Neurons and Neurotransmitters
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
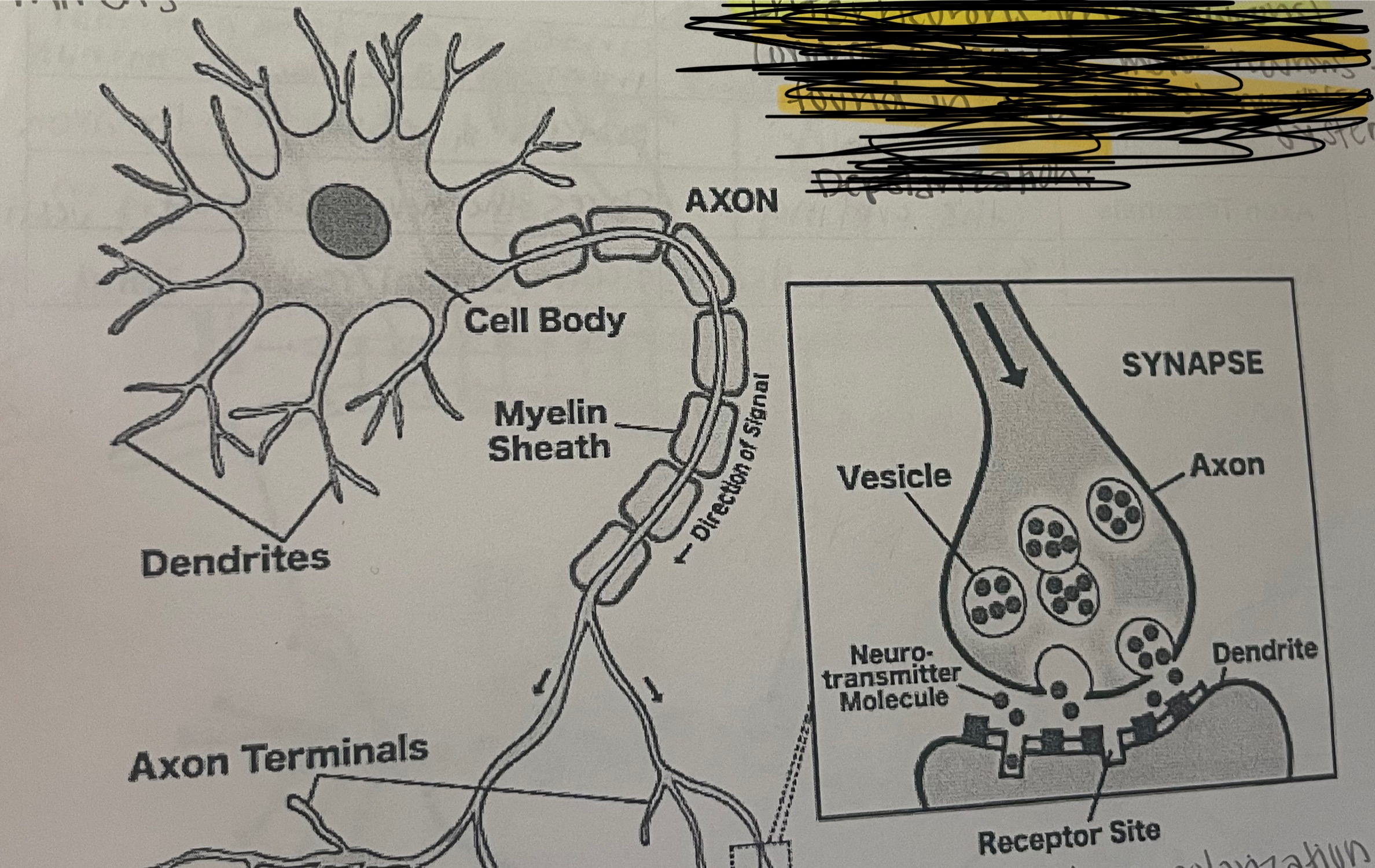
Nerve Cell
building block of nerves
Soma
cell body
life support center
Dendrites
neurons branches
receives messages from other neurons
Axon
info taker
carries the action potential from soma to the terminals
Myelin Sheath
protective layer that insulates axon
Axon Terminals
the ending
stores the neurotransmitters in vesicles
Action Potential
neural impulse
electrochemical reaction along the cell
Glial Cells
clean up brains debris, transport nutrients to neuron, hold neuron in place, keep them healthy
Sensory neurons (afferent neurons)
carry info IN to the CNS
Motor neurons (efferent neurons)
carry info OUT of CNS
E EXIT
Vesicles
portion of the axon terminals
Interneurons (relay neurons)
connect sensory and motor neurons in CNS
Sodium Potassium Pump
transport sodium ions out of cell and potassium ions fill into the cell
Excitatory effect
neurotransmitters effect makes it more likely to receive neurons
Threshold
depolarization must reach for an action potential to occur
Inhibitory effect
neurotransmitters effect makes it less likely to receive neurons
when an action potential reaches the end of a neuron neurotransmitters are released into the synapse. the neurotransmitters rapidly cross the synapse to fit into receptor sites on the dendrites of the next neuron