Selection Changes Allele Frequencies
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/23
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
1
New cards
fitness
the survival and reproductive success of an individual with a particular phenotype
component of fitness:
* survival to reproductive age
* mating succes
* fecundity
component of fitness:
* survival to reproductive age
* mating succes
* fecundity
2
New cards
natural selection is more effective in large populations
* For each population there are two alleles one is slightly beneficial as it raises the fitness by 5%
* We start the population off with the beneficial allele at 10% and we watch how the allele spreads in the population
* The frequency of the beneficial allele raises to 100% until generation 120
* With 1000 individuals there is a steadily fixation there is variability
* With a population of 100 we see a lot more variability reaches fixation
* Two become fixed for the non-beneficial allele at generation 20 and 60
* When we have a population of 10 individuals, there is extremes, already fixation by generation 25 what we have observed, is a
combined effect of natural selection, and drift at large population size is the force, and the forces of selection favouring the beneficial deals over power drift of the beneficial allele, however, as the population size decreases, despite advantage of the beneficial allele the effects of drift overpower
* We start the population off with the beneficial allele at 10% and we watch how the allele spreads in the population
* The frequency of the beneficial allele raises to 100% until generation 120
* With 1000 individuals there is a steadily fixation there is variability
* With a population of 100 we see a lot more variability reaches fixation
* Two become fixed for the non-beneficial allele at generation 20 and 60
* When we have a population of 10 individuals, there is extremes, already fixation by generation 25 what we have observed, is a
combined effect of natural selection, and drift at large population size is the force, and the forces of selection favouring the beneficial deals over power drift of the beneficial allele, however, as the population size decreases, despite advantage of the beneficial allele the effects of drift overpower
3
New cards
Ronald fisher
* populations are large with lots of missing
* natural selection will “take control”
* held the notion that populations were extremely large with lots of mixing of alleles - selection would play huge role
* natural selection will “take control”
* held the notion that populations were extremely large with lots of mixing of alleles - selection would play huge role
4
New cards
seawall wright
* populations are often smaller and subdivided with little gene flow bwtn
* drift is very important
* populations are quite small, often divided into many subpopulations with little gene flow, given this, he said that drift would be more important
* drift is very important
* populations are quite small, often divided into many subpopulations with little gene flow, given this, he said that drift would be more important
5
New cards
Motoo Kimura
* lots of variation in populations but most do not influence phenotype
* drift could account for a lot of this allelic variation
* although there was considerable variation within populations most of the variation is within non-coding sequences (introns) very few will influence phenotype. He said that drift would play a role
* drift could account for a lot of this allelic variation
* although there was considerable variation within populations most of the variation is within non-coding sequences (introns) very few will influence phenotype. He said that drift would play a role
6
New cards
pleiotropy
multiple phenotypes traits associated w/ a single gene
7
New cards
antagonistic pleiotropy
the beneficial effect for one trait but detrimental effects for another trait
* sometimes called a trade-off
* sometimes called a trade-off
8
New cards
additivity
effects of alleles can be predicted by summing the number of copies that are present
* incomplete dominance
* incomplete dominance
9
New cards
dominance
dominant allele masks presence of recessive allele in heterozygous
10
New cards
negative frequency-dependent selection
common phenotype is deleted against and rare phenotype are favoured
11
New cards
heterozygote advantage
heterozygosity confers greater fitness than homozygotes
12
New cards
cystic fibrosis
* autosomal recessive genetic disorder
* chromosome 7
* excessive mucous production leaden to sever dmg to the pancreas, liver, and kidneys but especially the lungs
* pancreatic issues lead to poor nutrient absorption
* mutation in the CFTR gene
* chromosome 7
* excessive mucous production leaden to sever dmg to the pancreas, liver, and kidneys but especially the lungs
* pancreatic issues lead to poor nutrient absorption
* mutation in the CFTR gene
13
New cards
CFTR
* The mutated CFTR contains a deletion of the TTT codon, this is a deletion of phenylalanine from the polypeptide sequence. This deletion is called the delta F508
* Delta refers to change, insertion, or deletion
* F stands for phenylalanine
* 508 stands for the nucleotide position
* The horizontal black lines in the image (a) represent how the proteins sit in the plasma membrane, the blow-up picture on the right shows where the deletion has occurred
* The second image (b) shows at the top a normal functional CFTR after post - translational folding. The bottom line shows the mutated CFTR shows the mutated CFTR and with the absence of phenylalanine , the receptor cannot properly form.
* Delta refers to change, insertion, or deletion
* F stands for phenylalanine
* 508 stands for the nucleotide position
* The horizontal black lines in the image (a) represent how the proteins sit in the plasma membrane, the blow-up picture on the right shows where the deletion has occurred
* The second image (b) shows at the top a normal functional CFTR after post - translational folding. The bottom line shows the mutated CFTR shows the mutated CFTR and with the absence of phenylalanine , the receptor cannot properly form.
