Earth Science Regents Review
1/293
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
294 Terms
THESE CARDS ARE IN THEMATIC ORDER
the unit will be in capital letters
INTRO TO EARTH SCIENCE

4 Main Branches of Earth Science
Geology, Astronomy, Meteorology, Oceanography
Geology
The study of the materials that make up the earth's surface (Rocks, Minerals, Etc.)
Astronomy
The study of objects beyond the earth (Space, planets, stars, meteors)
Meteorology
the study of the weather, climate and the atmosphere
Oceanography
the study of the nearly 75% of the earth that is covered by water
3 Main Earth Systems
Lithosphere, Hydrosphere, Atmosphere
Lithosphere
the rigid outer shell of the earth (Crust)
Types: Oceanic/Continental
Continental Crust
-Less Dense (2.7 g/cm^3)
-Thicker
-Made of mostly granite
Oceanic Crust
-More Dense (3.0 g/cm^3)
-Thinner
-Made of mostly basalt
Hydrosphere
Water on in and around earth
-97% is saltwater; 3% freshwater
Atmosphere
Layer of the gasses that surround the earth
4 Layers
1. Troposphere
2. Stratosphere
3. Mesosphere
4. Thermosphere
(R/T Pg. 1)
Observation
The use of 1 or more of the 5 senses to learn something about the environment
-Problems: Accuracy- senses are limited
-Solutions: Use instruments to extend out senses
Classification
Group objects based on similar characteristics
-helps to organize
-makes studying and understanding easier
Inference
Logical conclusion/educated guess based on observations
-More observations=Better _____________
Frame of Reference
Something to compare to; the starting point
What are the 2 most common Frame of References?
Time and Space
Measurement
a comparison to a known standard
-2 parts to every measurement: Quantity and Unit
Metric System
SI= Systeme International
Quantities
Length, Mass, Volume
Units
Meter (m); Grams (g); Liters (l)
Scientific Notation
Way of simplifying large numbers (Values) so they are easier to work with
EX:
4,600,000= 4.6 x 10^9
4.09 x 10^-2 = .0409
.00432 = 4.32 x 10^-3
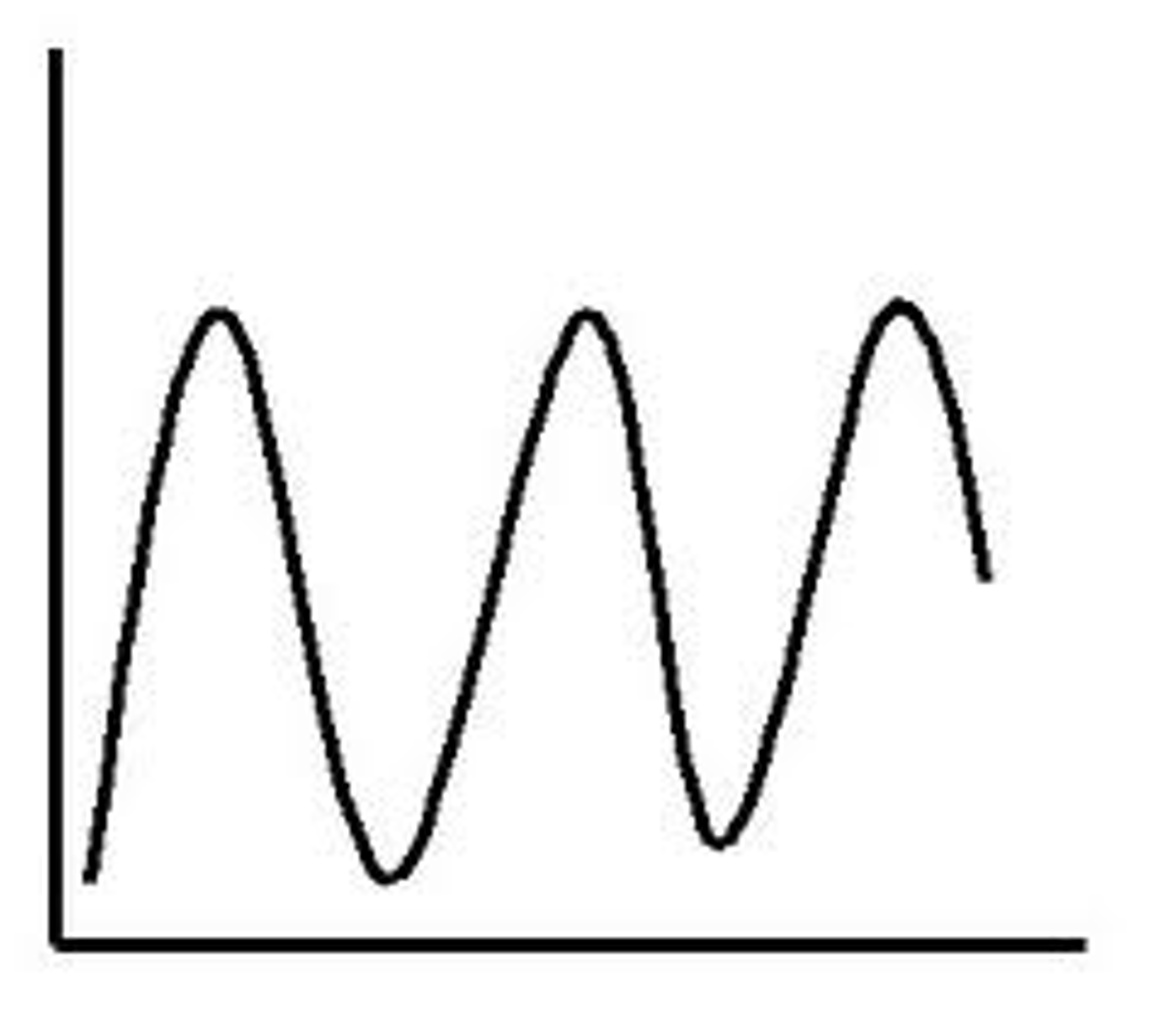
Cyclic
