Endocrine System Slide I
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Not including MLC
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Endocrine System
slowly acting by using chemical messengers called hormones
Endocrine glands
ductless glands that produce/release hormones into the blood stream through diffusion
Endocrine organs
lack the structural or anatomical continuity typical of most organ system instead endocrine tissue is tucked away in separated regions of the body
Chemical classification of hormones
Amino acid based molecules
Steroids
Eicosanoids
Steroids
Derived from cholesterol
ex. sex hormones
Eicosanoids
diverse lipids made from 20-carbon fatty acid (arachidonic acid)
have localized effect
Leucotrienes
lipid derivatives that act as chemicals signals that mediate inflammation and some allergic reactions
Prostaglandins
made from highly active lipids found in the cells’ plasma membranes
plays roles in regulation of blood pressure (increase), blood clotting, inflammation, and labor contractions
Autocrines
chemicals that exert their effects on the same cells that secrete them
smooth muscle prostaglandins effect smooth muscle cell contraction
Paracrines
affect cell types other than those releasing the chemicals
Target cells and target organs response
can only be stimulated when there is a specific protein receptor present in the plasma membrane or in its interior
What happens in the target cell?
Produce changes in membrane permeability or potential
Stimulate synthesis of proteins or regulatory molecules (enzymes)
Activate or deactivate enzymes, induce secretory activity
Stimulate mitosis
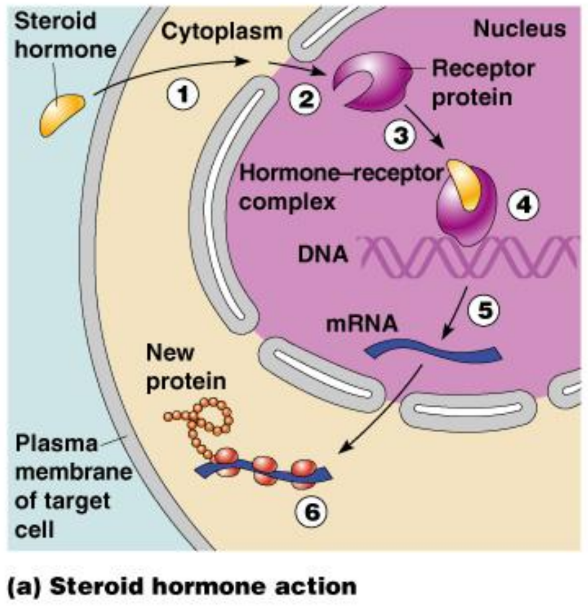
Steroid Hormone Action
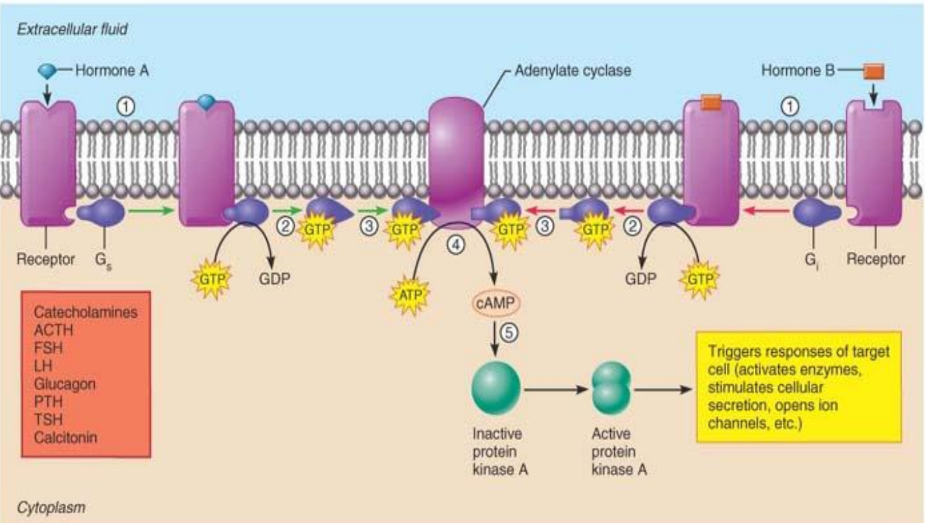
Nonsteroid/Water-Soluble Hormone Action
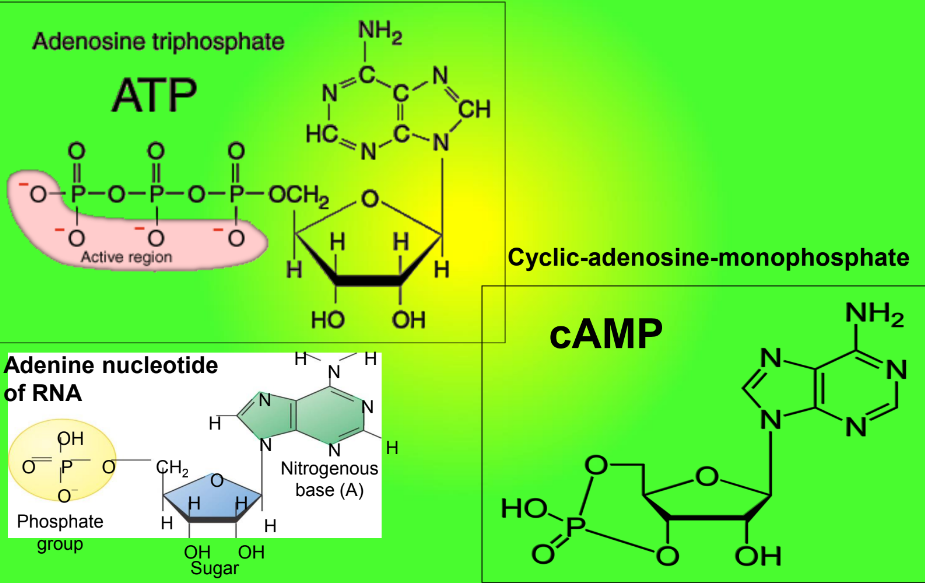
Structures of ATP & cAMP (Cyclic- adenosine-monophosphate)
Target Cell Specificity
must have specific membrane or intracellular receptors to which hormones can bind
Target cell response depends of 3 factors
Blood levels of the hormone
Relative number of target cell receptors
Affinity of the receptor for the hormone
Concentration of a hormone
reflects its rate of release, the rate of inactivation and removal from the body
Half-life of a hormone
duration of time a hormone remains in the blood and is shortest for water soluble hormones
Target organ duration and response
varies widely among hormones
Permissiveness
occurs when one hormone cannot exert its full effect without another hormone being present
Synergism
occurs when more than one hormone produces the same effects in a target cell, and their combined effects are amplified
Antagonsim
Occurs when one hormone opposes the action of another hormone
Events occurring in a negative feedback mechanism
some internal or external stimulus
Hormone secretion
Hormone levels rise
Inhibit further hormone release (even while promoting responses in their target organs
(blood levels of many hormones vary only within a very narrow range)
Endocrine gland stimuli
humoral
neural
hormonal