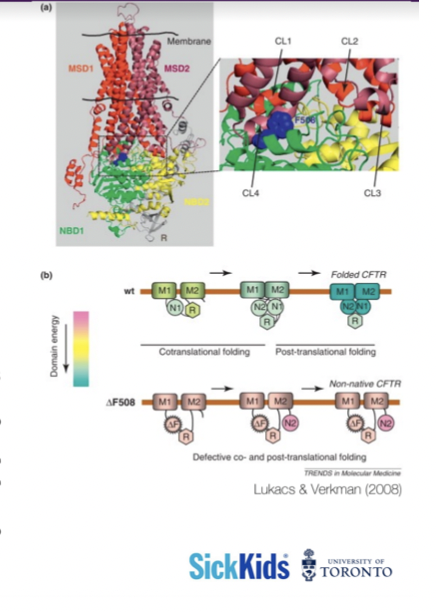
14
New cards
King Charles II
* numerous deformities
* he was the result of numerous generations of inbreeding
* Not only was Charles effected, many offspring in the family were too
* As the inbreeding coefficient increased, the probability of survival (a measure of fitness) decreased
* 20-30% chance a child would survive past 10 years old
* he was the result of numerous generations of inbreeding
* Not only was Charles effected, many offspring in the family were too
* As the inbreeding coefficient increased, the probability of survival (a measure of fitness) decreased
* 20-30% chance a child would survive past 10 years old
15
New cards
16
New cards
17
New cards
18
New cards
population subdivision
* Across these landscapes populations can have a subdivision, differentiation on the left is a representation of a population, with no subdivisions, showing a solid blue fill entire region.
* In the middle, is intermediate subdivision populations. Here is still quite similar evidence by the same colour throughout the populations are becoming isolated, but still maintaining some degree of gene flow
* Populations on the right would be an extreme subdivision. There’s no gene flow between the subpopulations, they’ve diverged significantly from each other and in the original and different colours over time
* extreme subdivision could lead to speciation
* In the middle, is intermediate subdivision populations. Here is still quite similar evidence by the same colour throughout the populations are becoming isolated, but still maintaining some degree of gene flow
* Populations on the right would be an extreme subdivision. There’s no gene flow between the subpopulations, they’ve diverged significantly from each other and in the original and different colours over time
* extreme subdivision could lead to speciation
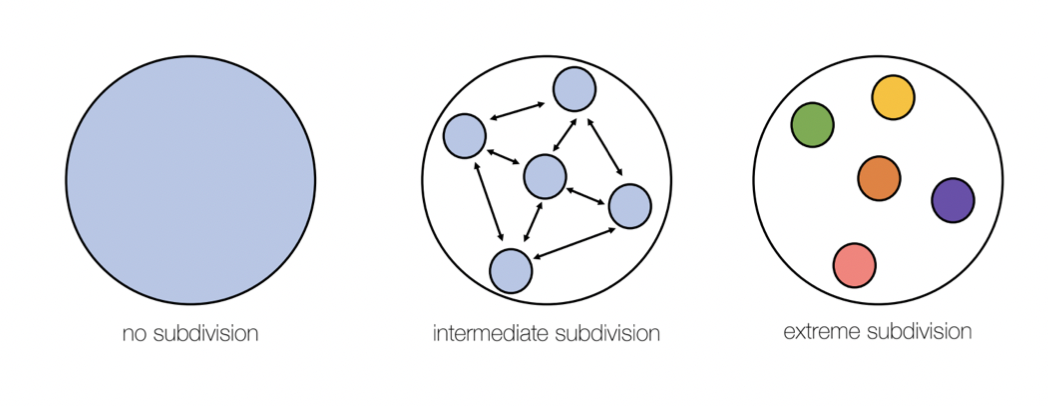
19
New cards
Fst - a measure of population differentiation
* a calculated value that measures the extent of submission Amon subpopulations
* a measure of genetic distance
* can be influenced by population size and time since divergence
* comparing FST between subpopulations can inform us if particular regions of the genome that Mae be under selection
* The above figure shows that populations play a role in FST: when populations are small (n=10) FST quickly rises from low to complete differentiation
* FST values and rate of increase is a function of population size
* We can use this to tell us which parts of the genome are under selection
* The bottom figure plots the position of the nucleotide position on chromosome 7 and plots FST on the y axis
* The blue dots are arranged in a range of 0.1-0.25
* Some of the FST exceed the range which are outliers- show locations in the genome where the two sub populations are different
* a measure of genetic distance
* can be influenced by population size and time since divergence
* comparing FST between subpopulations can inform us if particular regions of the genome that Mae be under selection
* The above figure shows that populations play a role in FST: when populations are small (n=10) FST quickly rises from low to complete differentiation
* FST values and rate of increase is a function of population size
* We can use this to tell us which parts of the genome are under selection
* The bottom figure plots the position of the nucleotide position on chromosome 7 and plots FST on the y axis
* The blue dots are arranged in a range of 0.1-0.25
* Some of the FST exceed the range which are outliers- show locations in the genome where the two sub populations are different
20
New cards
gene flow (migration) can counteract drift
* Lack of arrows = no gene flow
* Different colours = diverging
* When we have gene flow, there are thin arrows the alleles move from one subpopulation to the next and over time they become more similar
