CH 15- Special Senses- Smell, taste and vision
1/206
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
207 Terms
Olfaction
Sense of smell
Occurs in response to odors stimulating sensory receptors in the olfactory region of the nasal cavity
Olfactory epithelium

Olfactory epithelium
Contains cell bodies and dendrites of ~10 million olfactory neurons
Dendrites extend to the epithelial surface
Olfactory vesicles
Olfactory hairs
Basal cells
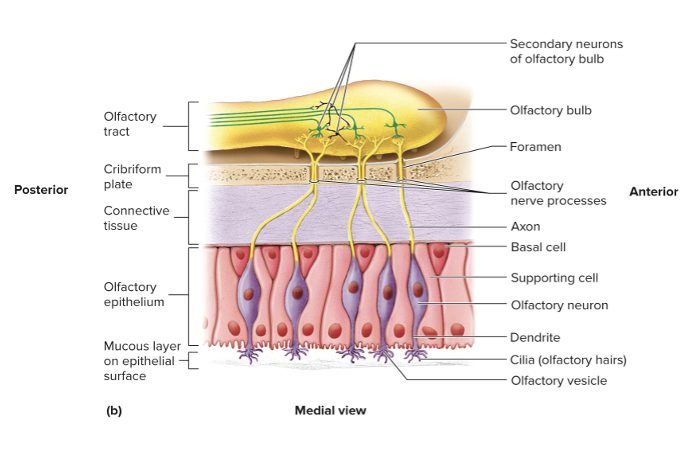
Olfactory vesicles
Bulbous enlargements at the ends of dendrites
Olfactory hairs
Cilia on olfactory vesicles that are covered in thin mucous film
Basal cells
Replace olfactory cells every 2 months
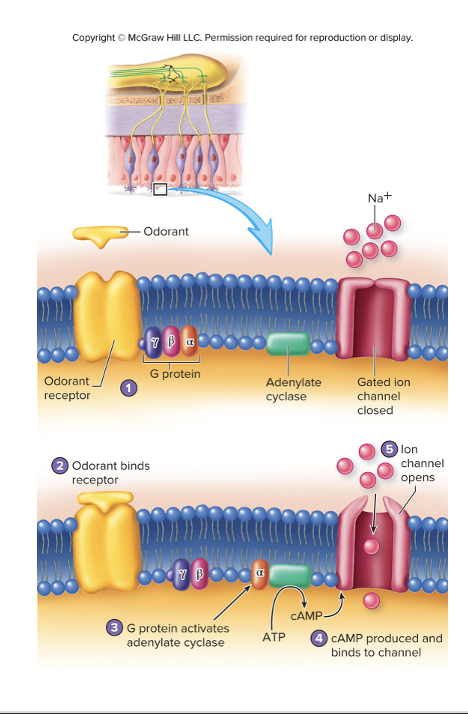
Odorants
Airborne molecules that enter into nasal cavity and dissolve in fluid covering the olfactory epithelium
Bind to odorant receptors (chemoreceptors)
1000 different odorant receptor molecules
Regulate multiple intracellular pathways involving G proteins, adenylate cyclase, and ion channels allowing for detection of ~4000 smells
Seven primary classes
Seven primary classes
Camphoraceos (mothballs)
Musky
Floral
Pepperminty
Ethereal (fresh pears)
Pungent
Putrid
Neuronal Pathways for Olfaction
Complex pathways involving in multiple areas of the cerebrum
Olfactory stimuli causes perception of specific odors and emotional and autonomic responses
Majority of neurons in olfactory cortex areas in the temporal and frontal lobes to perceive odors
Piriform cortex
Some olfactory neurons project to secondary olfactory areas involved in emotional and autonomic responses
Include hypothalamus, hippocampus, and structures of the limbic system

Taste
Gustation
Taste buds
Sensory structures of taste
Small, oval structures located along the edge of papillae on the tongue, palate, lips and throat
Taste (gustatory) cells
Taste hairs
Basal cells
Supporting cells
Taste gustatory cells
About 50 sensory cells per taste bud
Taste hairs
Microvilli that extend through the taste pore of the taste bud
