using resources everything
1/114
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
115 Terms
What are ceramics?
Non-metallic, inorganic solids made by heating substances to high temperatures.
What are the properties of ceramics?
✅ Hard and brittle
✅ High melting points
✅ Good insulators of heat and electricity
✅ Resistant to corrosion
Why is clay useful for making pottery and bricks?
✅ It is soft when wet, so it can be shaped.
✅ It hardens when fired at high temperatures.
✅ It is strong and durable when set.
What is glass?
A transparent ceramic made by melting sand (silicon dioxide) and cooling it rapidly.
What are the properties of glass?
✅ Transparent
✅ Hard but brittle
✅ Resistant to chemicals
What are the two main types of glass their composition, properties and uses?
Type of Glass | Composition | Properties | Uses |
|---|---|---|---|
Soda-lime glass | Sand, limestone, sodium carbonate | Cheaper, easy to shape, brittle | Windows, bottles |
Borosilicate glass | Sand, boron trioxide | Higher melting point, resistant to heat | Lab glassware, ovenware |
What determines the properties of a polymer?
Type of monomers used.
conditions under which they were made
What are thermosoftening polymers?
Polymers with weak intermolecular forces between individual tangled chains, no crosslinks, allowing them to melt and reshape when heated.
What are their properties ( thermosoftening)?
✅ Softens when heated.
✅ Easily moulded into new shapes.
What are some uses of thermosoftening polymers?
✅ Plastic bags
✅ Water bottles
What are thermosetting polymers?
Polymers with strong cross-links between chains, making them rigid and heat-resistant with a high melting point as a lot of energy is needed to overcome these crosslinks
What are their properties ( thermosetting)?
✅ Does not melt when heated.
✅ Hard and durable.
What are some uses of thermosetting polymers?
✅ Electrical sockets
✅ Cooking pan handles
What is a composite?
A material made by combining two or more materials to improve properties.
How do composites work?
They have:
Reinforcement (strong material like fibres or fragments).
Matrix (binder) that holds the reinforcement together.
recall some examples of composites with their properties and uses
Composite | Properties | Uses |
|---|
Fibreglass | Strong, lightweight, waterproof | Boats, helmets |
Carbon fibre | Stronger and lighter than metal | Aerospace, sports cars |
Concrete | Hard, strong under compression | Buildings, bridges |
Wood (natural composite) | Strong, flexible, natural | Furniture, construction |
How is LDPE made ( low density polyethene) and its uses and properties
moderate temperatures
high pressure
catalyst
properties - flexiible, weaker
uses - carrier bags
How is HDPE made ( high density polyethene) and its uses and properties
low temperature
low pressure
catalyst
properties - rigid, stronger
uses - drainpipes
explain why HDPE has a higher density than LDPE
because in HDPE polymer chains are closer together so more atoms per unit of volume
What is the Haber Process used for?
It is used to manufacture ammonia from nitrogen and hydrogen.
What is ammonia used for?
Ammonia is mainly used to make fertilisers.
explain how the haber process works
The purified gases are passed over a catalyst of iron at a high temperature (about 450°C) and a high pressure (about 200 atmospheres). Some of the hydrogen and nitrogen reacts to form ammonia. The reaction is reversible so some of the ammonia produced breaks down into nitrogen and hydrogen:
nitrogen +hydrogen ⇌ammonia
What is the word equation for the Haber Process?
Nitrogen + Hydrogen ⇌ Ammonia
What is the balanced symbol equation for the Haber Process?
N₂(g) + 3H₂(g) ⇌ 2NH₃(g)
Why is the Haber Process a reversible reaction?
Ammonia can break down back into nitrogen and hydrogen.
Where does the nitrogen come from?
The air (which is 78% nitrogen).
Where does the hydrogen come from?
Reacting methane with steam (from natural gas).
Conditions for the Haber Process
Condition | Value Used | Why This Value? |
|---|
Temperature | 450°C | High enough for a fast reaction but not too high to reduce ammonia yield. |
Pressure | 200 atmospheres (200 atm) | Increases ammonia yield (favours forward reaction) without being too expensive/dangerous. |
Catalyst | Iron | Speeds up the reaction without affecting yield. |
What does the iron catalyst do?