continually repeated in the same way
-predictable
-best predicted when data is collected over a long period of time
EX:
-Water cycle
-Earths Rotation
-revolution of earth
-moon phases
Non-Cyclic
does not repeat
-not predictable
-no pattern
EX:
-Weather
-Volcanos
-Earthquakes
-Tsunamis
Interface
Boundary where 2 different materials/ systems meet of interact
-Change happens here
-energy is exchanged
Equilibrium
a balance between 2 of more systems
Static Equilibrium
No Movement but overall balance
Dynamic Equilibrium
Movement but overall balance
(Earth is mostly in a state of static equillibrium)
Mass
the amount of matter in an object
-doesnt change from place to place
Weight
The affect of gravity acting on an object
-Can change from place to place
Volume
The amount of space an object takes up
-Regular Solid = lwh
-Irregular solid= water displacement
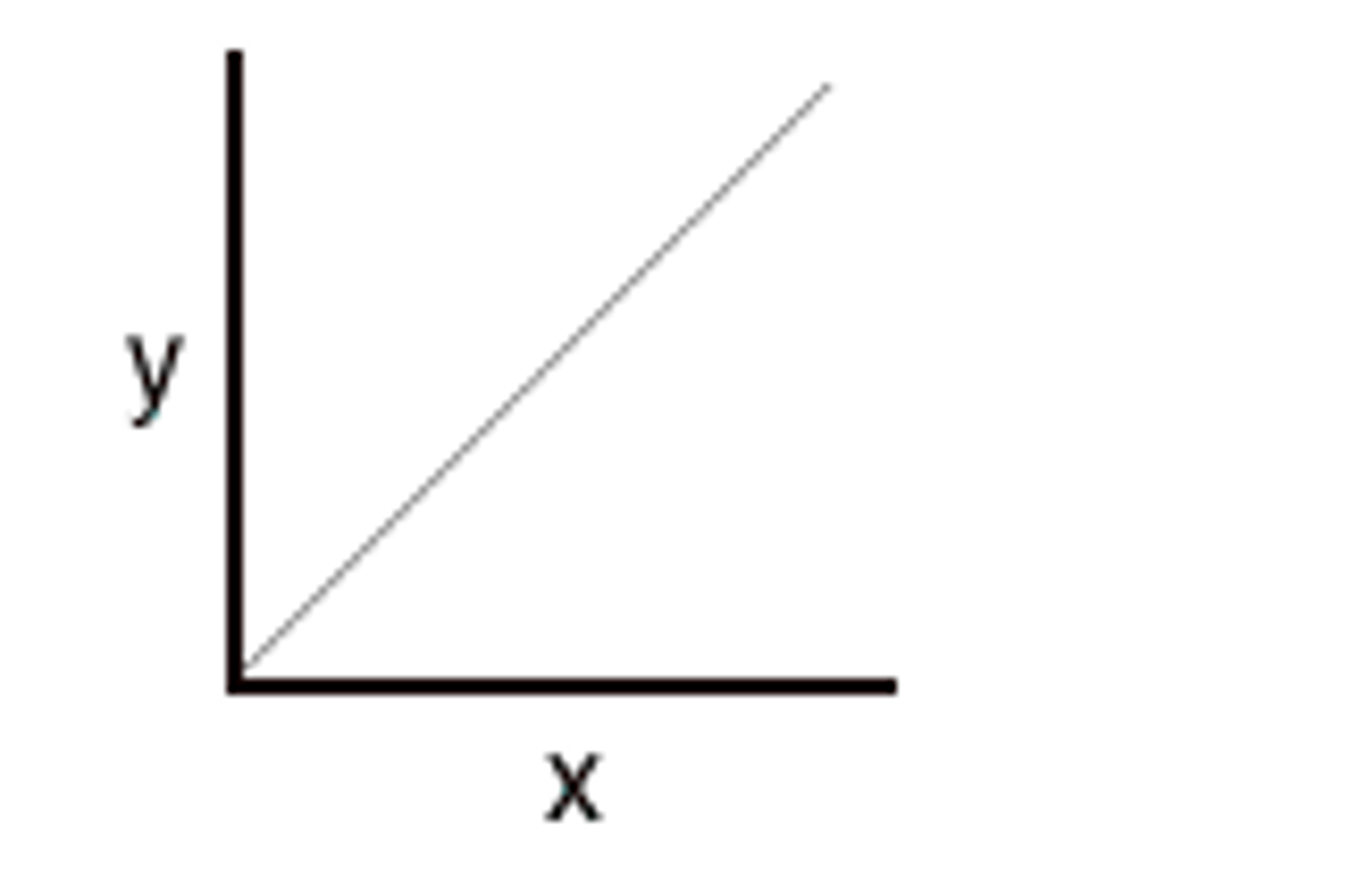
Direct Relationship
When the independant variable goes up, the direct variable goes up
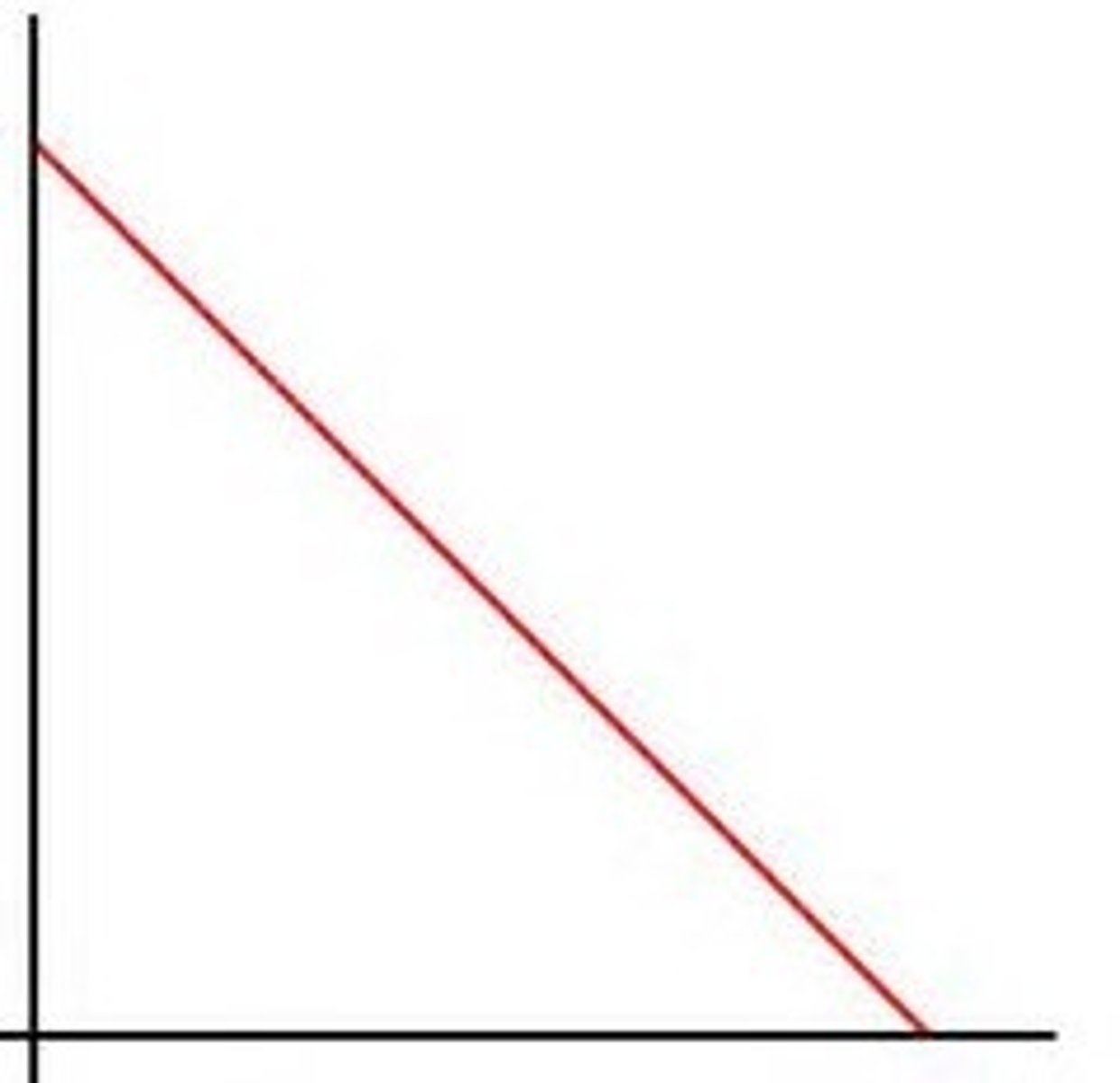
Inverse/ Indirect Relationship
When independant variable goes up the dependent variable goes down and vice versa
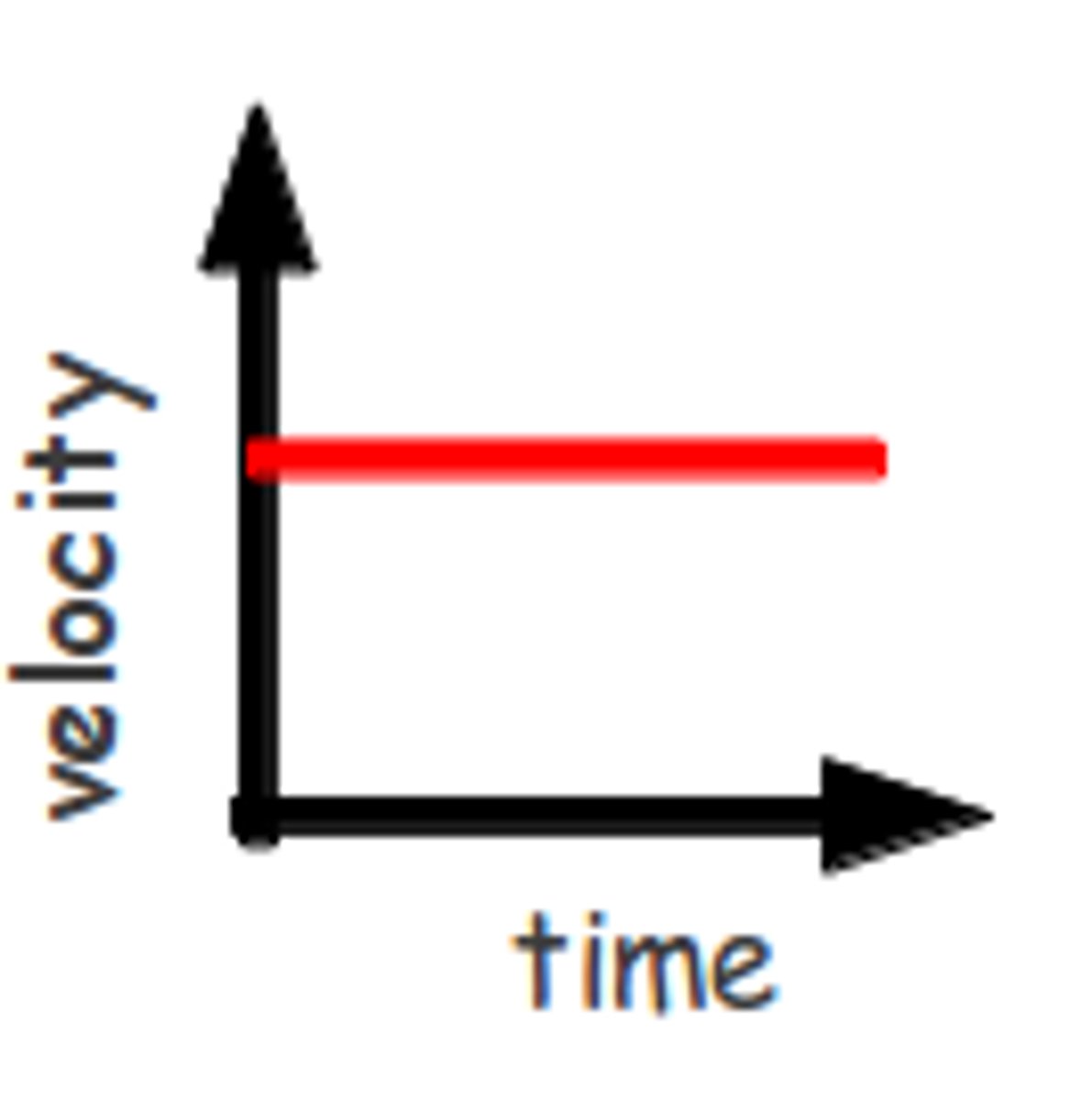
Constant Relationship
The DV stays the same while the independent variable changes
Rate of Change
Change in Value/ Time
-Rate can decrease
- If the line is straight it's a constant rate
Pollution
When the concentration of any substance reaches a level that adversely (Negatively) affects plants, animals, humans, or the environment
Natural Sources of Pollutants
Volcanic Ash
Pollen
Forest Fires
Manmade Pollutants
(Anthropogenic)
-nuclear waste
-CO2 Emissions
Toxins
Hazardous waste materials
-Carcinogenic (Cancer causing)
Density
mass/volume
Density vs. Temperature
-as temperature increases the density decreases (Object rises)
-INDIRECT
-As temperature decreases, density increases (Object sinks)
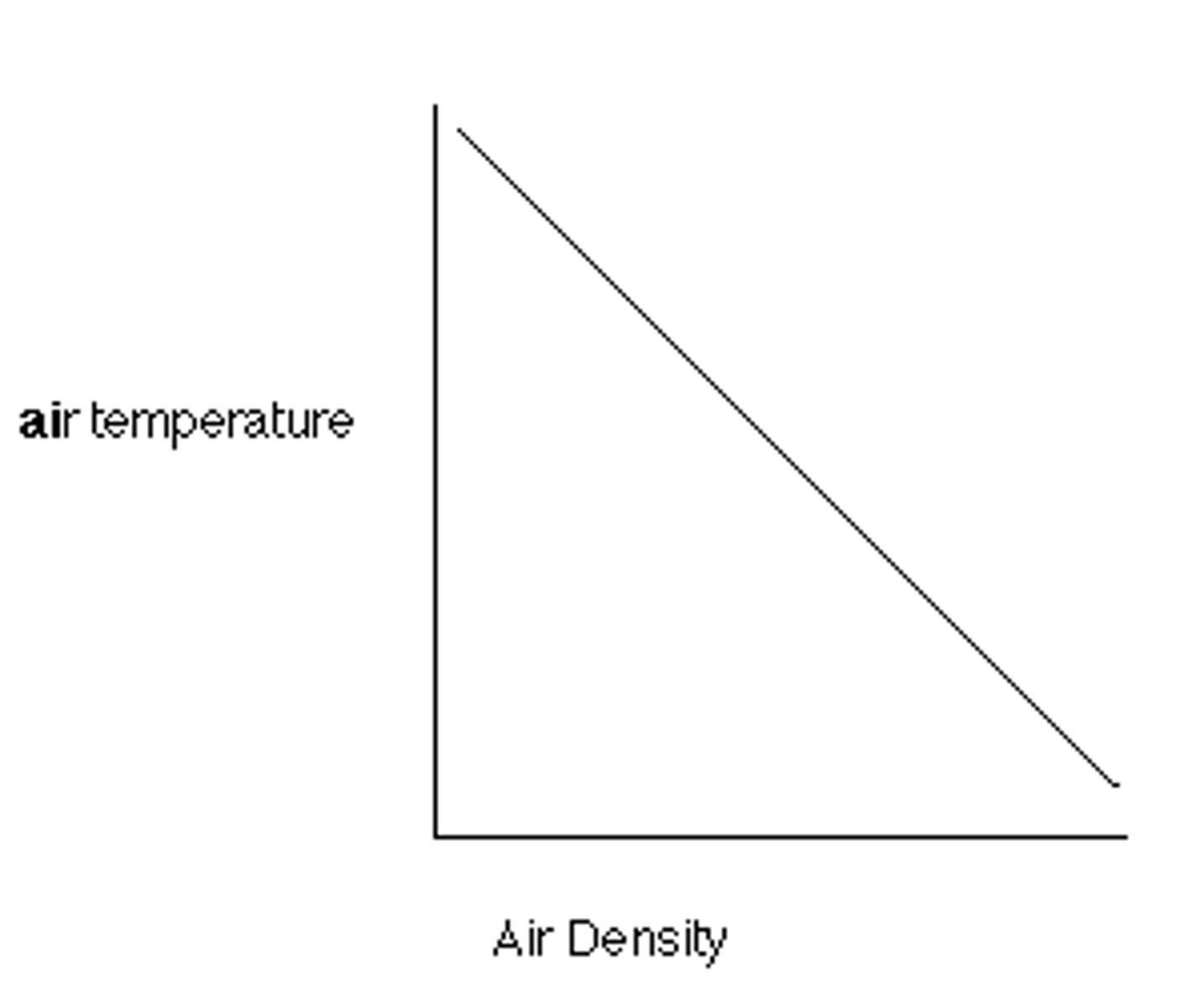
In what phase is an object most dense (Exception of Water)
Solid Phase (Then liquid then gas)
In what phase is water most dense?