Replaced about every 10 days throughout life
Basal cells
develop into new taste cells
Supporting cells
Support taste cells
Lingual Papillae
Filiform
Vallate
Folliate
Fungiform
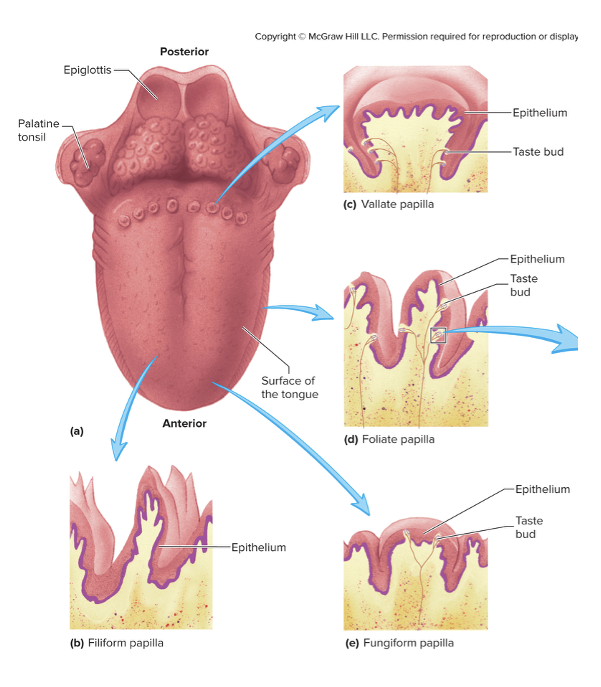
Filiform
Filament shaped
Most numerous
No taste buds
Give rough surface on tongue
Vallate
Largest and least numerous (8-12)
Form V-shaped row along the border and anterior and posterior parts of the tongue
Foliate
Leaf shaped
Folds on the sides of the tongue
Contain most sensitive taste buds
Numerous in children and decrease with age
Fungiform
Mushroom shaped
Scattered on the superior surface of the tonge
Tastants
Substances that dissolve in saliva and enter taste pores and stimulate taste cells
Have short connections that release neurotransmitters to secondary sensory neurons
Five taste classes
Five taste classes
Salty
Sour
Sweet
Bitter
Umami
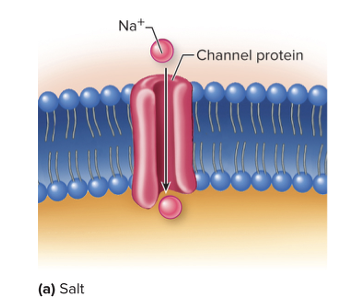
SALTY
Na+ diffuses through Na+ channels on the surface of the taste cells causing depolarization
Low sensitivity
SWEET
Tastant (sugar) binds to G protein-couple receptor molecules on taste hairs of taste cells
Leads to depolarization
Low sensitivity

SOUR
H+ of acids cause depolarization by three mechanisms
Enter the cell directly through H+ channels
H+ bind to ligand-gated K+ channels and block K+ from exiting the cell
H+ can open ligand-gated channels for other positive ions allowing them to enter the cell
BITTER
Alkaloid tastants stimulate via G protein mechanism
Highly sensitive
Detects toxins
UMAMI
Results from amino acids (glutamate)
Depolarization via G protein mechanism
Influences of taste
Texture of food
Temperature of food
Adaptation of taste can occur within 1-2 seconds after perception complete adaptation within 5 minutes
Occurs at the level of the taste bud and in the CNS
Olfactory sensations
Neural Pathways for taste are carried by three cranial nerves
Facial nerve (CN VII)
Glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)
Vagus nerve (CN X)
