Cell structure
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
98 Terms
Eukaryotic vs prokaryotic cell
Eukaryotic cells contain membrane-bound organelles; prokaryotic cells do not
What are organelles
Structures found inside a cell
Nucleus size usually
5-10 μm
Draw a nucleus
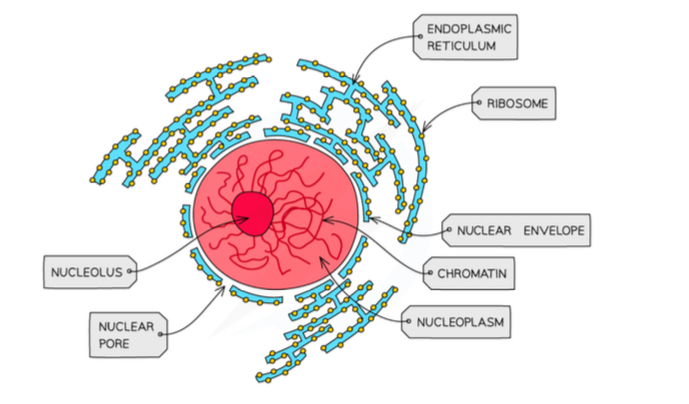
What kind of cells is the nucleus in
All eukaryotic cells except red blood cells
What separates the nucleus from the cytoplasm
Nuclear envelope (double membrane)
Why does the nuclear envelope have pores
Allow mRNA and ribosomes out; allow enzymes in
What is chromatin
Material which chromosomes are made from; found in the nucleus
What is the nucleolus
Structure inside the nucleus where ribosomes are produced
What surrounds the nucleus
Rough endoplasmic reticulum + ribosomes
Size of mitochondria usually
0.5-1μm
Name features of the nucleus
Nucleolus, chromatin, nucleoplasm, nuclear envelope, nuclear pores
Function of a mitochondrion
Site of aerobic respiration in all eukaryotic cells
Describe structure of mitochondria
Surrounded by double membrane; inner membrane folds to form cristae
What are cristae
Structures formed by the inner membrane of a mitochondrion
What is the matrix
Inside cristae of mitochondria; contains enzymes needed for aerobic respiration
Where are mitochondria found
Eukaryotic cells; self replicating so abundant in cells where much metabolic activity takes place to provide energy
Chloroplast size usually
2-10μm
Where are chloroplasts found
Plant cells which photosynthesise
Chloroplast structure
Double membrane, then thylakoid membranes form grana joined together by lamellae
What are thylakoids
Membrane bound structures in chloroplasts containing chlorophyll; site of photosynthesis
What else do chloroplasts contain other then thylakoids
Small circular pieces of DNA, ribosomes, stroma (like cytoplasm)
Ribosome structure
No membrane
Where are ribosomes normally found in cells
Cytoplasm/RER
Describe the structure of a ribosome
Complex of ribosomal RNA (small subunit) and proteins (large subunit)
What kind of proteins do ribosomes bound to the exterior of RER synthesise
proteins to be exported outside the cell
What kind of proteins do ribosomes free in the cytoplasm synthesise
Proteins that will be used inside the cell
What part of protein synthesis happens on the ribosome
Translation
What kind of cells can the rough endoplasmic reticulum be found in
Plant and animal cells
What makes the rough endoplasmic reticulum “rough”
Surface covered in ribosomes
Describe the structure of the rough endoplasmic reticulum
Formed from folds of membrane continued from the nuclear envelope
What is the function of the rough endoplasmic reticulum
