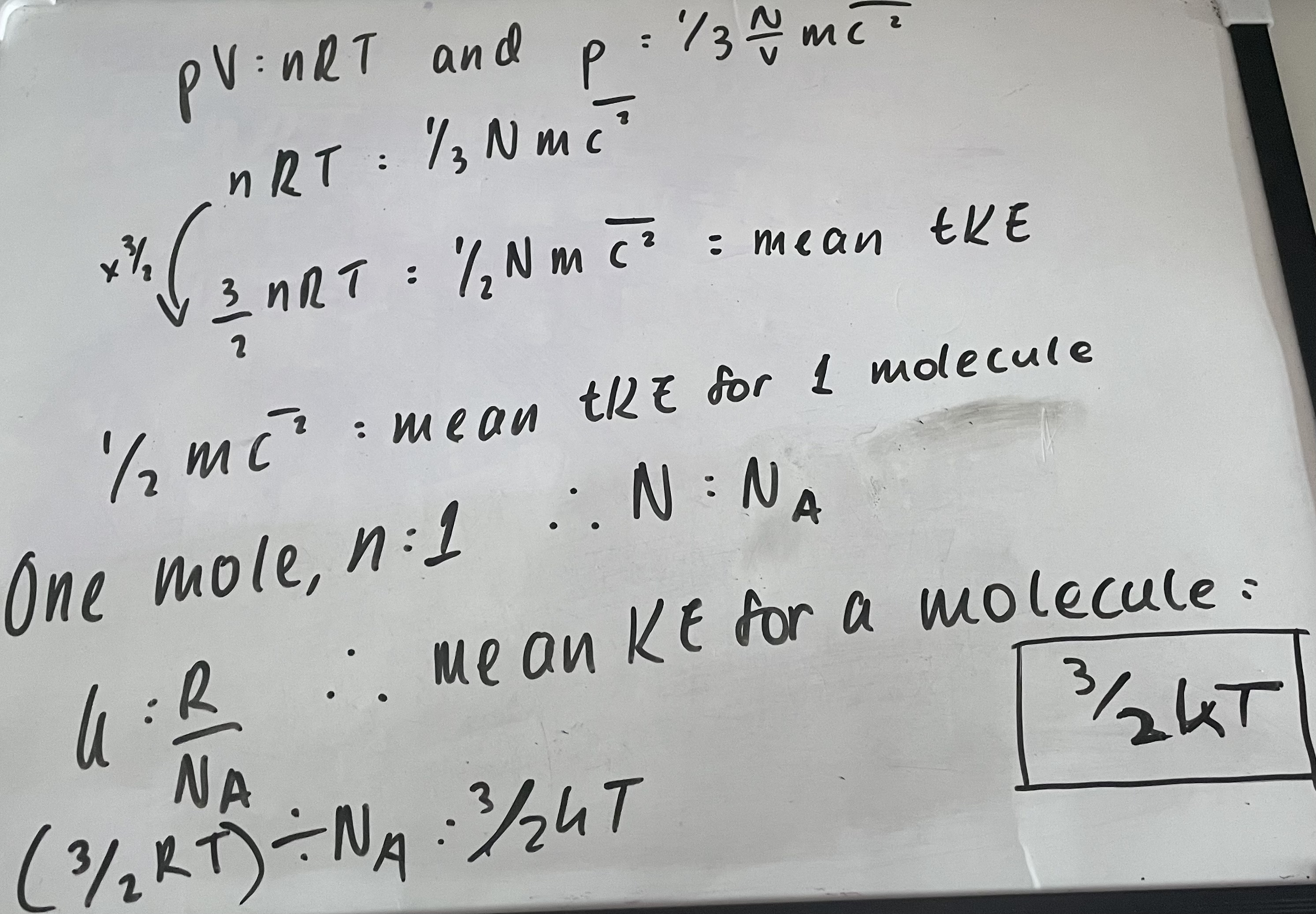
What are the 3 fundamental gas laws?
pV = constant
V/T = constant
p/T = constant
In the 3 fundamental gas laws, what is the value of the constant dependent on?
Mass of the gas
How do you calculate root mean square speed?
Add the square of the speeds, divide by the number of speeds. Square root
The equation pV=nRT works for many real gases as long as what?
The temperature and pressure of the gases aren’t too extreme