Neuronal Pathways for taste
Axons of cranial nerves carry information to the tractus solitarius of the medulla oblongata
Fibers from the nucleus of the tractus solitarius extend to the thalamus and decussate at the level of the midbrain
Neurons from the thalamus project bilaterally to the taste areas in the insula of the cerebrum
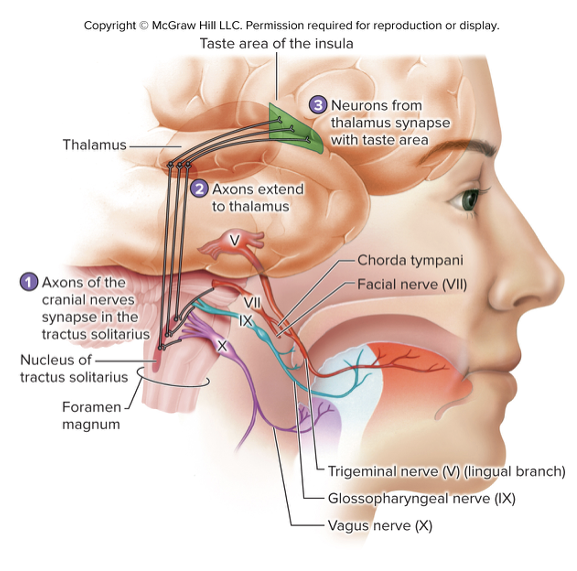
Three cranial nerves that carry taste
Facial nerve (CN VII)
Chorda tympani – branch of the facial nerve that transmits taste sensation from anterior 2/3 of the tongue
Glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)
Carries taste sensation from posterior 1/3 of the tongue, vallate papillae, and superior pharynx
Vagus nerve (CN X)
Carries taste sensation from the root of the tongue and epiglottis
Visual system
Includes eyes, accessory structures, optic nerves (CN II), and pathways
Eye
Optic nerve and tracts
EYE
Includes eyeball and lens
Respond to light and initiate afferent action potentials
Optic nerve tracts
Transmit action potentials from the eye to the brain
Accessory Structures of the Eye
Important for maintenance and protection of the eyes
Protect, lubricate, move, and aid in the function of the eye
Accessory Structures of the Eye includes:
Eyebrows
Eyelids
Eyelashes conjunctiva
Lacrimal apparatus
Extrinsic eye muscles
EYEBROWS
Hairs superior to the orbits
Prevents perspiration from running into the eye
Helps shade eye from direct sunlight
EYELIDS
With eyelashes protect eyes from foreign objects by blinking
Blinking helps lubricate the eye by spreading tears
Regulates amount of light entering the eye
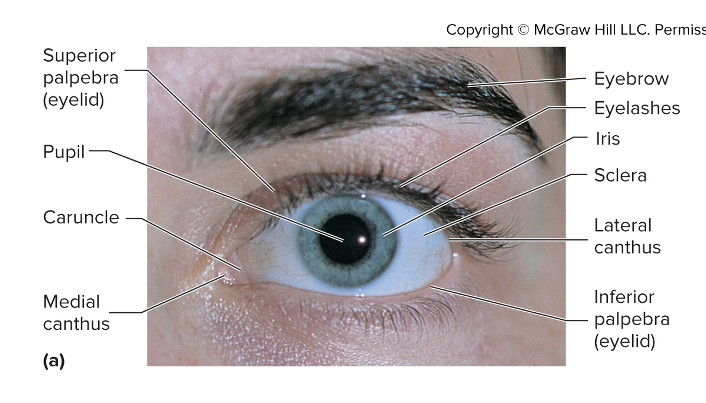
Palpebral fissure – space between eyelids
Canthi – angles where the superior and inferior eyelids meet (medial and lateral)
Caruncle – small reddish/pink mound in the medial canthus, houses modified sebaceous and sweat glands
Eyelashes – 2-3 rows of hairs at the free edges of the eyelids
Ciliary glands – modified sweat glands that lubricate the eyelashes