It speeds up both forward and backward reactions so equilibrium is reached faster.
How is ammonia separated from the unreacted gases?
✅ Ammonia condenses into a liquid when cooled.
✅ Unreacted nitrogen and hydrogen are recycled back into the reactor.
What are NPK fertilisers?
Fertilisers that contain Nitrogen (N), Phosphorus (P), and Potassium (K) to help plants grow.
Why are fertilisers important?
✅ Increase crop yield.
✅ Replace nutrients removed by previous crops.
How is nitrogen supplied in fertilisers?
From ammonia, which is used to make ammonium nitrate (NH₄NO₃).
How is ammonium nitrate made?
Ammonia + Nitric Acid → Ammonium Nitrate
NH₃ + HNO₃ → NH₄NO₃
How is phosphorus supplied in fertilisers?
From phosphate rock, which must be treated because it is insoluble.
What acids are used to treat phosphate rock and what salts do they form?
Nitric acid → phosphoric acid and calcium nitrate are produced
The phosphoric acid is neutralised with ammonia forming ammonium phosphate
Sulfuric acid → Produces single superphosphate. ( a mixture of calcium phosphate and calcium sulfate)
Phosphoric acid → Produces triple superphosphate. ( calcium phosphate)
How is potassium supplied in fertilisers?
From potassium chloride (KCl) or potassium sulfate (K₂SO₄), both of which are soluble and can be used directly.
why must fertiliser compounds be soluble in water
so they can be absorbed by the root hair cells:
What is a life cycle assessment (LCA)?
A method used to assess the environmental impact of a product over its entire lifetime, from raw materials to disposal.
What are the four main stages of an LCA?
Raw material extraction – Obtaining resources from the Earth.
Manufacturing and processing – Converting raw materials into a product.
Use and operation – The product’s impact while being used.
Disposal – How the product is dealt with at the end of its life (landfill, recycling, etc.).
What are the environmental impacts of extracting raw materials?
Uses energy
depletes finite resources.
Causes pollution (e.g., mining damages habitats).
What are the environmental impacts of manufacturing and processing?
Requires energy
produces waste.
Some processes release harmful gases (e.g., CO₂ from factories).
What are the environmental impacts of product use?
Some products release pollutants (e.g., car emissions).
Energy consumption (e.g., electrical appliances).
Some products (e.g., reusable bottles) have low impact in this stage.
What are the environmental impacts of disposal?
Landfill takes up space and may cause pollution.
Incineration releases CO₂ but can generate energy.
Recycling reduces waste but requires energy.
How does an LCA help compare products?
It allows scientists to determine which product has a lower environmental impact.
Why are some LCAs not fully reliable?
Some stages are difficult to quantify (e.g., estimating pollution levels), and LCAs can be biased if companies manipulate data for marketing.
Compare the LCA of a plastic bag vs. a paper bag.
Stage | Plastic Bag | Paper Bag |
|---|
Raw Material | Crude oil (finite resource) | Trees (renewable but deforestation) |
Manufacturing | Requires energy, produces waste | Uses lots of energy and water |
Use | Reused many times | Often used once |
Disposal | Non-biodegradable, landfill issues | Biodegradable, decomposes faster |
✅ Plastic bags may be better overall if reused multiple times, despite their impact on disposal. |
Why is it important to reduce resource use?
To conserve finite resources (e.g., metals, fossil fuels).
To reduce pollution and waste.
To lower energy consumption and environmental impact.
What are the three key ways to reduce resource use?
Reduce, Reuse, Recycle
How does reducing help sustainability?
Using fewer raw materials reduces extraction and lowers energy use in manufacturing.
How does reusing help sustainability?
Extends a product’s life, meaning fewer new items need to be made. Example: Refilling glass bottles instead of making new ones.
How does recycling help sustainability?
Converts waste materials into new products.
Uses less energy than producing new materials.
Reduces landfill waste.
How is glass recycled?
