Aortic regurgitation and diseases
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
What is Aortic Valve regurgitation?
•In this condition, the aortic valve doesn't close properly, causing blood to flow backward into the left ventricle.
Aortic Regurgitation is also called?
Aortic Insufficiency
What happens when a patient has (AI)?
Incompetent AOV that permits backward diastolic flow from the aorta into the left ventricle.
What type of murmur is heard with AI?
High-pitched, blowing, diastolic decrescendo murmur at left sternal border
SEvere AI is called an
Austin Flint Murmur
What is AAO?
Acute aortic dissection, infective endocarditis, trauma
Chronic AI
AO dilatation, Aortic Stenosis
Bicuspid AV, incomplete closure, IE, RHD,
Quad AOV
Treatment for AI
•Serial echos
•AOV repair or replacement
Echo findings for AI
Echo findings (2D, M-mode, CFD, & Doppler)
•Determine Mild vs severe AI
•Use P½t slope to measure the spectral waveform
Complications of AI?
•Over time, LV Volume Overload leading to LVD & decreased LVFX & HF
• Increased risk IE
•CP
•Dizziness
•Exertional dyspnea
•Syncope
M-MODE findings
(5) AMVL diastolic flutter
(6) severe, acute AR à sudden increase in preload à LVEDP > LAP so MV closes early &
(7) AOV opens early
(8) normal AOV systolic flutter
(9) AR à closed cusps à abnormal AOV diastolic flutter
What views do we use color flow of the Aorta?
ALL VIEWS- PSLAX,APICAL 5 CH, SUPRA STERNAL, SAX AORTA, Apical 3 CH
Measure AI vena contracta in which view
The PLAX view>6mm is severe AI
With Aortic Regurgitation where do we place the CW cursor?
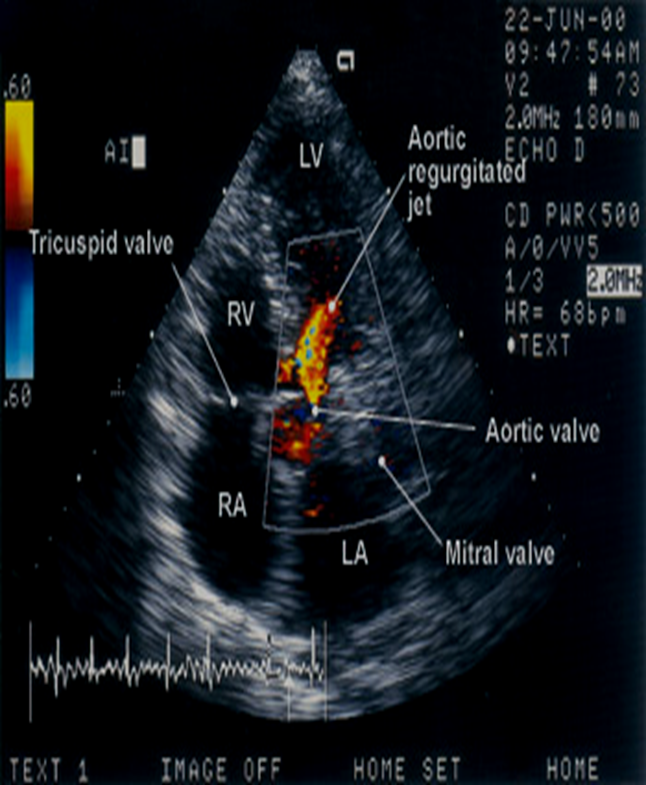
Through the AI JET
Aortic Regurgitation =
Antegrade flow
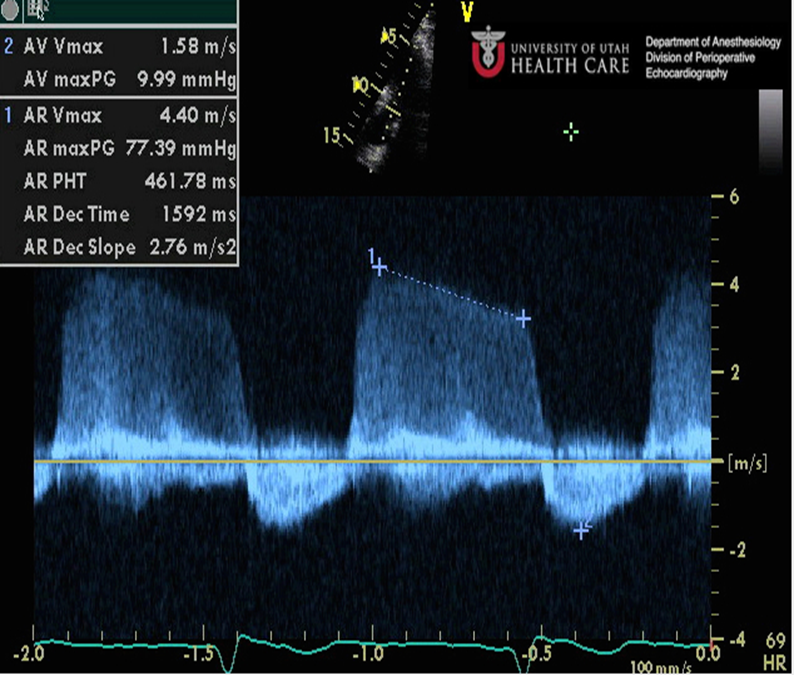
Measure PHT slope
Mild AR will have what waveform?