Sty – inflammation of the ciliary glands
Meibomian (tarsal) glands – sebaceous glands near the inner margins of the eyelid that secrete sebum to lubricate the lids
Chalazion – infection or blockage of the meibomian gland
Sty
Inflammation of the ciliary glands
Meibomian (tarsal) glands
Sebaceous glands near the inner margins of the eyelid that secrete sebum to lubricate the lids
Chalazion
Infection or blockage of the meibomian gland
Layer of the eyelid superficial to deep
Thin layer of skin
Thin layer of areolar connective tissue
Layer of skeletal muscle (orbicularis oculi and levator palpebrae superioris muscles)
•Tarsal plate – crescent shaped layer of dense connective tissue helping to maintain shape of the eye
•Palpebral conjunctiva
Accessory Structures of the Eye: Tarsal Plate
Crescent shaped layer of the dense connective tissue helping to maintain shape of the eye
What is the conjunctiva
Thin, transparent mucous membrane associated with the eyelids and exposed areas of the eye
What does the conjunctiva produces
Secretions help lubricate the surface of the eye
Parts of the conjunctiva
Palpabreal conjunctiva
Bulbar conjunctiva
Superior and inferior conjunctival fornices
Conjunctiva: Palpebral conjunctiva
Covers the inner surface of the eye
Conjunctiva: Bulbar conjuncitva
Covers the anterior white surface of the eye
Conjunctiva: Superior and inferior conjunctival fornices
Points where the palpebral and bulbar conjunctive meet
Conjunctivitis
Inflammation of the conjunctiva caused by infection or other irritation
Acute contagious conjunctivitis (pink eye) is caused by____
bacterium
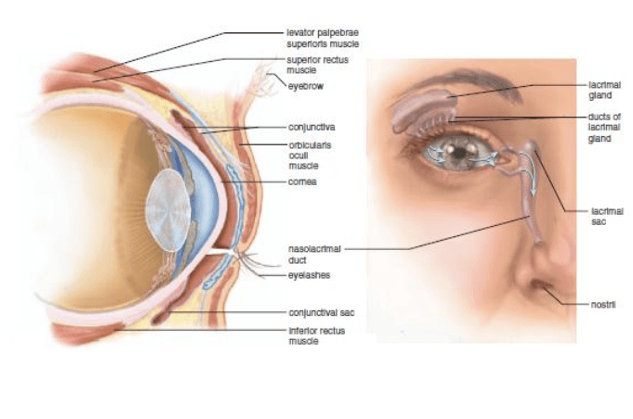
The lacrimal apparatus is formed by ____
Lacrimal gland
Tears
Nasolacrimal duct
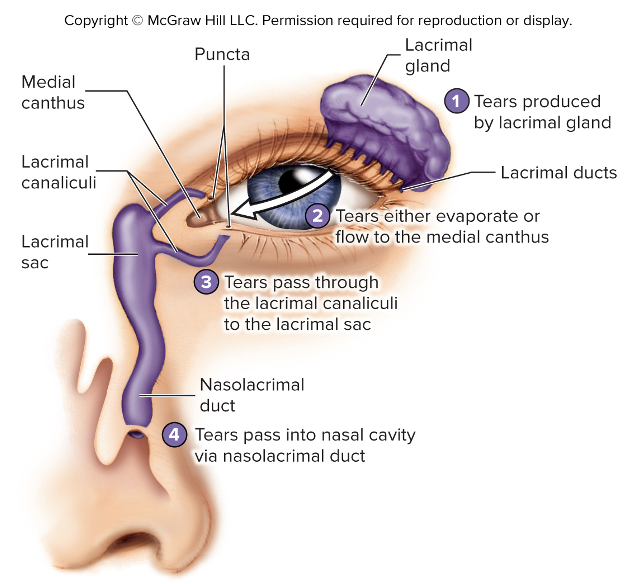
Lacrimal gland is located in
Superolateral corner of the orbit
Lacrimal glands produce
tears that exit through several lacrimal ducts
The lacrimal glands are innervated by____
parasympathetic fibers from facial nerve (CN VII)
What do tears do?
