Photosynthesis #6: BIO 1A (editing)
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
what cellular activities require energy?
metabolizing (‘breaking down’ molecules)
synthesizing (‘buildin’) molecules
fighting pathogens
exporting wastes
cell division & growth
reproduction
Process of breaking down carbon based food
animals: digest food first
plants: create food in simple form (glucose) - no need for digestion
energy extracted form food molecules through cellular respiration (occurs in mitochondria)
Energy transformation
plants transform solar energy into chemical energy stored within organic molecules (photosynthate)
sunlight (solar energy): 6CO2 (carbon dioxide) + 6HH2O (water) → C6H12O6 (glucose) + O2 (oxygen)
chemical energy (atp)
energy available in molecules that is released in a chemical reaction
chemical energy (potential energy) in amylose (polysaccharide in starch) due to structure of amylose molecules
ATP (adenosine triphosphate)
immediate energy source that fuels all activities of all organisms
potential chemical energy isstored in chemical bonds in ATP
- fuels all cell activities
Where are ATP molecules stored?
In phosphate bonds
adding phosphate group to ATP required alrge amount of energy, created high-energy chemical bonds
breaks high-energy phosphate bond, releases energy
ATP is a fragile molecule
What is ATP ‘used” to break?
used by breaking a high-energy bond to release energy
breaking phosphate bond changes ADP to ATP
Energy released is used by cell to do ‘work’
What energy is used to recharge ADP to ATP?
ADP ‘recharged’ to ATP by adding a phosphate group to ADP
recharged from diphosphate to triphosphate
ADP → ATP comes from breakdown of glucose in cellular respiration
What is ATP? Where is ATP? Where does it come from?
a type of molecule that functions as the cell’s ‘rechargeable battery’
ATP is in every cell
ATP is recharged from ADP through cellular respiration
What does ATP do? How does it work? How is it recharged?
ATP molecules provides the energy necessary for everything cells do
ATP is used by breaking a high-energy bond to released energy, changing ATP to ADP
energy from breaking glucose down is used to recharge ADP to ATP; 3rd phosphate group added to ADP
How many molecules are produced from 1 glucose molecule through cellular respiration?
38 ATP molecules
Where does glucose come from?
Through the process of photosynthesis where plants transform the energy of sunlight into chemical energy stored within organic molecules → glucose+oxygen byproduct
What organisms performs photosynthesis?
performed by plants, algae, and cyanobacteria
all photosynthetic organisms have chlorophyll pigments that capture light energy form the sun, also possess other pigments to capture solar energy
How do eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms perform photosynthesis differently?
Eukaryote organisms have chloroplasts while prokaryotes have no chloroplasts
Photosynthesis and cellular respiration reactions
Photosynthesis (builds glucose → anabolic) : CO2 + H20 + energy from sunlight to produce glucose + O2
CO2 + H2O = C6H12O6 (glucose) + O2
Cellular respiration (breaks down glucose → catabolic) : uses glucose + O2 To produce ATP + heat + H2O + CO2
C6H12O6 (glucose) + O2 = ATP + heat + H2O + CO2
How is glucose broken down?
glucose is broken down through cellular respiration to fuel plant growth and activities
excess glucose stared as starch
Where does most photosynthesis take place?
Most photosynthesis takes places inleaves
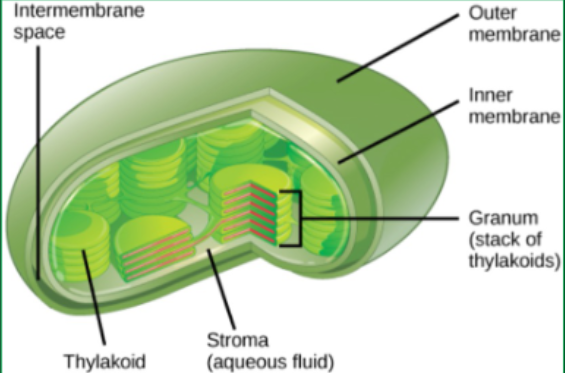
Chlorophyll - important light-absorbing pigment located within chloroplasts
chloroplasts concentrated in upper surfaces of leaves in most plants
What does the stomata do?