Flatter MS waveform and steeper AR Waveform.
Pressure diffrence gradually decreases and the AR slowly moves back through the closed AOV→LV
This creates a flatter Doppler waveform and a high Pressure Half time.
What will we see with severe AR?
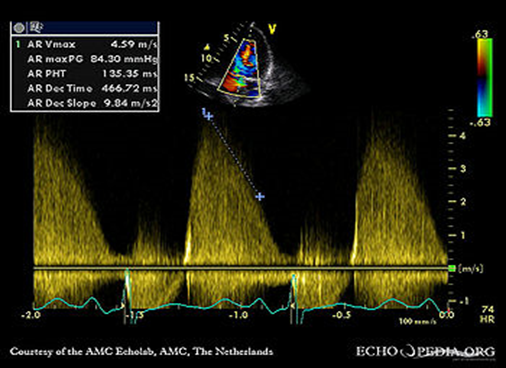
Larger the defect, the faster the AO empties→ LV
The faster the AO pressure drops _> The steeper he LVP rises
This creates a steeper Doppler waveform and a LOWER pressure half time.
The steeper the slope the more
Severe AI is.
Mild AR grading
Pressure half time would be >500 ms
AR grading Moderate
Pressure half time 500 to 200 ms
AR grading Severe
Pressure half Time <200ms
If the regurgitation jet fills LVOT at a ratio:
<25% this suggests
mild regurgitation
If the regurgitation jet fills LVOT at a ratio:
<25 to 65% this suggests
moderate regurgitation
If the regurgitation jet fills LVOT at a ratio:
>65% This suggests
Severe regurgitation
The transducer is placed in the suprasternal notch
Angle inferior with the indicator towards the left ear sometimes 12 o'clock evaluate
Evaluate the Ascending
and Descending Aorta
For dilation, dissection,
coarctation & AI flow reversal
Normal Spectral Doppler waveform through the descending aorta is
retrograde
IF AORTIC REGURGITATION IS SEVERE IT WILL
BACKFLOW INTO THE DESCENDING AORTA AND APPEAR ABOVE THE BASELINE (ANTEGRADE)
•Coarctation of the aorta is considered a
A critical congenital heart defect
CoA defect occurs when
a baby’s aorta does not form correctly as the baby grows and develops during pregnancy
What does PREDUCTAL, JUXTADUCTAL, POSTDUCTAL mean?
above
At
Below
What does a dilated Aortic root entail?
Enlargement of the Ao root, abnormal balloon like bulge/dilatation anywhere along AO
The dilated aortic root may be associated with
underlying aortic valve abnormalities as seen with bicuspid aortic valve. It may also lead to the awareness of important underlying connective tissue disorders like the Marfan’s syndrome.
Why is it imperative that the dilated aortic root be observed?
It is imperative that the dilated aortic root be observed carefully over time with serial imaging studies and that timely resection of the aneurysm be carried out before catastrophic complications such as aortic dissection, aortic rupture, or congestive heart failure from aortic insufficiency occur.