Moisten surface of the eye, lubricate eyelid, wash away foreign objects
How many tears are produce in a day?
~1 mL/day
Tears contain_____
salt, mucus, and lyzozomes (enzymes that kills certain bacteria)
Nasolacrimal duct
Beginning in the inferomedial corner of the orbit
How many extrinsic eye muscles are there?
6
The Extrinsic eye muscles 6 muscles_____
4 run straight anteroposteriorly
2 run at an angle to the globe of the eye
4 extrinsic eye muscles that run anteroposteriorly
Superior rectus m.- innervated by the oculomotor nerve (CN III)
Inferior rectus m.- innervated by the oculomotor nerve (CN III)
Medial rectus m.- innervated by the oculomotor nerve (CN III)
Lateral rectus m.- innervated by the abducens nerve (CN VI)
2 extrinsic eye muscles that run at an angle to the globe of the eye
Superior oblique m.- innervated by the trochlear nerve (CN IV)
Inferior oblique m.- innervated by the oculomotor nerve (CN III)
Eye
Hollow, fluid filled sphere
The eye is composed of ____
Three layers (tunics)
Fibrous tunic- outer layer
sclera and cornea
Vascular tunic- middle layer
choroid, ciliary body, iris
Nervous tunic- inner layer
retina
The fibrous tunic is composed of____
Sclera and Cornea
Fibrous tunic:Sclera
White outer layer
Posterior 5/6 of the eyeball
Loosely attached to the bulbar conjunctiva
Fibrous tunic:Sclera is composed of ____
Dense collagenous connective tissue with elastic fibers
Fibrous tunic:Sclera maintains and protects _____
Maintains the shape of the eyeball, protects its internal structures
Fibrous tunic:Sclera provides____
Attachment point for the muscles that move it
Fibrous tunic:Cornea
Continuos with the sclera
Avascular, transparent structure that allows light to enter
Refracts (bends) light
Fibrous tunic:Cornea consists of____
Connective tissue matrix containing collagen, elastic fibers and proteoglycans with simple squamous epithelial cells on either side
Parts of the Vascular Tunic
Choroid
Ciliary body
Iris
The vascular tunic contains_____
Most of the blood vessels of the eye
Short ciliary arteries
A large number of melanin containing pigment cells and appears black in color
What are short ciliary arteries in vascular tunic
Arteries that pierce the sclera and provide arteries to the vascular tunic
branches of the ophthalmic artery that branches off the internal carotid artery
Vascular Tunic: Choroid
Thin layer
Portion associated with the sclera
Vascular Tunic: Ciliary body parts
Continuous with the choroid