Liquid (4 degrees C)

Density vs. Pressure
When Pressure increases, density increases
EARTH'S SHAPE AND COMPOSITION
Earth's Shape
Oblate Spheroid- Slightly flattened at the poles and slightly bulging around the equator (ALWAYS CHOOSE THE MOST PERFECT CIRCLE)
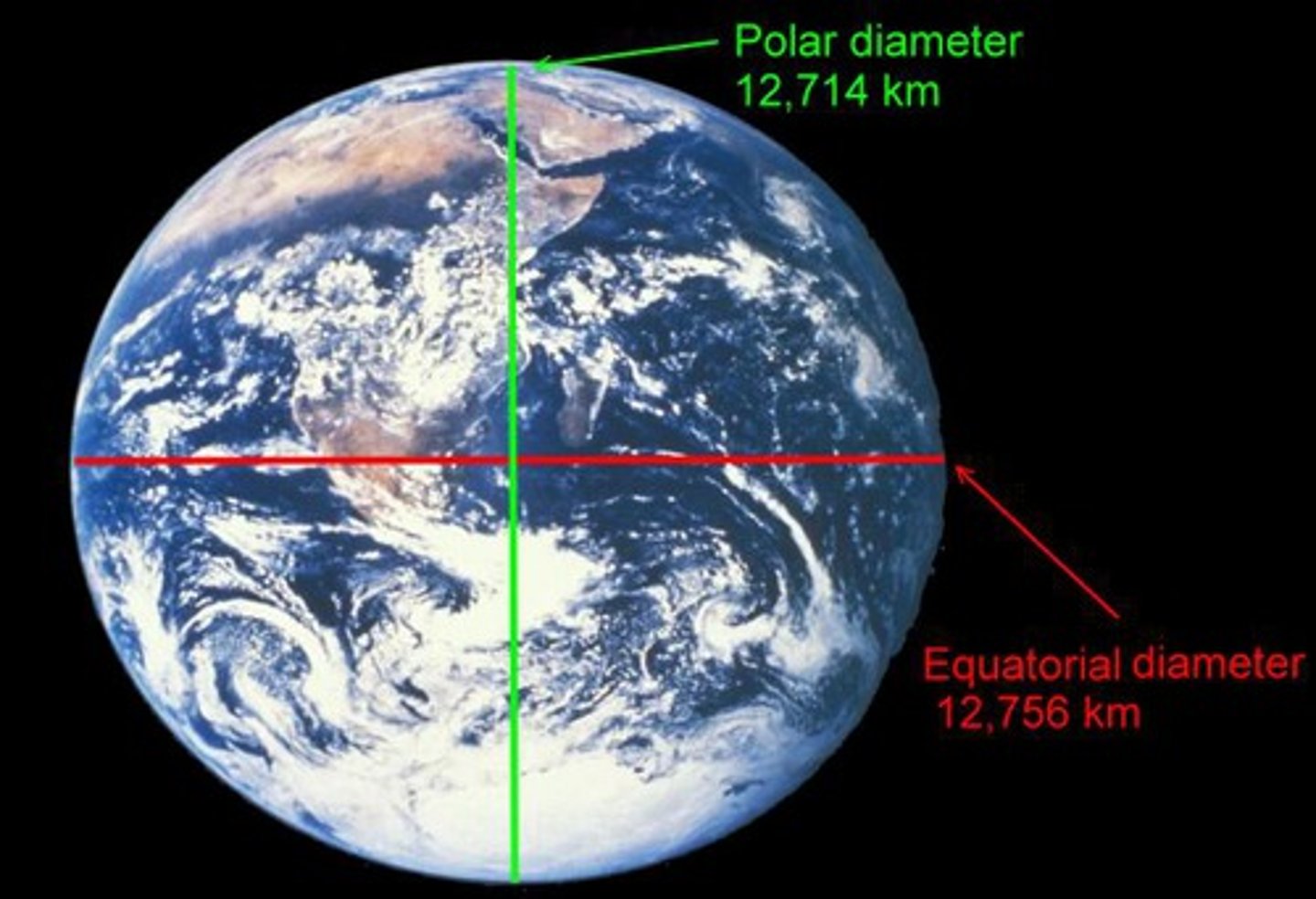
Proof of Earth's Shape
Tall Masted Ships- mass slowly sinks below the horizon when viewed from a distance
Satellite Photos- Best Evidence
Luner Eclipse- Sun casts a shadow of the earth onto the moon (Shows curvature of the earth)
Gravity difference- the closer you get to earth's core the greater the gravitational attraction (Greater attraction at the poles vs. the equator
Angle to Polaris- (See next Card)
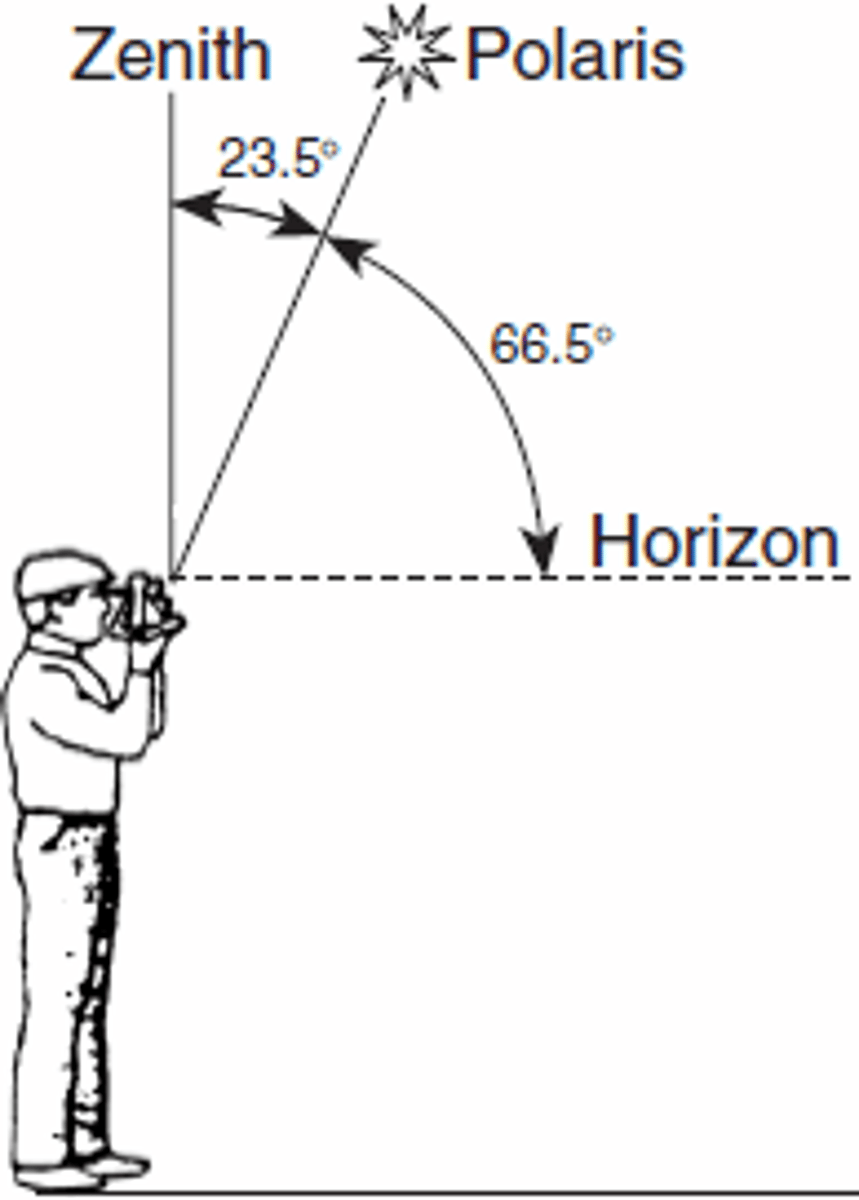
Angle to Polaris
Evidence of earths shape
-Astrolabe: measures the angle to polaris (Between the earths surface and polaris
THE ANGLE TO POLARIS IS EQUAL TO YOUR LATITUDE ONLY IN THE NORTHERN HEMISPHERE
-Light from polaris travels to us in perfect parallel lines
*As you travel from the equator (0) to the north pole (90), the angle increases (and vice versa)
4 Major Earth Zones
Crust, Mantle, Outer Core, Inner Core
(REFERENCE TABLE PAGE 10)
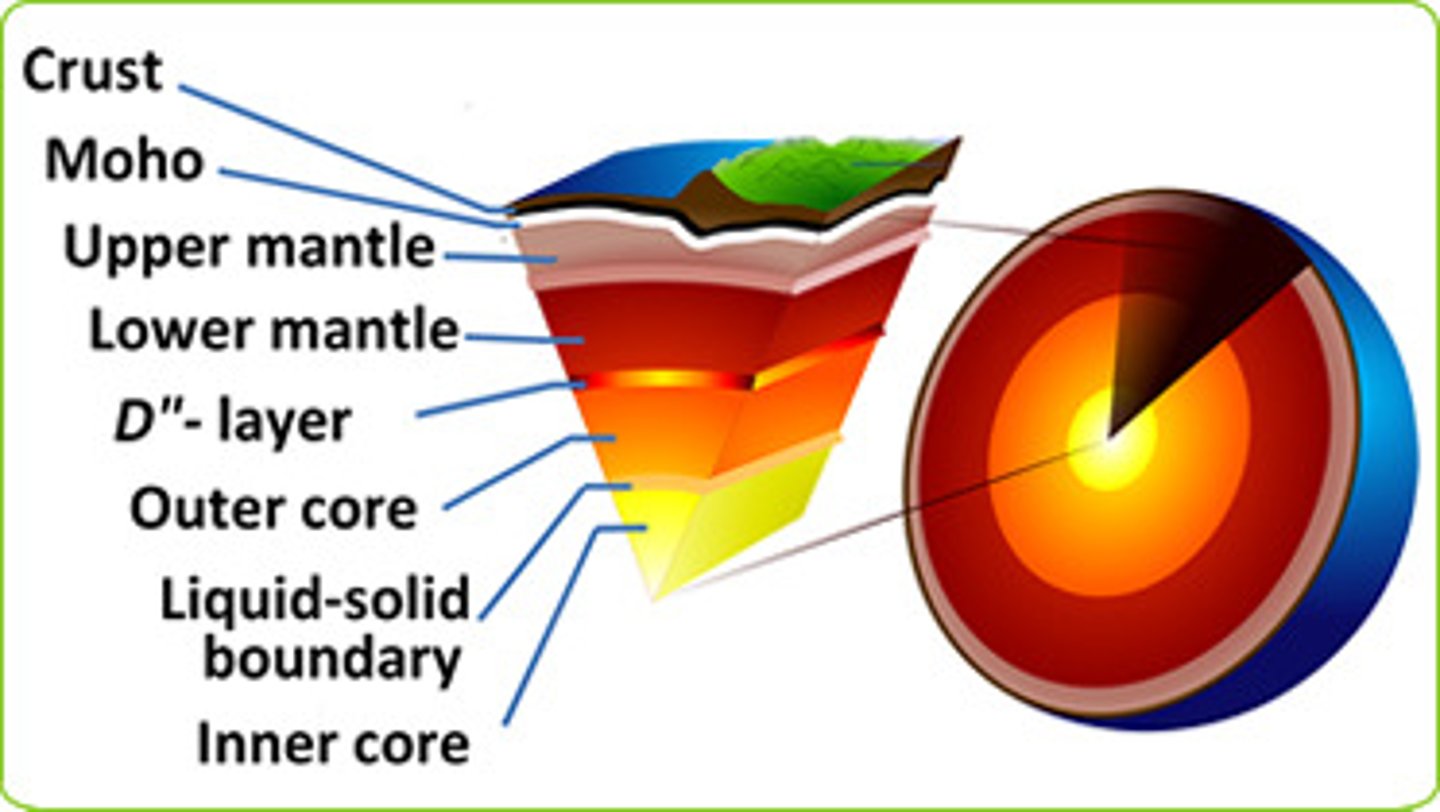
Lithosphere (Crust)
the rigid outer shell of the earth (Crust)
Types: Oceanic/Continental
Continental
-Less Dense (2.7 g/cm^3)
-Thicker
-Made of mostly granite
Oceanic
-More Dense (3.0 g/cm^3)
-Thinner
-Made of mostly basalt
moho
Mohorouicic
-discontinuity line
-interface between the crust and the upper mantle
Mantle
-Not a rigid solid but not a liquid
Asthenosphere
Upper portion of the mantle
Outer Core
Liquid
-Iron and Nickel
Inner Core
Solid
-Iron and Nickel
What happens to density, pressure and temperature as you go deeper into the earth?