a virtual ring that is formed by joining the imaginary distal attachments of the three aortic leaflets
The Aortic Annulus
Normal AORTIC PARAMETERS

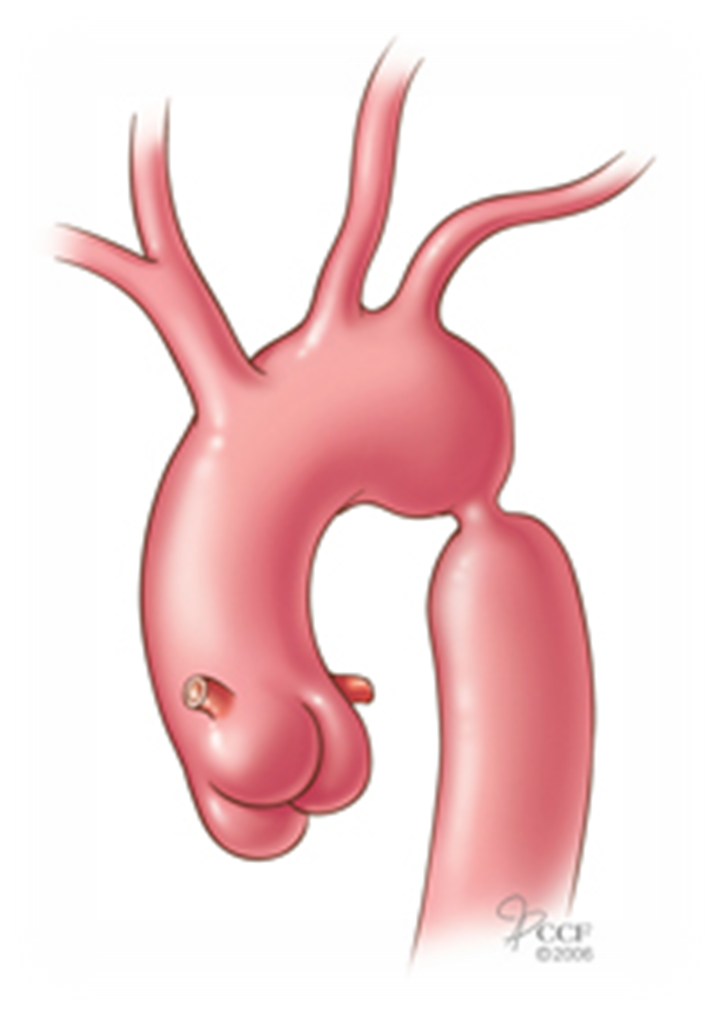
An Aortic dissection is a serious condition in which
the inner layer of the aorta tears. Blood surges through the tear, causing the inner and middle layers of the aorta to separate (dissect). If the blood-filled channel ruptures through the outside aortic wall, aortic dissection is often fatal.
Risk factors of AI
oHTN
oatherosclerosis
oAO aneurysm
oBicuspid Aortic Valve (Bicuspid aortic valve (BAV) is associated with degeneration of the medial layer of the aorta)
oAO coarctation
oconnective tissue disorder
ochromosomal aberration
oinflammation/infection
opregnancy
otrauma
+ men, 60 – 80 years of age, cocaine use, extreme weightlifting
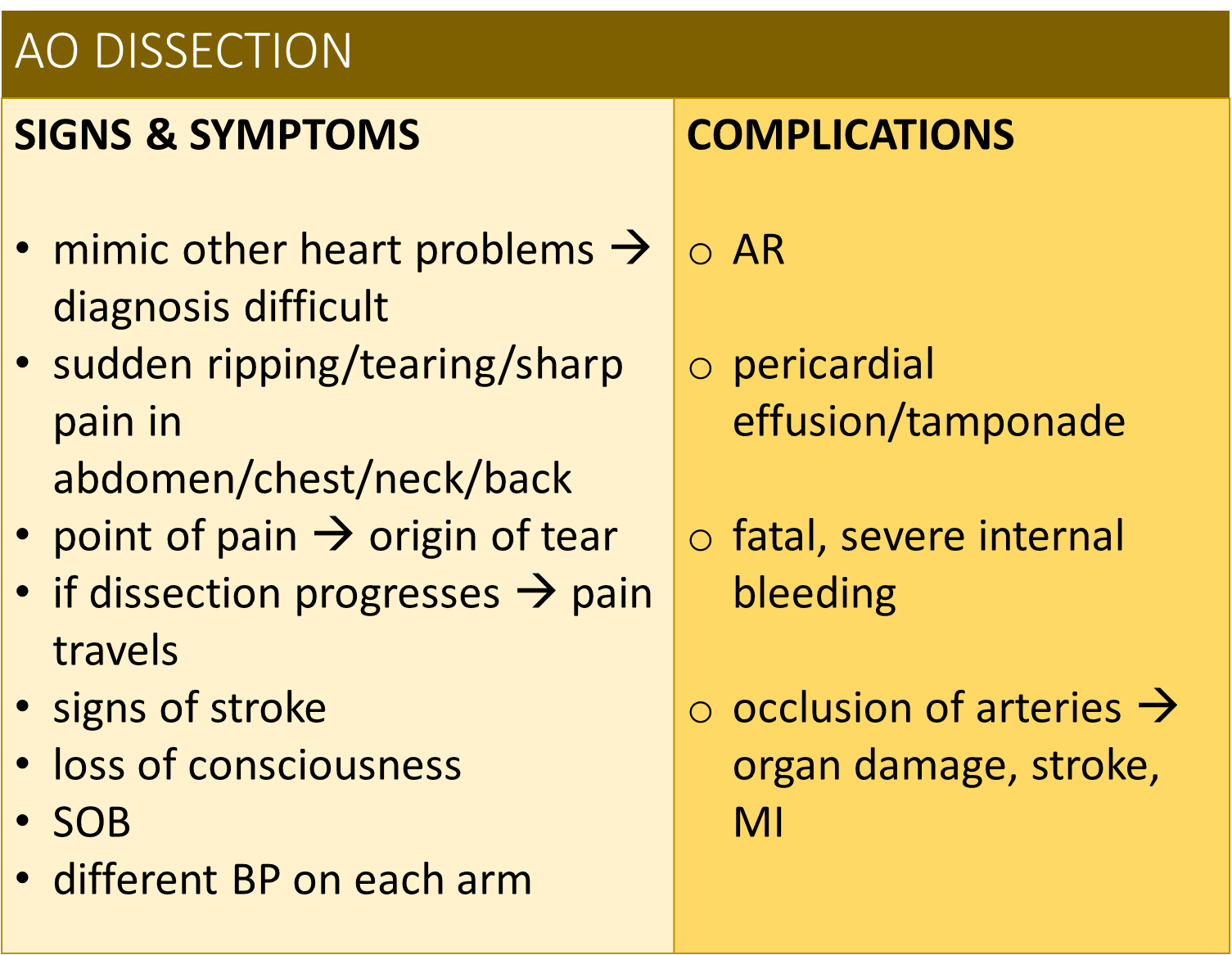
AO Dissection Signs and symptoms= Complications
Ehlers Danols Syndrome
Connective tissue disorder causing excessively elastic or stretchy skin and joints
Echo Findings include aortic root dilation, sinus of valsva aneurysm, bicuspid aortic valve, MVP, ASD and common atrium
Increased risk Aortic dissection
Aortic Dissection