* If the amount of gene flow increases - thicker arrows then, gene flow can wipe out any differentiation between the subpopulation
* Genetic constitutions are now similar - a melding of the colours
* Gene flow plays an important role in the migration of alleles and can counteract the effects of drift
* Different colours = diverging
* When we have gene flow, there are thin arrows the alleles move from one subpopulation to the next and over time they become more similar
* If the amount of gene flow increases - thicker arrows then, gene flow can wipe out any differentiation between the subpopulation
* Genetic constitutions are now similar - a melding of the colours
* Gene flow plays an important role in the migration of alleles and can counteract the effects of drift
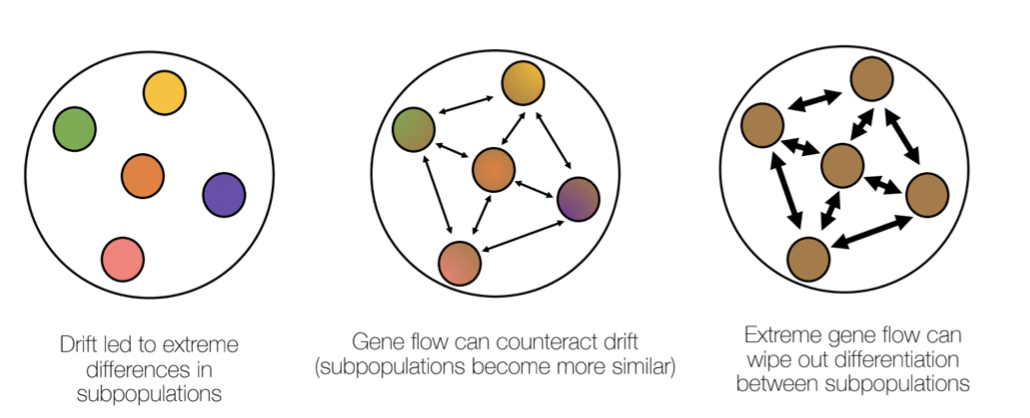
21
New cards
gene flow can counteract the loss of alleles due to drift
* Studied stag beetles which showed morphological variation in body size mainly in males.
* The most obvious trait that varies between populations is the size of a mandibles
* On the far right, is the figure and on the far left is a figure from their paper showing variation in males from three sub populations the and then a female on the right for comparison
* They found that the amounts of gene flow population varied shown by the thickness of arrows
* The most obvious trait that varies between populations is the size of a mandibles
* On the far right, is the figure and on the far left is a figure from their paper showing variation in males from three sub populations the and then a female on the right for comparison
* They found that the amounts of gene flow population varied shown by the thickness of arrows
22
New cards
level of gene flow can depend on the range of movement of the organism
* Shows genetic distance in sheep, bear, coyotes, and lynx
* Smaller FSTs are common which is why the scale only goes up to 0.3
* The lynx has extensive movement across their range - can have home ranges up to 50 squared km - a lot of movement which causes a lot of gene flow (FST is very low) - very little defferiation - one huge population
Sheep:
* Very little movement - do not leave their home
range, higher amount of FST ( higher genetic
distance) - as distance increases
* Very genetically distinct from each other
* Smaller FSTs are common which is why the scale only goes up to 0.3
* The lynx has extensive movement across their range - can have home ranges up to 50 squared km - a lot of movement which causes a lot of gene flow (FST is very low) - very little defferiation - one huge population
Sheep:
* Very little movement - do not leave their home
range, higher amount of FST ( higher genetic
distance) - as distance increases
* Very genetically distinct from each other
23
New cards
how does having a high degree of differentiation affect bighorn sheep?
\- Human disturbance affects population structure by imposing barriers between population
24
New cards
humans disturbance affects populations structure by imposing barriers btwn populations
* The relative amount of gene flow (y-axis) and distance on the (x-axis)
* Sheep are inherently challenged by how small their home range is, mountains function as islands
* Under normal circumstances, the rates of gene flow decrease as a function to distance (blue triangles and dash line) but if humans introduce a barrier, like a road that just further decreases gene flow between some populations as evidenced in the pink circles in the solid lines
* Sheep are inherently challenged by how small their home range is, mountains function as islands
* Under normal circumstances, the rates of gene flow decrease as a function to distance (blue triangles and dash line) but if humans introduce a barrier, like a road that just further decreases gene flow between some populations as evidenced in the pink circles in the solid lines