female reproductive system
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
Female reproductive system
group
of organs that produces oocytes and sex
hormones, provides the site for
fertilization, and supports embryo and
fetal development until birth.
• Consists of the:
• Paired Ovaries and Oviducts (uterine
tubes)
• Uterus
• Vagina
• External genitalia
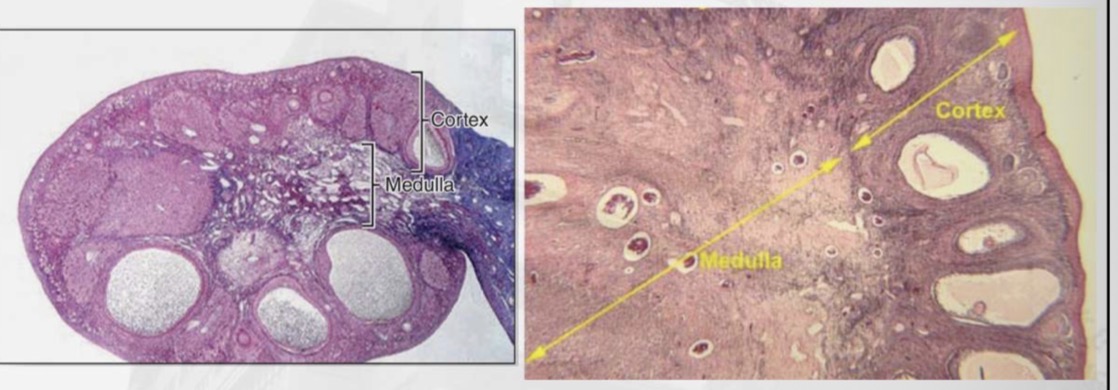
Ovaries
almond-shaped organs
responsible for oocyte production and steroid
hormone secretion.
tunica albugine
Each ovary is covered by a surface (germinal)
epithelium and a dense connective tissue
capsule called
Ovarian cortex
contains highly cellular
connective tissue with numerous ovarian
follicles, while the medulla contains loose
connective tissue and blood vessels; there is no
sharp boundary between the two.
Ovaries microscopy
Ovarian follicles
is a functional unit
consisting of an oocyte surrounded by
follicular (granulosa) cells and a basal
lamina.
Hormonal regulation stages
• Primordial
• Primary
• Secondary (antral)
• Mature (Graafian)
Primordial follicle
• Primary oocyte arrested in prophase I
• Surrounded by a single layer of flattened
follicular cells
• Located in the superficial ovarian cortex
• Present from fetal life
Unilaminar Primary Follicle
• Oocyte increases in size
• Surrounded by a single layer of cuboidal
follicular (granulosa) cells
• Zona pellucida begins to form
• No antrum present
Primary follicle
Unilaminar primary follicle
Multilaminar primary follicle
Unilaminar Primary Follicle
• Oocyte increases in size
• Surrounded by a single layer of cuboidal
follicular (granulosa) cells
• Zona pellucida begins to form
• No antrum present
Multilaminar primary follicle
• Oocyte continues to enlarge
• Surrounded by multiple layers of granulosa cells
• Well-defined zona pellucida
• Follicle remains avascular and lacks an antrum
SECONDARY FOLLICLE
• Appearance of a fluid-filled antrum
• Theca interna and theca externa are well defined
• Actively produces estrogen
(Antral)
Mature follicle
(Graafian)
• Very large follicle with a single, prominent antrum
• Oocyte surrounded by corona radiata and attached by
the cumulus oophorus
• Bulges at the ovarian surface
• Ready for ovulation
Corpus luteum
temporary endocrine gland
formed from the ruptured ovarian follicle after
ovulation.
• It secretes progesterone and estrogens to prepare
and maintain the endometrium for implantation.
• If pregnancy occurs, it is maintained by human
chorionic gonadotropin (hCG).
• If pregnancy does not occur, it degenerates after about
10–12 days (mensturation).
Corpus albicans
is the fibrous, scar-
like remnant formed from the degenerated
corpus luteum.
• It consists mainly of dense connective
tissue.
• It has no hormonal function and gradually
regresses over time.