The intima will detach from reaming layers of the wall allowing blood flow in the true and false
may involve aortic annulus causing acute aortic insuffiency
May involve one or both coronary artieries causing interription of conary flow and possibly an acute myocardial infraction
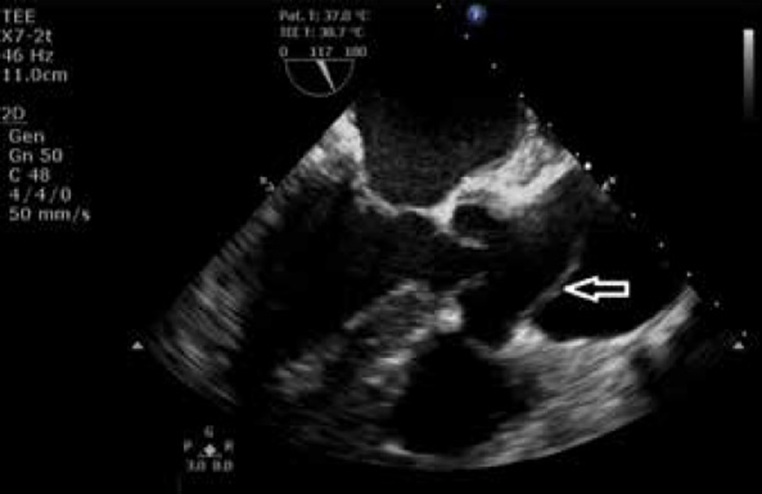
_______the preferred sonographic technique for evaluation of a potential dissection cardiovascular emergency
TEE
With Aortic Dissection _______is most commonly affected by shearing forces
The intima
With Aortic dissection, Aortic wall constantly subjected to forceful left ventricular ejection of blood during _____.
systole
Aortic Dissection Most commonly occurs
just distals to the origin of the left subclavian artery
associated with systemic htn blunt chest trauma, strenous activity, inflammotory disease
AO dissection
Patient usually experienes a painful ripping or tearing sensation in the chest when the dissection occurs, pain usually radiates to the _____
back
some congeitial disorders including _____, _______, and_______ carry increased risk of dissection
marfan syndrme, ehlers danols syndrome and turner syndrome
_________ usually demonstrates widening of the mediastinum
chest x ray