Gas exchange is regulated through stomata— small openings on the bottom of surface of leaves
CO2 gas is absorbed through stomata
O2 gas and water vapor released through stomata
Chlorophyll location
in thylakoid membrane within chloroplasts within mesophyll cells within leaf and other green parts of plant
Solar energy wavelengths
solar energy measures as waves
shorter wavelengths (violet-blue) have higher energy
longer wavelengths (red) have lower energy
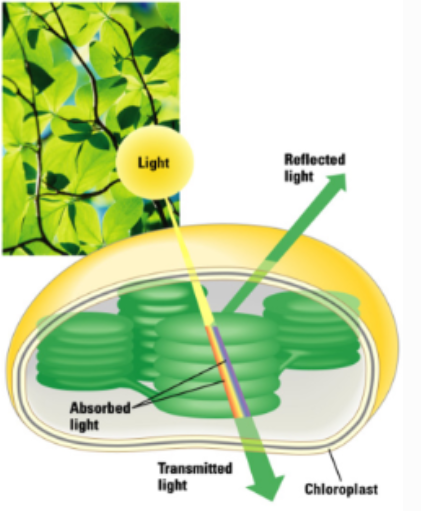
Why are plants green?
chlorophyll pigments absorb violet-blue and red light, therefore reflect green light
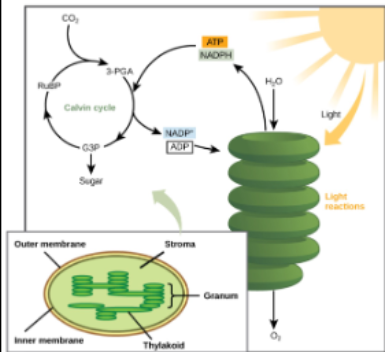
What are the two stages of photosynthesis in the chloroplasts?
Stage 1. Light dependent readtions (LDR): provides energy for calvin cycle
convert light energy into chemical energy (ATP & NADPH)
Stage 2. Calvin cycle: energy from LDR used to synthesize glucose
uses chemcial energy from LDR to power the synthesis of glucose molecules
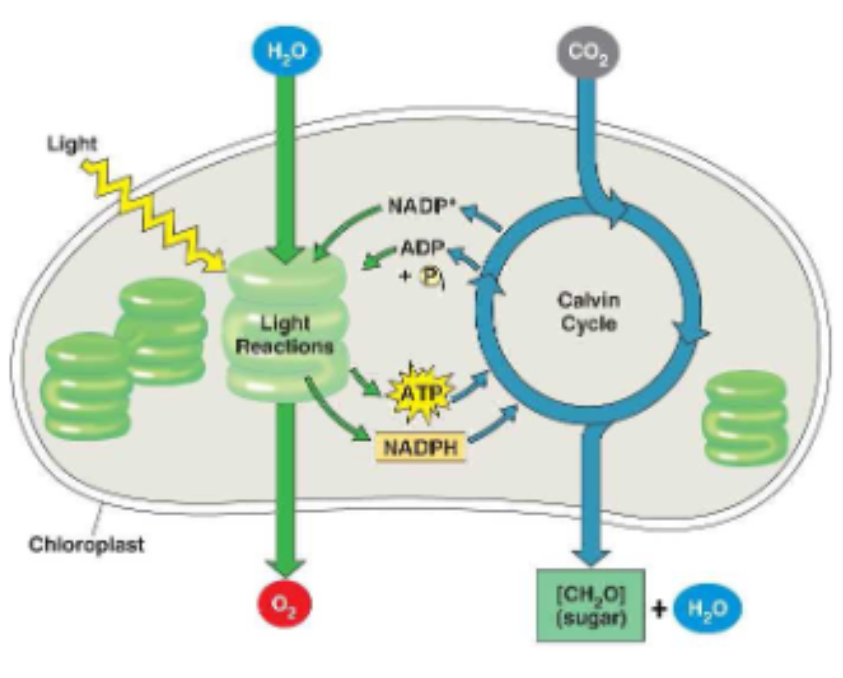
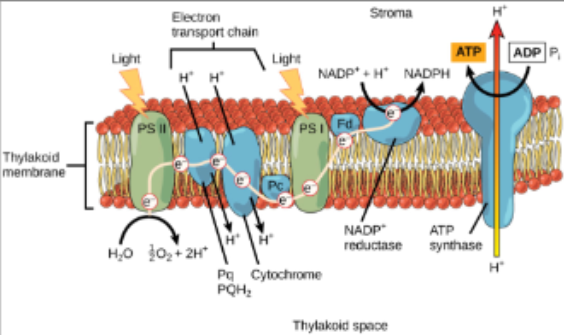
Stage 1: Light dependent reactions (LDR) - water required :p
LDR converts light energy into chemical energy
occurs within photosystem - group of pigment molecules and proteins (in thylakoid membrane) - like a light gathering antenna
photon (unit of light) absorbed by 1st chlorophyll molecules in photosystem → electron excited & break free; H2O = O2 + 2H
O2 waste product released through sotmata
electron (transport of H+ ions) now passed down series of proteins (stroma into thylakoid) that makes up an electron transport chain creating (portential) energy
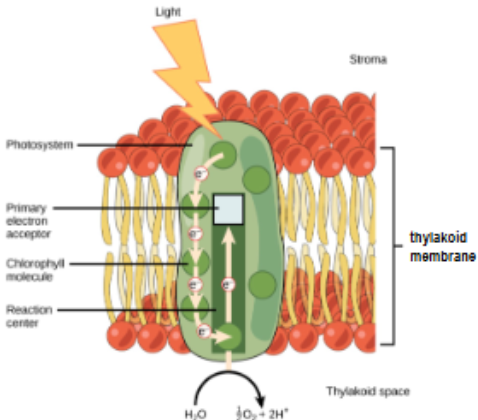
Stage 1: Light dependent reactions (LDR) Steps
light energy absorbed
water molecules split
electron donated by 1st chlorophyll replaces by splitting H2) molecules into O2 + 2HO2 released as waste product
energy-carrying molecules ATP & NADPH produced
