Chapter 13 - Chemical Kinetics
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
rate =
change in concentration of a reactant or product over an interval of time.
rate of disappearance (reactions) is neg
rate of apperance (products) is pos
to make the rates equal to each other, divide each rate by their respective coeff in the chem eqn
reaction mechanism
depends on reaction rate
and concen dependence
rate law
k[A]^m[B]^n[C]^p
k is the constant
the exponents give
the rxn order
can be positive integers or fractions
is det thru experiment so you often have to interpret a table
1st order
exp in rate law = 1
means that the rate goes up by a factor of 2 if the concentration goes up by a factor of 2
2nd order
exponent in rate law = 2
if the concen goes up by a factor of 2, the rate goes up by a fatcor of 4
3 → 9
0 order
expoennt on rate law = 0 so the whole thing = 1
to interpret the rate law
you must find the shit where all other concens are constant (initial and final are the same)
rate of rxn =
the rate law expression
so you can calc the k constant after figuring out the exponents for the compounds
units of k
L/mol*s
integrated rate law for 0 order
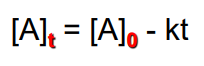
integrated rate law for first order rxn
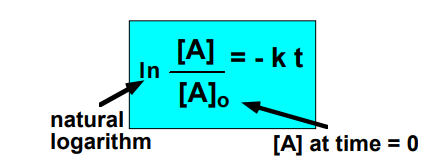
half life
time taken for half of a reactant to be consumed
[A]t = 1/2*[A]0
reaction after 2 half lives → ¼ of the reactant remains
reaction after 3 half lives → 1/8 of the reactant remains
2^#ofhalflives
integrated rate law for 2nd order
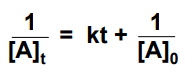
reactions require (according to collision theory)
activation en
correct geo
a reaction that requires low activation en happens earlier so the smallest hill features the fastest rxn
another way to find k
where Ea is the activation en and A is the freq factor
this makes a line of lnk vs 1/T
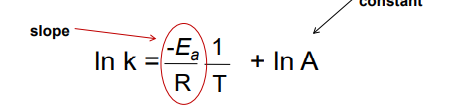
RATE DETERMINIG STEP
the slowest step in a rxn is rate determinng in the rxn mechanism
correlating mechanism with rate law
elementary steps must add up to the overall balance eqn
the mech must correlate with the OBSERVED rate law, aka the rate determing step
the rate law also would not have a compound that was made and consusumed in the mechanism (does not end up in final eqn)
homo catalysrt
catalyst = same phase as the reactants
hetero catalyst
when the catalyst is in a diff phase than the reactants