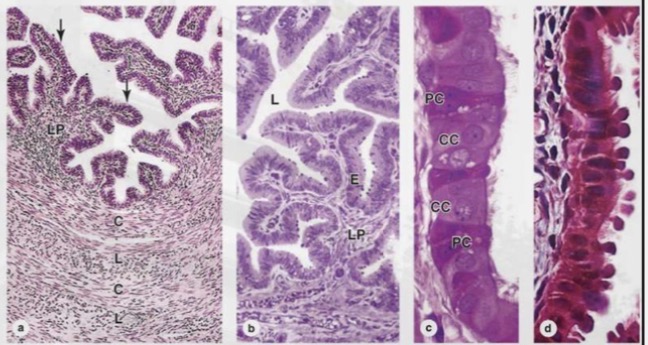
Uterine tube
paired structures that
transport the oocyte and are the usual site of
fertilization.
• They are divided into:
• Infundibulum (with fimbriae)
• Ampulla (site of fertilization)
• Isthmus
• Uterine part.
Uterine tube microscopy
The wall consists of:
• Folded mucosa with
ciliated and secretory
cells
• Smooth muscle layer
for peristalsis
• Outer serosa
Uterus
a pear-shaped, thick-
walled muscular organ that
supports implantation, pregnancy,
and parturition.
• It consists of the fundus, body,
cervix, and isthmus
Uterine wall
• Perimetrium (outer serosa/adventitia)
• Myometrium (thick smooth muscle
layer responsible for contractions)
• Endometrium (inner mucosa that
undergoes cyclic hormonal changes)
endometrium
divided into a basal
layer (permanent) and a functional layer
(cyclically thickens and is shed during
menstruation).
Uterus microscopy
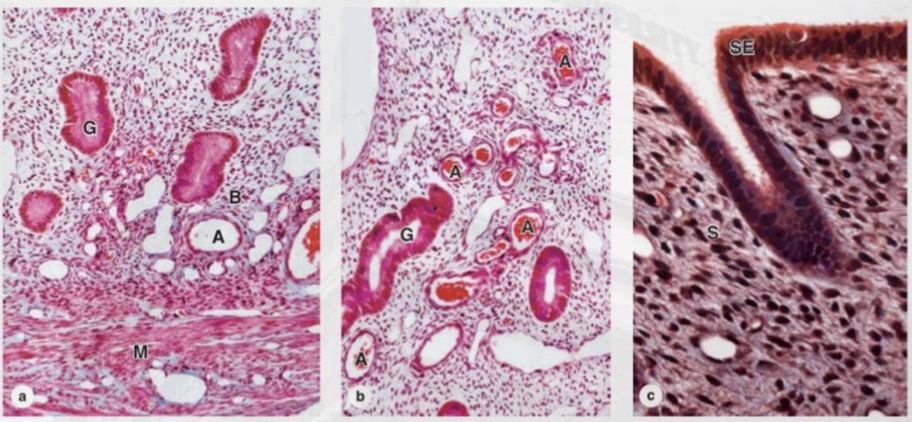
Cervix
the lower, cylindrical portion of the uterus
that connects the uterine cavity to the vagina.
Cervical canal
the passage within the cervix
that connects the uterine cavity to the vagina.
Internal os
the opening of the cervical canal
into the uterine cavity.
External os
the opening of the cervical canal
into the vagina.
transformation zone
area in the cervix where simple columnar epithelium (endocervix) meets
stratified squamous epithelium (ectocervix).
• It is located near the external os and shifts position with age, hormonal changes, and pregnancy.
• This zone is clinically important because it is the most common site of cervical epithelial dysplasia and
cervical carcinoma.
Vagina
fibromuscular canal that
connects the cervix to the external genitalia
and serves as the copulatory organ and birth
canal.
lacks glands; lubrication
comes mainly from cervical mucus and
vestibular glands.
• Rich elastic fibers and smooth muscle
allow distensibility during intercourse
and childbirth.
Vagina layers
• Mucosa (stratified squamous
nonkeratinized epithelium)
• Muscular layer (smooth muscle)
• Adventitia (connective tissue)
Vaginal epithelium
glycogen under estrogen influence;
bacterial metabolism produces lactic
acid, creating an acidic pH that protects
against pathogens.
External genitalia
(Vulva)
collectively called the vulva,
are the external structures of the female
reproductive system.
• Components include the vestibule, labia minora,
labia majora, and clitoris.
• These structures are covered by stratified
squamous epithelium and are richly supplied with
sensory nerves.
• The vulva plays an important role in protection of
the vaginal opening and sexual arousal.
Labia majora
skin with hair follicles, sebaceous &
sweat glands
Labia minora
thin skin, no hair, richly vascular
and innervated
Clitoris
Erectile tissue, highly innerveted
Vestibule
openings of urethra and vagina;
Bartholin (greater vestibular) glands open here