THEY ALL INCREASE
Coordinate Systems
Need at least 2 coordinates to locate position (GRID)
Latitude and Longitude
Used to locate positions on Earth's Curved surface
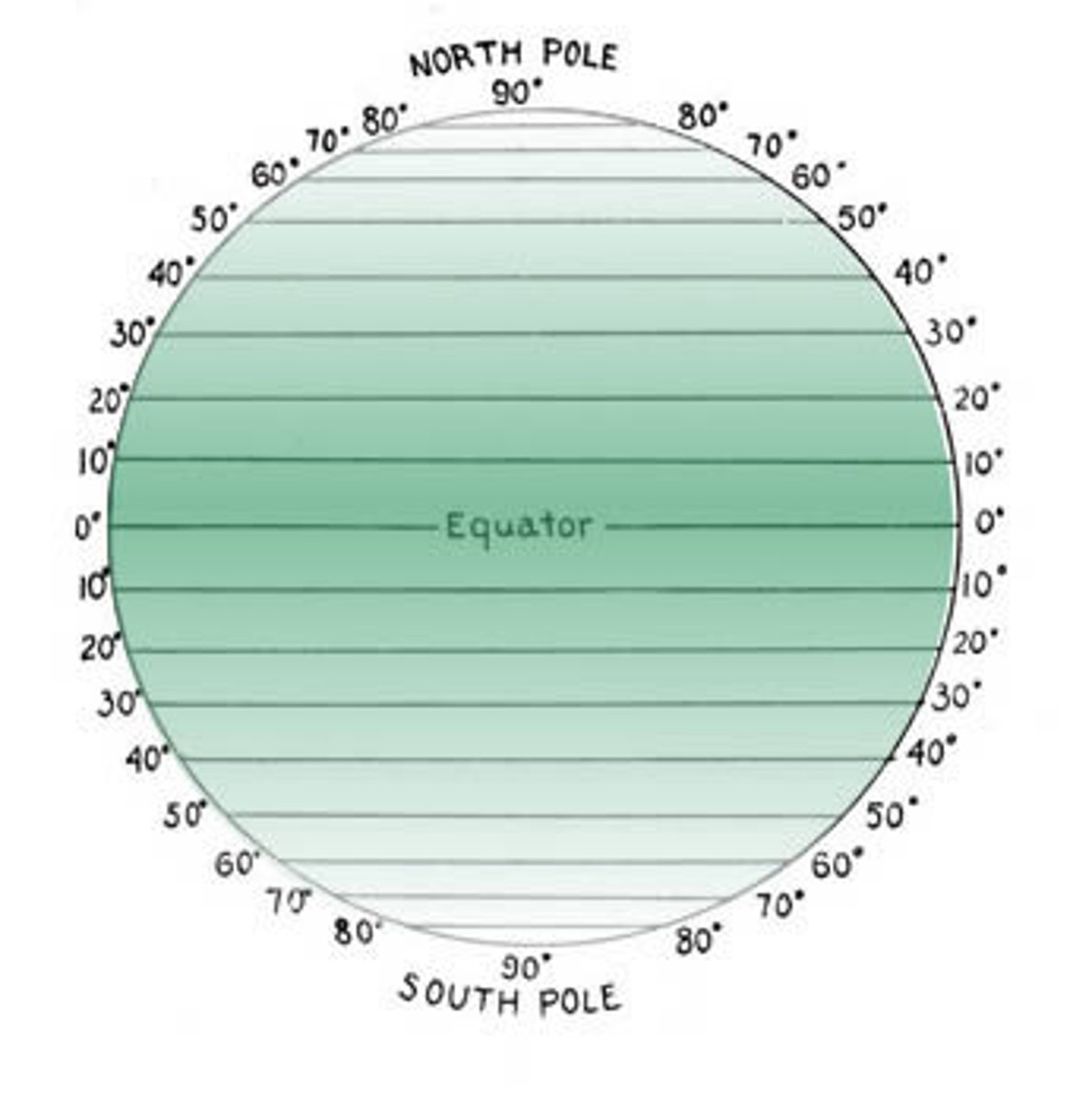
Latitude
-Parallel to the Equator
-Ranges from -0 degrees- 90 degrees North
-0 degrees- 90 degrees South
-In northern hemisphere latitude is = to angle of polaris
Longitude
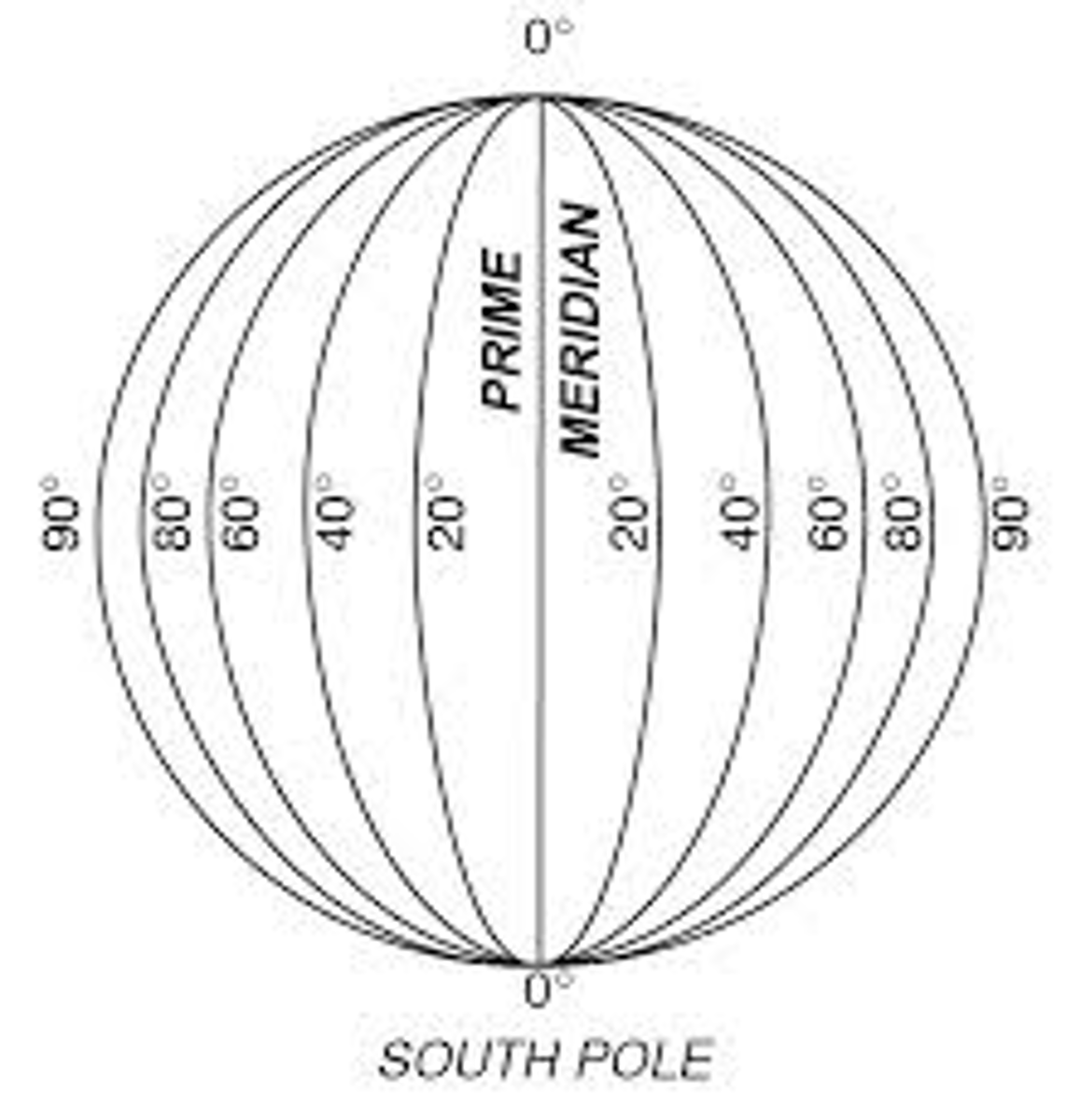
-Not Parallel; All meet at poles
-0 degrees = Prime Meridian (Greenwich, England)
-Ranges from- 0 degrees - 180 E
- 0 degrees- 180 W
International date line: 180
LONGITUDE TELLS TIME
Minutes
1 degree of latitude/ longitude can be broken down into smaller units called minutes (')
(60 Minutes between each line)
EXAMPLE:
43°N-------------------------------43°N
------- 42° 45' N
------- 42° 30' N
------- 42° 15' N