electron transport chain of H+ ions from stroma to thylakoid of higher ion concentration to low ion concentration → creates potential energy
Produces: ATP (energy carrier), NADPH (energy carrier), O2 (waste product)
Stage 2 Photosynthesis Calvin Cycle
calvin cycles uses chemical energy generated by LDR to produce glucose
energy needed to synthesize glucose comes from LDR (ATP & NADPH)
energy from ATP & NADPH is used to fix carbon and convert it into glucose
6 molecules of CO2 fixed to create 6-carbon glucose molecules
ADP & NADP+ are then returned to LDR and are recharged
Carbon fixation: carbon is ‘fixed’ from it's inorganic form (gas) into organic molecules (glucose)
Carbon cycle
plants are net producers of atmospheric O2 and net consumers of CO2
photosynthesis consumes CO2 and releases O2
cellular respiration consumes O2 and releases CO2 as a byproduct
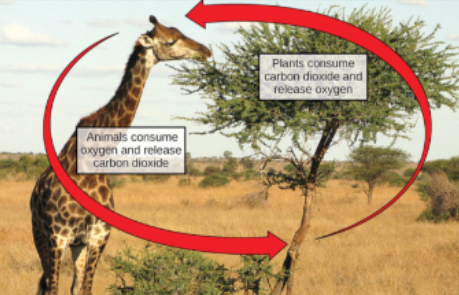
Cycle of carbon dioxide production and consumptions in plants
organisms produce CO2 as a byproduct of cellular respiration
plants release some of CO2 into atmosphere
platns consume some of the CO2 (produced by their own cellular respiration) in photosynthesis
plants take in additional atmosphere CO2 through stomata (consumed in photosynthesis)
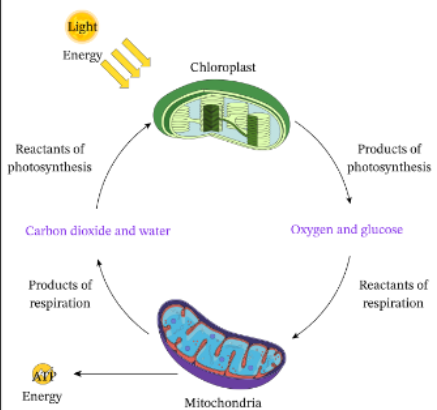
Cycle of oxygen production and consumption in plants
net producer of O2
plants release O2 through stomata, byproduct of photosynthesis
some of the O2 from photosynthesis used for cellular respiration
plants also take in atmospheric O2 to perform cellular respiration
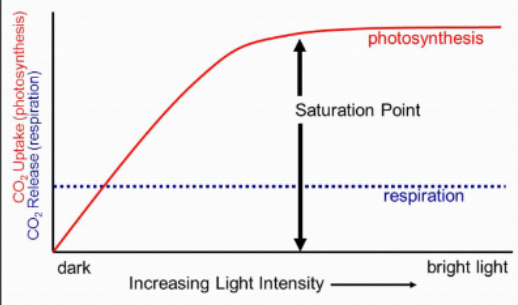
Light compensation point
level of light intensity at which rate of photosynthesis = rate of respiration
Asexual reproduction
reproduction involving only one parent
offspring genetically identical to parent (clones)
rapid & effective, no need to find mate
produces more offspring than sexual reproduction
Sexual reproduction
combines genes from two different individuals to form new indv.
