5 - Stress & Physical & Mental Health
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
Stress
External demands placed on an organism
Stress
Organism’s internal biological and psychological responses to such demands
Stress & DSM
Significant component of multiple DSM diagnostic categories
Nature of stressor
Experience of crisis
Life changes
Individual perception
Individual stress tolerance
Lack of external resources and socual supports
Factors creating Predisposition to Stress:
Nature of stressor
This refers to what kind of stress you’re facing — whether it’s physical, emotional, long-term, or sudden.
Example:
A student constantly facing heavy workloads every week (chronic stressor) may feel more stressed than someone dealing with a one-time event like a surprise quiz (acute stressor).
Experience of crisis
a major disruption or difficult situation that overwhelms your usual coping abilities.
Example:
Losing a loved one, a breakup, or being involved in a car accident can cause severe emotional distress that makes it harder to handle even small problems afterward.
Life changes
Major life transitions, whether positive or negative, can bring stress because they require adjustment.
Example:
Moving to a new city, starting college, or even getting married are all life changes that can make someone feel anxious or uncertain.
Individual perception of stressor
How a person interprets or views a stressor affects their stress level. Two people can experience the same thing but feel differently.
Example:
One student might see an exam as a fun challenge, while another might see it as a terrifying event that could ruin their future.
Individual stress tolerance
This means how much stress a person can handle before breaking down — some people naturally have higher or lower tolerance.
Example:
A student who practices mindfulness and keeps a healthy routine may stay calm during finals week, while another student might feel completely overwhelmed by the same workload.
Lack of external resources and social supports
Not having support from family, friends, or resources (like money, counseling, or time) makes stress harder to manage.
Example:
A working student struggling with tuition and deadlines may feel more stressed if they have no one to talk to or no financial help.
Severity
Chronicity
Timing
Degree of impact
Level of expectation
Controllability
Characteristics of Stressors: (6)
Life changes
Perception of benefits
Crisis > _______ > _______
Sympathetic-adrenomedullary system (SAM)
Hypothalamic-pituitary adrenocortical (HPA)
2 of body’s systems respond when stressor is perceived:
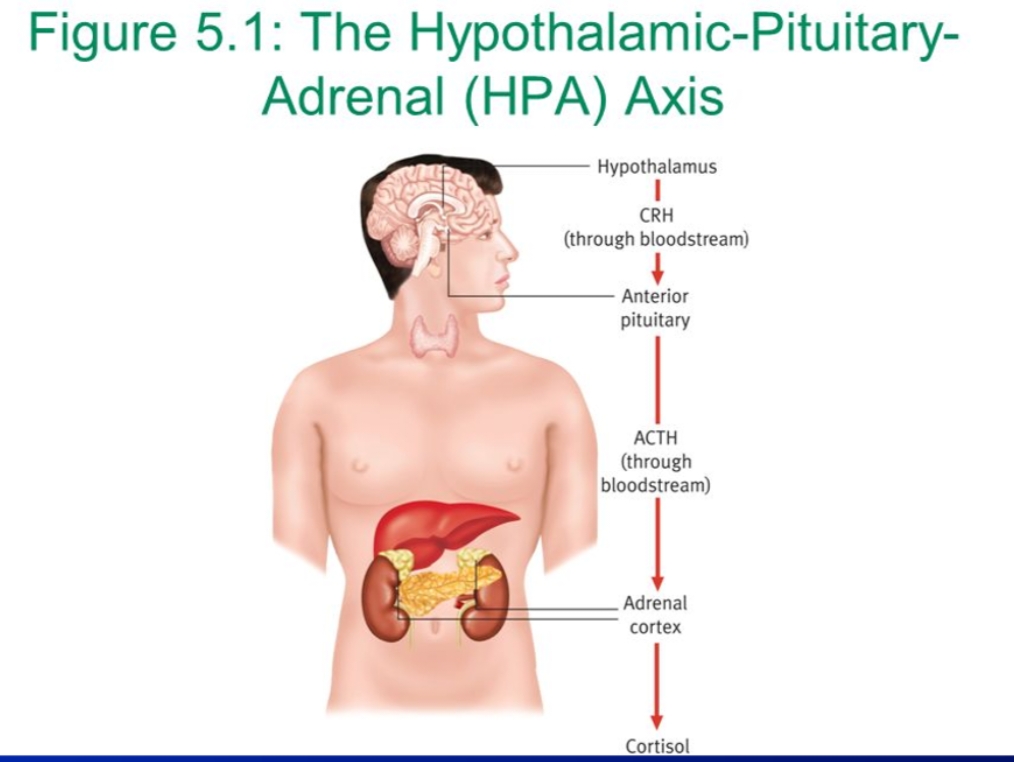
Hypothalamus
CRH
Anterior Pituitary
ACTH
Adrenal Cortex
Cortisol
The Hypothalamic Pituitary Adrenal (HPA) Axis:
Allostasis
Is process of adaptation or achieving stability through change
Allostasis
Results in wear and tear on body
Psychoneuroimmunology
Study of interaction between nervous system and immune system
Immune System
Protects body from such things as viruses and bacteria
Immune System
Provides leukocytes
Leukocytes
front lines of defense
Immune System
Communicates with brain via cytokinesis
Depression
Associated with compromised immune function beyond stressors that precipitated depression
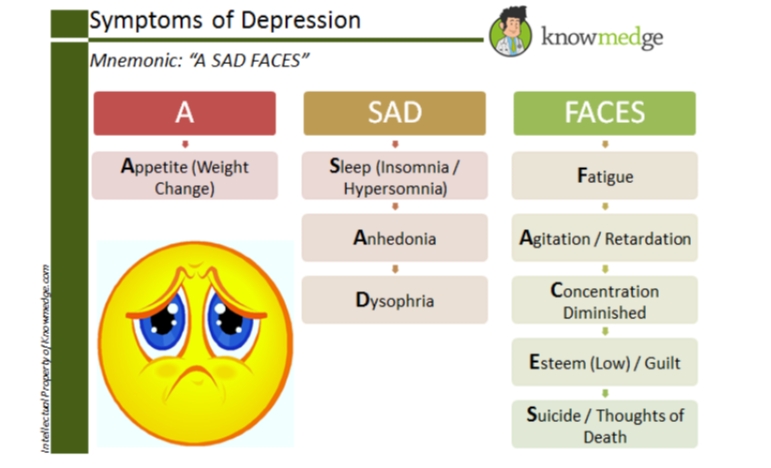
Appetite (Weight Change)
Sleep (Insomnia / Hypersomnia)
Anhedonia
Dysphoria
Fatigue
Agitation / Retardation
Concentration Diminished
Esteem (Low) / Guilt
Suicide
Symptoms of Depression:
“A Sad Faces”
Depressed Mood
Feeling sad, empty, or hopeless most of the day, nearly every day.
Optimism
Negative affect
Many psychological factors can affect relationship between stress and health:
Hypertension
Coronary heart disease
Risk and causal factors
Cardiovascular Disease