42°N--------------------------------42°N
Latitude and Time
LATITUDE TELLS TIME
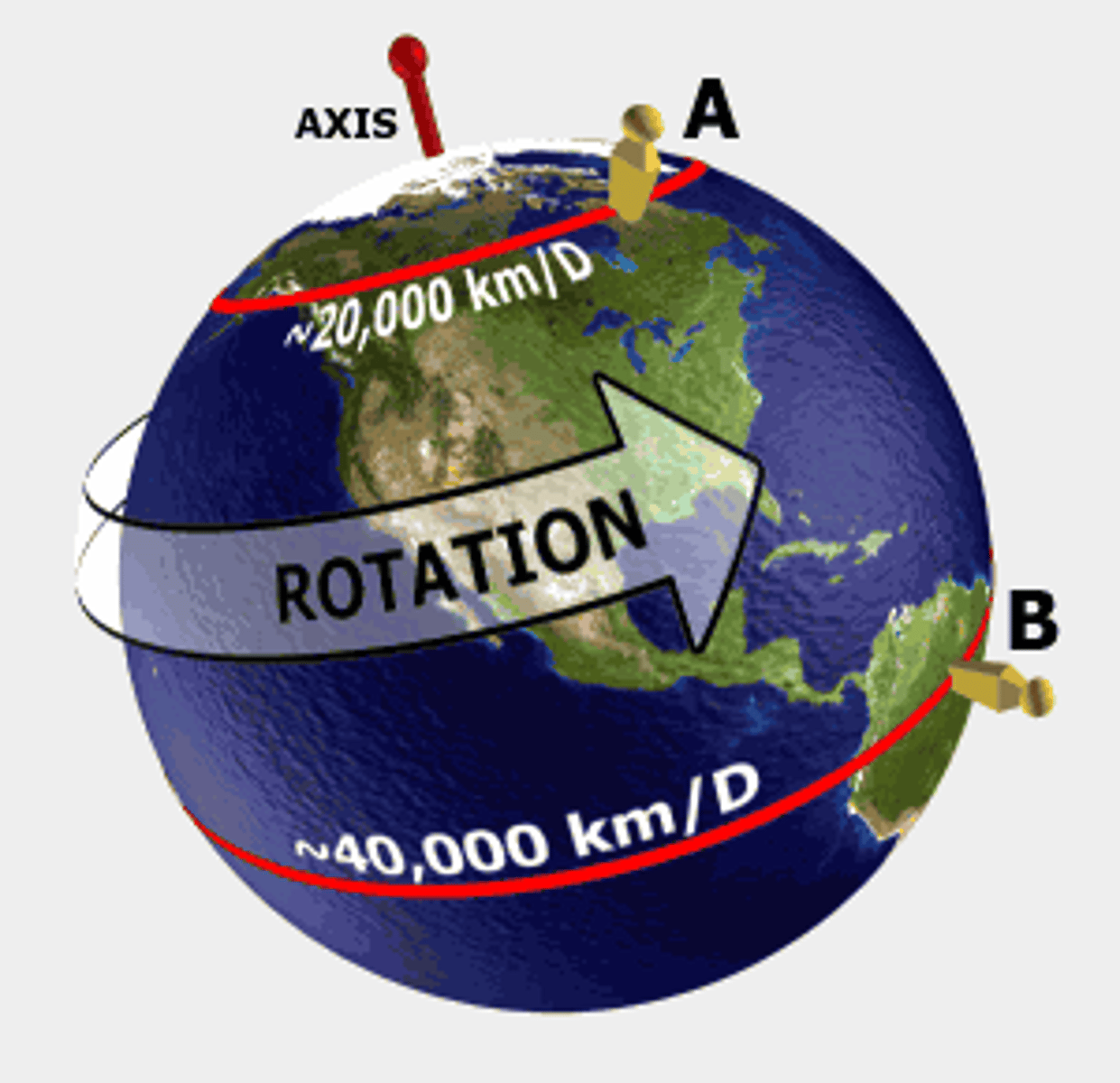
One Complete Rotation:
-360°
-24 Hours
15° PER HOUR
-Locations west of the Prime Meridian are earlier and locations east of the Prime Meridian are later
What direction does the earth rotate?
West to the East
Solar Noon
The time when the sun is most overhead for your location. This time is not the same for everyone.
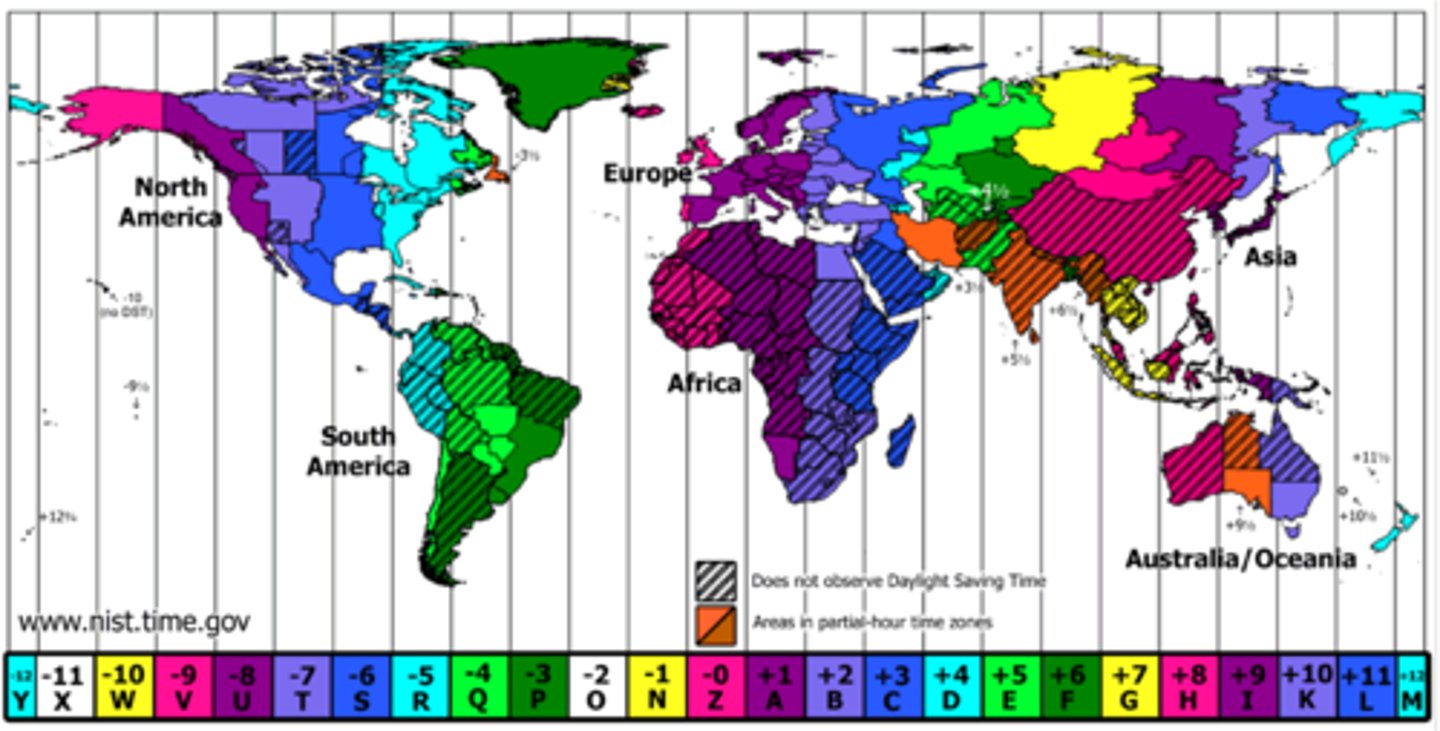
Timezones
24 Different Time Zones
-4 continental timezones in the US
*Eastern= 75° W
*Central= 90° W
*Mountain= 105° W
*Pacific= 120° W
-2 Others
*Alaskan- 150° W
*Hawaiian-Aluetian= 165° W
FIELD MAPS
Field
A field is a given region that has definite boarders/boundaries and every location has a measurable quantity
2 General Classes of Fields
