Naming and forming carboxylic acids
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
What functional group do carboxylic acids contain?
Carboxyl group (-COOH).
How are carboxylic acids named?
Find the longest carbon chain and add ‘-ioc acid.’
The carbon on the carboxyl group is always the first carbon.
The carboxyl group will be at the end of the molecule.
What type of acid are carboxylic acids?
Weak acids- they only partially dissociate to produce H+ ions.
CH3COOH(aq)⇌ CH3COO−(aq)+ H+(aq)
Explain why carboxylic acids are able to react as acids.
The hydrogen from the carboxyl group can be donated (Brønsted-Lowry acid).
This is because the negative charge which results from the loss of a hydrogen ion can be shared over the carbon and oxygen of the carbonyl group.
This delocalisation of charge stabilises the carboxylate ion and the following equilibrium occurs.
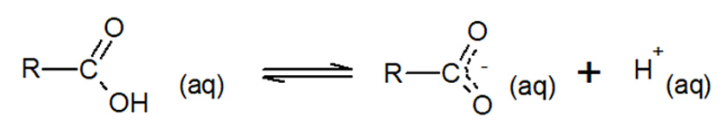
How are aliphatic carboxylic acids formed?
From oxidation of primary alcohols and aldehydes.
State the reagents / conditions needed to form carboxylic acids from primary alcohols and aldehydes.
An oxidising agent is used: acidified Cr2O72- , alkaline MnO4-
The reaction is heated under reflux.
Reflux is used as the aldehydes are often more volatile than their corresponding carboxylic acid, so whether the starting chemical is an alcohol or aldehyde, it ensures the reactant mixture stays in solution so that the further oxidation can take place.
What is an aromatic carboxylic acid?
A benzene ring with a -COOH group directly bonded to it.
How do you test for a carboxylic acid?
By reacting the carboxylic acid with sodium carbonate / sodium hydrogen carbonate.
CO2 gas is formed- effervenscence is observed.