Sorted by colour.
Crushed and melted.
Remoulded into new glass products.
How are metals recycled?
Separated from other waste. The amount of separation required for recycling depends on the material and the properties required of the final product.
Melted and reshaped into new products.
eg. some scrap steel can be added to iron from a blast furnace to reduce the amount of iron that needs to be extracted from the ore
What are the challenges of recycling metals?
Sorting different metals can be difficult.
Removing impurities takes time and energy.
What is potable water?
Water that has been processed and is safe for human consumption but not necessarily pure (may contain dissolved substances).
What are the key properties of potable water?
- pH between 6.5 and 8.5
- little dissolved substances
- free of bacteria or harmful microbes
Where and how is potable water obtained in the UK?
From fresh water sources (e.g., reservoirs, rivers, lakes)
Filtration (removes solids like sand and gravel) using a wire mesh screen or passing the water through filter beds to remove undissolved substances
Sterilisation (kills microbes using chlorine, ozone, or UV light)
what is surface water
water that can collect in lakes, resevoirs etc
what is groundwater
water that collects in aquifiers ( porous rocks that store water underground) underground
How is potable water obtained from seawater?
Through desalination by distillation or reverse osmosis (removes salt but requires lots of energy).
how does desalination workk
distillation - Seawater is heated until it evaporates. Water vapour is cooled and condenses, leaving salt behind.
OR
reverse osmosis - a process that involves the use of membranes. When salt water is put through a semi-permeable membrane, only water molecules can pass through it. This happens as the membrane stops larger molecules and ions passing through
Why is desalination not widely used in the UK?
It requires a lot of energy, making it expensive and unsustainable. Instead it’s used in regions with a very hot climate
Why are new methods of metal extraction needed?
High-grade ores are running out
traditional mining is harmful to the environment.
What is phytomining how is it done?
Using plants to absorb metal compounds from soil. The plants are grown in areas containing the metal of interest . As the plants grow the metals are taken up through the plants vascular system.The plants are then burned to ash. Dissolve ash in an acid to create a solution containing the metal and extract the metal via electrolysis
what is bioleaching
Bioleaching uses bacteria to produce leachate solutions that contain metal compounds.
What are the advantages of phytomining?
✅ Reduces the need for traditional mining.
✅ Can extract metals from low-grade ores.
✅ Helps clean contaminated land.
uses low energy
What are the disadvantages of phytomining?
❌ Slow process (plants take time to grow).
❌ Produces CO₂ when plants are burned.
the yield fo extracted metal is lower compared to traditional mining
phytomining relies on soil and climate conditions which may not always be reliable
only works with specific metals and plants
can be expensive
What are the advantages of bioleaching?
✅ Can extract metals from low-grade ores.
✅ Uses less energy than traditional mining.
✅ No large-scale environmental damage like open-cast mining.
What are the disadvantages of bioleaching?
❌ Process is slow.
❌ Can produce toxic chemicals that need to be contained.
lower yield of extracted metal compared to trad. mining
can be expensive
How are metals extracted from solutions in phytomining and bioleaching?
Electrolysis (if the metal is reactive).
Displacement using a more reactive metal (e.g., scrap iron to extract copper).
What is corrosion?
The gradual destruction of metals due to chemical reactions with substances in the environment.
What is rusting?
The corrosion of iron or steel when exposed to oxygen and water.
What is the word equation for rusting?
Iron + Oxygen + Water → Hydrated Iron(III) Oxide (Rust)
What are the conditions required for rusting?
Both oxygen and water must be present.
How does rust weaken iron?
Rust is soft and flaky, so it crumbles away, exposing more iron to further corrosion, until the iron completely degrades and disspears
Does aluminium corrode in the same way as iron?
No, aluminium forms a protective aluminium oxide layer, preventing further corrosion.
How do barrier methods prevent corrosion?
They block oxygen and water from reaching the metal surface.
What are three common barrier methods?
Painting/coating with plastic – Used for cars, fences, bridges.
Oiling/greasing – Used for moving parts like bike chains.