Scaler and Vector
Scaler Field
Decreases completely in terms of amount
ex: 20°C
Vector Field
Involves an amount and a direction
ex: wind (17mph/east)
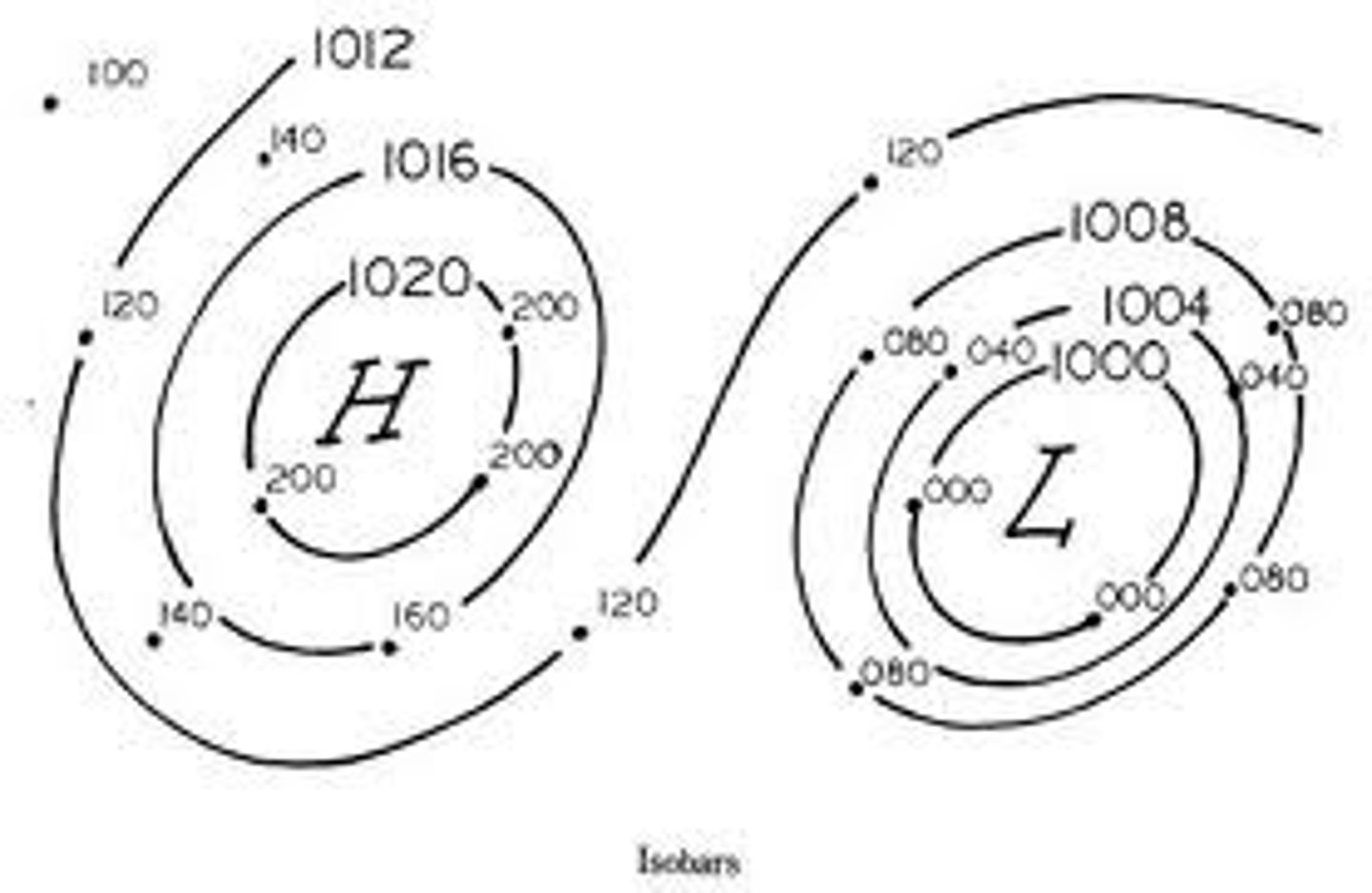
Field Map
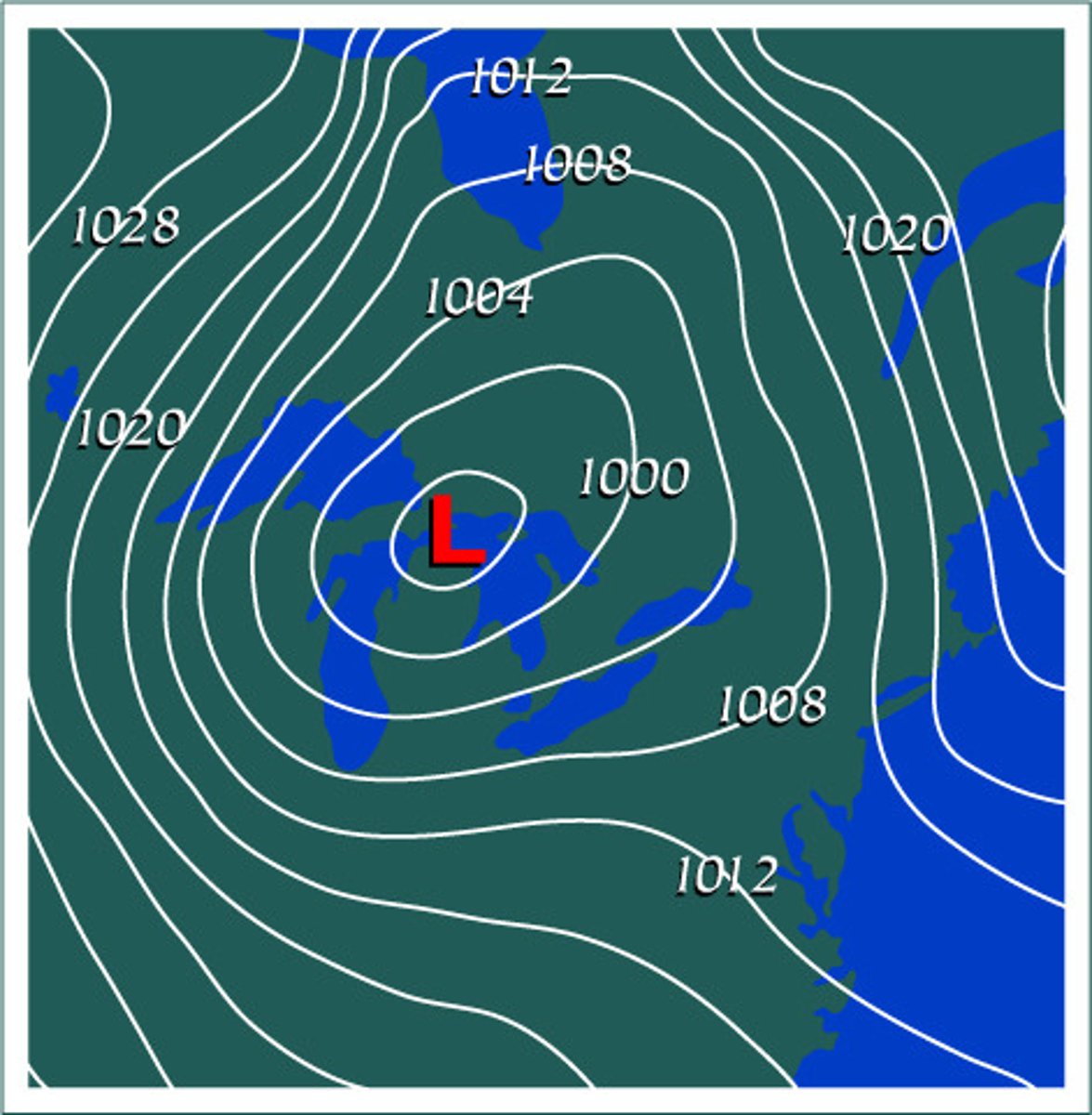
Isolines
Lines connecting points of equal value
EX: isobars- air pressure
isotherms- temperature
Rules For Connecting Isolines
1. Check Interval
2. Connect all points of equal value
3. ISOLINES NEVER CROSS
4. Isolines must run through the boarders of the field (with the exception of circles)
Source
Region where value is the highest
Sink
Region where value is the lowest
Movement of Energy
Source to Sink (High concentration -> low concentration)
Gradient
Change in field value/ Distance
WHEN LINES ARE CLOSER TOGETHER THEY HAVE A HIGHER GRADIENT
Topographic/ Contour Maps
