Geo 1045 Sg 8 Oceans and Coasts
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Tsunami Generation
Displacement of large water volumes by subduction zone earthquakes, underwater landslides, volcanic eruptions.
Signs of Tsunami
Rapid recession of water, exposed sea floor, loud roaring noise.
Tsunamis vs. Wind-Driven Waves
Tsunamis have longer wavelengths (>100 km) and travel faster (up to 700 km/h); wind waves are much smaller and slower.
Tsunamis vs. Wind-Driven Waves
Tsunamis have longer wavelengths (>100 km) and travel faster (up to 700 km/h); wind waves are much smaller and slower.
Destructive Nature of Tsunamis
Massive volume and high momentum allow deep inland penetration and widespread devastation.
Hurricane Formation
Requires sea surface temperatures >26.5°C (80°F), low wind shear, and moist air in the mid-troposphere.
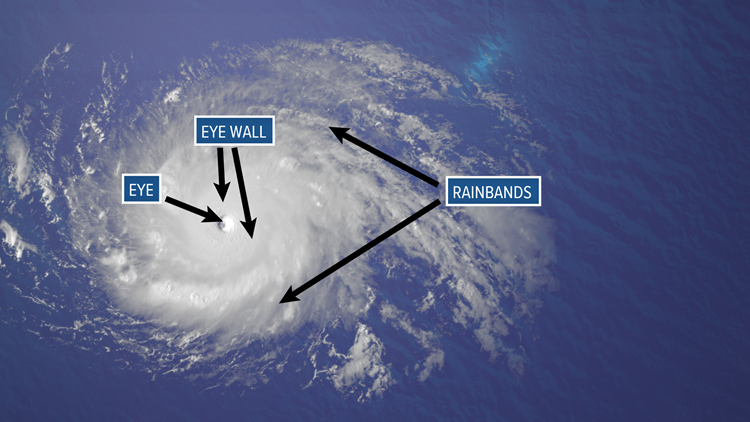
Hurricane Structure
Eye (calm)
Eyewall (intense winds)
Rainbands (spiraling bands of heavy rain).
Hurricane Destruction
High winds, storm surge (sea level rise), heavy inland flooding.
Coral Bleaching Cause
Stress (especially heat stress) causes coral to expel symbiotic algae (zooxanthellae), leading to whitening and often death.
Wind-Driven Waves
Formed by friction between wind and surface water; characterized by crest, trough, wavelength, and wave height.
Coastal Erosion
Driven by wave energy, currents, storms, and rising sea levels.
Beach Protection Measures
Seawalls, groins, breakwaters; can cause downdrift erosion, reducing sediment supply.
Negative effects of Seawalls
Negative effects of Beach Groins
Negative effects of breakwaters
Coastal Wetlands
Marshes and mangroves that buffer coasts against storms and provide vital ecosystems.
Emergent vs. Submergent Coasts
Emergent: Uplifted by tectonics or glacial rebound.
Submergent: Drowned by rising sea levels or land subsidence.
Processes Leading to Coastline Changes
Tectonic uplift/subsidence, sea-level changes (eustatic, isostatic).
Beach Sediment Budget
Balance between sediment input (rivers, cliff erosion) and output (longshore drift, storms).
Dam Effects
Trap sediments upstream, starving coastal beaches of replenishment material.
Width of Intertidal Zone
Determined by tidal range, wave energy, and slope of coastal profile.
Coastal Material Types
Sandy beaches (mobile, dynamic), rocky coasts (resistant to erosion), muddy coasts (fine sediments, low energy environments).