Ciliary ring- outer portion
Ciliary processes- inner processes that attach to suspensory ligaments
produce aqueous humor
Ciliary muscles- smooth muscle organized into outer radial fibers and inner circular fibers that regulate the thickness of the lens
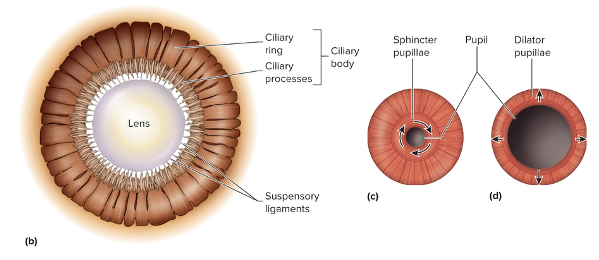
Vascular Tunic: Iris
Portion visible through the cornea
Color depends on the amount of melanin present
Attached to the ciliary body
Vascular Tunic: Iris is composed of
Mainly smooth muscle that regulates the size of the pupil (allows light to enter)
Sphincter pupillae- circular group, innervated by parasympathetic fibers from the oculomotor nerve (CN III)
Dilator pupillae- radial group, innervated by sympathetic fibers
Nervous Tunic: Retina consists of
Pigment layer- composed of pigmented simple cuboidal epithelium
Neural layer- responds to light, contains numerous photoreceptors
120 million rods
6-7 million cones
numerous relay neurons
Nervous Tunic: Retina
Macula
Fovea centralis
Optic disc
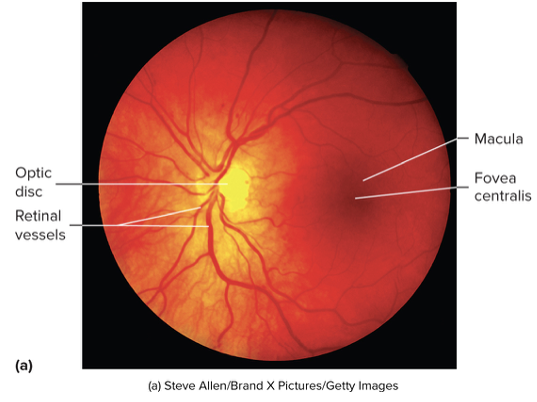
Nervous Tunic: Retina Macula
Small, yellow spot near the center of the posterior retina
Nervous Tunic: Retina Fovea centralis
Center of the macula where light is most focused when looking directly at an object that contains only cones
Highest point of visual acuity
Nervous Tunic: Retina Optic disc
White spot medial to macula that the central retinal artery enters and the central retina artery enters and the central retinal vein exits and where axons exit to from the optic nerve
Lacks photoreceptors (blind spot)
Chambers of the eye
Anterior chamber
Posterior chamber
Vitreous chamber
Anterior chamber
Between the cornea and iris
Filled with aqueous humor
Posterior chamber
Between iris and lens
Filled with aqueous humor
Vitreous Chamber
Larger chamber posterior to the lens
Filled with vitreous humor
The aqueous humor helps maintain______
Intraocular pressure that keeps the eyeball inflated and helps maintain eyeballs shape
The aqueous humor _____ light
Refracts
The aqueous humor provides_____
Nutrition for the structures of anterior chamber
The aqueous humor is produced by____
Ciliary processes
The Aquou
Lens-Capsule
Highly elastic, transparent cover of the lens
Electromagnetic Spectrum
Entire range of wavelengths (frequencies) of electromagnetic radiation
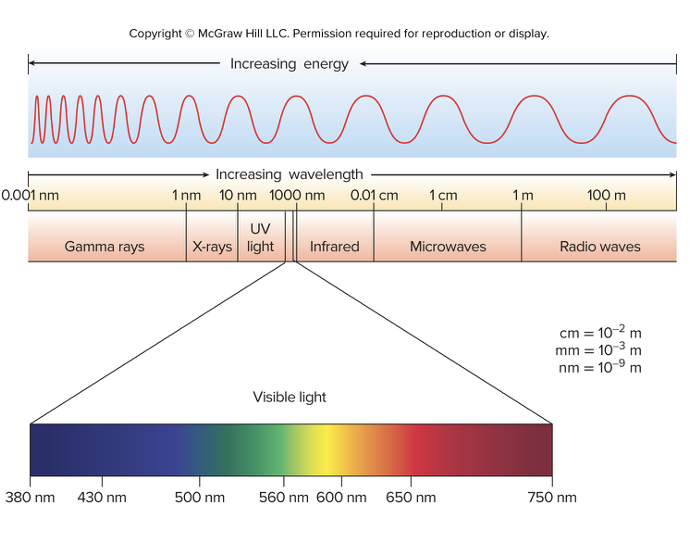
Electromagnetic spectrum- Visible light
Portion that can be detected by the human eye
Visible spectrum- 380-750nm