-Shows elevation on earths surface
-Isolines on a contour map are called Contour Lines
-Space between the lines is called the contour interval (CI)
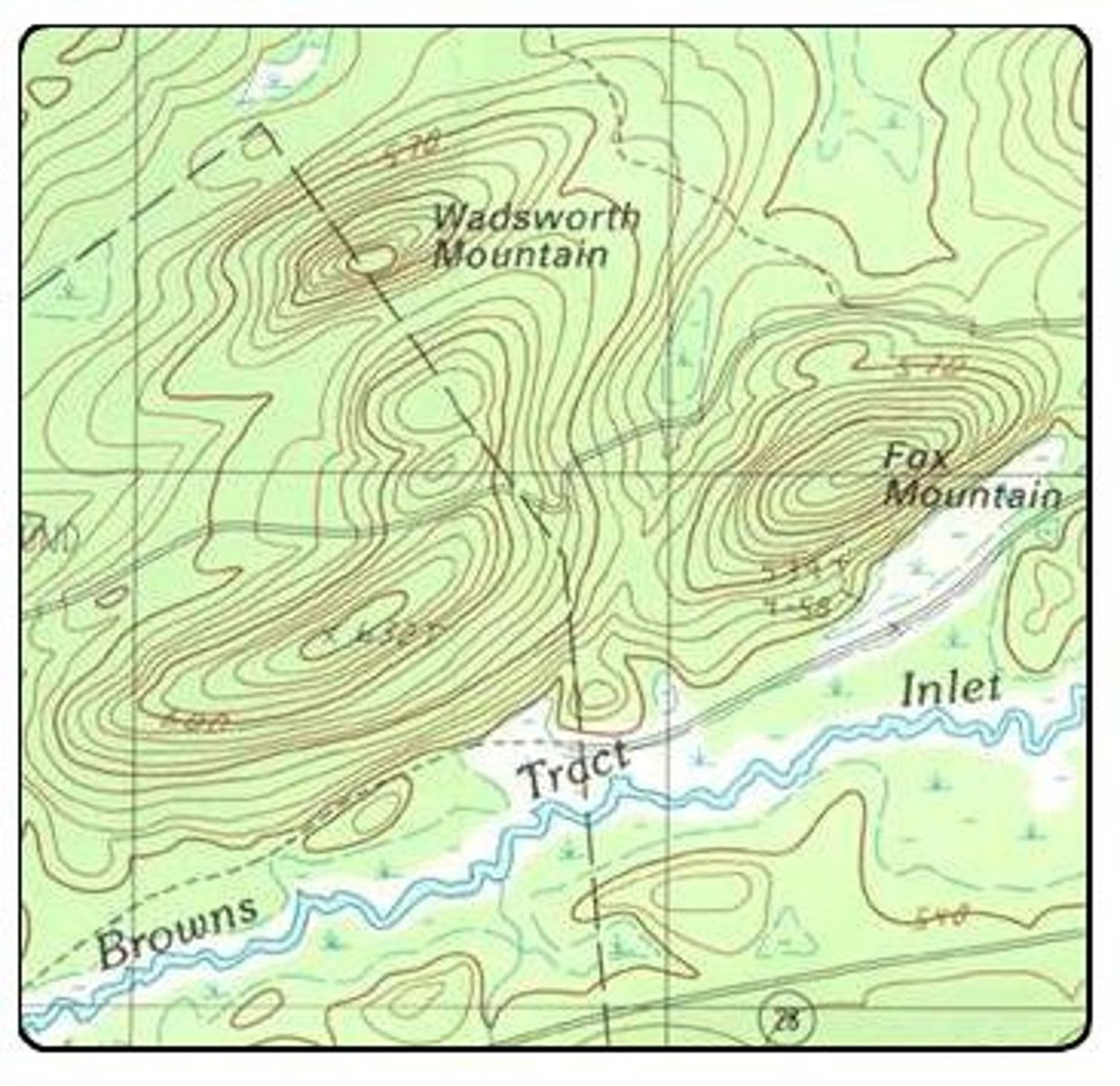
Depressions
*Anytime a regular contour line is next to a a hactured contour line, the value of both lines is the same
Hactured lines indicate a depression
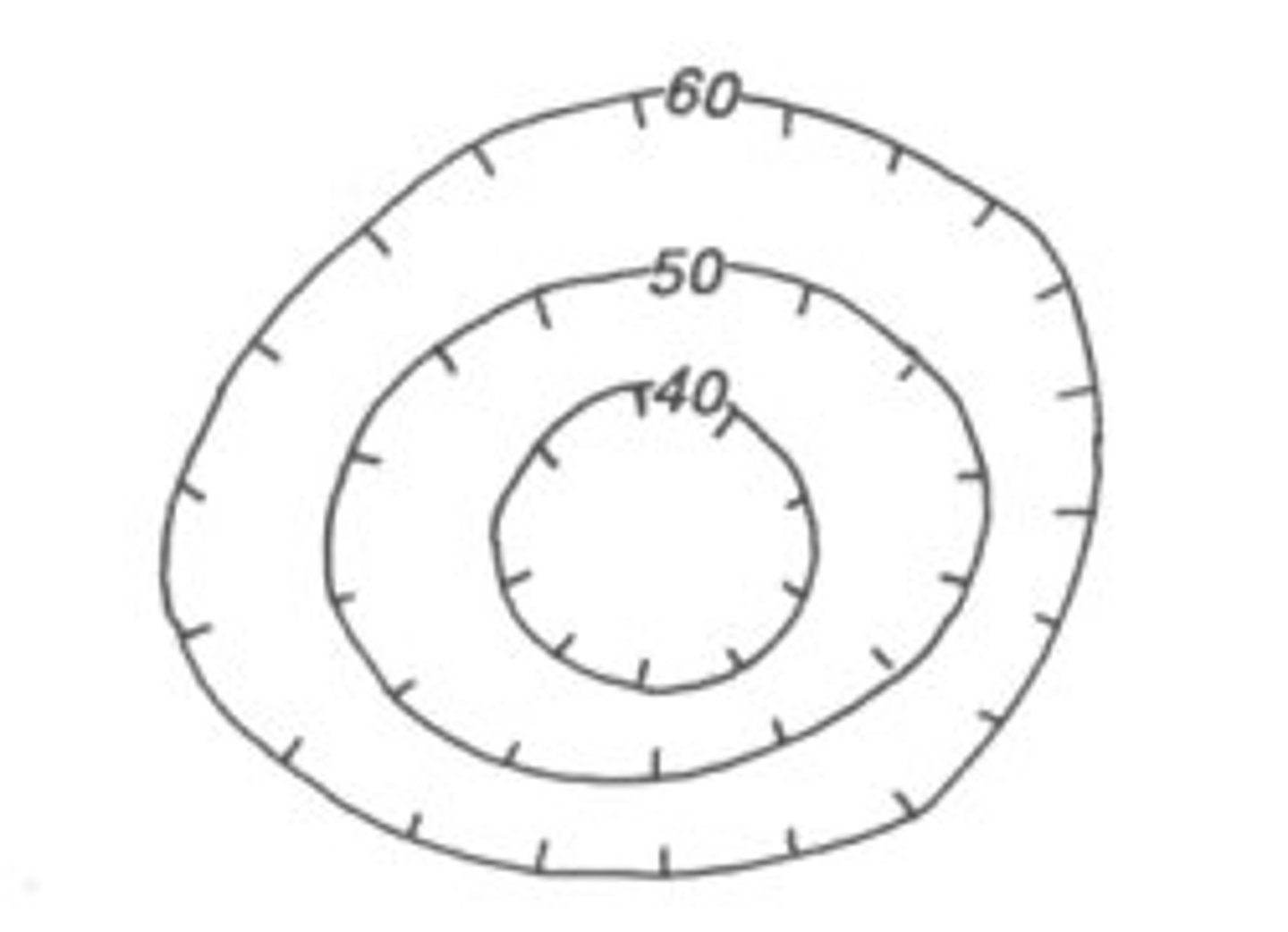
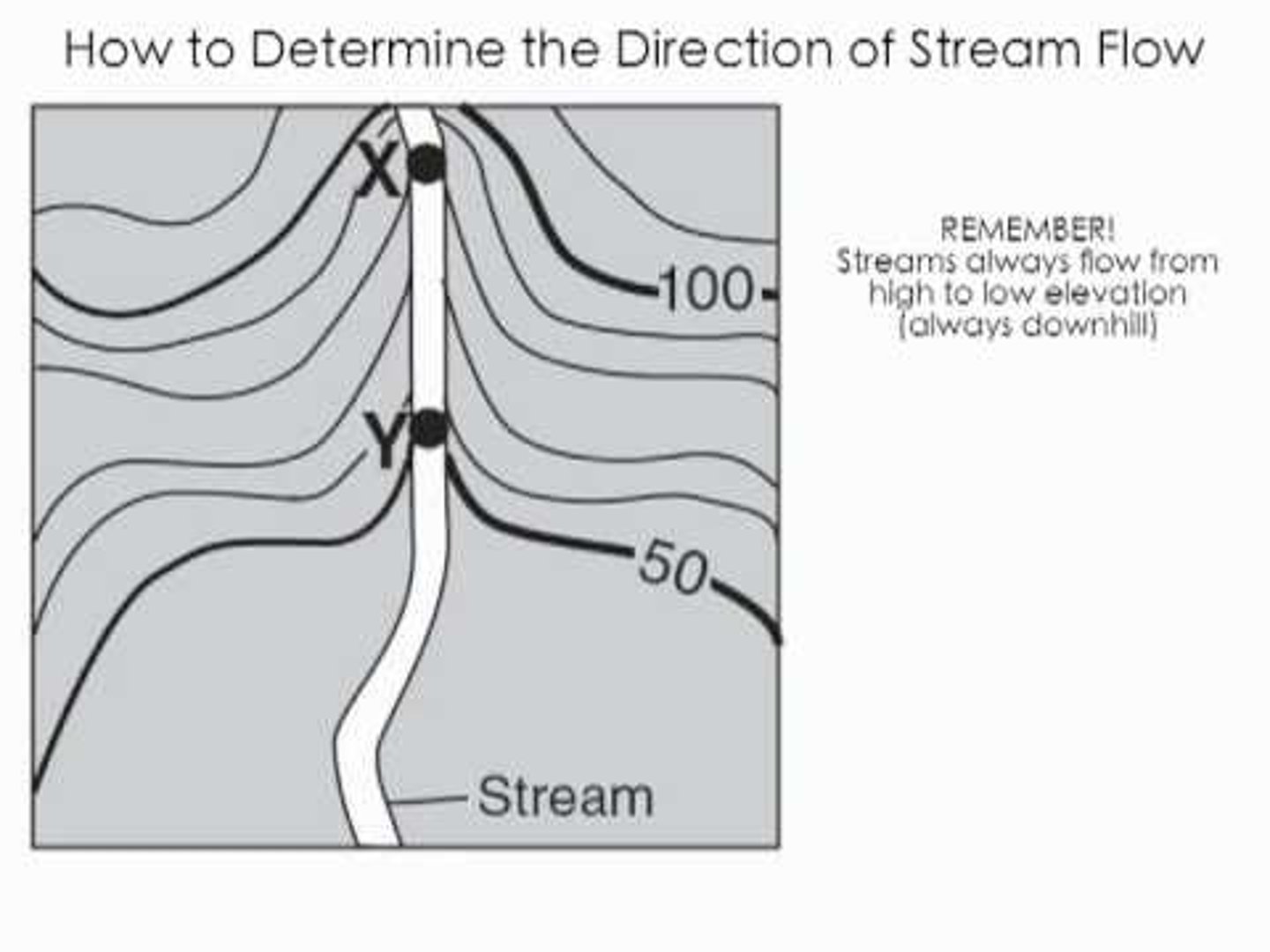
Streams in Contour Maps
Flow the opposite way the lines are pointing; Flow towards ocean; Flow from high to low
ROCKS AND MINERALS
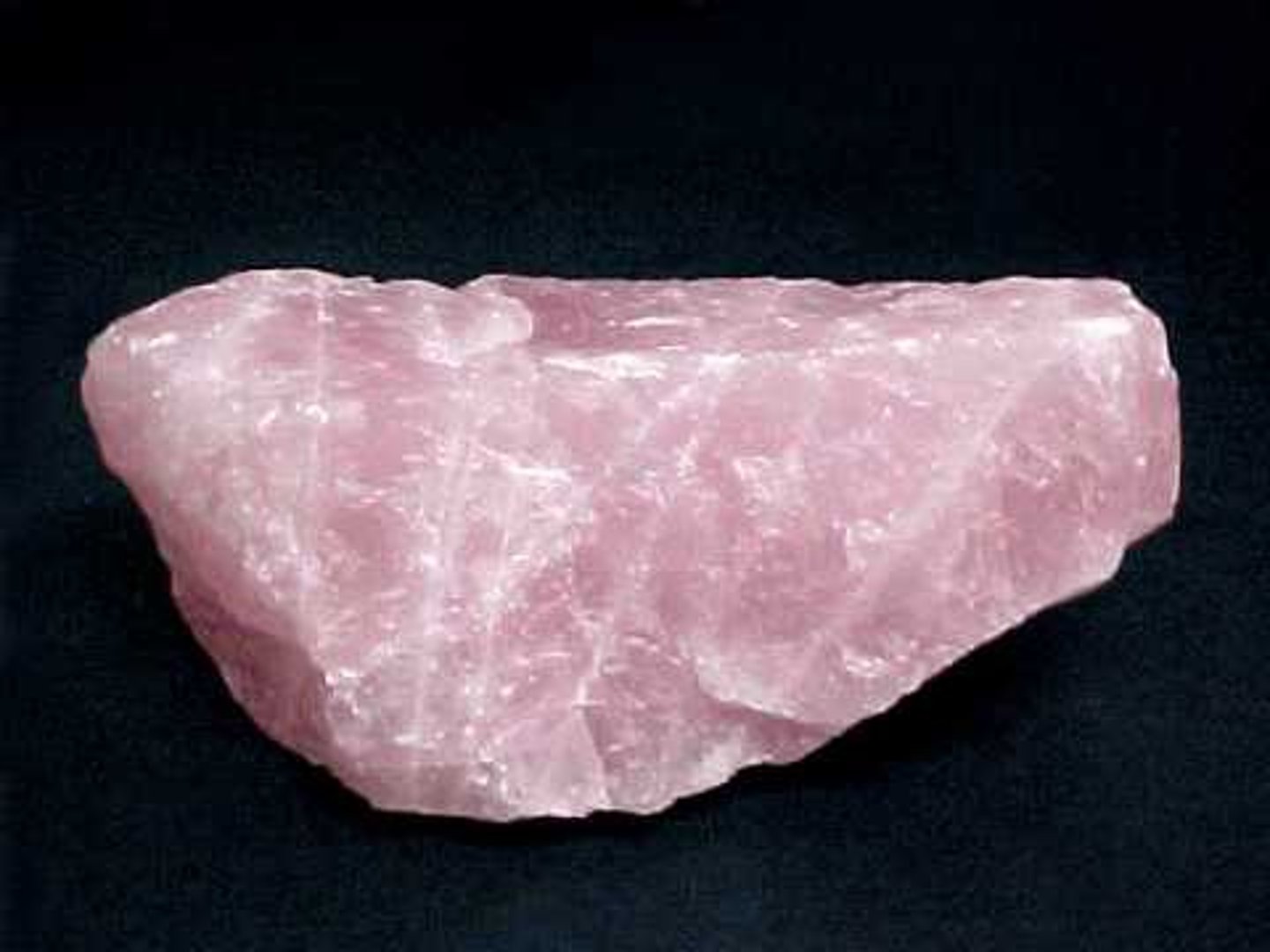

Minerals
Elements-> Minerals-> Rocks
1. Naturally Occurring
2. Inorganic-> Not from once living material
3. Crystalline Solid
(Water when frozen is a mineral)
Exception- Coal-> It is organic
What is the Most common rock forming mineral in NYS?