Study in this area includes:
Hypertension
involves persisting systolic and diastolic blood pressure
Chronic hypertension & disease
Hypertension & ethnicity
Hypertension & anger management
Hypertension: (3)
Normal
Systolic: below 120
Diastolic: below 80
Prehypertension
Systolic: 120-139
Diastolic: 80-89
Stage 1 Hypertension
Systolic: 140-159
Diastolic: 90-99
Stage 2 Hypertension
Systolic: 160+
Diastolic: 100+
Systolic Pressure
measured when the blood vessel wall contracts
Diastolic Pressure
is measured when the wall relaxes between beats
Type A
Type D
Risk & Causal Factors in Cardiovascular Disease
Certain personality patterns are linked:
Type A
is characterized by excessive competitive drive, extreme commitment to work, impatience or time urgency, and hostility
Type A
Many of us know people who are like this, and the term _____ is commonly used in everyday language.
Type D
have a tendency to experience negative emotions and also to feel insecure and anxious.
Biological interventions
Psychological interventions
Treatment of Stress-Related Physical Disorders:
Surgical procedures
Lipid-lowering medications
Aspirin or other anticoagulants
Antidepressant medications
Biological Interventions: (4)
Surgical procedures
These are operations done by doctors to treat or repair parts of the body.
Lipid-lowering medications
These are drugs that help reduce cholesterol or fats in the blood, lowering the risk of heart disease.
Aspirin or other anticoagulants
These medicines prevent blood clots, improving circulation and reducing the risk of stroke or heart attack.
Antidepressant medications
These help balance chemicals in the brain that affect mood and emotions, treating conditions like depression or anxiety.
Emotional disclosure
Biofeedback
Relaxation and meditation
Cognitive-behavior therapy (CBT)
Psychological interventions: (4)
Emotional disclosure
Expressing or talking about one’s feelings, especially about stressful or painful experiences.
Biofeedback
A technique that helps a person learn to control body functions (like heart rate or breathing) by using sensors that show how the body reacts to stress.
Example:
Watching your heartbeat on a monitor and practicing ways to slow it down through relaxation.
Relaxation and meditation
Activities that calm the mind and body, helping to reduce stress, anxiety, and tension.
Cognitive-behavior therapy (CBT)
A type of talk therapy that helps people identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors.
Example:
Learning to replace thoughts like “I’ll fail” with “I can improve with practice.”
Adjustment Disorder
Posttraumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
Some DSM disorders are triggered by exposure to stress: (2)
Adjustment Disorder
having a hard time coping with a big change or stressful event in life —
Adjustment Disorder
Maladaptive response to common stressor within 3 months of stressor
— The person reacts in an unhealthy or extreme way to a stressful situation, and this happens within three months after the event.
Adjustment Disorder
Symptoms disappear when stressor ends or person adapts
— The emotional or behavioral problems (like sadness, anxiety, or acting out) usually go away once the stressful situation is over or the person learns to cope better.
Adjustment Disorder
👉 Explanation:
Tony lost his job and has been unemployed for 16 months. This life change is a stressor — something that causes emotional strain. He’s doing his best to find work, but when nothing happens, he feels hopeless, questions himself, and misses his old routine.
These feelings and behaviors show a maladaptive response (difficulty coping) to a stressful situation (job loss). However, Tony is still trying to stay optimistic, showing he’s trying to adapt.