Electroplating – Coating the metal with a less reactive metal (e.g., chromium, tin).
What is sacrificial protection?
Attaching a more reactive metal (e.g., zinc or magnesium) to iron, which corrodes instead of iron.
Why does sacrificial protection work?
The more reactive metal oxidises first, preventing iron from corroding.
Where is sacrificial protection used?
✅ Ship hulls
✅ Underground pipelines
What is galvanising?
Coating iron or steel with zinc to prevent rusting.
How does galvanising prevent corrosion?
✅ Zinc acts as a barrier (stopping oxygen and water from reaching iron).
✅ Zinc provides sacrificial protection if the coating is scratched.
how to investigate rusting of iron with three test tubes
.
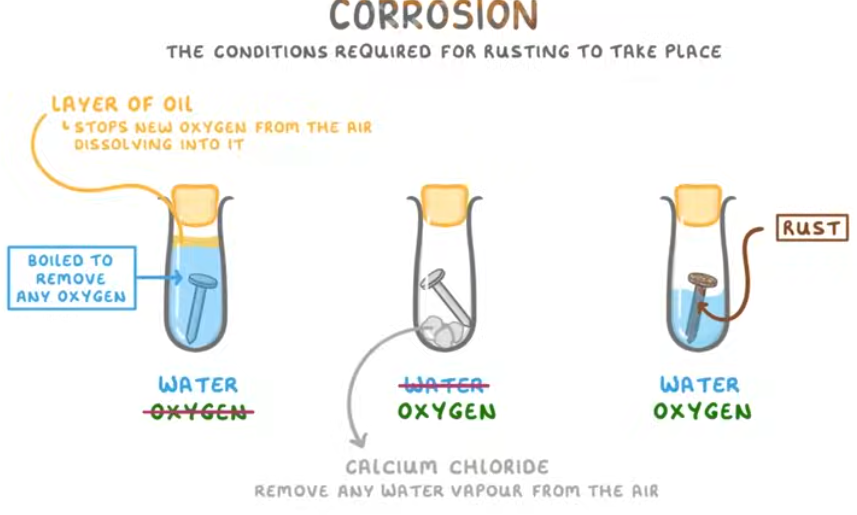
What is an alloy?
A mixture of a metal with other elements (metals or non-metals) to improve its properties.
Why are alloys stronger than pure metals?
Different-sized atoms disrupt the metal’s regular structure making the layers distorted, making it harder for layers to slide over each other.
How do alloys compare to pure metals?
✅ Stronger and harder than pure metals.
✅ More resistant to corrosion in many cases.
✅ Designed for specific uses (e.g., lightweight, strong, corrosion-resistant).
What is steel?
An alloy of iron mixed with carbon and sometimes other metals (e.g., chromium, nickel).
uses of low carbon steel, high carbon steel and stainless steel
Type of Steel | Composition | Properties | Uses |
|---|---|---|---|
Low-carbon steel | Iron + a small amount of carbon | Soft, easily shaped | Car body panels |
High-carbon steel | Iron + more carbon | Hard, brittle | Cutting tools, bridges |
Stainless steel | Iron + chromium + nickel | Corrosion-resistant, strong | Cutlery, surgical tools |
What is bronze used for?
✅ Statues
✅ Medals
✅ Ship propellers
What is brass used for?
✅ Musical instruments
✅ Plumbing fittings
✅ Door handles
Why is gold alloyed?
Pure gold is too soft, so it is mixed with other metals to make it harder and more durable.
What is gold alloy used for?
✅ Jewellery
✅ Electrical components
How is the purity of gold measured?
In carats (e.g., 24-carat gold is 100% pure, 18-carat gold is 75% gold).
Why is aluminium alloyed?
Pure aluminium is soft, but alloys make it stronger while keeping it lightweight.
What are aluminium alloys used for?
✅ Aeroplanes (light but strong).
✅ Car bodies.
what is bronze an alloy of
copper and tin
what is brass an alloy of
copper and zinc
What is wastewater?
Water that has been contaminated by human activity, including sewage, industrial waste, and agricultural run-off.