Folds and processes proteins that have been made at the ribosomes (once they have passed into cisternae)
What is a cisternae
Fluid-filled space (enclosed by membrane) found in endoplasmic reticulums and Golgi
What do the cisternae do
Form channels for transporting substances from one area of a cell to another
Why is the smooth endoplasmic reticulum “smooth”
No ribosomes on surface
What does the smooth endoplasmic reticulum do
Produce, process and involved in storage of lipids, carbohydrates and steroids
Describe the structure of the Golgi apparatus
Stack of flattened cisternae
Where is the SER found
Also next to the nucleus with the RER
Describe the function of the Golgi apparatus
Modifies proteins and lipids
Draw the structure of the Golgi apparatus
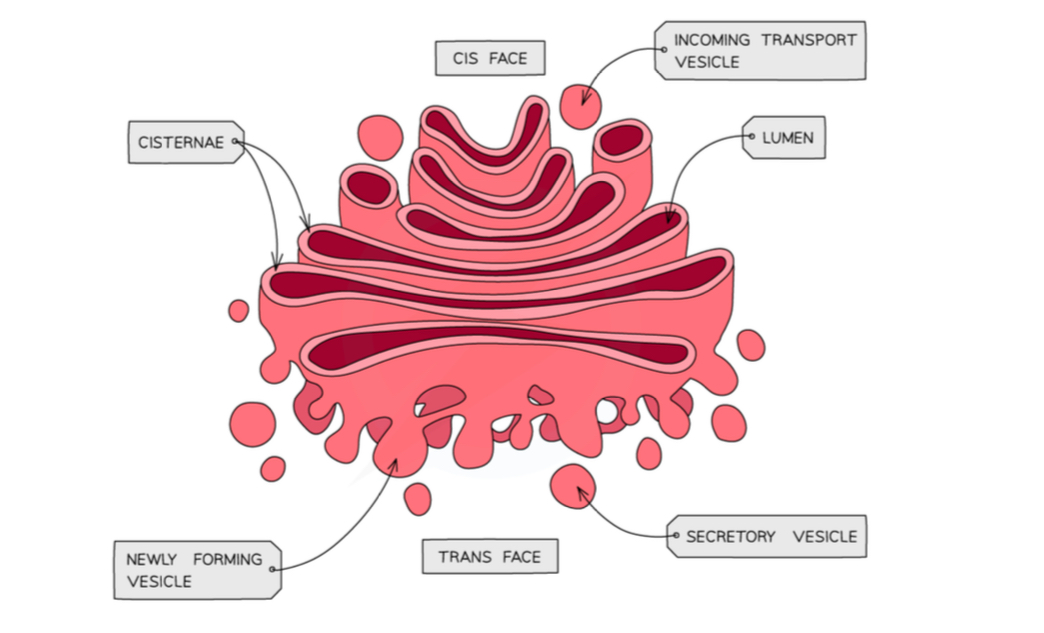
Where do transport vesicles come in to the Golgi apparatus
Cis face
Where do secretory vesicles leave the Golgi apparatus from
Trans face
What are lysosomes
Special form of vesicle containing hydrolytic enzymes
What do hydrolytic enzymes do
Break down biological molecules
What are lysosomes for
Breaking down waste material e.g. worn out organelles; used in immune system and apoptosis
Apoptosis meaning
Programmed cell death
Are lysosomes membrane bound
Yes
What are centrioles
Hollow fibres made of microtubules
What are microtubules
Polymers of the protein tubulin
What do a pair of centrioles (perpendicular to form an X) form
Centrosome
Role of centrioles in eukaryotic cells
Play a role in assembly of spindle fibres during cell division; key part of protein complex which form cilia/flagella
Describe structure of cilia/flagella and how they move
9 pairs of microtubules in circle, 1 pair in the centre (9+2 structure); pairs move relative to adjacent pairs; creates bending motion
Proof that centrioles are not essential for spindle fibre assembly
Flowering plant cells form spindle fibres during cell division but do not have centrioles
Where are centrioles not found
Flowering plants; most fungi
What are cilia
Hair-like projections made from microtubules
What do cilia do
Allow movement of substances over cell surface (trachea) or sense chemicals around cell (nose)
What is a flagella
Projection like cilia made from longer microtubules
What do flagella do
Contract to provide cell movement e.g. sperm cells
Which organelles are involved in protein production?
Nucleus, ribosome, RER, Golgi, vesicles
Where are ribosomes manufactured
Nucleolus
Where is mRNA manufactured
Nucleus
Name the organelles of an animal cell
Plasma membrane; Nucleus; Rough/Smooth ER; mitochondrion; Golgi; ribosome; lysosome; cytoplasm
What do plant cells have that animal cells don’t?