Quartz
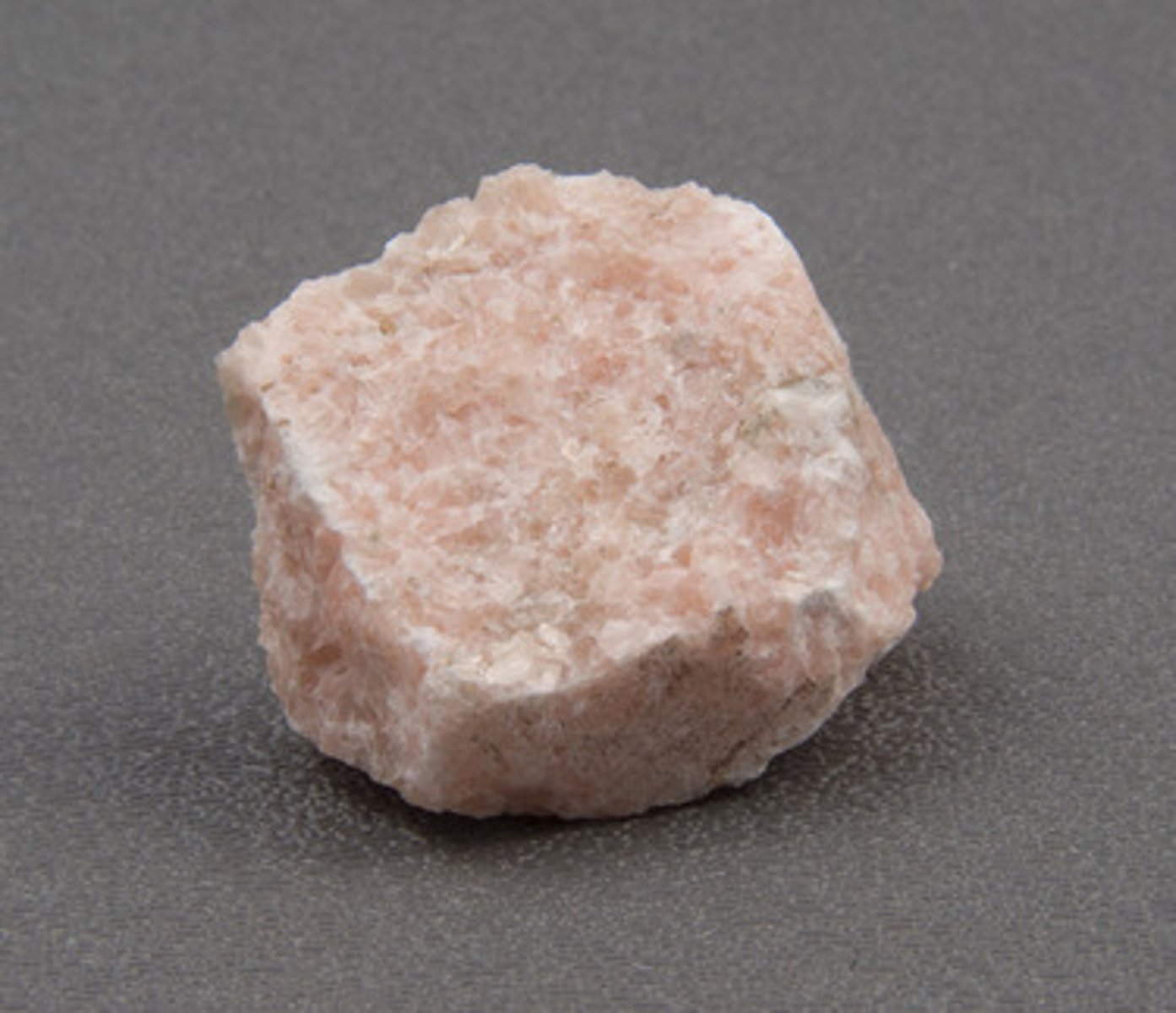
Monomineralic
Made up of only 1 mineral

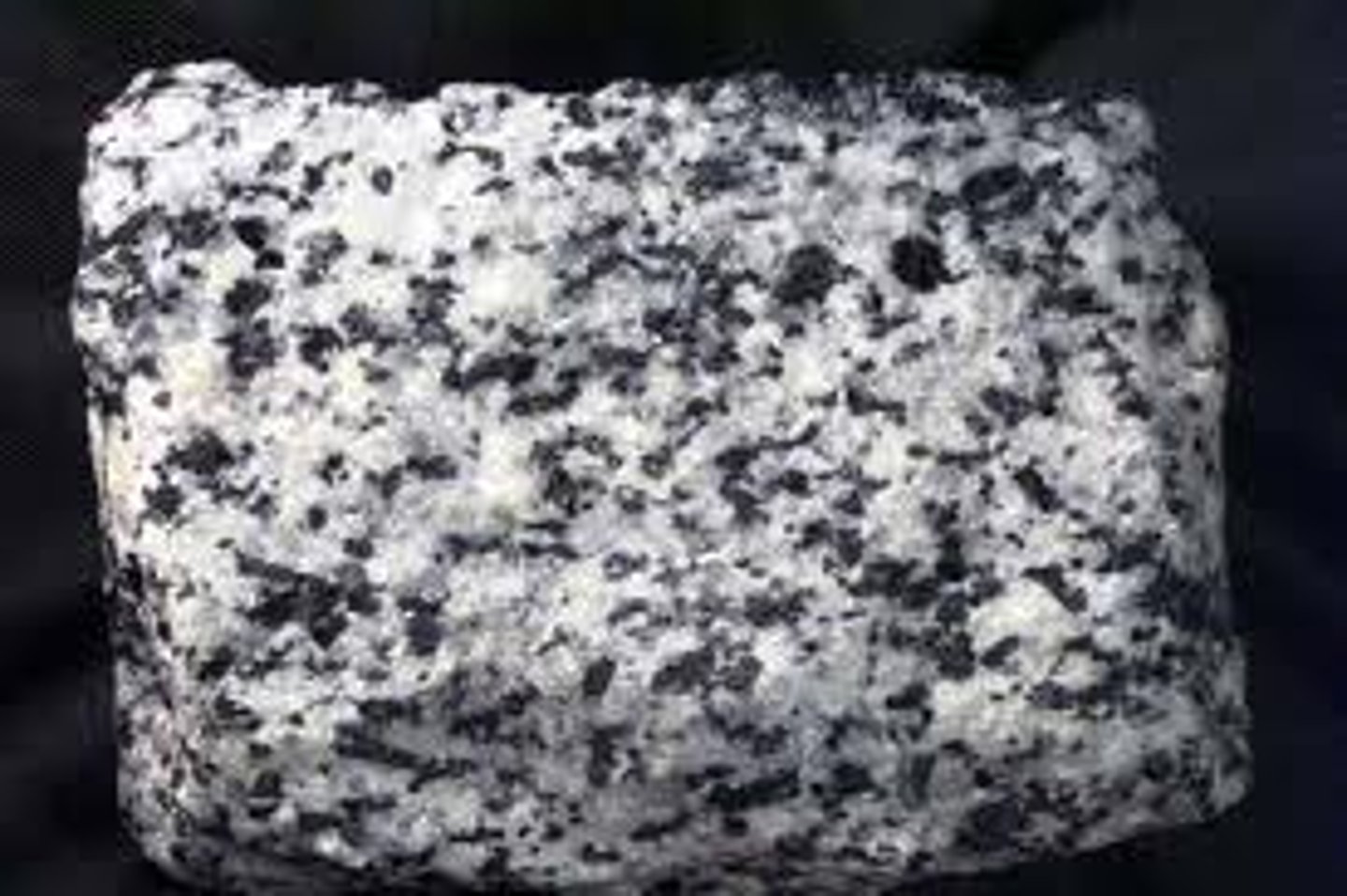
Polymineralic
Made up of more than 1 mineral

2 Most Abundant rock forming elements in the crust by % Mass
R/T pg. 1
-Oxygen= 46.1%
-Silicon= 28.2%
2 Most Abundant rock forming elements in the crust by % Volume
R/T pg. 1
-Oxygen= 94.04%
-Silicon= 1.42%
Silicates
When Oxygen and Silicon come together they form a Silicate
ex: O2 + Si = SiO2
Form a Tetrahedron Shape (3 sided pyramid w a base)
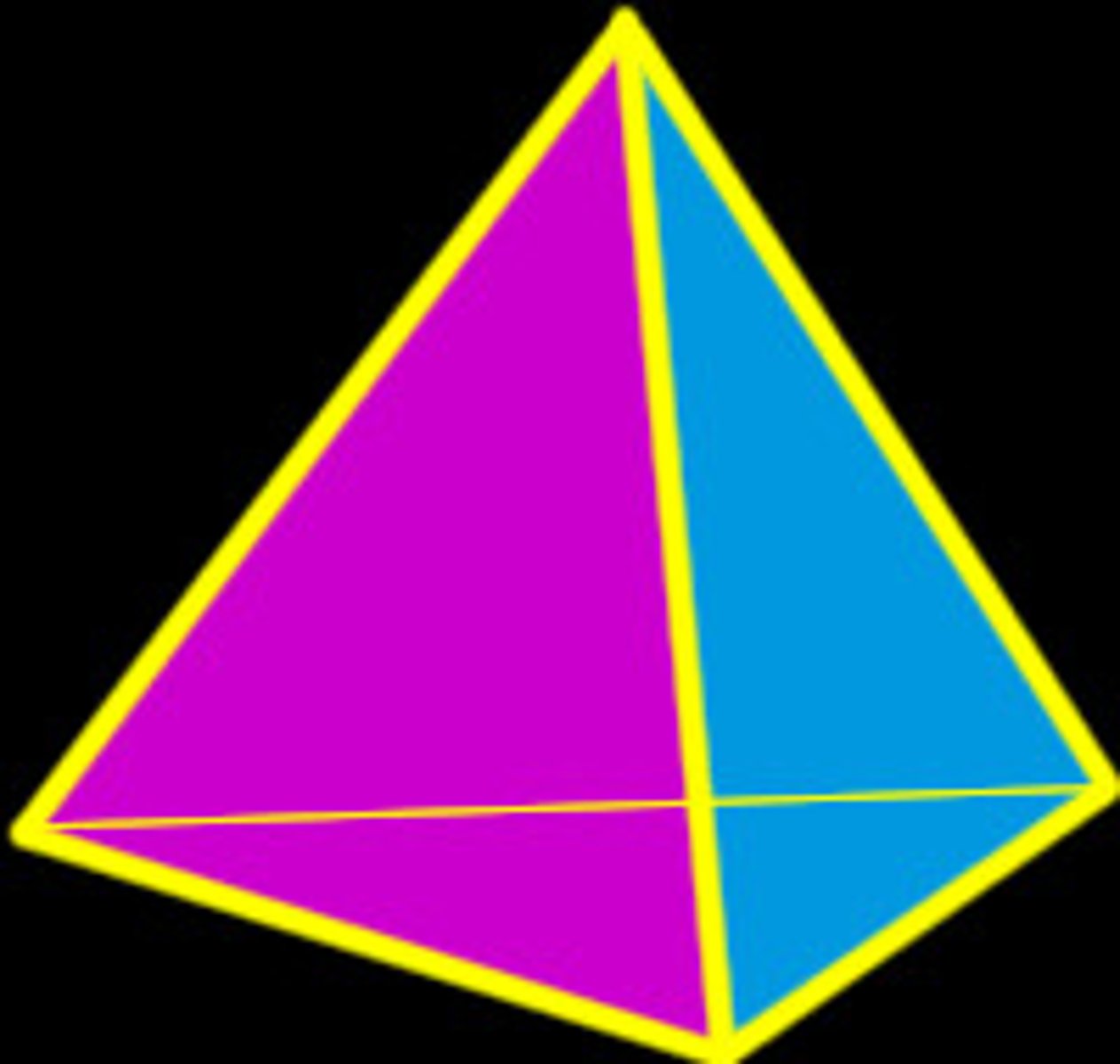
Properties of Minerals
Used to help identify a mineral
Color
Worst property to use
Problems
-1 mineral can have many different colors
-Many minerals can have the same colors
Streak
The color of the mineral in powdered form when streaked across a streak plate
-Problems- Same as color
Luster
The way in which light reflects off of the surface of a mineral
-Metalic vs. Non-Metalic
Hardness
"Scratch of be scratched"
MOH'S SCALE
1 (Softest)-> 10 (Hardest)
EX: Soft= Talc
Hard= Diamond
Cleavage vs. Fracture
The way an object breaks
Cleavage
Tendency of a mineral to break along definite planes of weaknesses
Breaks the same way every time
Fracture
Random Breakage
No definite angles
Chemical Test
When acid is placed on a mineral and checked for bubbling
*Indicates if a mineral is a carbonate
ex: Calcite
Specific Gravity
Density of a mineral compared to the density of water
What causes the properties of Minerals?
INTERNAL ARRANGEMENT OF ATOMS