haploid gametes fuse in fertilization
gametes produced through meiosis
offspring not identical copies of parents
Ploidy
number of complete sets of chromosomes in nucleus of each cell
n = number of chromosomes in one complete set
organisms vary in chromosomes number
Haploid (n) cells
1 set of chromosomes in nucleus
Diploid (2n) cells
2 sets of chromosomes in nucleus
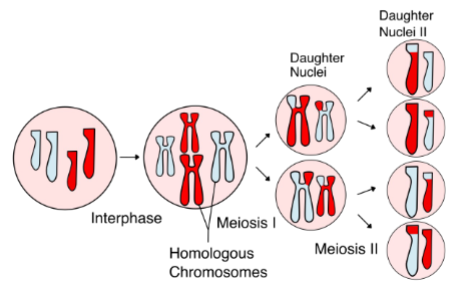
Meiosis “overview”
Diploid parents cell undergoes 2 rounds of cell division: Meiosis I & Meiosis II
Reduction division: Meiosis produces 4 haploid cells from the original diploid parent cell
produces genetic diversity - haploid daughter cells are genetically distinct from original parent cell and from each other
How do prokaryotes produce?
reproduce asexually through binary fission (form of cell division)
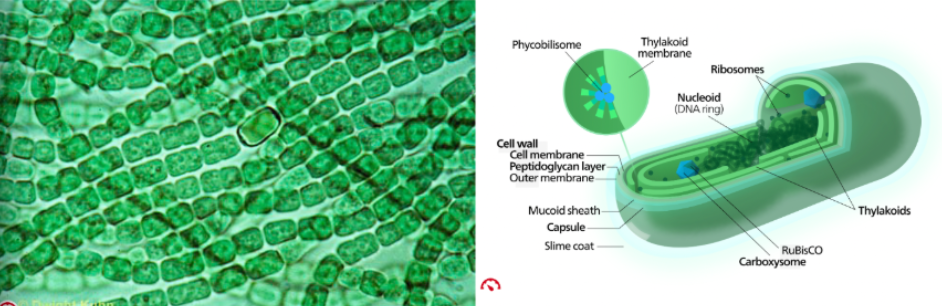
Cyanobacteria
prokaryotic organisms common in aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems
named for the blueish pigment phycocyanin, use to capture light energy in photosynthesis pigments (not all are blue & pigments not contained within organelles)
abundant components of marine and freshwater plankton
ecologically essential, accounting for much of primary production occurring on earth
photoautotrophs, use carbon dioxide and solar energy to produce their own carbon-based food (glucose)
only photosynthetic prokaryotes
Autotrophs
organisms that produce their own carbon-based good
Heterotrophs
organisms that acquire their carbon-based food by consuming other organisms or substances produced by other organisms
Endosymbiosis
process where chloroplasts originating as symbiotic cyanobacteria were incorporated by ancient unicellular eukaryotes as organelles sin
symbiosis in which one of the symbiotic organisms lives inside the other, leads to mutually beneficial relationship
cellular organization for cyanobacteria
some exist in purely unicellular while others aggregate into colonies
colonies taking form of filaments, sheets, or hollow spheres
allow some differentiation of function among individual cells that make up colony
don’t represent multicellularity
Dietary use of cyanobacteria
Spirulina is a type of cyanobacterium
high in protein
imoprtant food source
Volvox
colonial freshwater green algae in group chlorophyta
photosyntheic eukaryotes, belong to larger group archaeplastida
serve as importat food source for aquatic microorganisms
cellular organization volvox
idgaf !!
Haplontic life cycle
only multicellular stage is the haploid gametophyte
diploid phase, zygote → not multicellular (not referred to as ‘generation’ which would imply it’s multicellular
zygote: doesn’t grow via mitosis to become multicellular sporophyte → undergoes meiosis to produce haploid spores
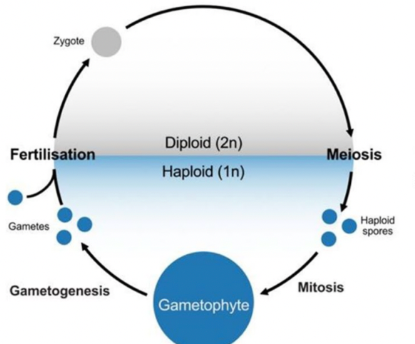
Haplodiplontic life ccle
All land plants have a haplodiplontic life cycle
characterized by alternation of two different multicellular generations: diploid sporophyte gen and haploid gametophyte gen
generation refers to multicellular plant
sporophytes are multicellular diploid plants
gametophytes are multicellular haploid plants
variation in haplodiplontic life cycle
dominance - live longer, generate offspring over mult. seasons, dom. gen.
nutritional dependence - gen. produces its own carbon- based food through photosynthesis (gen is ind.) if acquires much or all of its carbon based food from other gen (dependent)