Chloroplast; cell wall with plasmodesmata; vacuole
What is the membrane surrounding the vacuole called
Tonoplast
Which is further from nucleus: smooth or rough ER
Smooth
What is a plasmodesma / plasmodesmata (pl)
Channel in plant cell wall for exchanging substances with adjacent cells
What is contained in the vacuole
Cell sap
Describe the organelles in a prokaryotic bacteria cell
Cell wall (peptidoglycan); plasma membrane; chromosome; plasmid; ribosome; flagellum; mesosome
What is a mesosome
Site of aerobic respiration; at folds of membrane to increase SA to store more enzymes
3 reasons why the cytoskeleton is important
Provides mechanical strength to cells; aids transport within cells; enables cell movement
Are fungi eukaryotic
Yes
Describe how DNA is arranged in eukaryotic cells
Coiled around histone proteins in the nucleus; Linear
What is exocytosis (protein production)
Vesicles fusing with cell surface membrane to secrete proteins from cell
Where is mRNA manufactured
Nucleus (transcription)
Where are ribosomes manufactured for protein synthesis in the rER
Nucleolus
Which process proteins: RER or Golgi
Both
Draw a prokaryotic cell
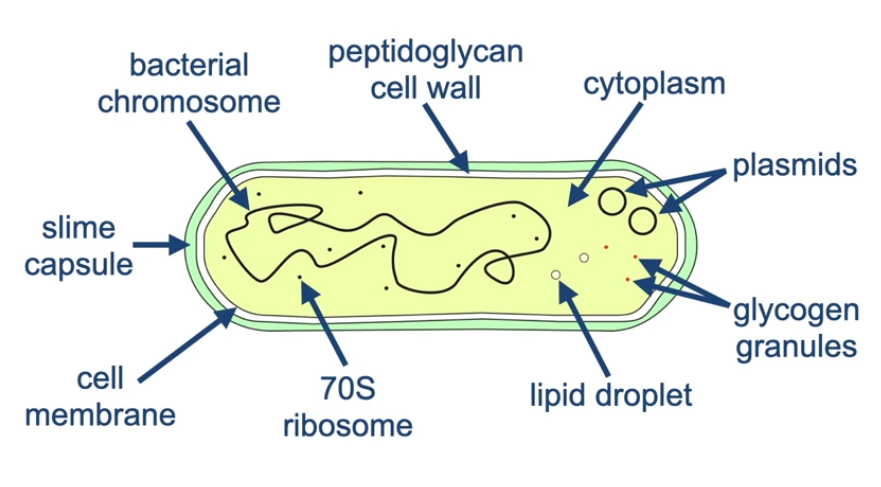
Are bacteria prokaryotic
Yes
Which is larger: prokaryotic or eukaryotic cells
Eukaryotic cells are much larger
Describe the DNA in prokaryotic cells
Circular chromosome; not bound to histone proteins; in cytoplasm; sometimes plasmids
What are plasmids
Small circles of DNA; relatively small number of genes
What is important about plasmids in bacteria
Often contain genes which make bacteria resistant to antibiotics
Are there ribosomes in prokaryotic cells
Yes
What is different about the ribosomes in prokaryotic cells vs eukaryotic
Prokaryotic ribosomes are smaller (70S), eukaryotic cells are 80S
What is the s in 70s ribosome
Unit showing how quickly organelles move in a centrifuge
What is peptidoglycan
Polymer formed between peptides and polysaccharide molecules
Role of cell wall for prokaryotes
Maintain cell structure; stop cell from bursting
Are prokaryotic and eukaryotic flagella the same
No, different structures
What are pili
Fine protein strands
What are pili for
Help bacteria cell attach to surfaces or other bacteria
What are the nutrient stores in a bacterial cell
Lipid droplets and glycogen granules
When can you see mesosomes
Infoldings in cell membrane of prokaryotic cells; can see using electron microscope
What is the cytoskeleton
Extensive network of protein fibres
What are the 2 main protein fibres found in the cytoskeleton
Microtubules, microfilaments
How does cytoskeleton help intracellular movement
Acts as a track along which organelles can move e.g. vesicles/chromosomes
Is there a spindle involved in prokaryotic cell division
No - occurs by binary fission
What does the spindle do in cell division
Separate chromosomes
What are peptides
Amino acids